Amines
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:23 AM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
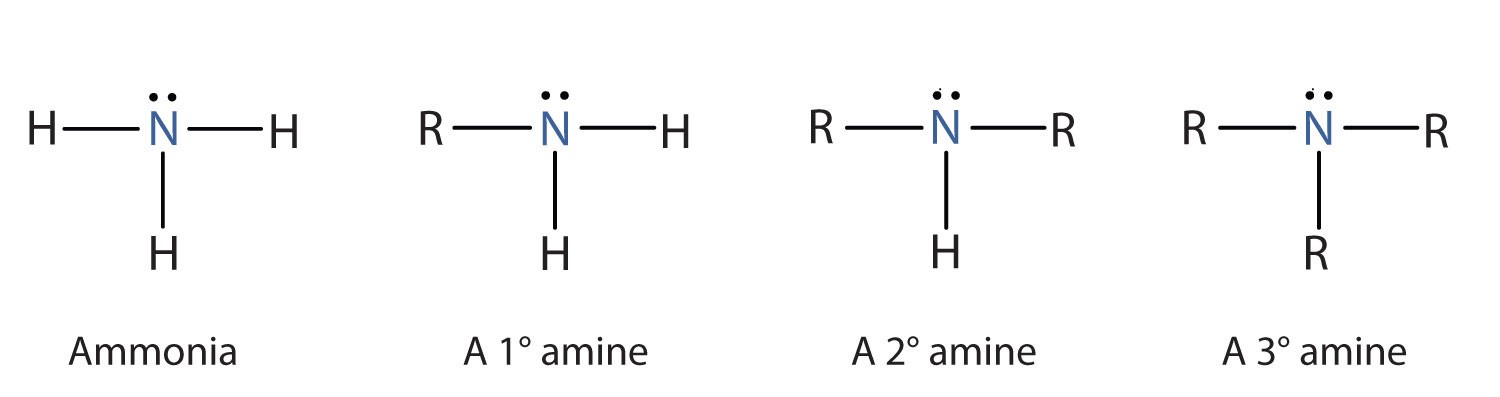
What is the difference between a primary, secondary and tertiary amine?
* primary → bonded to one R group
* secondary → bonded to two R groups
* tertiary → bonded to 3 R groups
* secondary → bonded to two R groups
* tertiary → bonded to 3 R groups
2
New cards
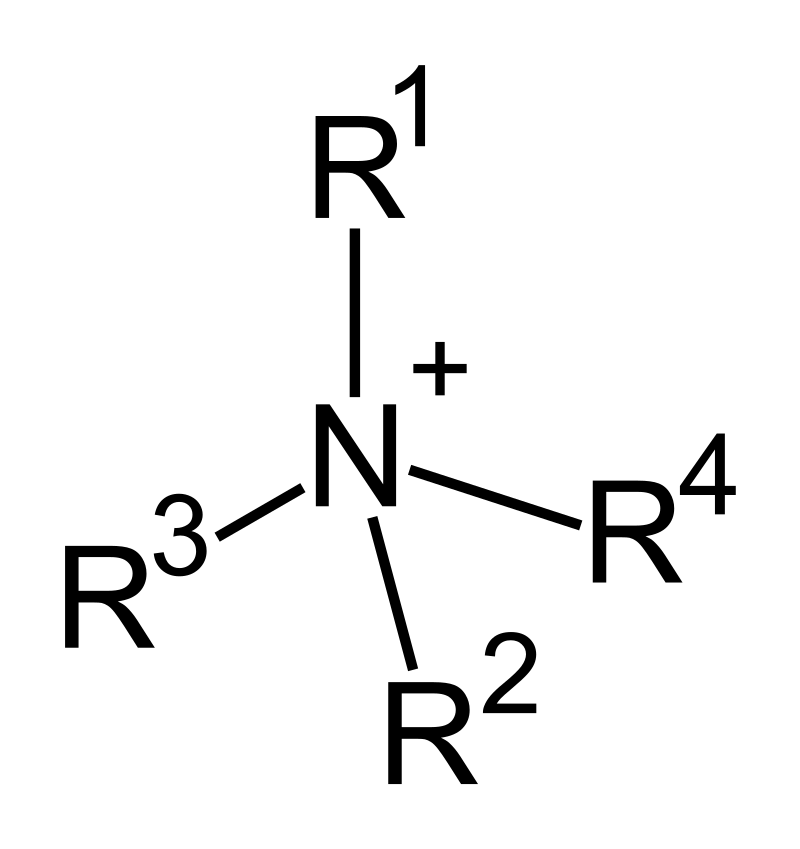
What are quaternary amines called and why?
* quaternary ammonium salts
* N bonded to 4 R groups instead of 3 → becomes a positively charged ammonium compound
* N bonded to 4 R groups instead of 3 → becomes a positively charged ammonium compound
3
New cards
How are amines named?
adding the prefix amino-
4
New cards
What are the reagents and conditions for making an amine from halogenoalkanes? Why is this reagent used?
* reagent: excess alcoholic ammonia
* amine produced has a lone pair so can attack another halogenoalkane and create an N-substituted molecule
* excess ammonia ensures all halogenoalkane molecules are reacted to prevent this
* conditions: reflux in excess, alcoholic solution under pressure
* amine produced has a lone pair so can attack another halogenoalkane and create an N-substituted molecule
* excess ammonia ensures all halogenoalkane molecules are reacted to prevent this
* conditions: reflux in excess, alcoholic solution under pressure
5
New cards
Draw the mechanism for the production of an amine from a halogenoalkane
See picture attached
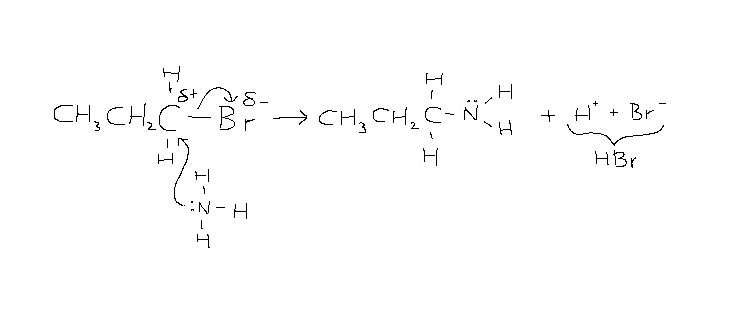
6
New cards
How are ammonium salts converted to their corresponding amine?
Adding alkali (NaOH)
7
New cards
What are the reagents for the production of amines from nitriles and what is this reaction called?
* LiAlH₄ in dry ether OR hydrogen with a nickel catalyst
* reduction reaction
* reduction reaction
8
New cards
What are the properties of 1°, 2° and 3° amines? (hint: lone pair)
the lone pair makes them:
* Lewis bases → lone pair donors
* Brönsted-lowry bases → proton acceptors
* Nucleophiles → provide lone pair to attack electron deficient centre
* Lewis bases → lone pair donors
* Brönsted-lowry bases → proton acceptors
* Nucleophiles → provide lone pair to attack electron deficient centre
9
New cards
What happens to the boiling point of an amine as the molecular mass increases?
boiling point increases
10
New cards
What is the difference between the boiling points of amines and corresponding alkanes? Why?
* amines have higher boiling points
* because of intermolecular hydrogen bonding
* because of intermolecular hydrogen bonding
11
New cards
What is the trend in solubility in amines? Are amines soluble in organic solvents?
* lower mass compounds are soluble in water → hydrogen bonding with solvent
* solubility decreases as molecules get heavier
* amines **are** soluble in organic solvents
* solubility decreases as molecules get heavier
* amines **are** soluble in organic solvents
12
New cards
What kind of bases are amines?
weak bases
13
New cards
Why are amines bases?
lone pair on N can accept proton
14
New cards
Which amines are stronger bases and why?
* tertiary (strongest) → secondary → primary → NH₃ → aromatic (weakest)
* alkyl groups push electrons towards N better than H therefore, lone pair more available in tertiary amines
* higher electron density on N = stronger base
* alkyl groups push electrons towards N better than H therefore, lone pair more available in tertiary amines
* higher electron density on N = stronger base
15
New cards
What does base strength depend on in amines?
how well N lone pair can accept H⁺ → if more electronegative N then stronger base
16
New cards
What are aromatic amines?
amino group directly bonded to a benzene ring
17
New cards
Are aromatic amines stronger or weaker bases than aliphatic amines? Why?
* weaker bases
* lone pair on N delocalises into the benzene ring → less available to accept proton
* lone pair on N delocalises into the benzene ring → less available to accept proton
18
New cards
What are the reagents and products of the ethanoylation (acylation) of primary amines?
* reagents: ethanoyl chloride
* products: N-substituted amide + HCl
* products: N-substituted amide + HCl
19
New cards
How is an alcohol made from an aliphatic amine? What are the observations of this reaction?
* add cold nitrous acid (HNO₂) at 5°C
* HNO₂ made **in situ** by adding sodium nitrite (NaNO₂) and HCl at or below 5**°**C
* aliphatic amine + HNO₂ → alcohol
* observations: bubbles of nitrogen gas
* HNO₂ made **in situ** by adding sodium nitrite (NaNO₂) and HCl at or below 5**°**C
* aliphatic amine + HNO₂ → alcohol
* observations: bubbles of nitrogen gas
20
New cards
What is the equation for aliphatic amine → alcohol?
CH₃CH₂NH₂ + HNO₂ → CH₃CH₂OH + N₂ + H₂O
21
New cards
What is the equation for amide → amine?
CH₃CONH₂ + 4\[H\] → CH₃CH₂NH₂ + H₂O
22
New cards
What is the reagent for amide → amine and what is this reaction called?
* LiAlH₄ in dry ether solvent
* reduction reaction
* reduction reaction
23
New cards
What is the equation for amide → nitrile?
CH₃CONH₂ → CH₃CN + H₂O
24
New cards
What is the reagent for amide → nitrile and what is this reaction called?
* P₄O₁₀
* dehydration reaction
* dehydration reaction
25
New cards
What are the equations for amide → carboxylic acid?
RCONH₂ + H₂O + H⁺ → RCOOH + NH₄⁺ (acid hydrolysis)
\
RCONH₂ + NaOH → RCOO⁻Na⁺ + NH₃ (alkaline hydrolysis)
\
RCONH₂ + NaOH → RCOO⁻Na⁺ + NH₃ (alkaline hydrolysis)
26
New cards
What are the conditions and reagents for amide → carboxylic acid?
* conditions: reflux
* reagents: acid/alkaline hydrolysis → H+ catalyst/ OH-
* need to protonate carboxylate salt for alkaline hydrolysis
* reagents: acid/alkaline hydrolysis → H+ catalyst/ OH-
* need to protonate carboxylate salt for alkaline hydrolysis
27
New cards
What are the conditions and reagents for the 1st step of azo dye formation? How is the catalyst removed?
* conditions: reflux
* reagents: tin catalyst + HCl followed by NaOH
* catalyst removed by filtration
* reagents: tin catalyst + HCl followed by NaOH
* catalyst removed by filtration
28
New cards
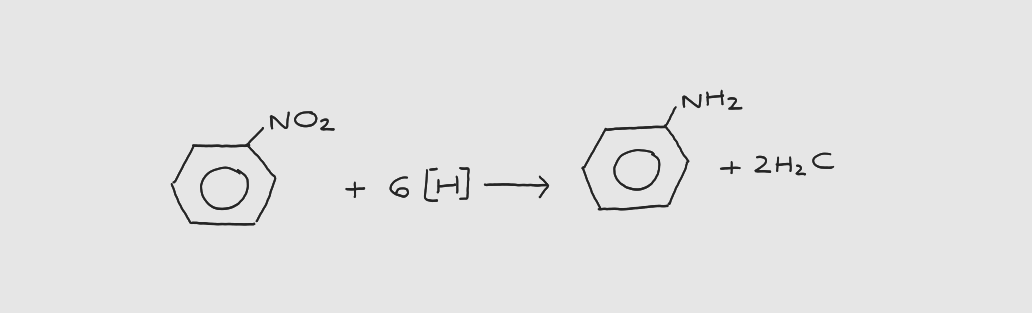
What is the 1st step of azo dye formation?
nitrobenzene → phenylamine
29
New cards
Why is NaOH needed in the 1st stage of azo dye formation?
liberates the phenylamine rather than the salt
30
New cards
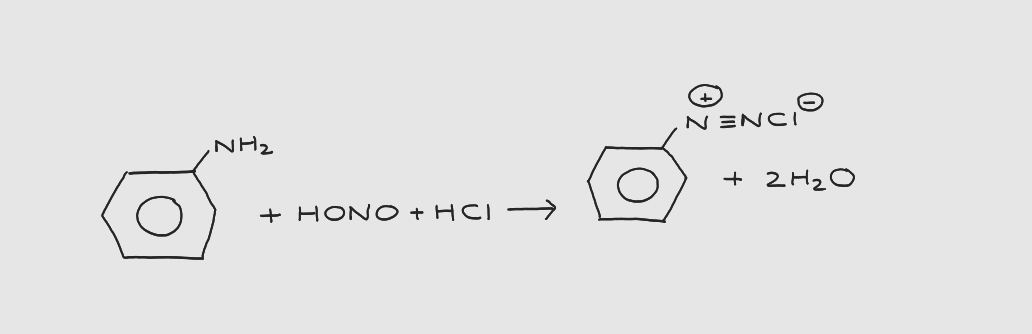
What is step 2 of azo dye formation?
phenylamine → diazonium salt
31
New cards
What are the conditions and reagents for the 2nd step of azo dye formation?
* reagents: nitrous acid (HONO or HNO₂) + HCl
* HONO prepared in situ by reacting sodium nitrite with HCl
* otherwise it decomposes
* conditions: 5°C
* HONO prepared in situ by reacting sodium nitrite with HCl
* otherwise it decomposes
* conditions: 5°C
32
New cards
What happens to the diazonium salt if the temperature is above 10°C?
* loses nitrogen gas
* OH group joins
* phenol made
* OH group joins
* phenol made
33
New cards
What happens to the diazonium salt if the temperature is below 10°C? How is it kept below 10°C?
* lone pairs present participate in benzene ring making it more stable
* due to overlap of p-orbitals in the diazo group with p-orbitals in ring
* carried out in ice
* due to overlap of p-orbitals in the diazo group with p-orbitals in ring
* carried out in ice
34
New cards
Why are only aromatics used in the production of diazonium salts?
aliphatic Diazonium salts are very unstable
35
New cards
What is step 3 in the formation of azo dyes?
coupling reactions → either with phenols or naphthalen-2-ol
36
New cards
What are the conditions and reagents for the coupling of diazonium salt with phenols? What is the colour of the azo dye produced and what else is produced in this reaction?
* conditions:
37
New cards
What is a chromophore? What is a chromophore in azo dyes?
* conjugated system that absorbs electromagnetic radiation in the UV-visible region of EM spectrum
* for azo dyes → -N=N- group (diazo group) → help conjugation in molecules which ^^**increases wavelength of light molecule can absorb**^^
* for azo dyes → -N=N- group (diazo group) → help conjugation in molecules which ^^**increases wavelength of light molecule can absorb**^^
38
New cards
How can chromophores be measured?
UV-vis spectroscopy
39
New cards
What is a conjugated system?
the overlap of pi-electrons in the -N=N- group and the pi-electrons of the 2 benzene rings
40
New cards
What are the conditions for the coupling of diazonium salt with naphthalen-2-ol? What is the colour of the azo dye produced?
* conditions: alkaline conditions
* red
* red
41
New cards
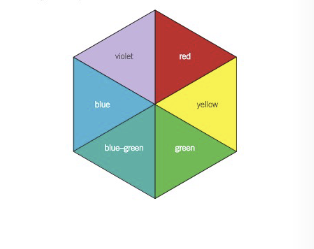
What determines the colour of a compound? How can this colour be found?
* complementary colour of the colour absorbed is the one transmitted
* can be found using a colour wheel
* can be found using a colour wheel
42
New cards
Which position is coupling usually favourable in? Where does coupling take place if this position is unavailable? What are these positions relative to?
* favourable in 4th position but if taken, occurs in 2nd
* relative to OH group
* relative to OH group