The mathematics of patterns and symmetries
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
A _____________________ is a repeated arrangement of numbers, shapes, colors and so on It can be related to any type of event or object
Pattern
If the set of numbers are related to each other in a specific rule, the the rule or manner is called a ____________
pattern
Sometimes, patterns are also known as a ___________
sequence
Patterns are ________ or ________ in numbers
finite
infinite
A _____________________ is a regularity in the world, in human-made design, or in abstract ideas
pattern
The elements of a pattern repeat in a ____________ manner
predictable
A _____________ is a kind of pattern formed of geometric shapes and typically repeated like a wallpaper design
Geometric pattern
Any of the senses may directly observe ____________
patterns
__________________ is defined as one shape is EXACTLY LIKE THE OTHER SHAPE when it is moved, rotated, or flipped
Symmetry
_______________ in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance
Symmetry
In mathematics, ____________ has a more precise definition, and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations including translation, reflection, rotation, or scaling.
Symmetry
According to Grunbaum and Shephard, a motif is “__________________”
any non-empty plane set
Any object drawn in a plane is a ____________
motif
A ______________ can be described as repetitions of a motif in the plane
pattern
An ___________________ is the rotation of a motif in a fixed angle about a fixed point.
Isometry
Each rotation of a figure is an _____________
isometry
The image of the basic motif under the additional number of rotation is a _____________
pattern
A ______________ changes the SIZE, SHAPE or POSITION of a figure and creates a new figure
Transformation
A ____________________ is either RIGID or NON-RIGID; another word for a rigid transformation is ISOMETRY
Geometry transformation
An ____________________ such as rotation, translation, or reflection, DOES NOT change the size or shape of the figure
Isometry
A _______________ is not an isometry since it either SHRINKS or ENLARGES a figure
dilation
What are the 4 types of transformation?
-
-
-
-
Translation
Reflection
Rotation
Dilation
The initial object to be transformed is called ___________
pre-image
The transformed object is called ___________
image
___________________ is a mathematical term used in geometry to describe a function that moves an object a certain distance. The object is not altered in any other way
Translation
___________________ is a transformation in which the figure or object is mirror image of the other
Reflection
_______________ is a transformation that turns a figure about a fixed point called the CENTER OF ROTATION. It can be done clockwise or counterclockwise
Rotation
Rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a fixed point called the __________________
Center of rotation
A ________________ is a transformation that changes the size of a figure. It can become smaller or larger, but the shape remains the same
Dilation
____________________ is the combination of translation and reflectoin
Glided reflection
The name ____________________ is attributed to John Conway, an English mathematician who is active in finite theory, knot theory, number theory, combinatorial game theory, and coding theory.
Frieze patterns
The name Frieze patterns is attributed to ____________, an English mathematician who is active in finite theory, knot theory, number theory, combinatorial game theory, and coding theory.
John Conway
________________ are patterns that REPEAT IN A STRAIGHT VERTICAL or HORIZONTAL LINE. There are found in architecture, fabrics, and wallpaper borders, just to name a few
Frieze patterns
What are the 7 types of Frieze Patterns?
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Hop
Step
Slide
Spinning Hop
Spinning sidle
Jump
Spinning jump

____________ is a pattern which only involves translation
Hop

_______________ is a combination of TRANSLATION and REFLECTION. It is also called GLIDE REFLECTION SYMMETRY
Step

________________ consists of TRANSLATION and VERTICAL REFLECTION symmetries
Slide
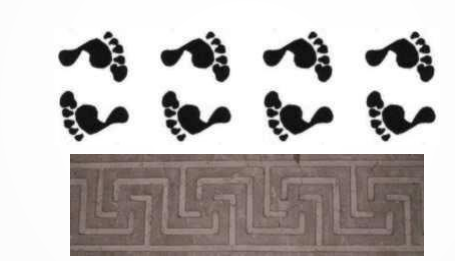
________________ contains TRANSLATION and ROTATION (by half turn or rotation at 180 degrees angle) symmetries
Spinning hop

_______________ contains TRANSLATION, GLIDE, REFLECTION and ROTATION (by a half-turn or rotation at 180 degrees angle) symmetries
Spinning sidle

_____________________ contains TRANSLATION and HORIZONTAL REFLECTION symmetries
Jump

_______________ contains ALL SYMMETRIES (translation, horizontal and vertical reflection, and rotation)
Spinning jump
If translation symmetry is added in a second, independent direction, one gets _______________. It turns out there are only ____ different wallpaper groups.
wallpaper groups
17
______________ comes from a greek word symmetria meaning TO MEASURE TOGETHER and is widely used in the study of geometry
Symmetry
Symmetry comes from a greek word __________ meaning ________________ and is widely used in the study of geometry
symmetria
to measure together
Mathematically, ___________________ means that one shape becomes exactly like another when you move it in some way: turn, flip, or slide
Symmetry
Not all objects have symmetry; if an object is not symmetrical, it is called _____________
asymmetric
Symmetry and pattern is widely used in fields of ____________ and _____________, it also appears in ________ and ______________
mathematics
arts
chemistry
biology
The __________________ for example is widely known to be symmetrical in nature
human anatomy
What are the 2 kinds of symmetry?
-
-
Bilateral symmetry
Radial symmetry
___________________ in which an object has two sides that are MIRROR IMAGES of each other
Bilateral symmetry
__________________, this is where a center point and numerous lines of symmetry could be drawn. One good example is the SPIDER WEB.
Radial symmetry
In the field of medical science, ______________ is the basis to detect anomalies in human bodies like disfigured parts of the body wherein one part being larger or smaller than its counterpart
Radial symmetry
Patterns in living things are explained by the biological processes of __________ and __________ selection
natural
sexual
One good example of patterns found in nature is the ______________________. Under favorable conditions, it doubles at regular intervals: 1, 2, 4, 8 or 2^n
bacterial population growth
_________________ is a pattern covering a place by fitting together replicas of the same basic shape
Tessellation
The word Tessellation comes from the Latin word “__________”, which means A SQUARE TABLET or die used in gambling.
Tessera
What are the 3 types of tessellation?
-
-
-
Regular Tessellation
Semi-Regular Tessellation
Demi-Regular Tessellation
A ______________ is made up of congruent REGULAR POLYGONS
Regular tessellation
_______________________ is also known as ARCHIMEDEAN tessellations and are regular tessellations of TWO OR MORE DIFFERENT POLYGONS around a vertex which has the same arrangement of polygons
Semi-regular tessellation
__________________ is an edge-to-edge tessellation, but the order or arrangement of polygons at each vertex is not the same
Demi-Regular Tessellation
The function which iterates a figure to make it smaller and smaller or bigger and bigger using a scaling factor is called ___________
Fractals
______________ are mathematical constructs characterized by SELF-SIMILARITY. This means that as one examines finer and finer details of the object, the magnified area is seen to be like the original but is not identical to it
Fractals
___________ is basically the same figure being smaller and larger while ___________ is just being categorized as being ALMOST IDENTICAL to the original
Dilation
Fractals
____________________ means REPEATING A PROCESS OVER AND OVER. It means repeating a function over and over
Iteration
The _______________________ (IFS) is a method for generating fractals involving a large number of calculations of a simple formula
Iterative Function System
__________________ is a special kind of iteration. With this, there is a given starting information and a rule for how to use it to get new information.
Recursion