Site Development and Earthworks in Planning 1
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Earthworks
Engineering projects involving soil processing for construction.
Excavation
Digging to prepare land for infrastructure projects.

Land Grading
Adjusting land configuration for stability and use.
Military Applications
Using earthworks for soil fortifications in defense.
Landscaping
Creating gardens or parks per property specifications.
Damming
Trapping water using earth to create barriers.
Site Grading
Technique to adjust slope before building construction.
Runoff Water
Water flow from surfaces needing proper drainage.
Erosion
Soil loss due to water or wind action.
Foundation Damage
Structural issues caused by improper land grading.
Basement Flooding
Water accumulation in basements due to poor drainage.
Slope Requirement
Minimum 5% slope for effective water runoff.
Cross Sections
Vertical slices of land used in earthwork calculations.
Cut Areas
Sections of land excavated during earthwork.
Fill Areas
Sections where material is added to raise land.
Excavation Volume
Amount of soil removed during excavation process.
Embankment Volume
Amount of fill material added for construction.
Surveying Textbooks
Resources detailing methods for calculating earthwork.
General Contractors
Professionals overseeing construction and grading projects.
Construction Foundation
Base structure requiring level ground for stability.
Engineering Projects
Large-scale constructions involving earth manipulation.
Infrastructure Projects
Essential constructions like roads, railways, and bridges.
Utility Piping System
Network of pipes for utility services.
Piping System
Interconnected pipes, fittings, and flanges.
Water Line
Pipes transporting potable water.
Drainage
System for removing excess water.
Sewage Disposal
System for managing wastewater.
Underground Communication Lines
Cables for telecommunication below ground.
Electrical Lines
Wires for electrical power distribution.
Tunnel
Horizontal underground passageway for various uses.
Shaft
Vertical opening for accessing underground areas.
Mining Tunnels
Excavations for extracting minerals and ores.
Transportation Tunnels
Passageways for vehicles and trains.
Water Supply Standards
Criteria for assessing water quality.
Physical Water Standards
Characteristics like color and taste.
Chemical Water Standards
Absence of industrial waste chemicals.
Biological Water Standards
Freedom from bacteria and human waste.
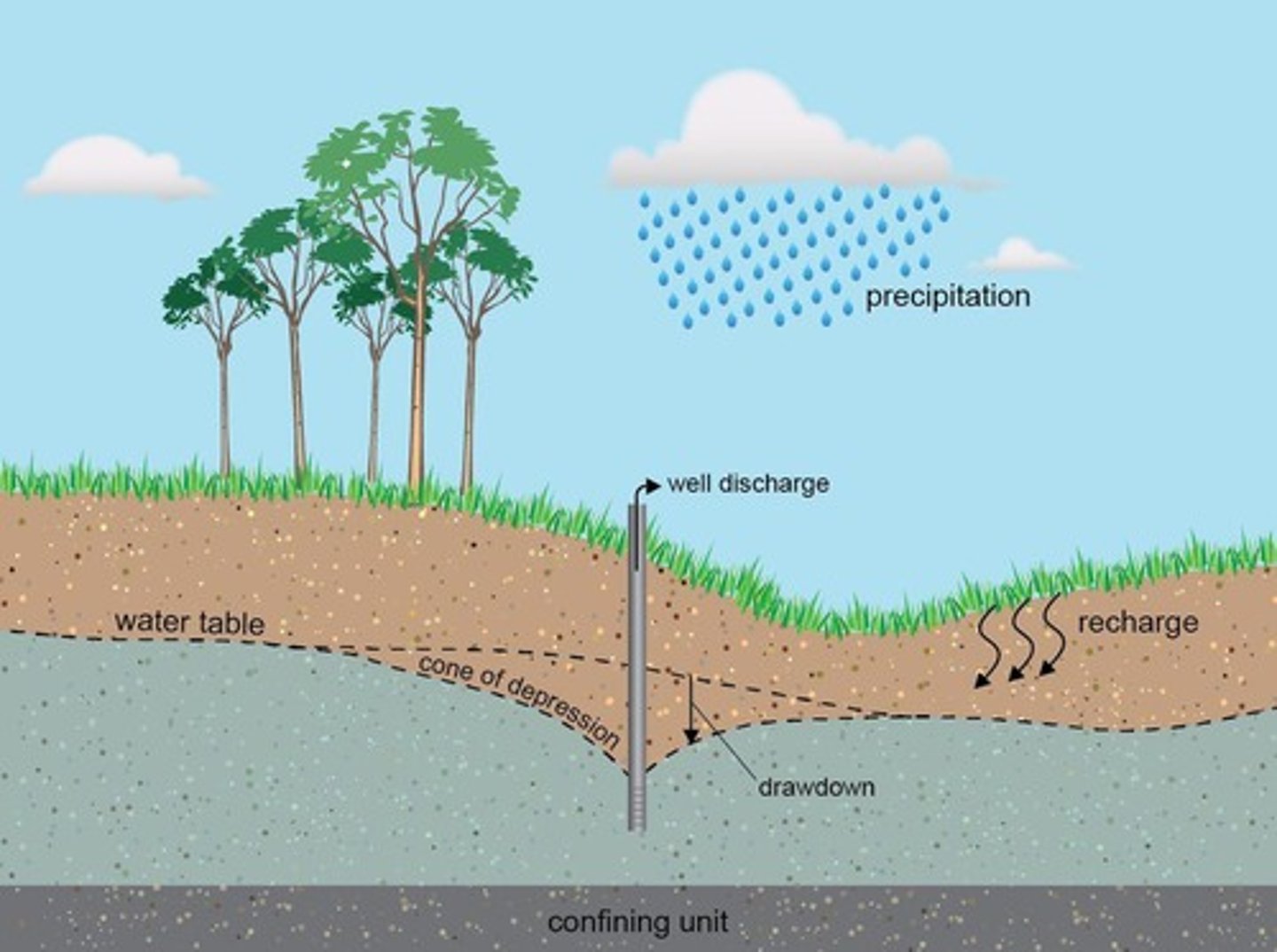
Groundwater
Water stored in underground rock voids.
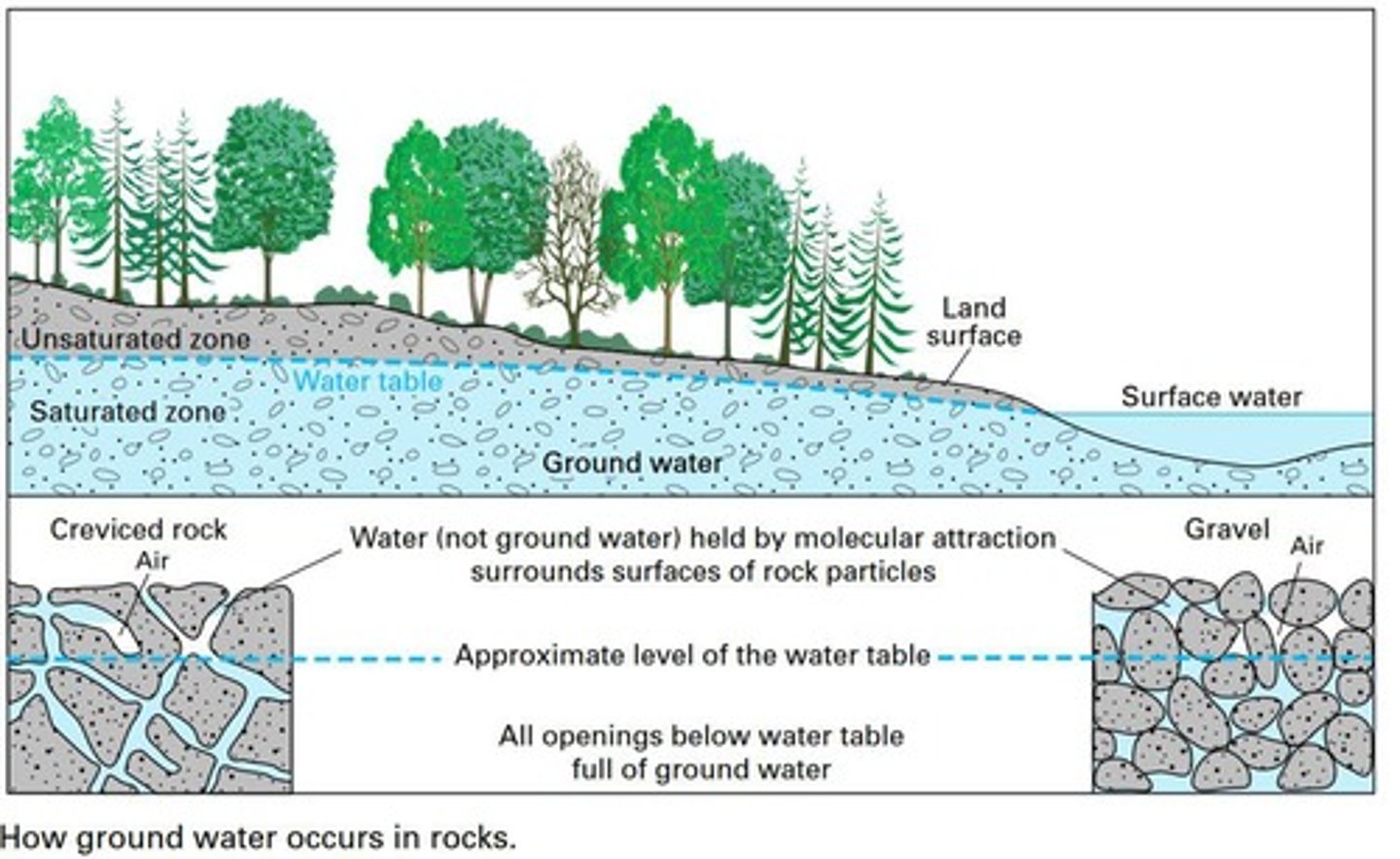
Aquifer
Geological formation storing significant groundwater.
Surface Water
Any water body above ground level.
Hydrologic Cycle
Movement of water on and below Earth.
Municipal Water Supply
City-managed system for public drinking water.
Water Consumption Types
Domestic, public, commercial, and industrial demands.
Domestic Water Demand
Water used for household activities.
Public Demand
Water needed for fire protection and public services.
Commercial Demand
Water used by businesses like stores and hotels.
Industrial Demand
Water required for manufacturing and production processes.
Variation in Demand
Differences in water needs based on community factors.
Average Daily Consumption
Daily water use measured per person.
US Domestic Consumption
Approximately 380 litres per person per day.
Total Demand
680 litres per person per day including all uses.
Developing Countries Consumption
Average of 15 litres per person per day.
World Average Consumption
Estimated 60 litres per person per day.
Airports Water Use
20 litres per passenger per day.
Bathhouses Water Use
40 litres per person per day.
Dwellings Water Use
400 litres per person per day.
Factories Water Use
100 litres per person per shift.
Hospitals Water Use
1200 litres per bed per day.
Shopping Centers Water Use
300 litres per 100 sq.m. of floor space.
Seasonal Variation
Water demand changes with weather and seasons.
Peak Demand
Up to 200% of average on hot days.
Residential Peak Hours
Morning and early evening demand spikes.
Commercial Demand Uniformity
Consistent water use during work hours.
Minimum Demand Hours
Lowest water use occurs predawn.
Water Use Patterns
Critical for designing efficient water systems.
Pumping and Distribution Systems
Engineered to meet community water demands.
Water Availability
Depends on building size, density, value.
Site Design
Ensures access for firefighting vehicles.
Firebreaks
Structures to prevent fire spread.
Fire Hose Access
Layout allows hoses to reach all sides.
Vegetation Control
Manage flammable plants near buildings.
Hydrant Placement
At least 2 hydrants within 500-600 ft.
Sewage Disposal
Process of eliminating sewage and effluent.
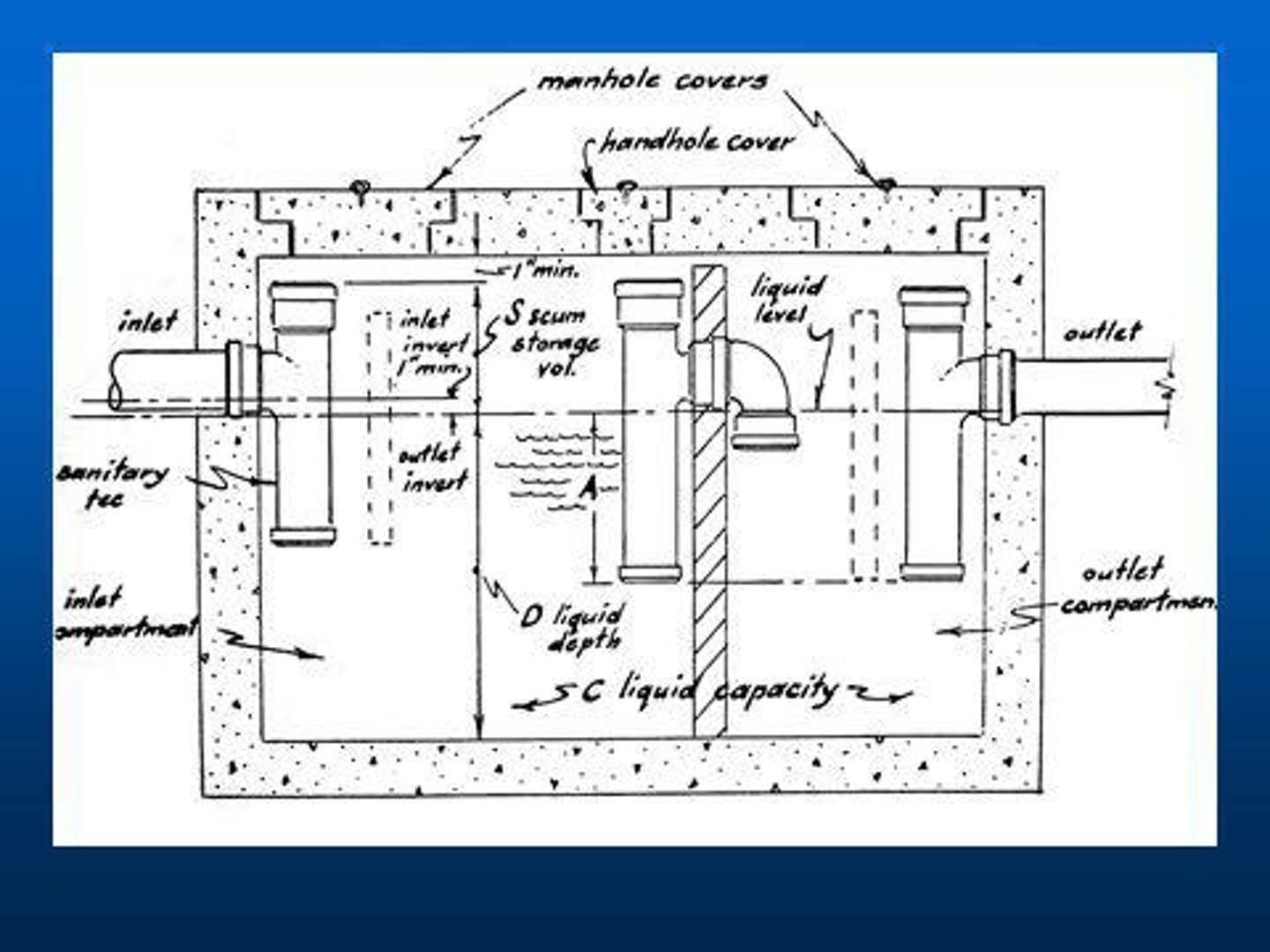
Health Risks
Improper disposal can cause serious illnesses.
Pollution Prevention
Avoid contaminating water supplies with sewage.
Insect Breeding
Prevent conditions for disease-carrying insects.
Wastewater Treatment Systems
Methods to treat and dispose of wastewater.
Municipal Sewer System
Centralized system for urban sewage disposal.
Cluster Treatment Systems
Includes septic systems and constructed wetlands.
On-site Treatment Systems
Individual systems like cesspools and composting toilets.
System Selection Factors
Location, geohydrology, development density, local laws.
Wastewater Treatment Plant
Facility using processes to treat industrial wastewater.
Runoff
Rainwater that does not infiltrate soil.
Drainage Systems
Directs water away from buildings to prevent flooding.
Storm Sewer System
Urban drainage connected to municipal sewers.
Flooding Risks
Inefficient drainage systems can lead to floods.
Surface Leveling
Ensures even surfaces for rooftops and landscapes.
Gutter
Channel directing water from roofs to downspouts.
Downspout
Pipe conveying rainwater from gutters to drainage.
Drainage System
Infrastructure preventing flooding by managing water flow.
Flooding
Overflow of water onto normally dry land.
Porous Surface Material
Materials like sand or gravel allowing water infiltration.
Elevated Pavers
Pavers raised above ground to facilitate drainage.
Erosion Control
Methods to prevent soil loss from wind or water.
Sediment Control
Techniques to manage soil particles during runoff.
Vegetation Protection
Preserving plants to stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
Mulching
Covering soil with organic material to retain moisture.
Runoff Velocity
Speed at which water flows over surfaces.
Swales
Shallow channels designed to manage water runoff.
Sediment Trapping
Capturing soil particles on-site to prevent loss.