Microscopy: History, Parts, and Usage of Light and Electron Microscopes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Primary function of a microscope
To magnify and visualize small structures and specimens.
Inventors of the first microscope in 1597
Hans and Zacharias Janssen.

Robert Hooke's significant contribution to microscopy
He modified the first compound microscope and coined the term 'cell' after viewing cork.
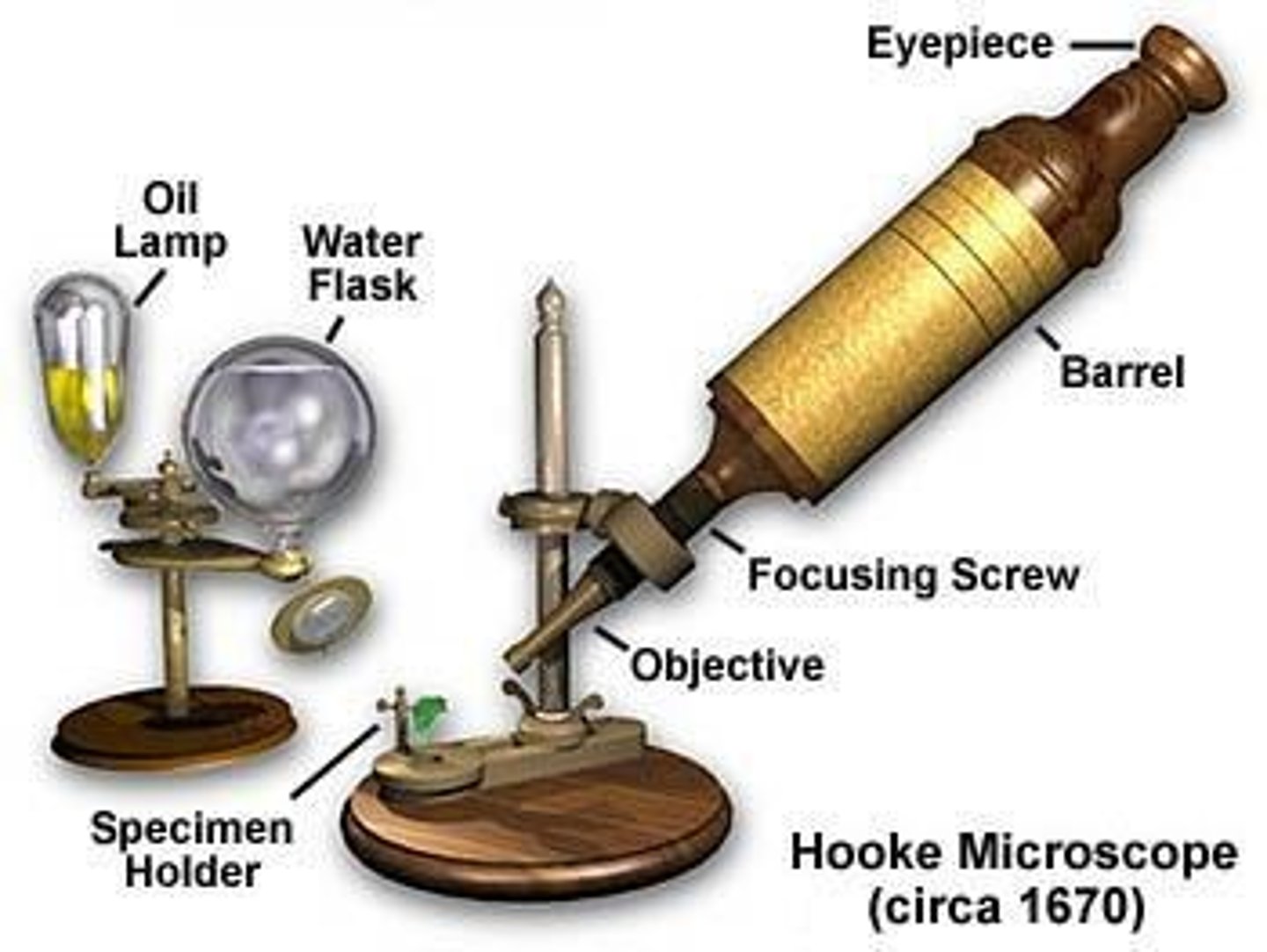
Anton van Leeuwenhoek's achievements in microscopy
He was the first person to see live cells and made pioneering discoveries on various microorganisms.
Significance of the electron microscope
It has greater magnifying power and resolution, capable of magnifying objects up to 500,000 times their actual size.

Basic structure of a compound microscope
It consists of a system of lenses that can invert images.
Main structural parts of a microscope
Head, arm, and base.
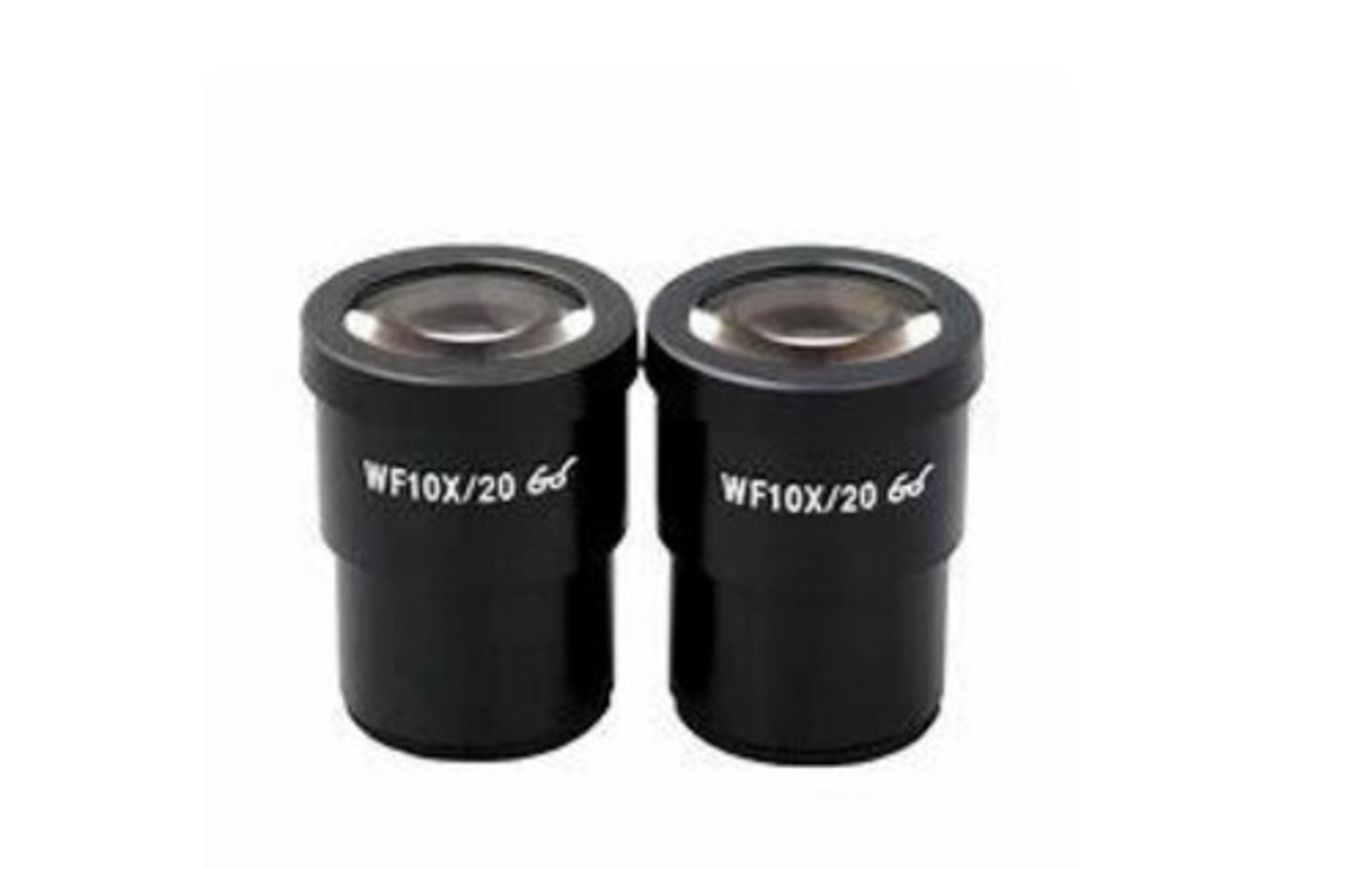
Role of the eyepiece in a microscope
It is used to look through the microscope and has a standard magnification of 10x.

Purpose of the objective lenses in a microscope
They are used for specimen visualization and have magnification powers ranging from 40x to 100x.
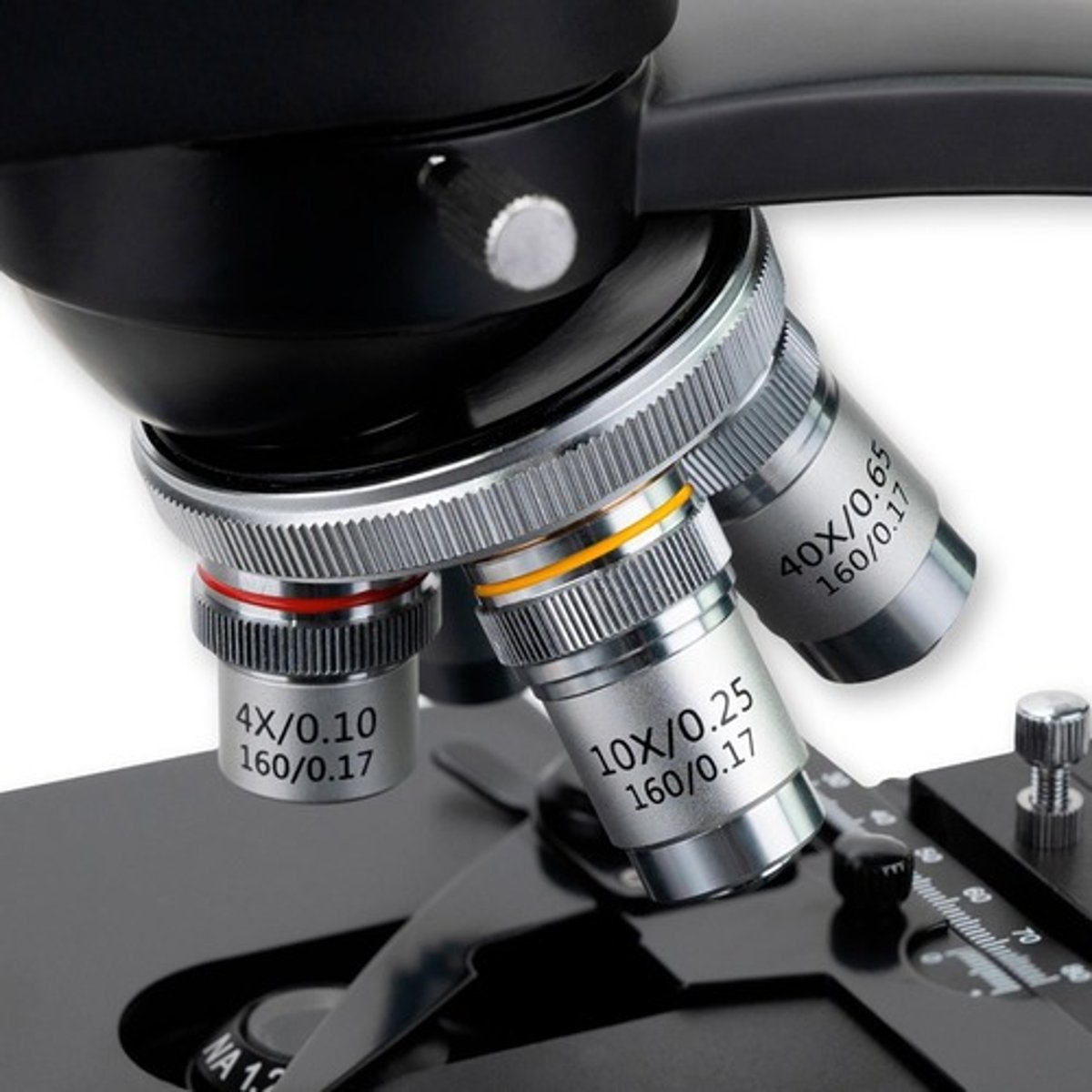

Function of the nosepiece in a microscope
It holds the objective lenses and allows for their rotation to change magnification.
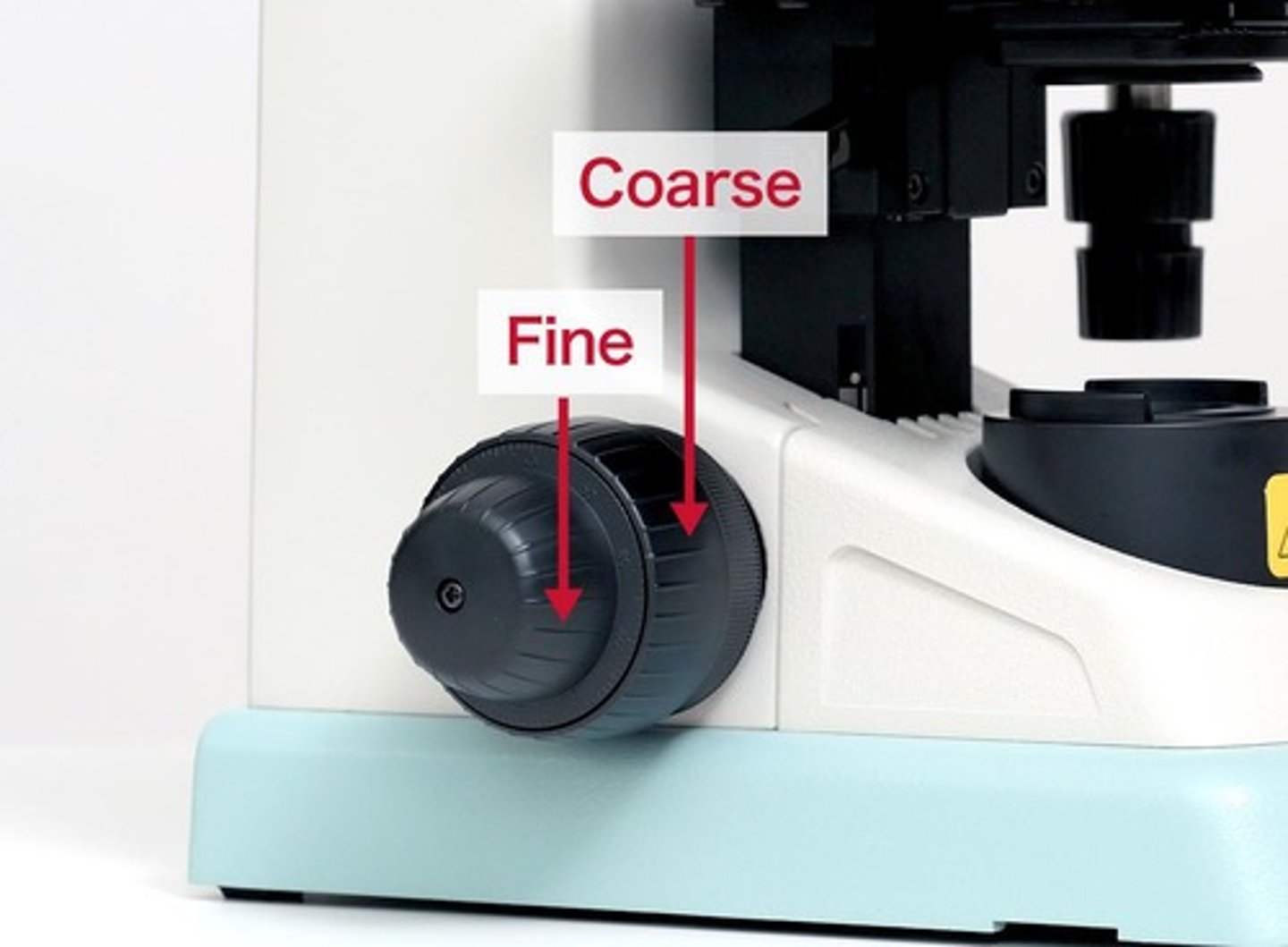
Two types of adjustment knobs on a microscope
Fine adjustment knobs and coarse adjustment knobs.
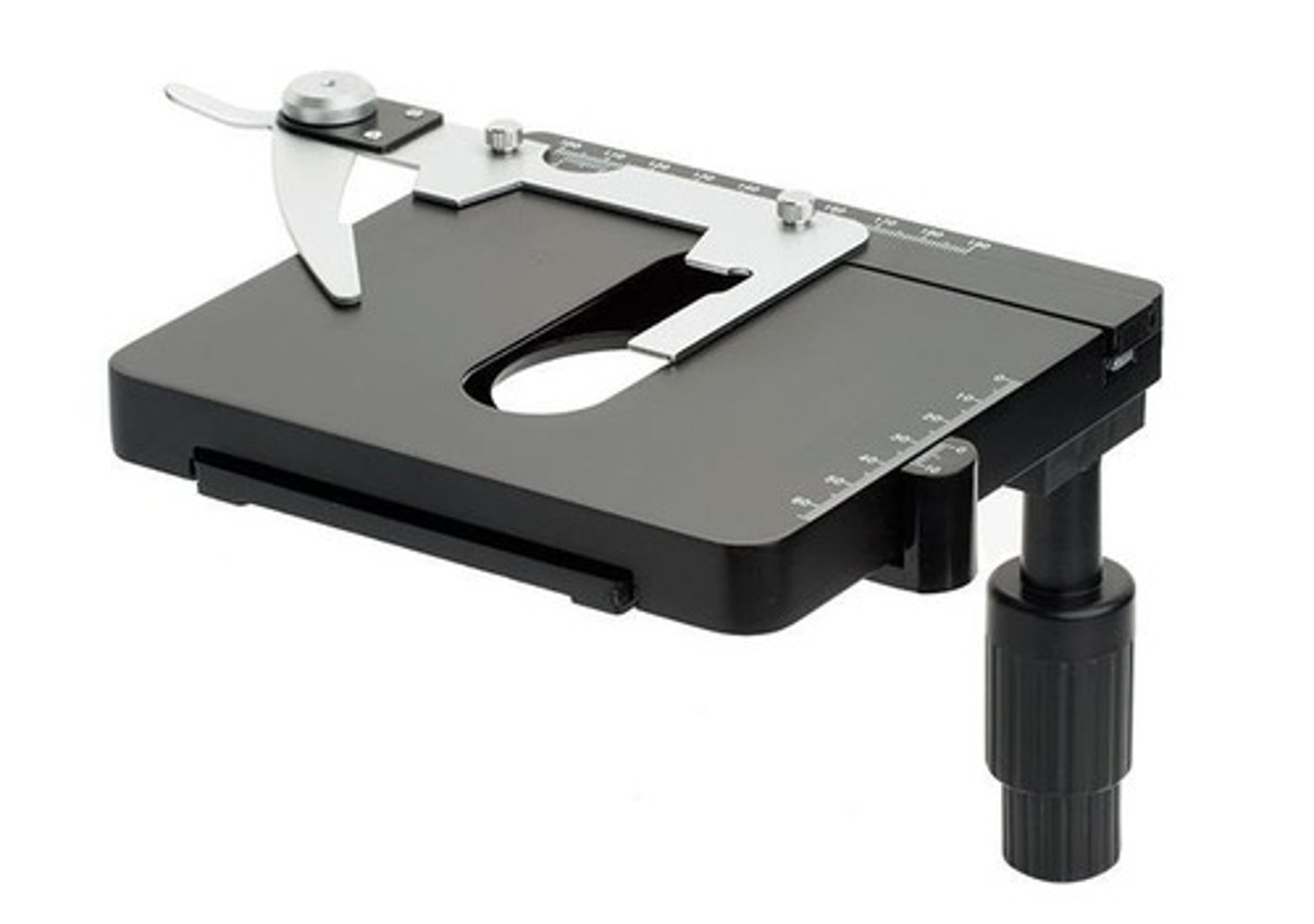
Function of the stage in a microscope
It is the section on which the specimen is placed for viewing.

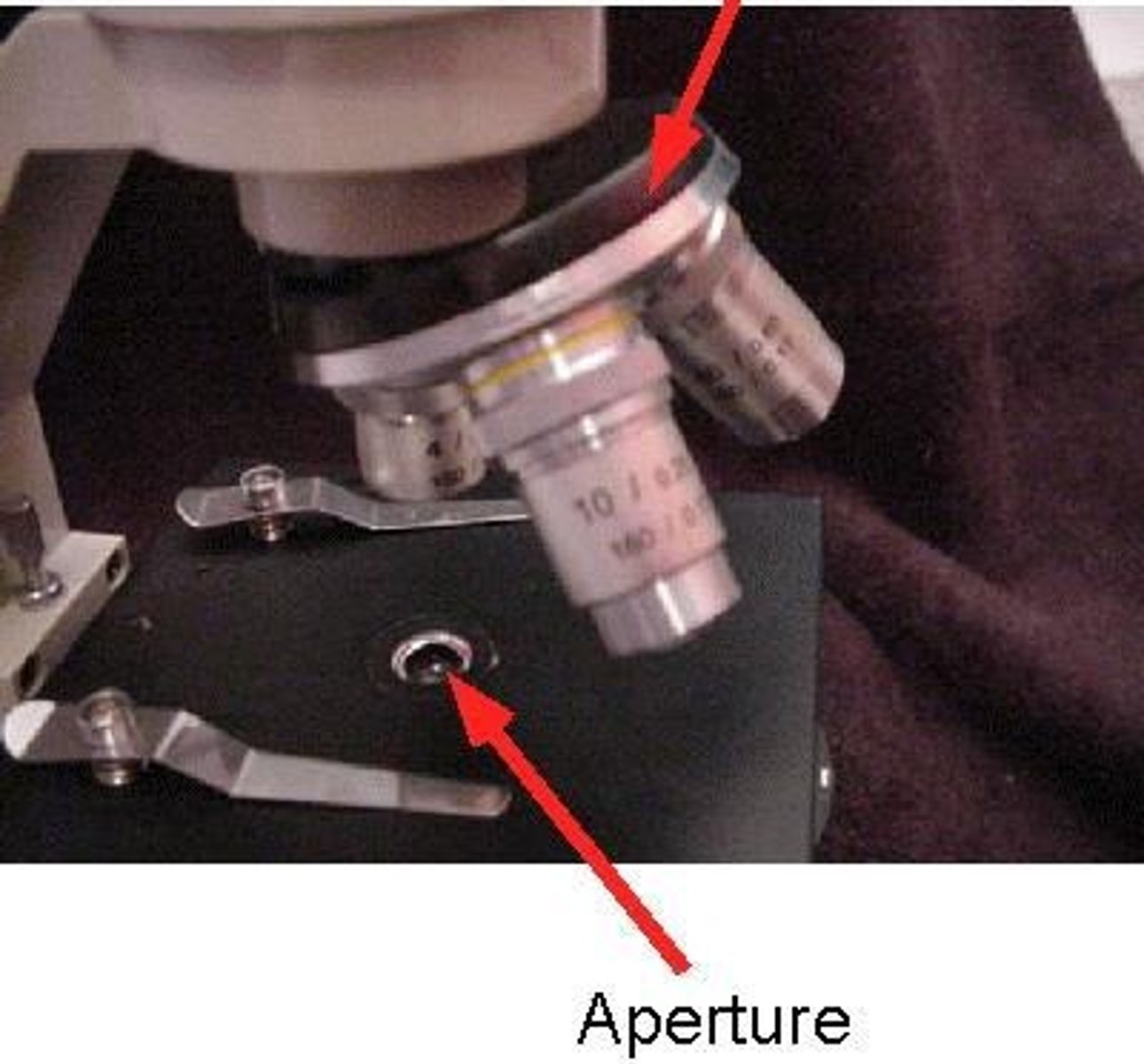
Purpose of the aperture in a microscope
It allows transmitted light from the source to reach the specimen.
Role of the microscopic illuminator
It serves as the light source for the microscope, located at the base.
Function of the condenser in a microscope
To collect and focus light from the illuminator onto the specimen.
Function of the diaphragm in a microscope
It controls the amount of light that reaches the specimen.
The Abbe condenser
A high-quality condenser designed for high magnification above 400x.
Purpose of the rack stop in a microscope
To control how far the stage can move, preventing damage to the specimen.

First step in using a light microscope
Turn the light microscope on and adjust the mirror to reflect light towards the eyepiece.
Action after placing the specimen on the stage
Look into the eyepiece and rotate the coarse adjustment wheel to bring the specimen into focus.
Achieving a clearer image of the specimen
By slowly rotating the fine adjustment wheel.
Requirement for thin specimens when using a microscope
To allow light rays to pass through for proper magnification.
Main idea of how a microscope works
It magnifies the structure of the specimen by bending light rays through lenses.
Standard magnification of the eyepiece
10x, with optional eyepieces ranging from 5x to 30x.
Function of stage clips in a microscope
To hold the specimen slides in place on the stage.
Significance of Robert Koch in microbiology
He discovered two infectious bacteria, tubercle and cholera bacilli.
Typical range of cell sizes visible under a light microscope
From about 0.001 mm to 0.1 mm long.
What should be done after examining a specimen under low power?
Switch to medium and high-power objective lenses and use the fine adjustment wheel as necessary.