Infectious Disease: Macular/Maculopapular Rash
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Macule
1. Flat skin lesion
2. Altered color
3. Less than 1 cm
Which type of skin lesion?
Papule
1. Elevated skin lesion
2. Growth of abnormal tissue
3. Less than 1 cm
Which type of skin lesion?
Maculopapular rash
A flat or elevated skin lesion with altered color that is less than 1 cm is known as a...
1. Viral exanthems
> Measles/Rubeola
> Rubella/German measles
2. Toxic Shock Syndrome (Staph, Strep)
3. Meningococcemia (Neisseria)
4. Leptospirosis
5. RMSF
6. Ehrlichiosis & Anaplasmosis
7. Dengue
8. Chikungunya fever
9. Typhoid fever
Which infections w/ a macular or maculopapular rash are required to be nationally notified?
Exanthems
Infections:
1. Parvovirus B19
2. HHV-6 and 7 (Roseola)
3. HHV-3 (Varicella zoster)
4. Measles
5. Rubella
6. Coxsackie A and Echovirus
7. GAS (Scarlet fever)
Non-specific widespread maculopapular skin rashes that are accompanied by systemic symptoms of inflammation such as fever, malaise, and headache are known as...
1. Hard Measles
2. 14 day Measles
3. Rubeola
What are the 3 alternate names for Measles?
Measles
Rubeola is also known as...
Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles
SSx:
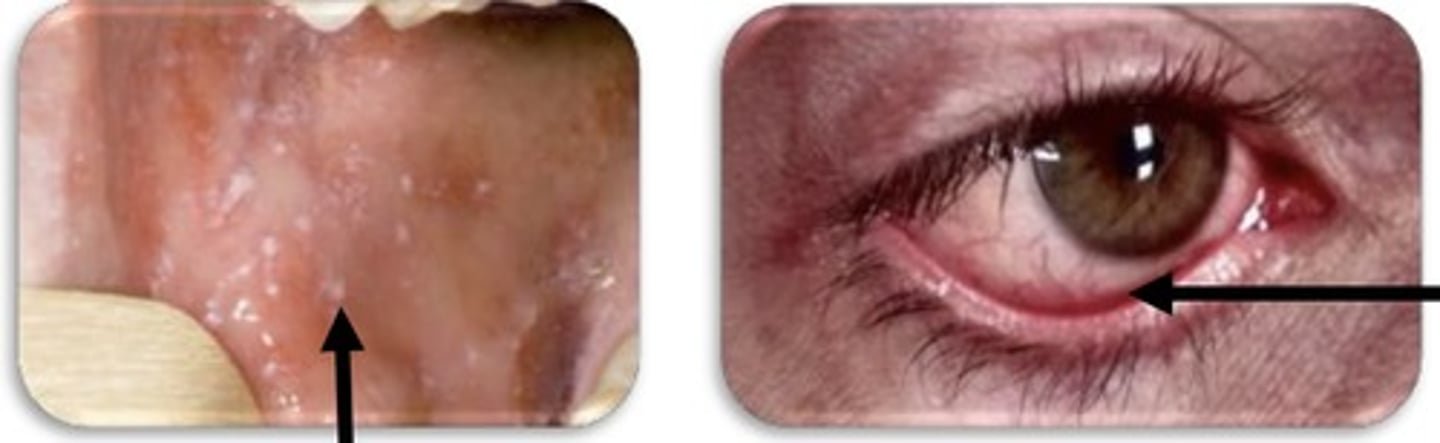
1. Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis
2. Koplik spots on buccal mucosa
3. Stimson line (transverse line of inflammation along lower eyelid)
4. Fever precedes rash
5. Exanthem = descending, begins on face or behind ears, starting at hairline, spares palms and soles
Labs:
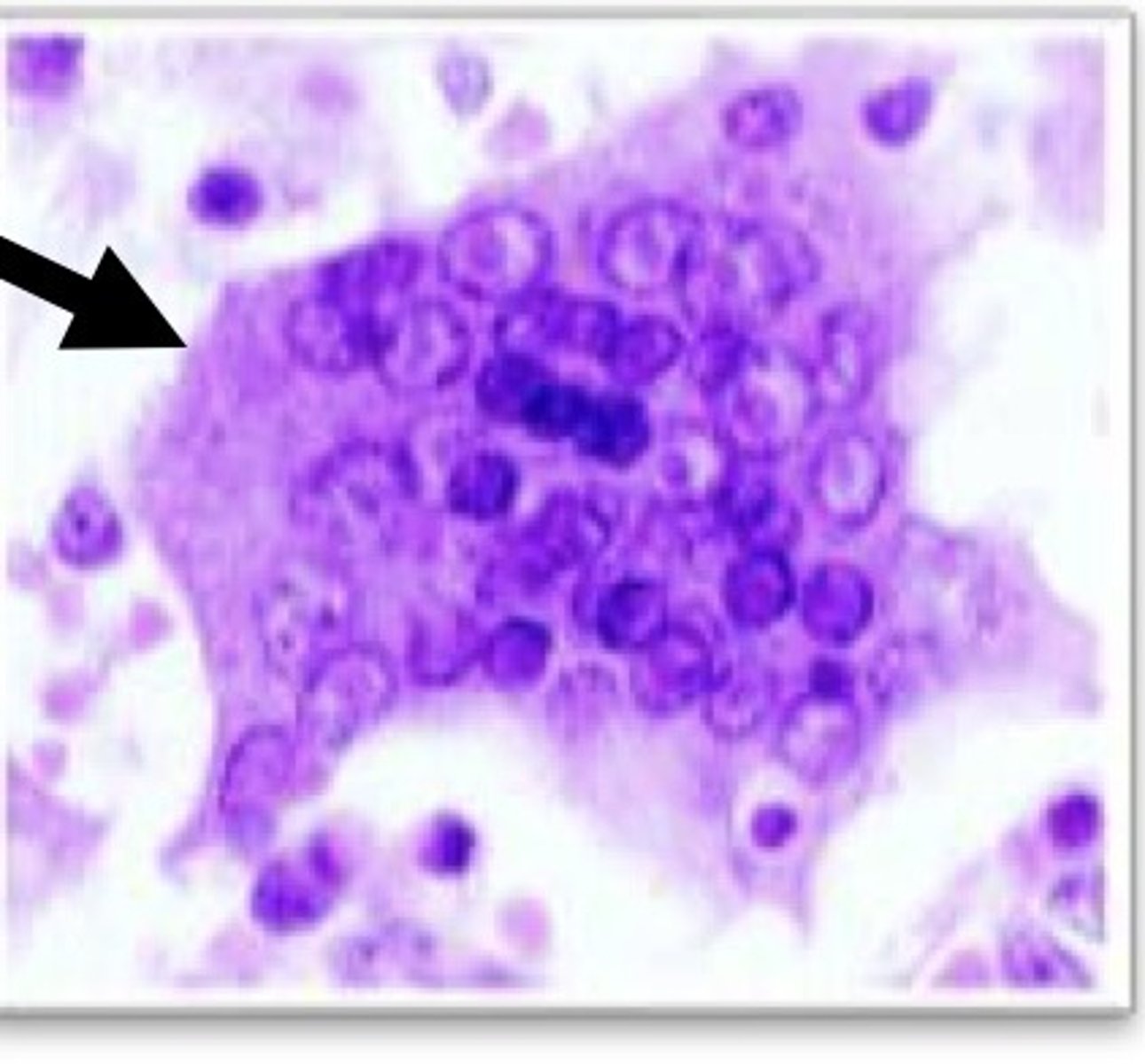
1. Warthin-Finkeldey cells (multinucleated giant lymphoid cells)
Dx?
Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles
SSx:
1. Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis
2. Koplik spots on buccal mucosa
3. Stimson line (transverse line of inflammation along lower eyelid)
4. Fever precedes rash
5. Exanthem = descending, begins on face or behind ears, starting at hairline, spares palms and soles
Labs:
1. Warthin-Finkeldey cells (multinucleated giant lymphoid cells)
Dx?
Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles
Which virus produces Warthin-Finkeldey cells (multi-nucleated giant lymphoid cells)?
Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles
Koplik spots (white lesions on buccal mucosa) are pathognomonic for...
1. Otitis media
2. Hearing loss
3. Pneumonia
4. Diarrhea
5. Vitamin A deficiency
If a high fever is persistent after the 4th day of rash, what complications can arise from Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles?
Vitamin A
What is often included in the treatment of Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles since its deficiency can cause complications?
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)
A rare progressive behavioral and intellectual deterioration caused by encephalitis and eventual death... no effective treatment...
Which complication of Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles ?
Rubeola (Measles) = not associated w/ congenital disease, but can infect the placenta
Rubella = associated w/ congenital disease
How does Rubeola (Measles) and Rubella affect pregnancy?
MMR or MMRV vax
*avoid giving to pregnant women or IC patients since it's a live vax
Measles (Rubeola) can be prevented w/...
1. German measles
2. 3 day measles
What are the 2 alternate names for Rubella?
Rubella/German measles/3 day measles
SSx:
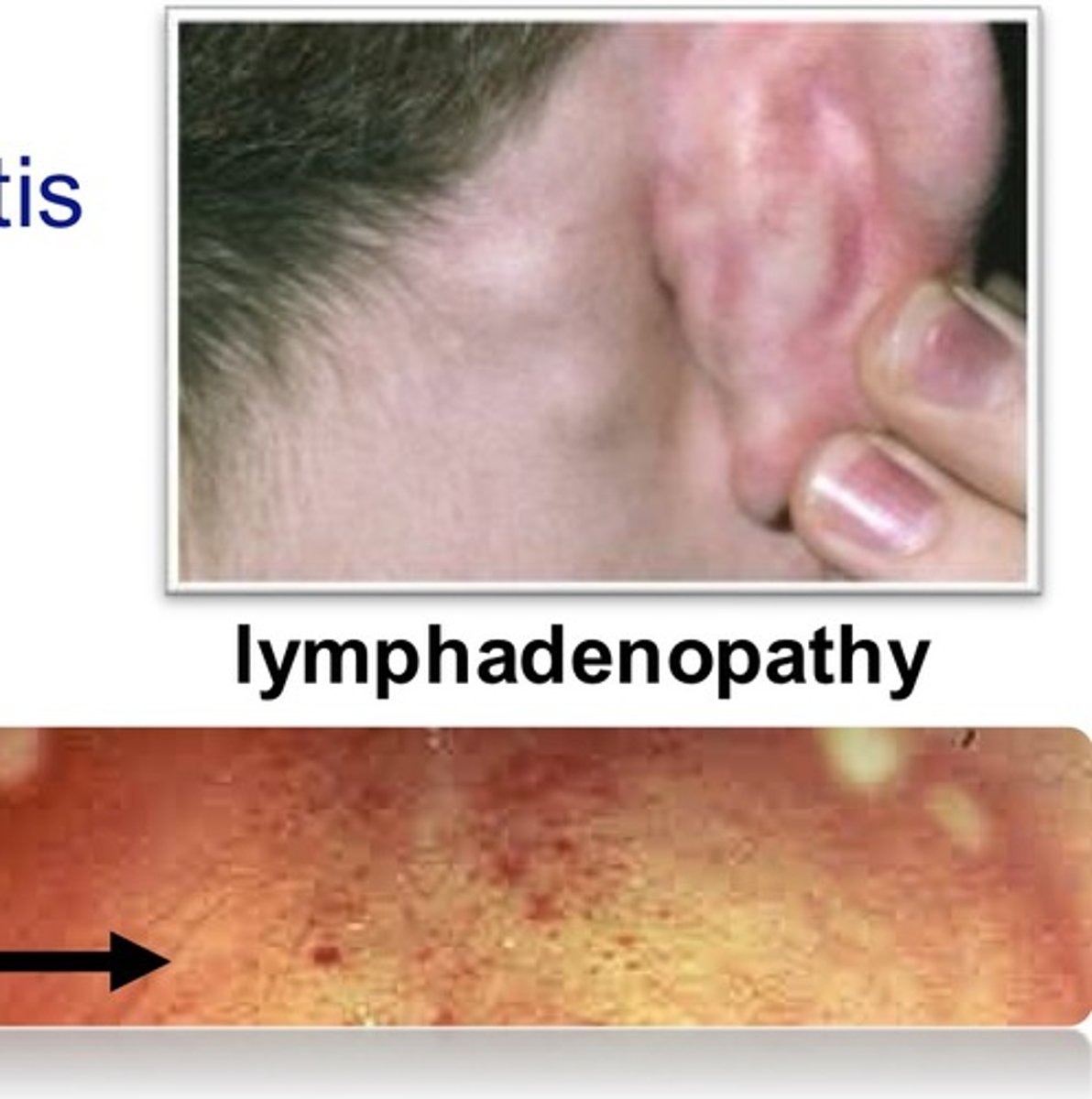
1. Tender LAD post-auricular/suboccipital/posterior cervical preceding a rash
2. Women get self-limiting polyarthritis
3. Forchheimer spots (petechial hemorrhage on soft palate)
4. Exanthem = non-confluent rash (widely spaced/discrete lesions), starts on face and descends, spares palms and soles, lasts up to 3 days and fades on face when descending
Dx?
Rubella/German measles/3 day measles
Which virus has been historically associated w/ Forchheimer spots (petechial hemorrhages on the soft palate)?
Toxoplasmosis
Other
Rubella
CMV
Herpes
*congenital diseases
What does TORCH stand for?
MMR or MMRV vax
*avoid giving to pregnant women and IC since it's a live vax
Rubella can be prevented w/...
1. Deafness
2. Eye abnormalities (retinopathy, cataracts, glaucoma, microphthalmia)
3. Congenital heart disease (PDA)
What is the classic triad of Congenital Rubella Syndrome?
Congenital Rubella Syndrome
SSx:
1. Deafness
2. Eye problems
3. Patent Ductus Arteriosus
4. Blueberry muffin rash
5. Growth restriction
6. CNS abnormalities
Dx?
Scarlatina
What is an alternate name for Scarlet Fever?
Scarlet Fever/Scarlatina (GAS)
SSx:
1. Abrupt onset of sore throat and fever
2. Pharyngitis/tonsilitis
3. No upper respiratory signs
4. Exanthem: sandpaper rash w/ diffuse red blush that blanches under pressure --> rash moves from neck and groin to extremities --> concentrating in groin, neck, and axilla
5. Pastia's lines (petechiae in creases)
Labs:
1. Increase in ASO titer
2. Anti-DNase B in serum
Dx?
Rheumatic fever & glomerulonephritis
What are 2 potential sequelae post-streptococcal infection?
Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles
1st day of rash = Koplik's spots on buccal mucosa, discrete rash
3rd day of rash = confluent maculopapules
Dx?
Rubella/German measles/3 day measles
1st day of rash = discrete rash
3rd day of rash = discrete rash
Dx?
Scarlet Fever (GAS)
1st day of rash = flushed cheeks, increased neck density, Pastia's sign, increased density in groin
3rd day of rash = strawberry tongue, increased density in axilla, positive blanching test
Dx?
Measles/Rubeola/Hard measles/14 day measles
An unvaccinated, 5 y/o child presents w/ fever, cough, coryza, non-purulent conjunctivitis for several days followed by white lesions on the buccal mucosa, painless cervical LAD, and a slowly descending increasingly confluent maculopapular rash lasting 1 week starting at the hairline but sparing the palms and soles.
Dx?
Rubella/German measles/3 day measles
A woman presents w/ fever and mild non-confluent maculopapular rash starting on the face that fades as it descends the body, lasting a few days, not involving palms and soles, accompanied w/ mild petechiae on the soft palate, tender LAD behind the ear, and polyarthralgia that persisted for several weeks. No history of vaccine.
Dx?
Scarlet Fever
A child presents w/ fever, toxicity, flushed face w/ circumoral pallor, erythematous sore throat, and a descending blanching, diffuse sandpaper body rash. Petechiae in creases of the elbows and knees followed by desquamation including palms and soles, strawberry tongue, and a positive ASO titer were found.
Dx?
Erythema infectiosum and Fifth Disease
What are 2 alternate names for Parvovirus B19 infection?
Parvovirus B19/Erythema Infectiosum/Fifth Disease
SSx:
1. Children: slapped cheek exanthem --> spreads in a reticular lace-like pattern
2. Adults: acute polyarthritic symptoms usually in females
3. Anemia may develop
Dx?
Pancytopenia/anemia (aplastic anemia)
What is a complication of Parvovirus B19 infection in all ages?
Hydrops fetalis (systemic edema)
What is a complication of neonatal erythema infectiosum (Parvovirus B19 infection)?
Roseola infantum and Exanthem subitum
*caused by HHV-6B and HHV-7
What are 2 alternate names for Roseola?
Roseola/Roseola infantum/Exanthem subitum
*caused by HHV-6B and HHV-7
SSx:
1. Sudden high fever (102-106)
2. Febrile seizures
3. Rapid recovery followed by "surprise" rash
> maculopapular confluent nonpruritic rash suddenly appears on the trunk after fever (no overlap)
Dx?
Pityriasis rosea
A reactivation of HHV-6 and HHV-7 causing an acute exanthem in adults is known as...
Congenital Roseola (HHV-6 and HHV-7)
What is the only known virus that can cause genetic inheritance of its infection since it can integrate into the chromosome of parental germline DNA?
Coxsackie A & Echovirus
Which 2 viruses cause nonpolio enteroviral rash?
Echovirus 9 & 16
Nonspecific exanthem (w/out vesicles) in children is most commonly caused by which virus?
Nonpolio Enteroviral rash (Coxsackie A and Echovirus)
SSx:
1. GI symptoms precede the rash
2. Respiratory symptoms (pharyngitis or summer croup)
3. Exanthem: mild macular or maculopapular descending nonpruritic rash that moves from face or neck to the trunk, can progress to palms and soles, oral vesicular lesions
Dx?
Nonpolio Enteroviral rash (Coxsackie A and Echovirus)
A young child presents w/ mild fever, nausea, and diarrhea for few days followed by sore throat, runny nose, cough, and mild descending maculopapular rash involving the trunk and neck lasting 2 days.
Dx?
Roseola/Roseola infantum/Exanthem subitum
*caused by HHV-6B and HHV-7
An infant rapidly develops a high fever lasting a few days and tender cervical LAD. Fever rapidly disappears followed by sudden appearance of a maculopapular rash starting on the trunk that lasts about 1 day, as well as petechiae on the soft palate.
Dx?
Parvovirus B19/Erythema Infectiosum/Fifth Disease
A child presents w/ low grade fever and a "slapped cheek" rash that spreads down to the extremities, becoming pruritic and lasting a couple weeks.
Dx?
Drug eruption = palms and soles heavily involved
Infections = symmetrical rash that usually spares palms and soles
How can you tell the difference b/t an exanthem caused by drugs vs infectious agents?
1. Rubella (common)
2. CMV
3. Toxoplasmosis
4. Enterovirus (Coxsackie)
5. EBV
What are the MCC of blueberry muffin rash in nenonates?
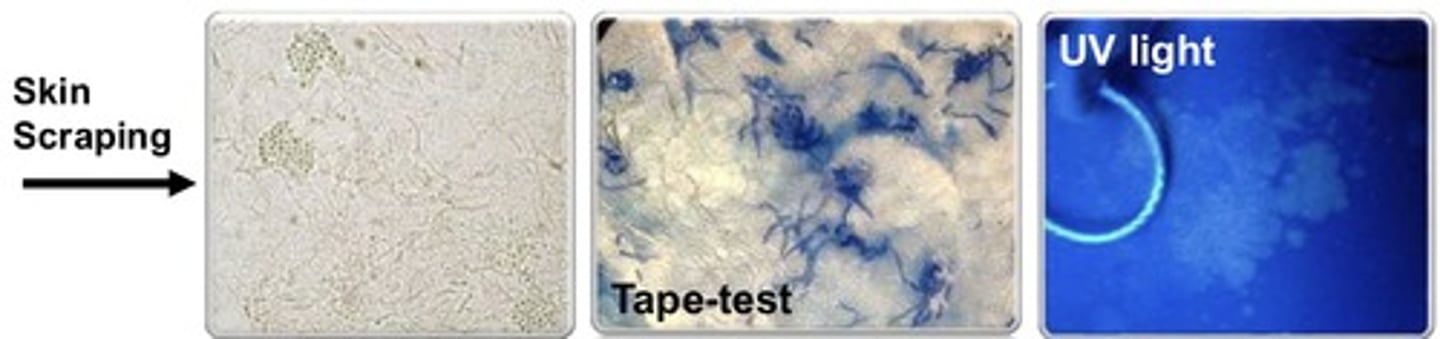
Tinea Versicolor/Pityriasis versicolor/Cutaneous malasseziasis
SSx:
1. Whitish or brown (hypo/hyperpigmented) "branny" scaling non-blanching superficial macules/maculopapules above the waist
Labs:
1. 10% KOH treated skin scrapings show round, short, fat hyphae and clumps of yeast cells (spaghetti and meatballs)
2. Wood's lamp shows fluorescence
Dx?
Toxic Shock Syndrome (gram positive cocci)
S. aureus = TSST-1 and enterotoxins = always GI sx
S. pyogenes = exotoxins = sandpaper rash, bullae, necrotizing cellulitis
SSx:
1. GI symptoms
2. Sudden fever (38.9 or 102) rapidly progresses to hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, and confusion
3. Erythematous macular rash resembling a sunburn
4. Desquamation of palms, soles, strawberry tongue
5. Rash may be sandpaper like
Dx?
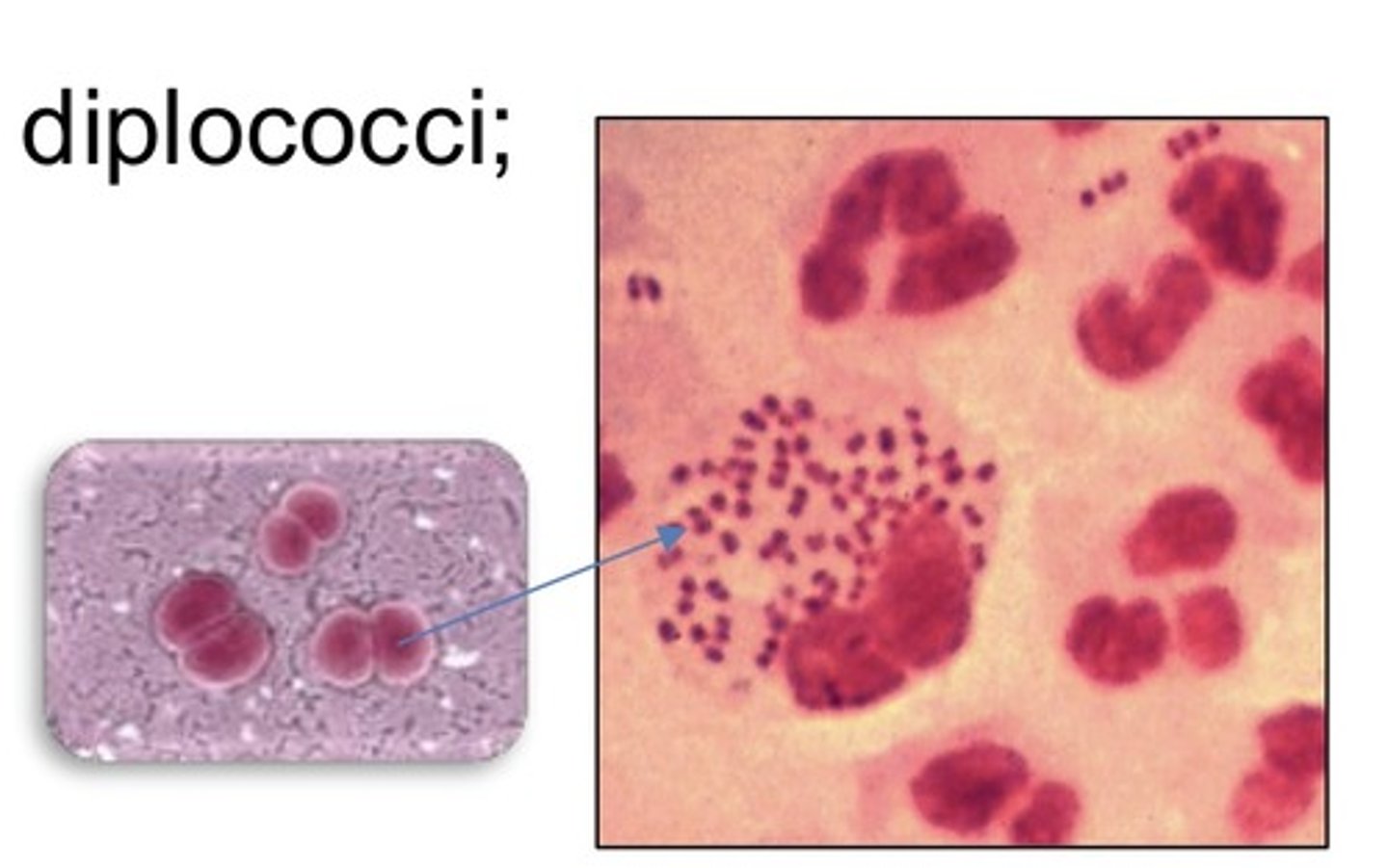
Meningococcemia (Neisseria meningitidis)
SSx:
1. Early RTI followed by fever and hypotension
2. Non-blanching macules and petechiae begin on trunk and legs and spread to areas where pressure is applied (hemorrhagic rash) --> ecchymoses w/ central necrosis
Labs:
1. Gram negative diplococci
Dx?
1. Septic shock
2. DIC
3. Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome (adrenal hemorrhage)
What is the triad of Fulminant Meningococcemia?
Meningococcal conjugated polysaccharide vax (MenACYW)
Meningococcemia can be prevented w/...
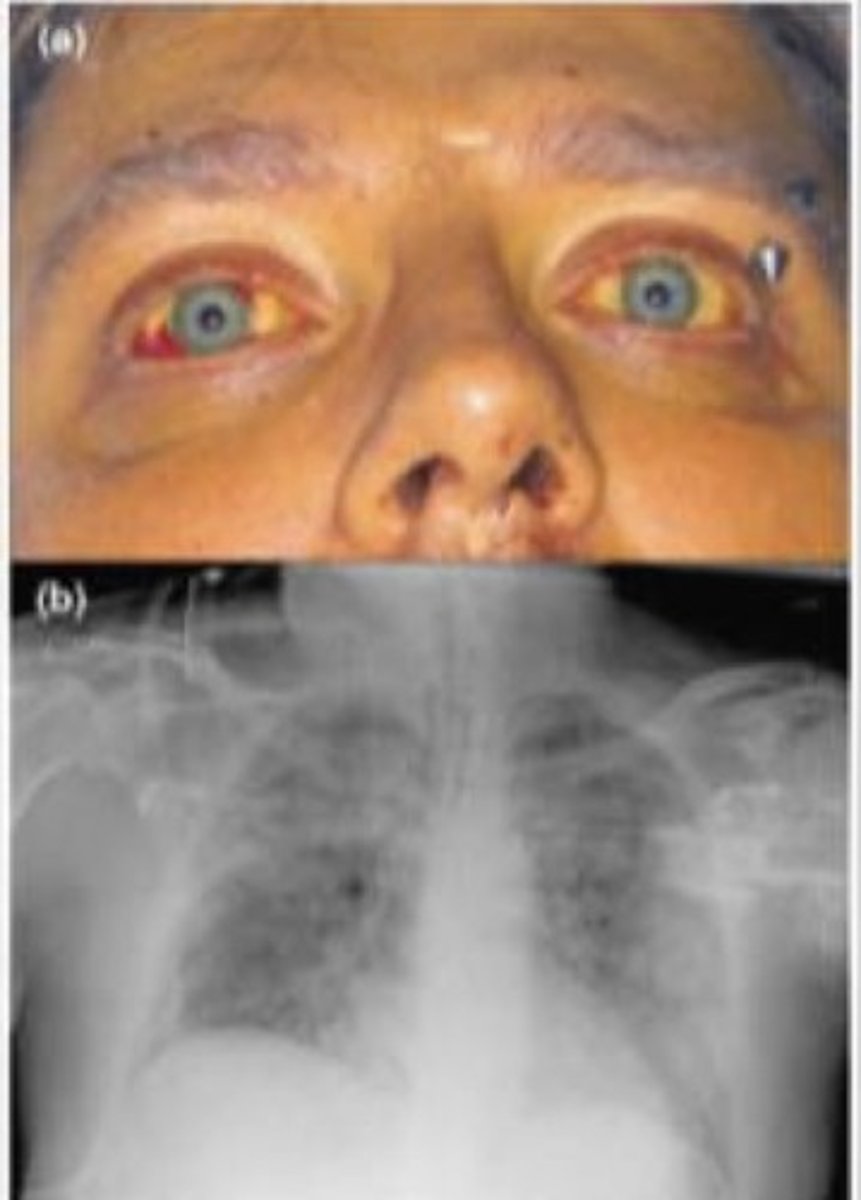
Weil's syndrome and Icteric leptospirosis
What are 2 alternate names for Leptospirosis?
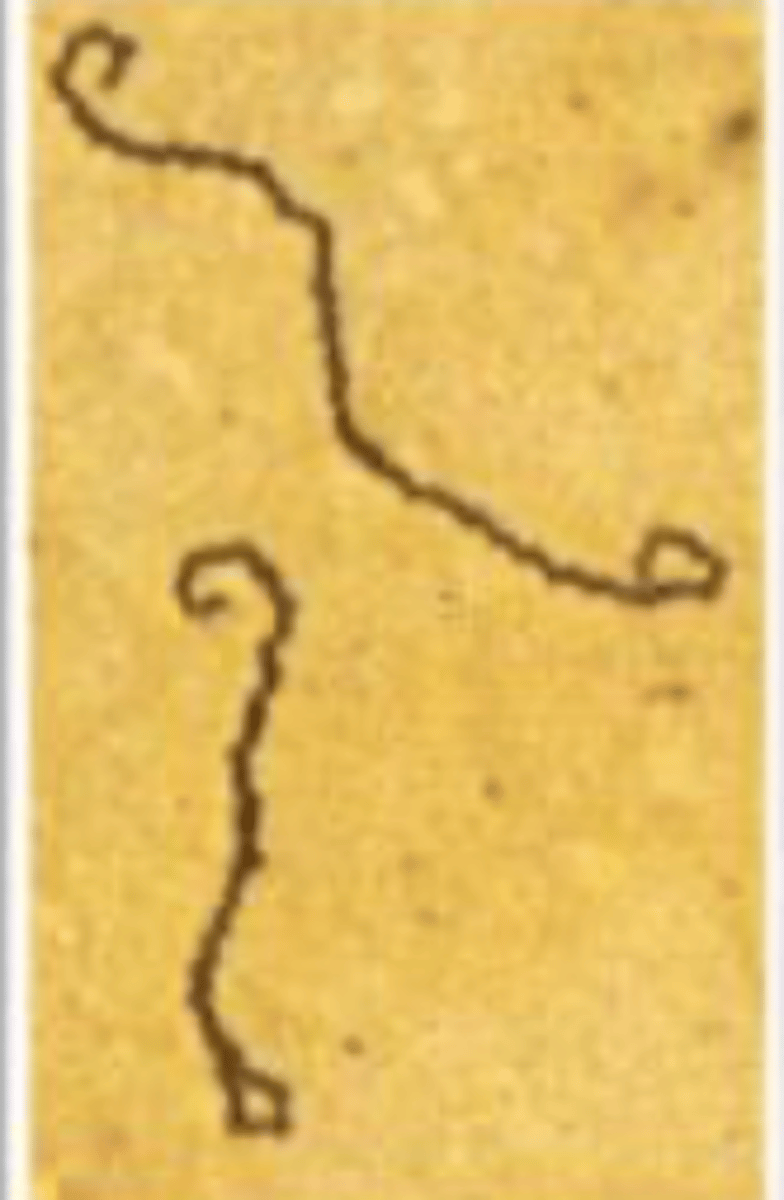
Leptospirosis/Weil's syndrome/Icteric leptospirosis
SSx:
1. Flu-like sx
2. Can progress to jaundiced immune phase
3. Uveitis
4. Kidney, liver, brain inflammation
5. Macular or maculopapular eruption on trunk and limbs
Labs:
1. Gram negative spirochete in blood or urine
Dx?

Weil's syndrome
> jaundice
> AKI
> hemorrhage
What is the severe form of Leptospirosis and what is the classic triad?
Toxic Shock Syndrome
An individual w/ compromised skin or mucous membranes develops high fever, hypotension, diffuse macular rash, hyperemic membranes (flushed appearance due to vasodilation) and toxicity (vomiting, confusion, myalgia). Desquamation, including palms and soles. Gram positive cocci isolated from blood culture.
Dx?
Meningococcemia
18 y/o college student presents w/ fever, severe headache, sore throat, malaise, hypotension, and non-blanching macules and hemorrhagic patches on the trunk and knees. Gram negative diplococci isolated from blood culture.
Dx?
Leptospirosis
Two students waded in waters at a rain-flooded farm to rescue farm animals present 1 week later w/ fever, chills, and maculopapular rash that progressed to hemorrhagic patches. Spirochete w/ hooked ends was isolated from blood culture.
Dx?
Malasseziasis/Tinea versicolor/Pityriasis versicolor
Young woman presents w/ mildly pruritic scaly non-tanning maculopapular rash on her back that showed up this summer. Micrograph shows hyphae.
Dx?
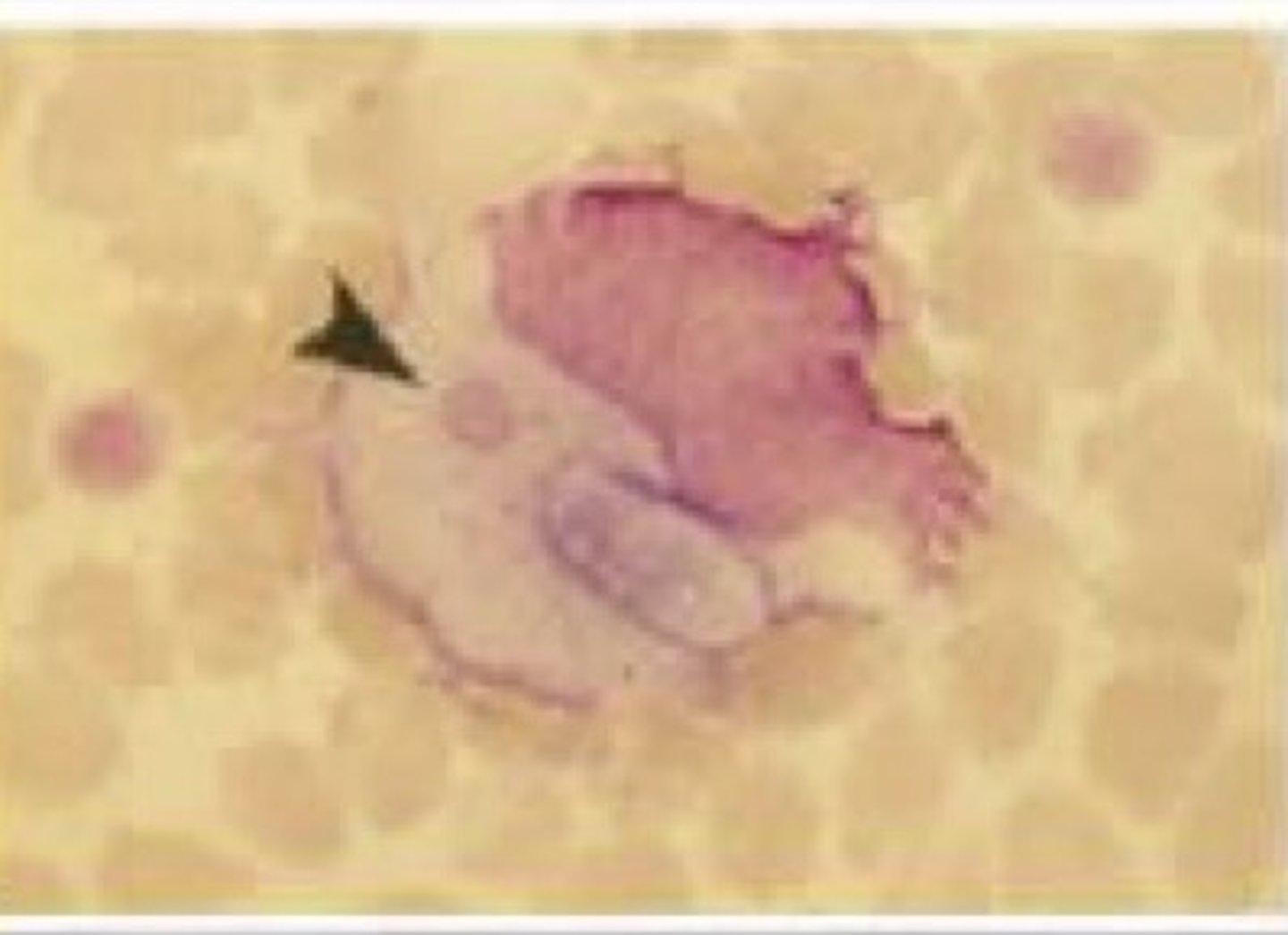
Human Monocytotropic Ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia chaffeensis)
SSx:
1. Fever and chills
2. Pinpoint maculopapular or petechial non-pruritic eruption or erythematous splotches... though rash not commonly seen due to phagocytes affected
3. Thrombocytopenia, left shift
History = near lone star ticks
Labs:
1. Monocytic infection
2. Gram negative, obligate intracellular pleomorphic coccobacillus
Dx?
Anaplasmosis/Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (Anaplasma phagocytophilum)
SSx:
1. Fever and chills
2. Pinpoint maculopapular or petechial non-pruritic eruption or erythematous splotches... though rash not commonly seen due to phagocytes affected
3. Thrombocytopenia, left shift
History = near Ixodes ticks
Labs:
1. Granulocyte infection
2. Gram negative, obligate intracellular pleomorphic coccobacillus
Dx?
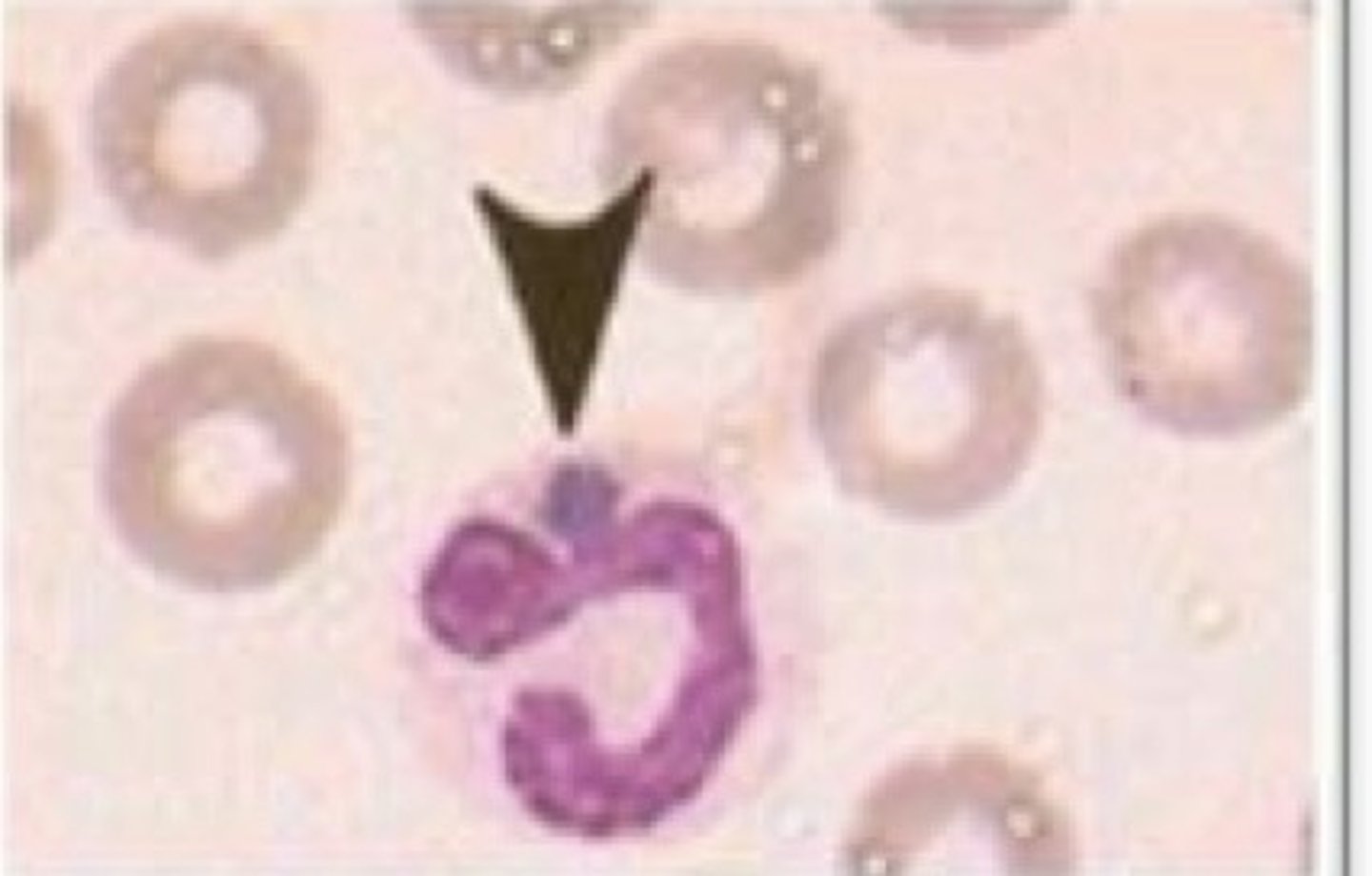
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (Rickettsia rickettsii)
SSx:
1. Flu sx
2. GI sx
3. Stiff neck
4. Thrombocytopenia
5. Ascending rash... non-pruritic macules begin on the wrists and ankles, spreading to trunk and face
6. Rash progresses to maculopapules then petechiae involving soles and palms
7. Periorbital and peripheral edema in children
8. No scabbed tick bite (eschar)
History = tick bite
Labs:
1. Gram negative obligate intracellular pleomorphic coccobacillus
Dx?
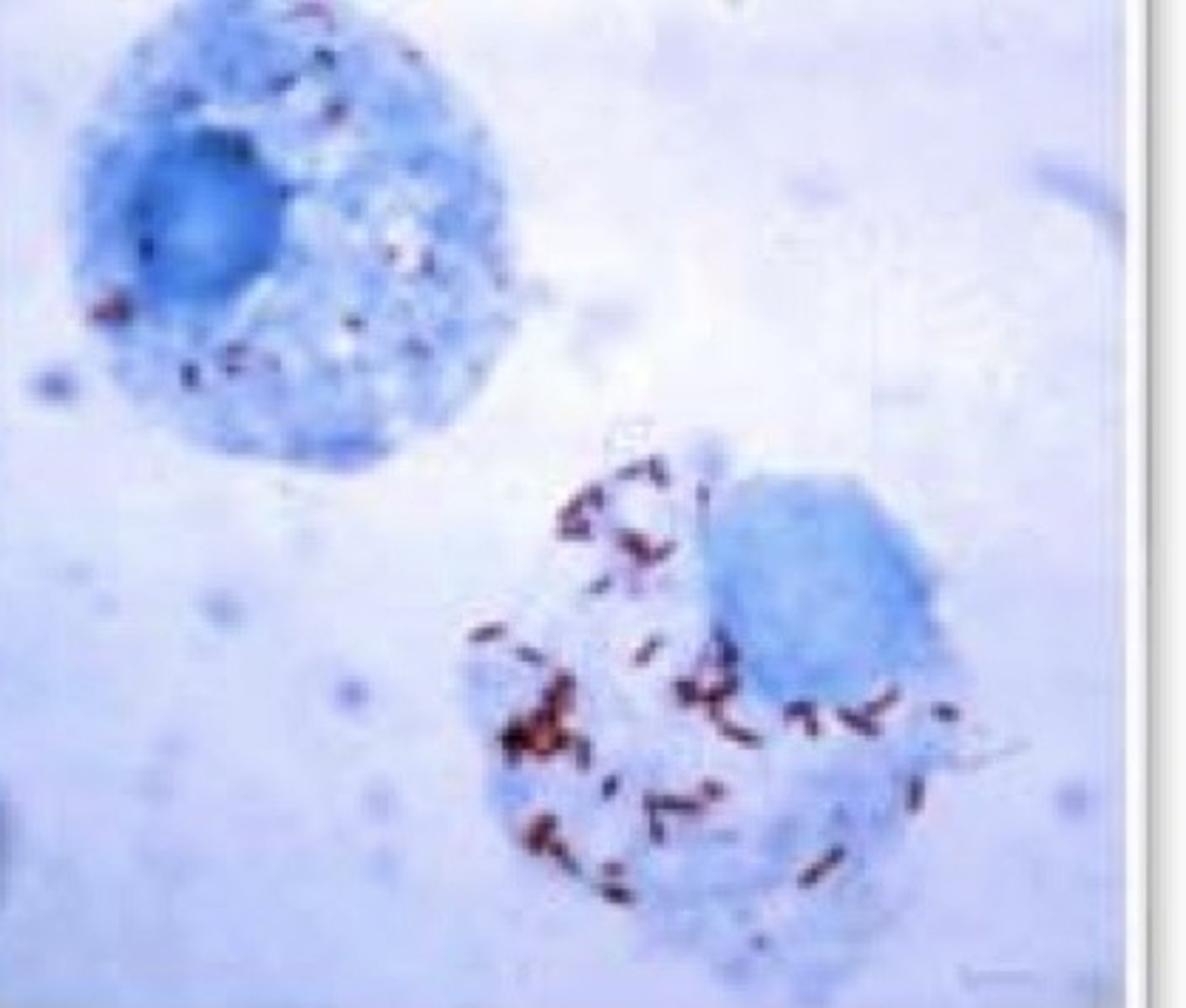
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (Rickettsia rickettsii)
If patients present w/ the following eschar (scabbed tick bite), what can immediately be ruled out?
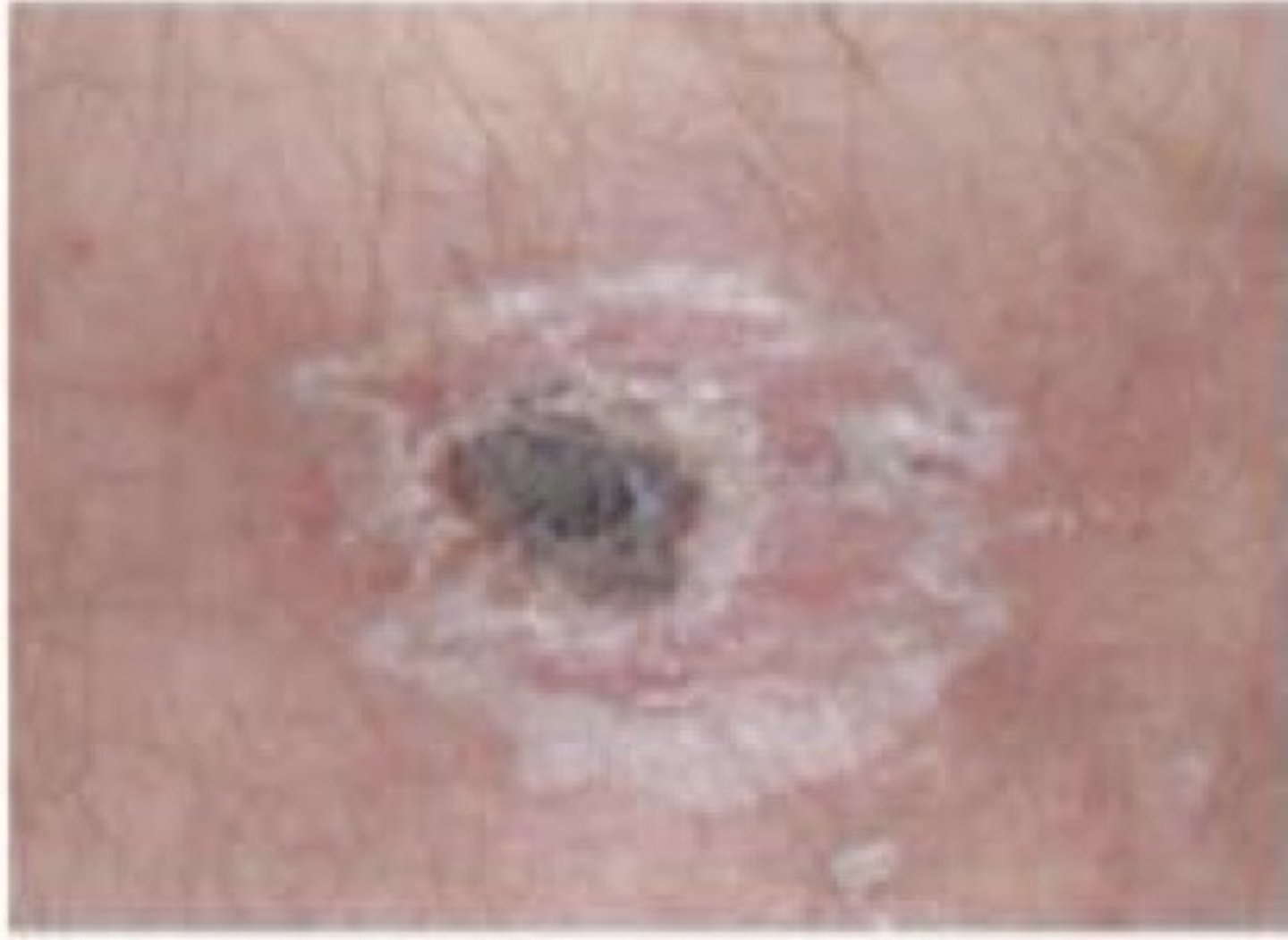
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (Rickettsia rickettsii)
What is the most deadly tick borne disease worldwide?
Typhus group rickettsiosis/Epidemic Typhus/Brill-Zinsser disease (Rickettsia prowazekii)
SSx:
1. Flu sx
2. Prolonged high fever (40/104)
3. Macular rash appears w/in few days of fever and is usually beginning on axilla and trunk and spreads centrifugally to extremities but typically spares the face, palms, and soles
4. Rash may become maculopapular, petechial, or purpuric --> ischemia and gangrene of fingers/toes
History = contact w/ lice or flying squirrel
Labs:
1. Positive non-specific Weil-Felix test
2. Gram negative obligate intracellular pleomorphic coccobacillus
Dx?
Typhus group rickettsiosis/Endemic Murine Typhus (Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia felis)
SSx:
1. Flu sx
2. Less severe
3. Macular rash appears w/in few days of fever and is usually beginning on axilla and trunk and spreads centrifugally to extremities but typically spares the face, palms, and soles
4. Rash lasts 1-4 days
History = contact w/ fleas
Labs:
1. Gram negative obligate intracellular pleomorphic coccobacillus
Dx?
Typhus group rickettsiosis/Endemic Murine Typhus (Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia felis)
An adult presents w/ fever, flu symptoms, headache, followed 5 days later by a rash spreading outward from the trunk to the limbs. Recent history of flea bites from frequent contact w/ stray animals and wildlife in southern Texas.
Dx?
Typhus group rickettsiosis/Epidemic Typhus/Brill-Zinsser disease (Rickettsia prowazekii)
50 y/o homeless person w/ high persistent fever, chills, severe headache and myalgia, confusion, and petechial rash on the trunk and limbs. Exam reveals body lice.
Dx?
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (Rickettsia rickettsii)
Patient presents w/ high fever (102-104, spiking at 106), severe headache and myalgia, confusion, and petechial rash concentrated on the extremities, involving the palms and soles, that quickly spreads to the trunk. History of tick bites.
Dx?
Ehrlichiosis
50 y/o camper in Arkansas presents w/ high persistent fever, headache, and sparse pinpoint rash on trunks and limbs following tick bite. Patient's monocytes contain morulae.
Dx?
Anaplasmosis
50 y/o camper in Maine presents w/ high persistent fever, headache, and sparse pinpoint rash on trunks and limbs following tick bite. Patient's granulocytes contain morulae.
Dx?
Bonebreak fever
What is another name for Dengue Fever?
Classic Dengue (w/out warning signs)
Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (w/ warning signs)
Dengue Shock Syndrome
What are the 3 types of Dengue Fever?
Dengue Fever
SSx:
1. High fever and blanching macular rash
2. Progresses to "saddleback" biphasic fever
3. Severe plasma leakage --> abrupt morbilliform or scarlatiniform centrifugal spreading maculopapular rash on trunk, face, etc
4. Palms and soles become bright red
5. Hemorrhagic signs
6. Bone pain
History = Aedes mosquito bite
Tests:
1. Positive tourniquet test (> 10 petechiae per in2)
Dx?
Children 9-16 w/ lab confirmed prior dengue virus infection and living in endemic US territories (Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands) to boost their antibody titer
The live recombinant Dengue vaccine, Dengvaxia, is approved for which patients?
Chikungunya Fever
SSx:
1. Abrupt high fever
2. Severe debilitating small joint polyarthralgia
3. Macular rash
4. Self limiting except for arthralgias
History = Aedes mosquito bite
Dx?
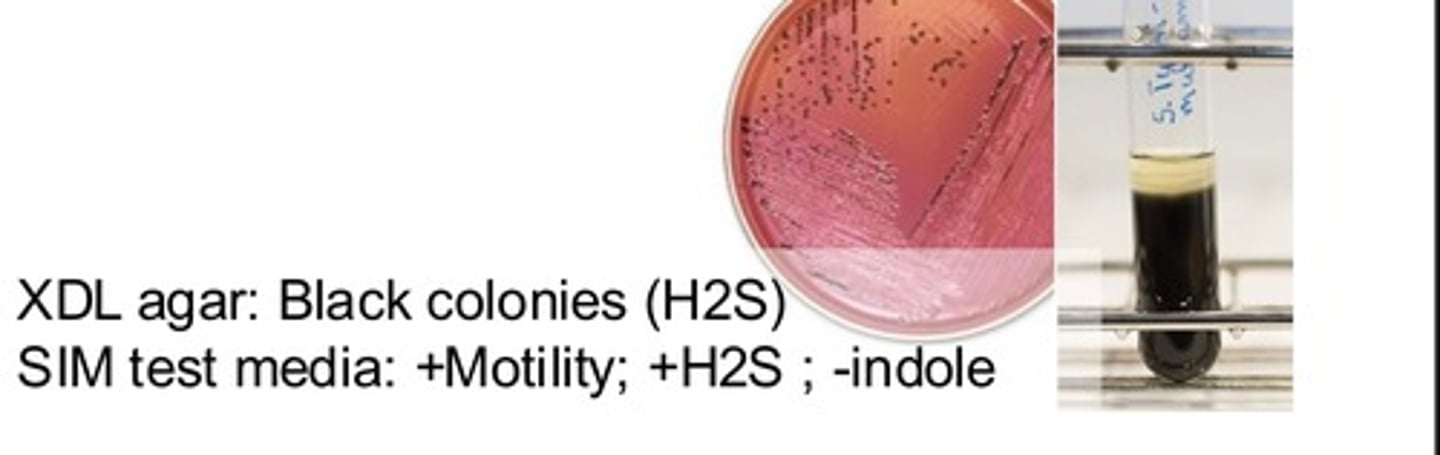
Typhoid (Enteric) Fever (Salmonella Typhi)
SSx:
1. GI sx
2. Fever 1 week post infection (up to 105)
3. GI sx worsen and flu sx appear
4. Rose spots (macules on abdomen, trunk, extremities)
Labs:
1. Gram negative bacillus
Dx?
1. Vi capsular polysaccharide subunit vax (> 2 y/o)
2. Live attenuated Ty21a oral vax (> 6 y/o)
What 2 vaccines exist for people to take prior to traveling to Typhoid Fever-endemic areas?
Dengue Fever w/ Warning Signs (Hemorrhagic fever)
Student on a mission trip in Puerto Rico presents w/ high fever that resolved and came back w/ severe headache, eye, muscle and bone pain, n/v, cough, maculopapular rash, red palms, bleeding gums, and pressure-induced petechiae. History of mosquito bites.
Dx?
Chikungunya Fever
Adult traveler returning from India w/ a history of sudden onset high fever, fatigue, headache, diffuse macular rash and severe polyarthralgia and edema of the hands and feet. Arthralgia of small joints has persisted for weeks although fever and rash have dissipated. History of mosquito bites.
Dx?
Typhoid Fever
Adult traveler returning from India presents w/ 1 week history of headache, fatigue, abdominal pain, and fever that has progressed in the last 3 days to high fever w/ diarrhea, vomiting w/ traces of blood, myalgia, and abdominal macular rash. Blood culture isolated a gram negative bacillus that was SIMs test positive for H2S and motility.
Dx?