plotke anatomy nervous system
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
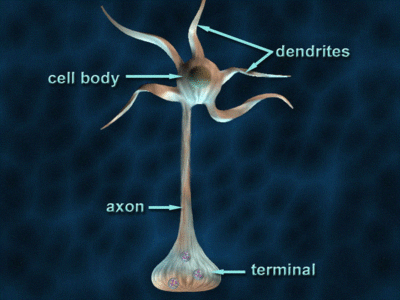
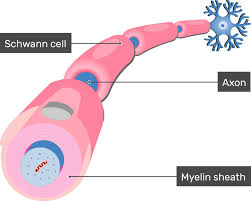
Axon
A long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
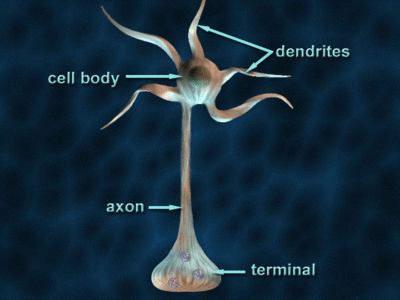
Dendrite
A short, branched extension of a neuron that receives signals from other neurons and transmits them toward the cell body.
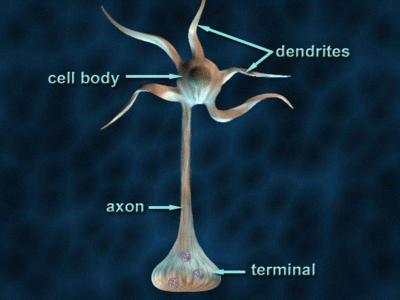
Cell Body
The spherical part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and organelles, serving as the metabolic center and integrating incoming signals from dendrites.
Schwann Cell
A type of glial cell that wraps around axons in the peripheral nervous system to form the myelin sheath.
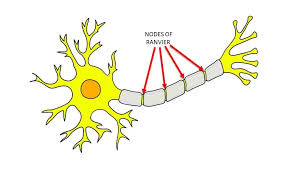
Node of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon that facilitate rapid conduction of nerve impulses.
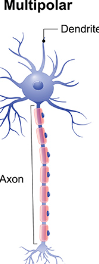
Multipolar Neuron
A type of neuron that has one axon and multiple dendrites, allowing it to receive and integrate a large amount of information.
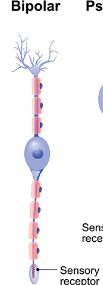
Bipolar Neuron
A neuron with two extensions, one axon and one dendrite, commonly found in sensory systems.
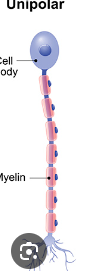
Unipolar Neuron
A neuron with a single process that splits into two branches, usually serving sensory functions.
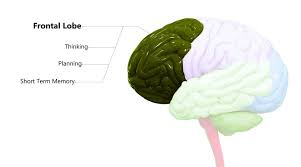
Frontal Lobe
The part of the brain associated with reasoning, planning, problem-solving, and emotional control.
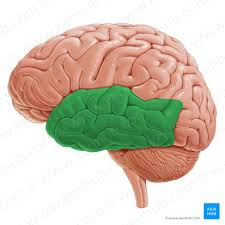
Temporal Lobe
The region of the brain involved in processing auditory information and encoding memory.
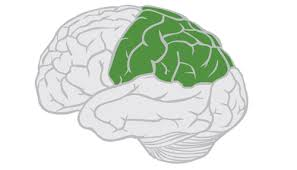
Parietal Lobe
The area of the brain responsible for processing sensory information from the body.
Occipital Lobe
The part of the brain that processes visual information.
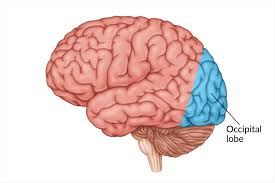
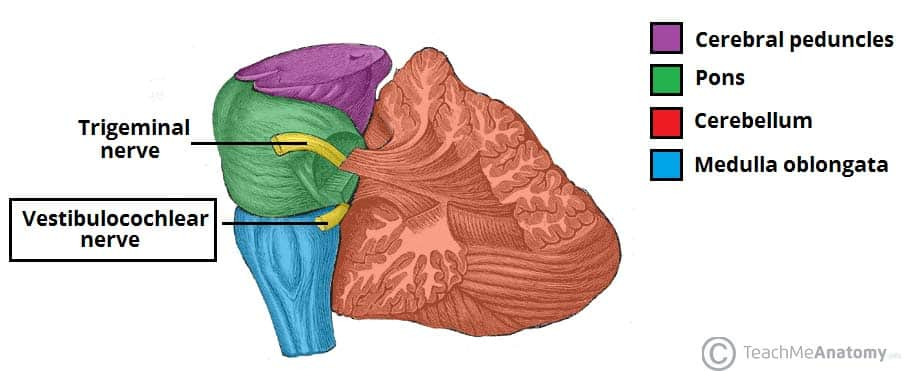
Cerebellum
A region of the brain that regulates motor control and coordination.
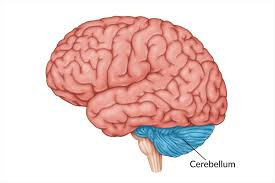
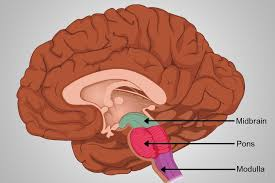
Pons
A structure in the brainstem that connects the upper and lower parts of the brain and regulates sleep and arousal.
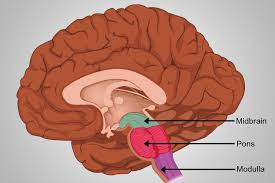
Midbrain
A portion of the brainstem that plays an important role in vision and hearing.
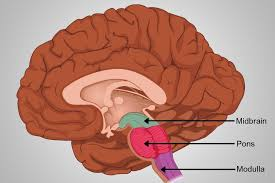
Medulla Oblongata
The area of the brainstem that controls vital functions such as breathing and heart rate.
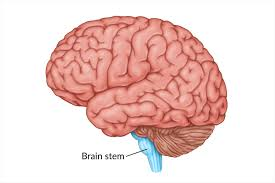
Brain Stem
The lower part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord and controls automatic functions.
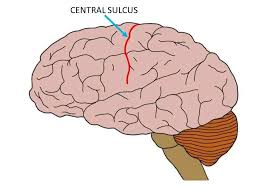
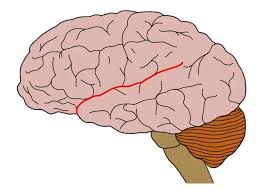
Central Sulcus
A prominent groove in the brain that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
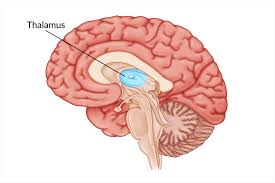
Thalamus
The brain's relay station for sensory information, directing it to appropriate areas for processing.
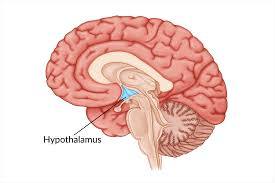
Hypothalamus
A region of the brain that regulates vital bodily functions, including temperature and hunger.
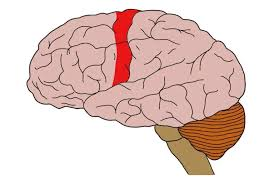
Precentral Gyrus
The part of the brain located in the frontal lobe that is responsible for motor control.
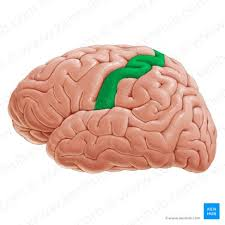
Postcentral Gyrus
The area of the brain located in the parietal lobe responsible for somatic sensation.
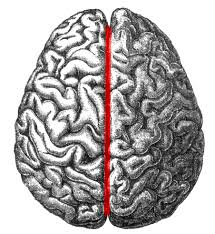
Longitudinal Fissure
The deep groove that separates the two hemispheres of the brain.
Corpus Callosum
A thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
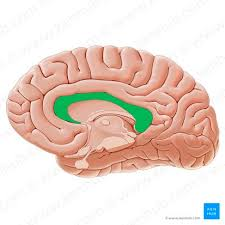
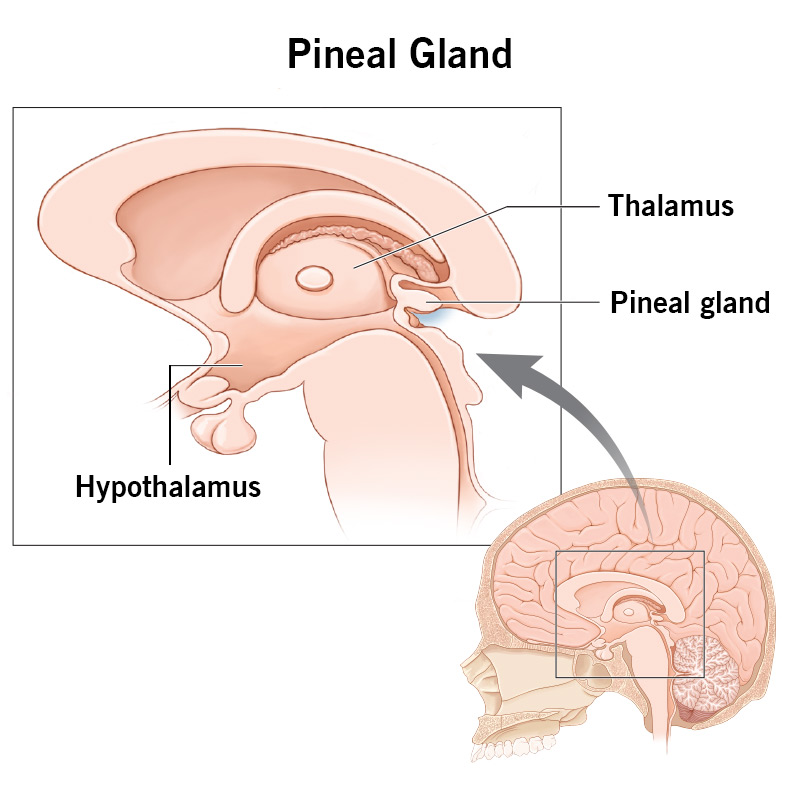
Pineal Gland
A small endocrine gland in the brain that produces melatonin, regulating sleep patterns.
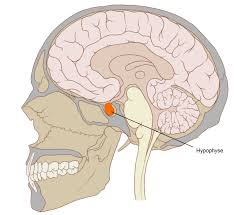
Pituitary Gland
The 'master gland' that controls other endocrine glands and regulates growth and metabolism.
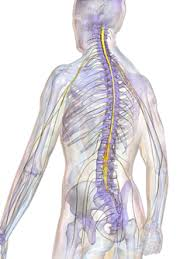
Spinal Cord
The cylindrical structure containing nerve tissue that connects the brain with the peripheral nervous system.
Lateral Sulcus
The groove that separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes.
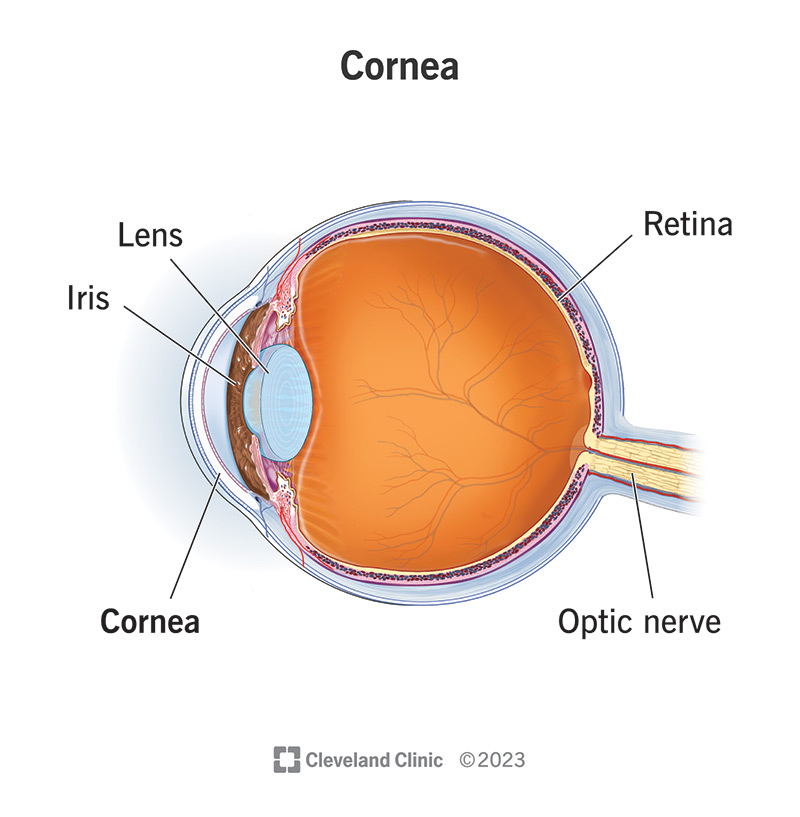
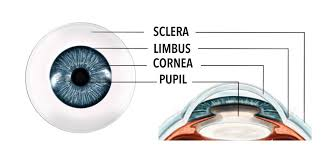
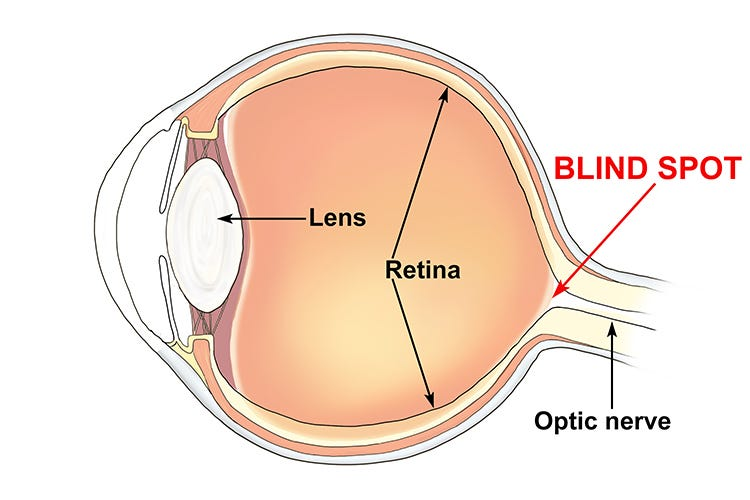
Cornea
The transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris and pupil, helping to focus light.
Sclera
The white outer layer of the eyeball that provides protection and structure.
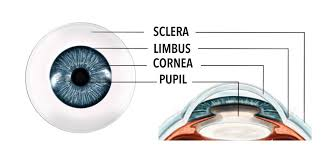
Pupil
The opening in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye.
Iris
The colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil and thus the amount of light entering the eye.
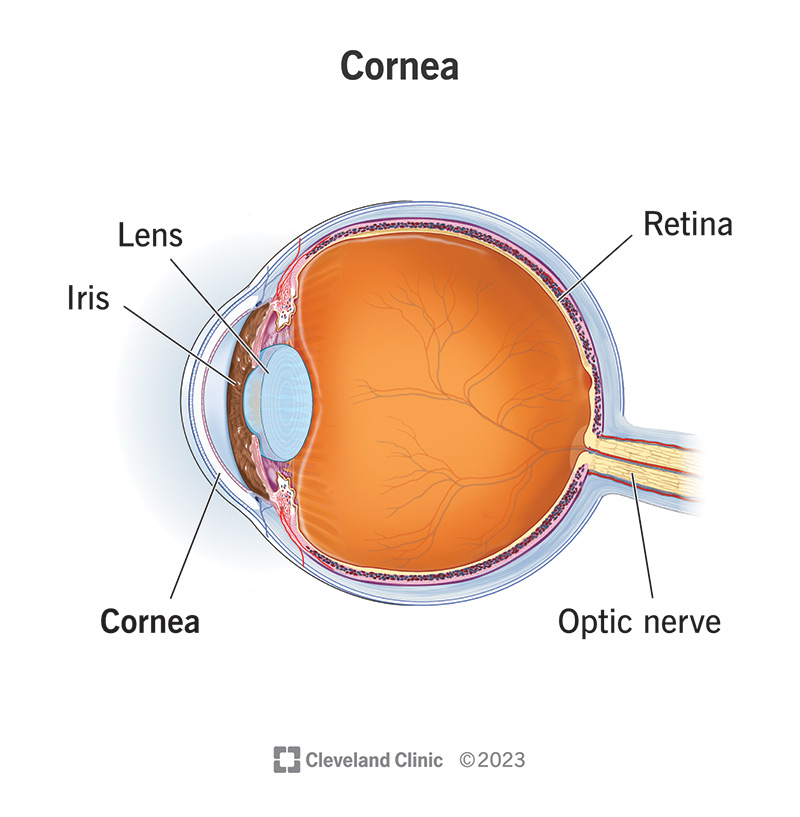
Lens
The transparent structure behind the pupil that helps focus light onto the retina.
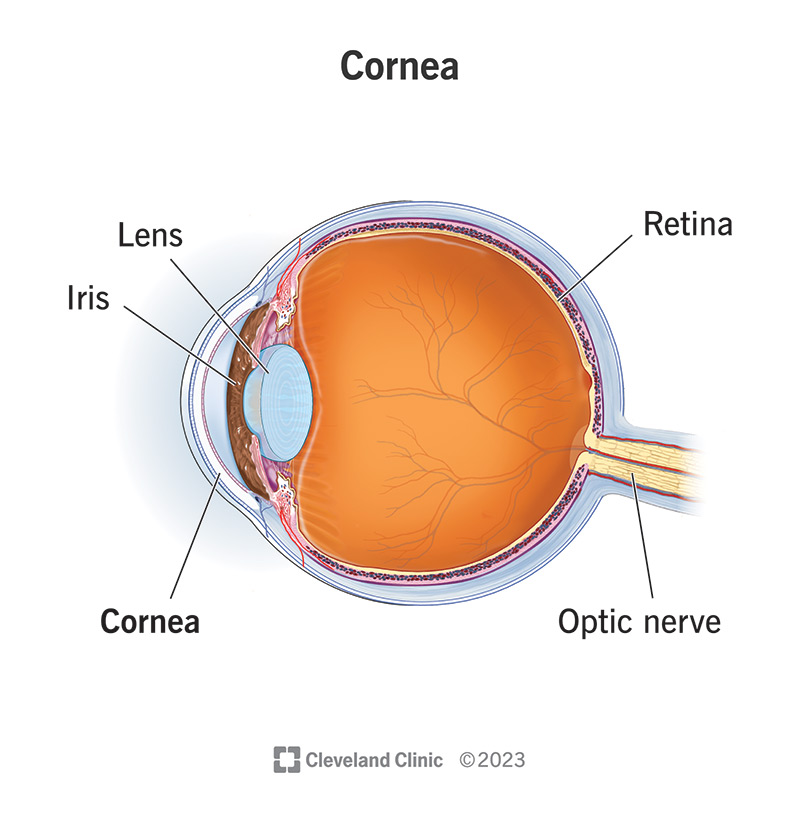
Retina
The layer at the back of the eye that contains photoreceptor cells and converts light into neural signals.
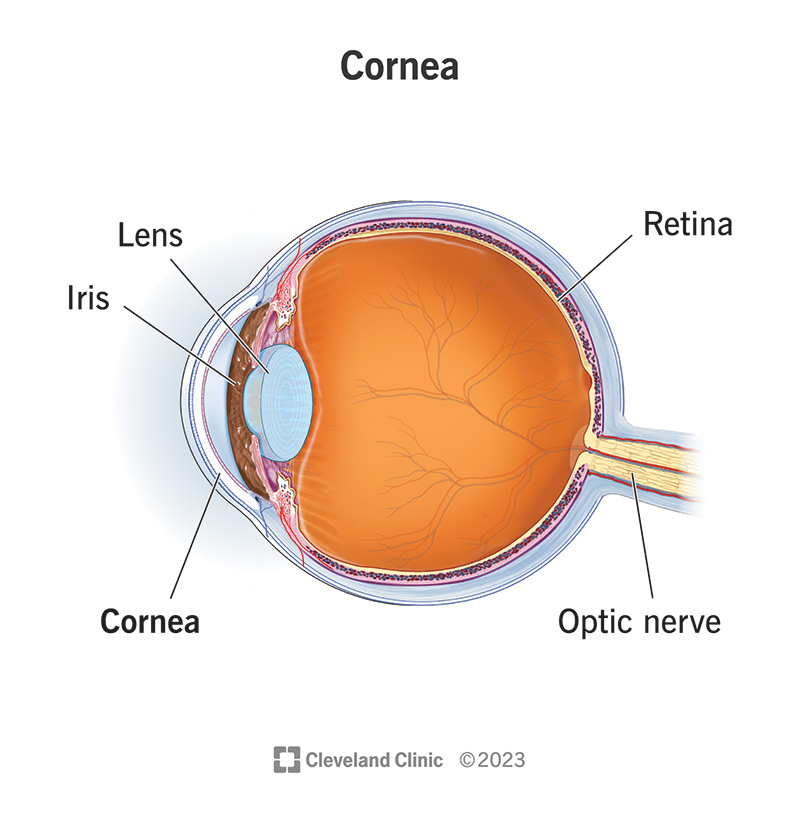
Optic Nerve
The nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain.
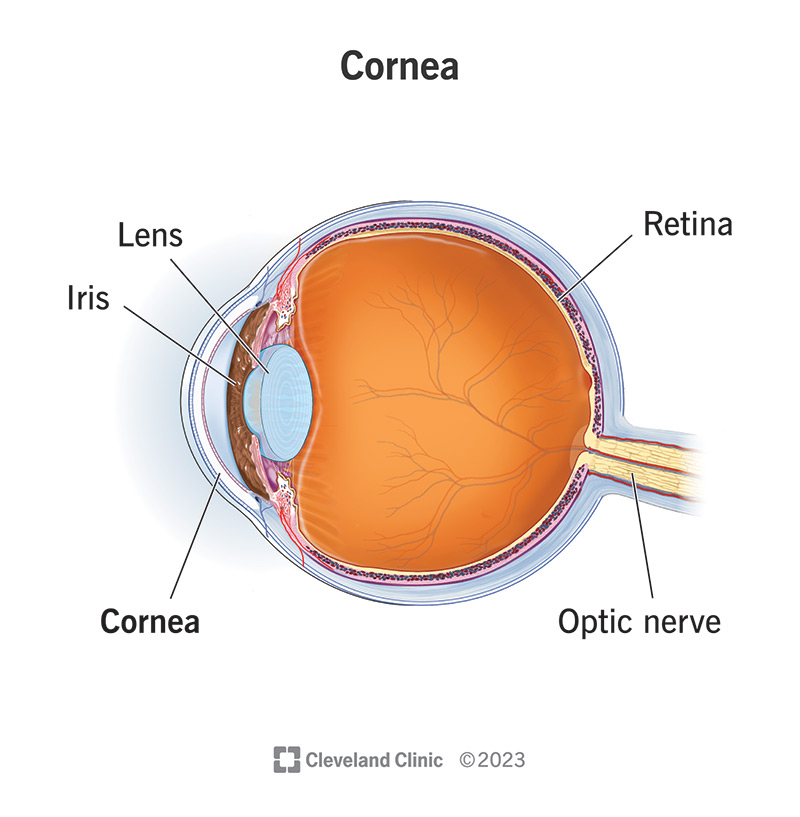
Blind Spot
The area on the retina without photoreceptors where the optic nerve exits the eye.
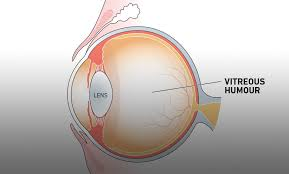
Vitreous Humor
The gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and retina.
Pinna
The external part of the ear that helps direct sound waves into the ear canal.
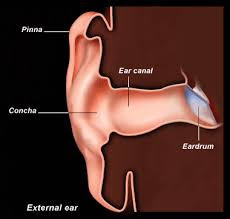
Ear Canal
The tubular structure that carries sound from the outer ear to the eardrum.
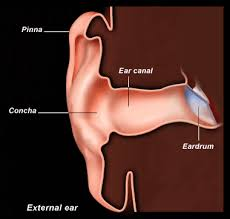
Tympanum
Also known as the eardrum, it vibrates in response to sound waves.
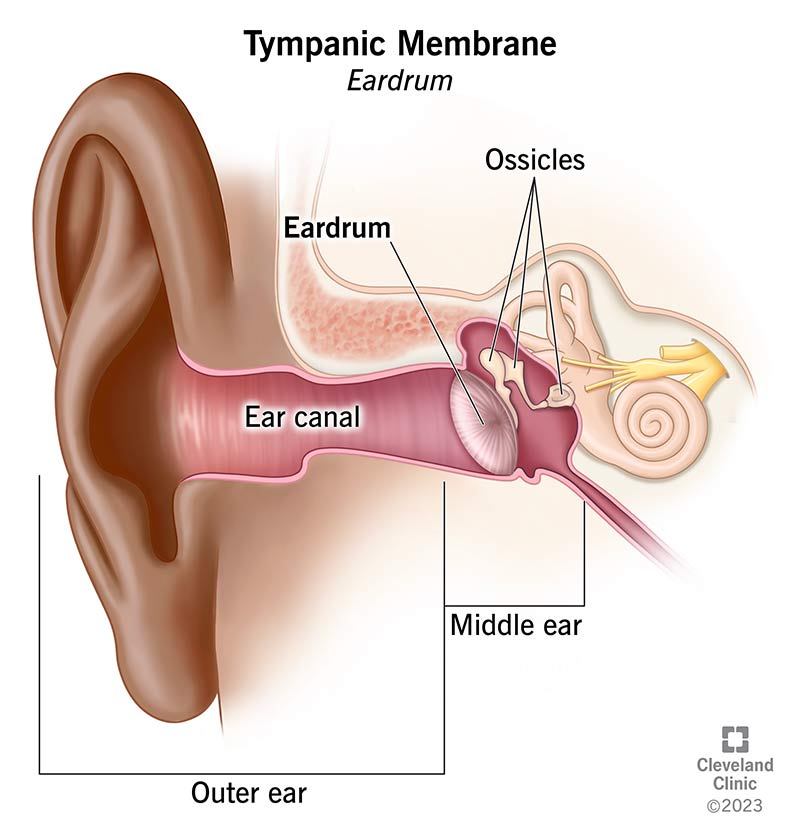
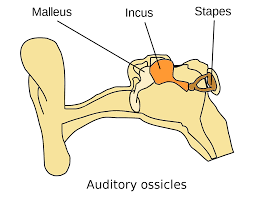
Auditory Ossicles
The small bones in the middle ear (malleus, incus, stapes) that transmit sound from the eardrum to the inner ear.
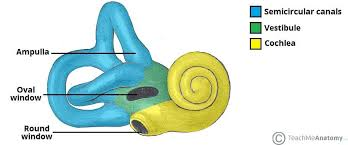
Vestibule
The part of the inner ear that helps with balance.
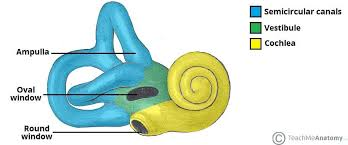
Cochlea
A spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear responsible for converting sound waves into nerve signals.
Cochlear Nerve
The nerve that carries auditory information from the cochlea to the brain.
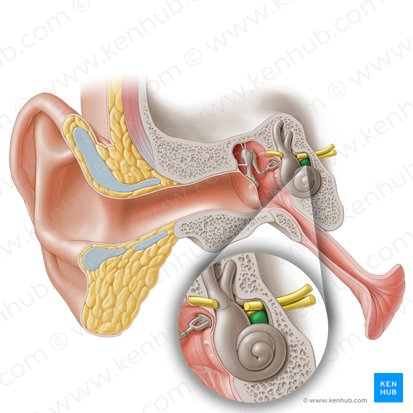
Endolymph
The fluid inside the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear.

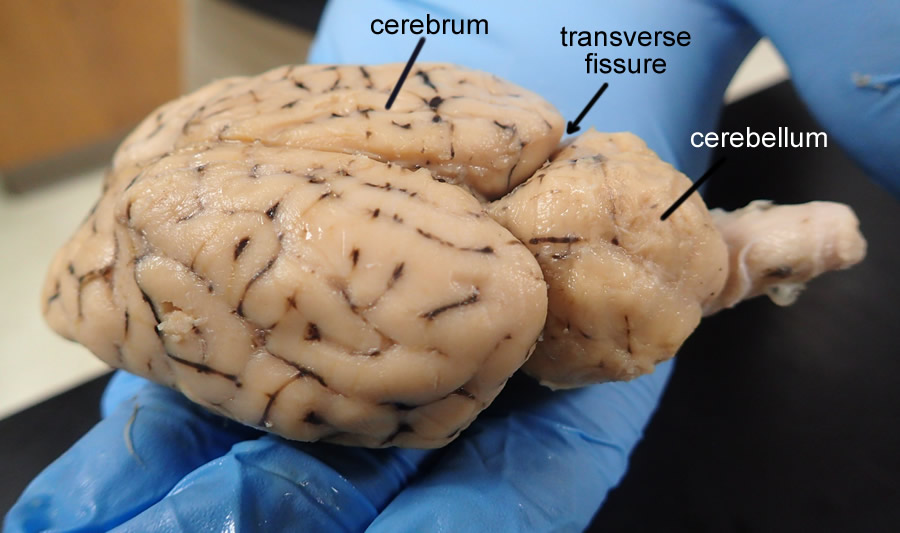
Transverse Fissure
The groove that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum.
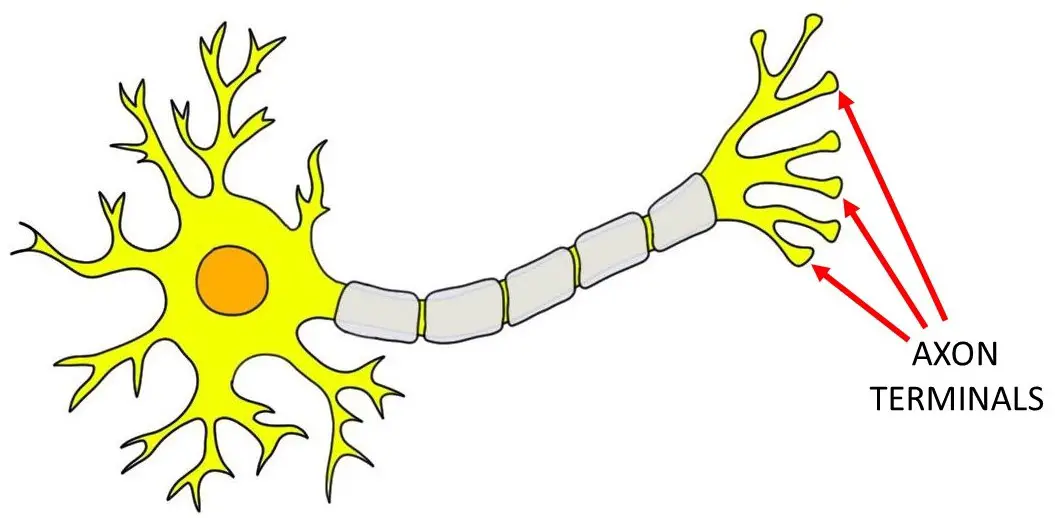
Axon Terminus
The ending part of an axon where neurotransmitters are released to communicate with other neurons.
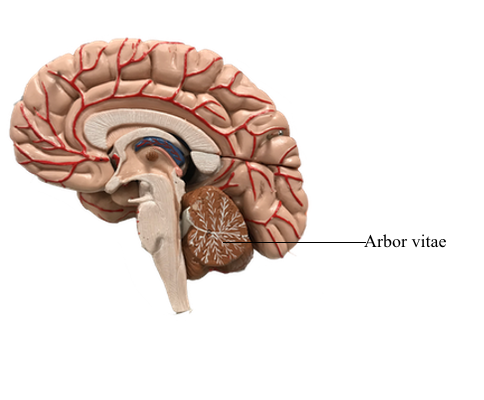
Arbor Vitae
The tree-like arrangement of white matter within the cerebellum.
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
The cranial nerve responsible for hearing and balance.