COPD and Asthma- Heemer
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are the 2 phenotypes of COPD?
chronic bronchitis
emphysema
What are the complications of COPD?
hypoxemia
hypercapnia
secondary pulmonary HTN
What risk factor is the leading cause of COPD?
SMOKING CIGS

a deficiency in what enzyme can lead to COPD?
a1-antitrypsin (AAT)
What are the subjective and objective signs and symptoms of COPD?
subjective: chronic cough, sputum production, dyspnea
objective- cyanosis, increased RR, barrel chest, spirometry tests
What test is used to diagnose COPD?
spirometry
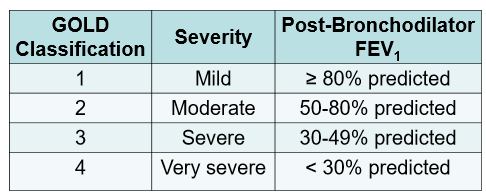
A FEV1/FVC ratio <_____% indicates COPD.
<70%
How is COPD classified by spirometry?
a. GOLD classification
b. WHO functional classification
c. ABE assessment tool
d. CAT COPD assessment tool
a
What are the 4 GOLD classifications for COPD?
What is some non-pharm tx for COPD?
smoking cessation
vaccination
pulmonary rehab
long-term oxygen therapy
surgery
What is the only intervention proven to affect long-term decline in FEV1 and slow progression of COPD?
smoking cessation
When is oxygen therapy indicated in COPD?
PaO2 ≤ 55 mmHg or SaO2 <88%
or
PaO2 >55 mmHg but <60 mmHg w/ RHF
What 2 classes of meds are COPD specific and not for use in asthma?
PDE-4 inhibitors
roflumilast
a1-antitrypsin replacement therapy
pooled human AAT
Oxygen therapy has evidence of improved survival in…
pts. w/ chronic hypoxemia
Studies have shown correlation between ___________________counts and the effect of ICS on COPD.
eosinophils
ICS shouldn’t be used if your eosinophil blood count is <_______ cells/uL.
ICS shouldn’t be used if your eosionophil blood count is <100 cells/uL.
ICS CAN BE used if your eosinophil blood count is >________ cells/uL.
ICS CAN BE used if your eosinophil blood count is >300 cells/uL.
The ABE assessment tool is used to assess pts. with COPD. The 3 main components of the assessment tool are:
mMRC
CAT
Exacerbation history
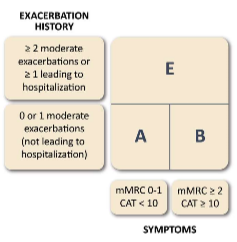
Explain the mMRC component of the ABE assessment tool:
basically, assesses dyspnea on a scale of 0-4
ex: 0 would be dyspnea w exercise and 4 would be dyspnea all the time
you check off the box that applies to you
placed in the A/B category based off the box you check off
Explain the CAT component of the ABE assessment tool:
basically, a COPD symptom test
assesses different symptoms on a scale of 0-5
placed in A/B category based off the score
Explain the Exacerbation history component of the ABE assessment tool:
based off frequency and severity of exacerbations
basically, if you have 2 or more exacerbations or 1 or more exacerbations leading to hospitalization= E category
if you have 0 or 1 moderate exacerbations no hospitalization in either A or B category depending on mMRC and CAT

Exacerbations are classified as mild, moderate, or severe. What do each of these mean?
mild- tx with SABA
moderate- tx with SABA plus antibiotics/steroids
severe- ER visit or hospitalization
What non-pharm tx is essential and recommended if you are in group A of the ABE assessment tool?
essential- smoking cessation
recom- physical activity
What non-pharm tx is essential and recommended if you are in group B and E of the ABE assessment tool?
essential- smoking cessation, pulmonary rehab
recom- physical activity
What is the initial pharm tx for Groups A, B, and E ?
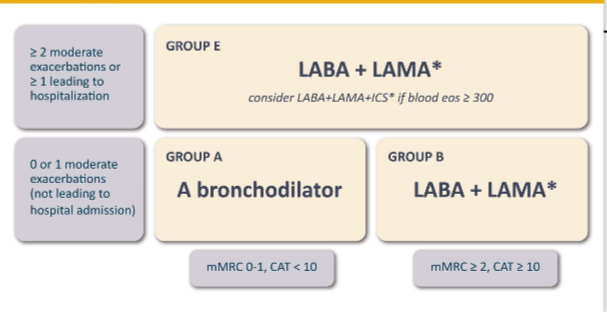
In addition to the initial pharm tx, what should be prescribed to all groups for immediate symptom relief?
rescue SABA
If initial tx fails and I wanted to do triple therapy with a LABA+LAMA+ICS, what must I first consider?
eosinophil count
MUST be >300
If my triple therapy doesn’t work and I want to use a COPD specific medication, what would I choose?
Roflumilast
When would I use antibiotics in COPD?
given to pts. w/ 2 or more cardinal symptoms:
increase in sputum purulence AND
Increase in sputum production AND/OR
worsening of dyspnea
Practice:
If I had an increase in sputum purulence and worsening dyspnea would I need an antibiotic? how long would I take that antibiotic if necessary?
yes—> take for 5-7 days
Practice:
A pt. has a CAT score of 7, mMRC of 1, and 0 moderate exacerbations in the last year. What group would the patient be placed in the ABE assessment tool?
A
Practice:
A pt. has a CAT score of 10, mMRC of 1, and 3 moderate exacerbations in the last year. What group would the patient be placed in the ABE assessment tool?
E
What factor leads to 60-80% of susceptibility to have asthma?
genetics
What is a KEY indicator of asthma?
wheezing
You have assessed the patient’s control of their asthma, but before making changes to a patient’s asthma medication regimen, what 3 additional things should be assessed?
patient education
adherence, inhaler technique
control of environment
reduce exposure to allergens
manage comorbidities
How is asthma classified in ppl ≥12 years of age?
intermittent
mild
moderate
severe
For intermittent classification answer the following:
symptoms (how many days/week)
nighttime awakenings (how often)
using a SABA for symptom control (how often)
interference with normal activity (none—> fully limited)
symptoms
≤2 days/week
nighttime awakenings
≤2x/month
using a SABA for symptom control
≤2 days/week
interference with normal activity
none
For mild persistent classification answer the following:
symptoms
nighttime awakenings
using a SABA for symptom control
interference with normal activity
symptoms
>2 days/week but not daily
nighttime awakenings
3-4x/month
using a SABA for symptom control
>2 days/week but not daily
interference with normal activity
minor limitation
For moderate persistent classification answer the following:
symptoms
nighttime awakenings
using a SABA for symptom control
interference with normal activity
symptoms
daily
nighttime awakenings
>1x/week but not nightly
using a SABA for symptom control
daily
interference with normal activity
some limitation
For severe persistent classification answer the following:
symptoms
nighttime awakenings
using a SABA for symptom control
interference with normal activity
symptoms
throughout the day
nighttime awakenings
often 7x/week
using a SABA for symptom control
several times per day
interference with normal activity
extremely limited
What is the recommended step for initiating tx in intermittent, mild, moderate, severe?
intermittent- step 1
mild- step 2
moderate- step 3 and consider short course of systemic corticosteroids
severe- step 4 or 5 and consider short course of systemic corticosteroids
What are the PREFERRED tx options in steps 1-6?
step 1- PRN SABA
step 2- ICS and PRN SABA or PRN ICS and SABA
step 3- daily and PRN combo of low dose ICS and formoterol
step 4- daily and PRN combo of medium dose ICS and formoterol
step 5- daily medium-high dose ICS-LABA-LAMA and PRN SABA
step 6- daily high-dose ICS-LABA+ oral systemic corticosteroids and PRN SABA
What device can be used to assess asthma control?
peak flow meter
If asthma is controlled for ____ months we can step dose.
3
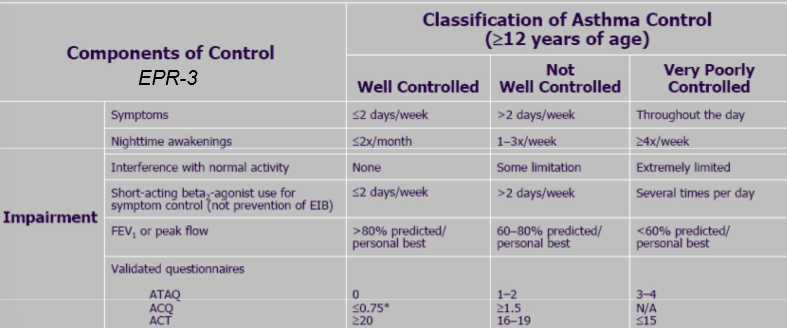
What classifies if our asthma is well controlled, not well controlled, or very poorly controlled?
How is exercise induced bronchospasm diagnosed?
exercise challenge