Deformation of solids
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Stress
The force per unit area causing deformation
Strain
A measure of the amount of deformation caused by stress
Stress
Stress = Force/Area Unit= Pa
Stress is not the same as pressure
Stress applies at the internal level whereas pressure applies externally to the surface of objects
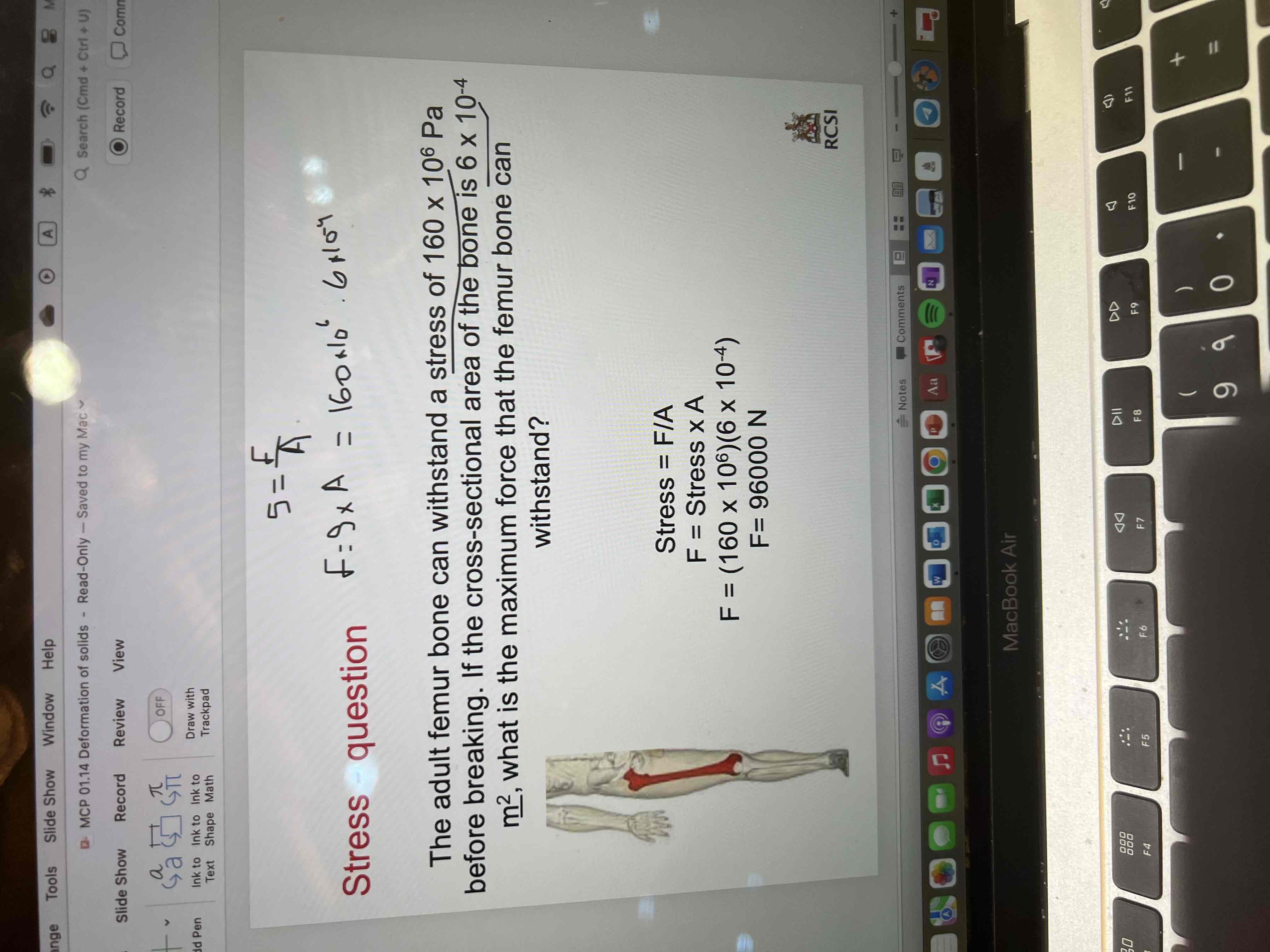
Stress question
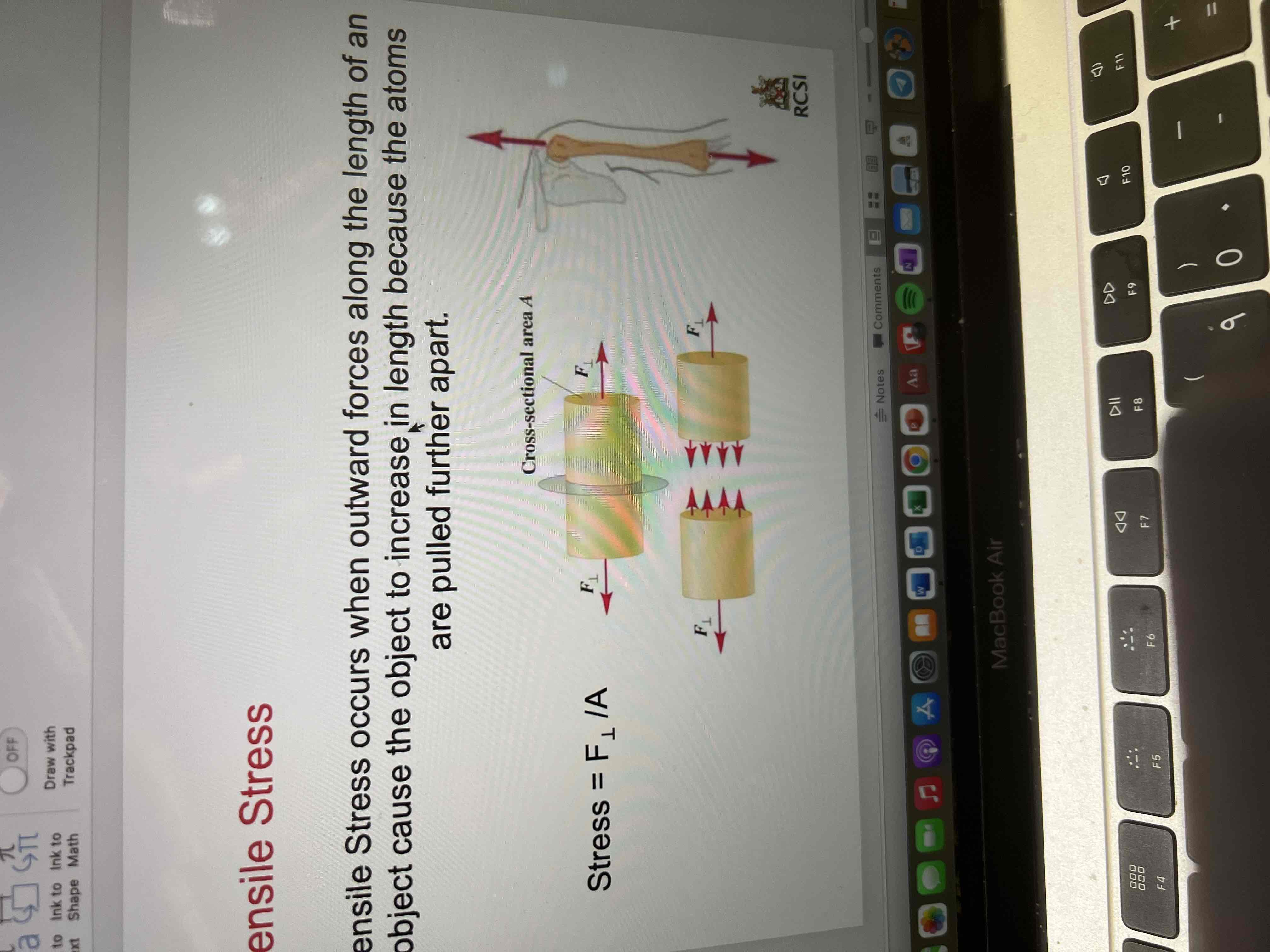
Tensile stress
Occurs when outward forces along the length of an object cause the object to increase in length because atoms are pulled further apart
Compressive stress
The opposite of tensile strength. Inward forces along the object length tend to decrease the length of an object because the atoms are pushed closer together

Volume stress
Changes the volume of an object. It occurs due to uniform pressure on all sides of the object that results in the object being compressed but retaining the same shape
Stress= Delta P

Shear stress
Changes the shape of an object but not it’s dimensions. It occurs when different forces act across the object at different points, warping or deforming the object as the atoms are forced sideways.
Stress= force / area

Tensile and compressive strength
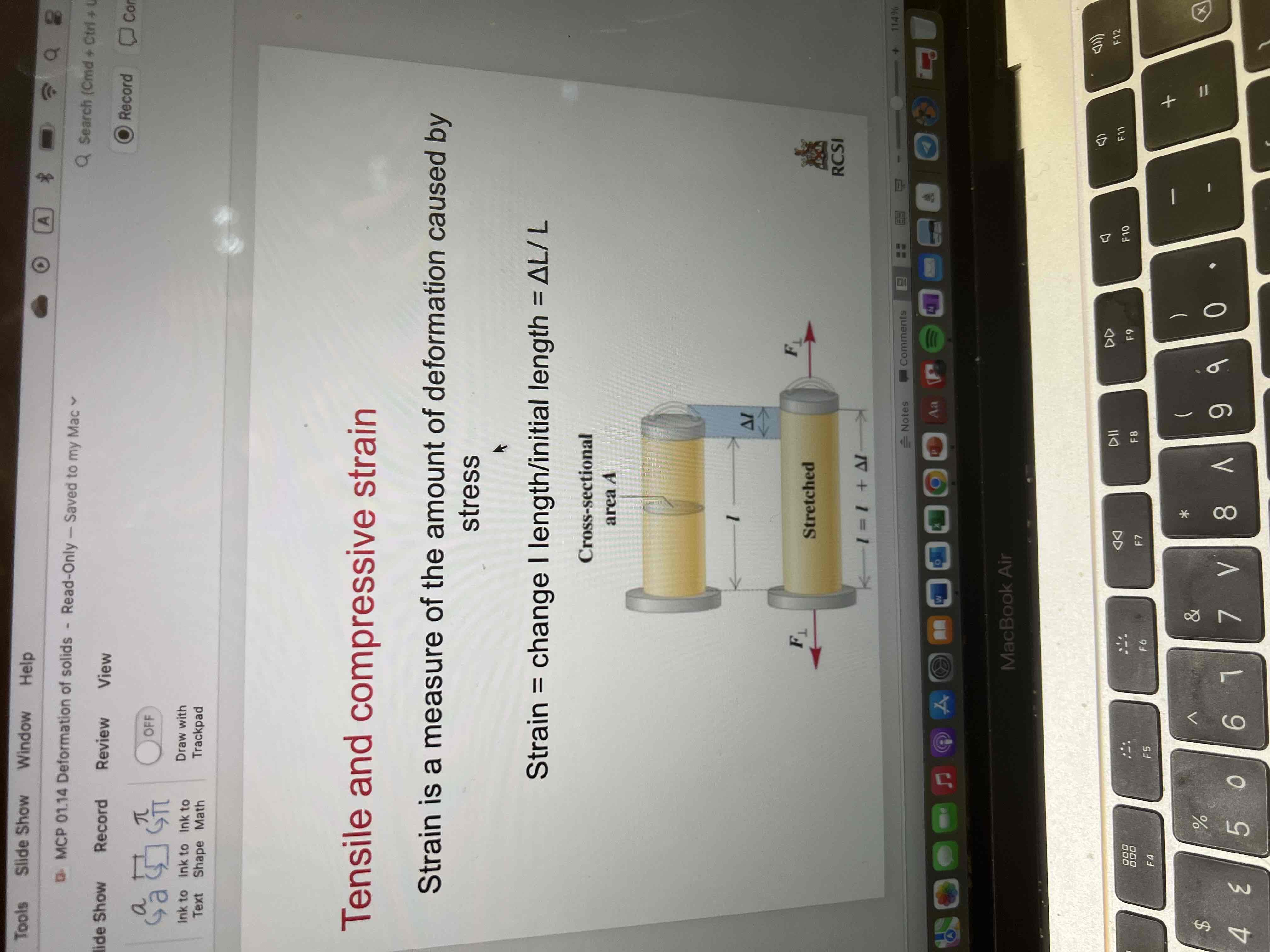
Strain is a measure of the amount of deformation caused by stress.
Strain = change in l length/initial length
Strain = delta L / L
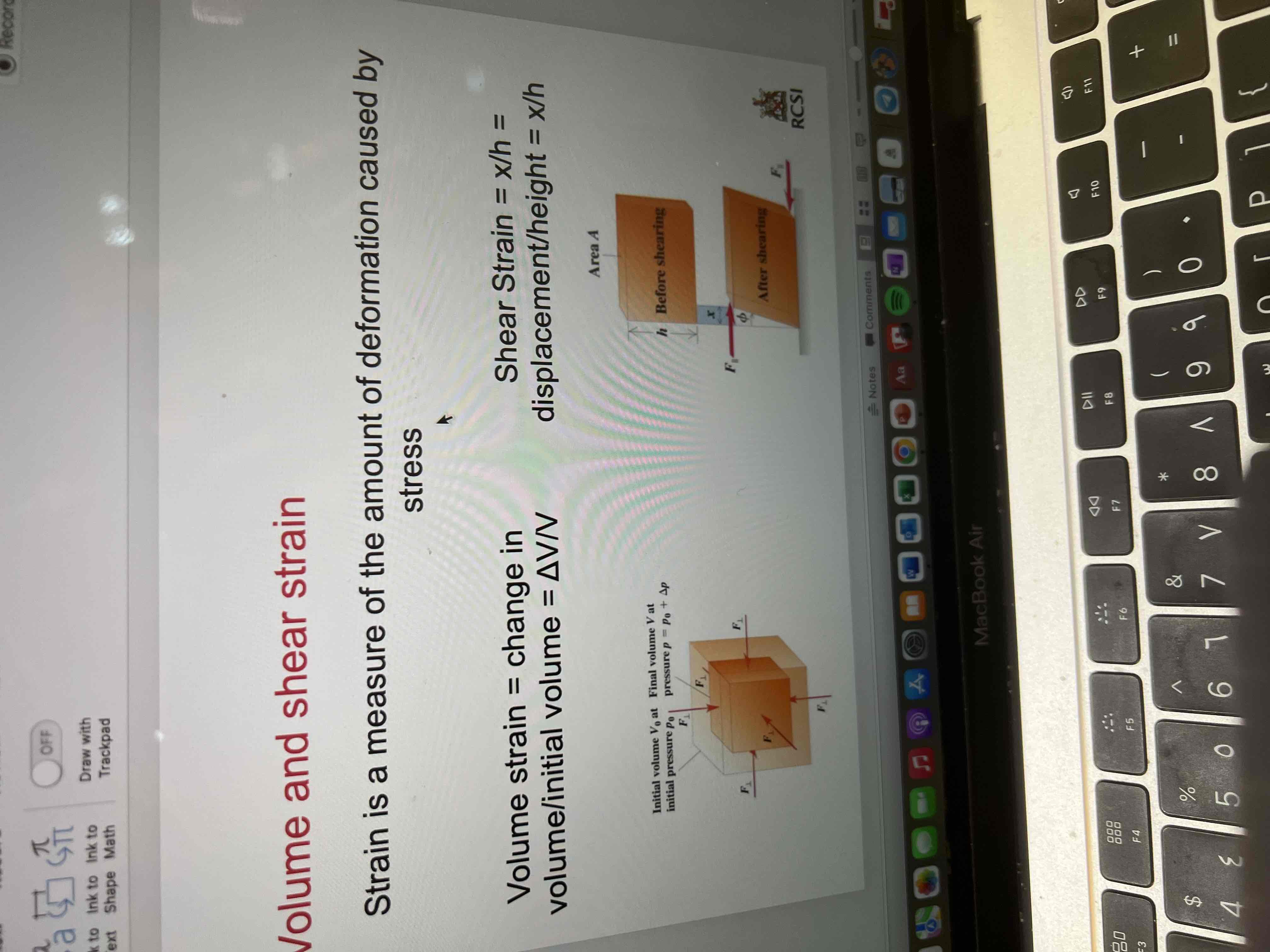
Volume and shear strain
Volume strain = change in volume/ initial volume
Volume strain = delta V/ V
Shear strain = displacement / height = x/h
Factors that affect strain
The type of material. qualified by a constant of proportionality
The materials dimensions; length, volume, area
Applied force / pressure
Bulk modulus
For a sufficiently small volume stress, stress and strain are proportional.
Stress= -B strain
B=-stress/strain = delta P / delta v/v
B = bulk modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a material, how easy it is to compress

Shear modulus
For a sufficiently small shear stress, stress and strain are proportional.
Stress= S strain
S= Stress/Strain = F/A / x/h
S= shear modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a material, how easy it is to shear

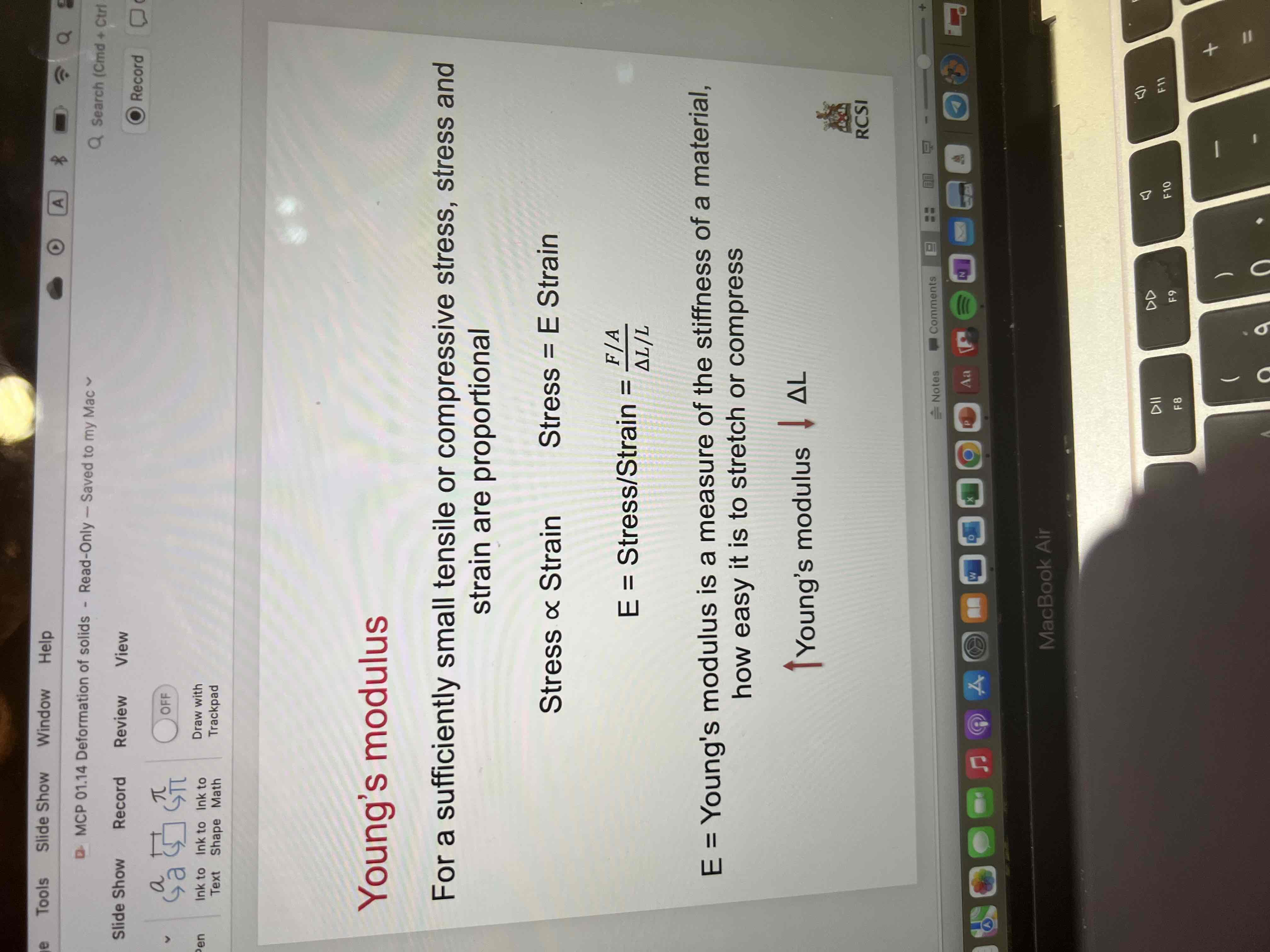
Young’s modulus
For a sufficiently small tensile or compressive stress, stress and strain are proportional
Stress= E strain
E= stress/strain = F/A / deltah/h
E= Young’s modulus is a measure of the stiffness of a material, how easy it is to stretch or compress
Young’s modulus formula rearrangement

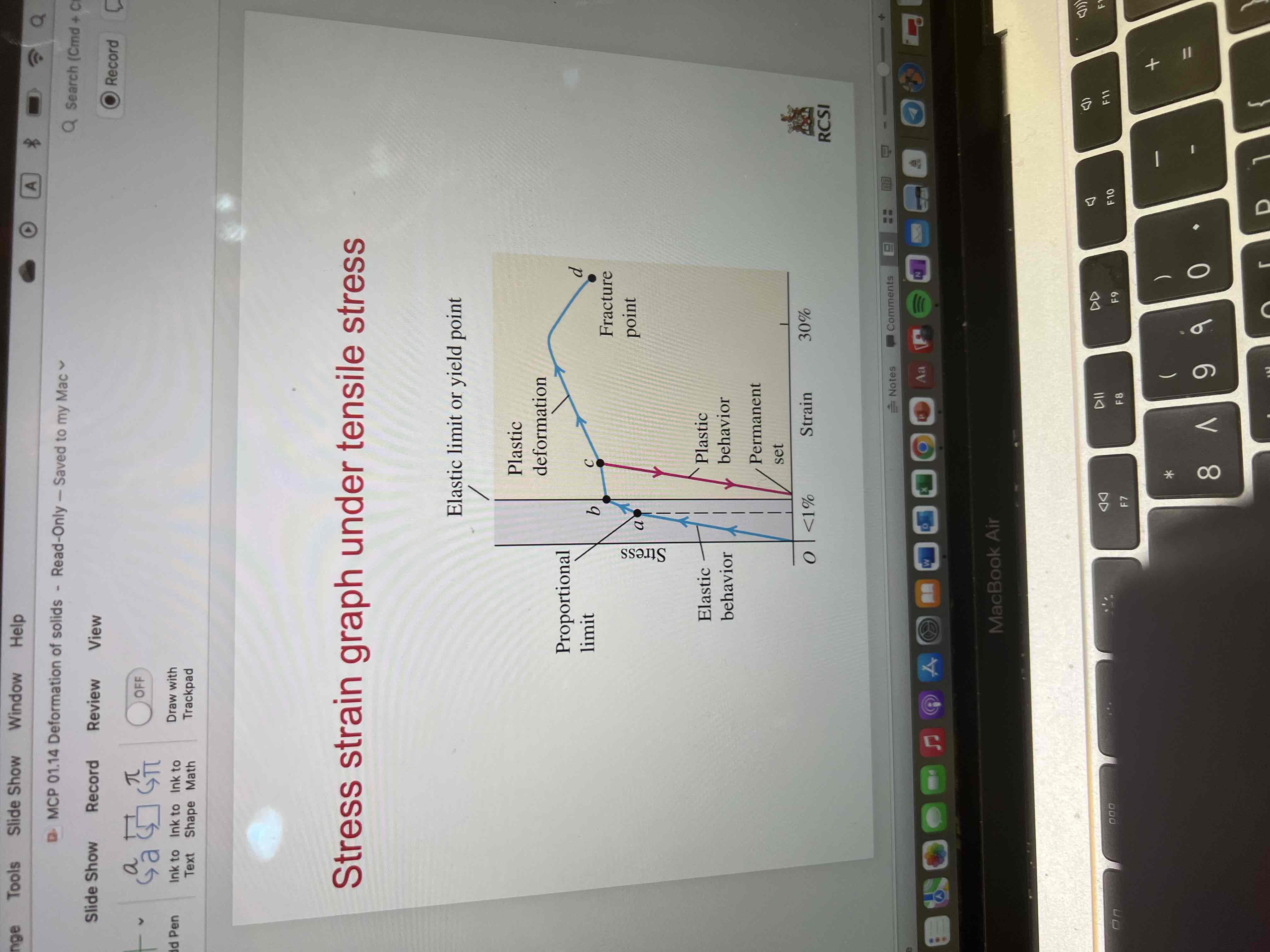
Stress strain graph under tensile strength
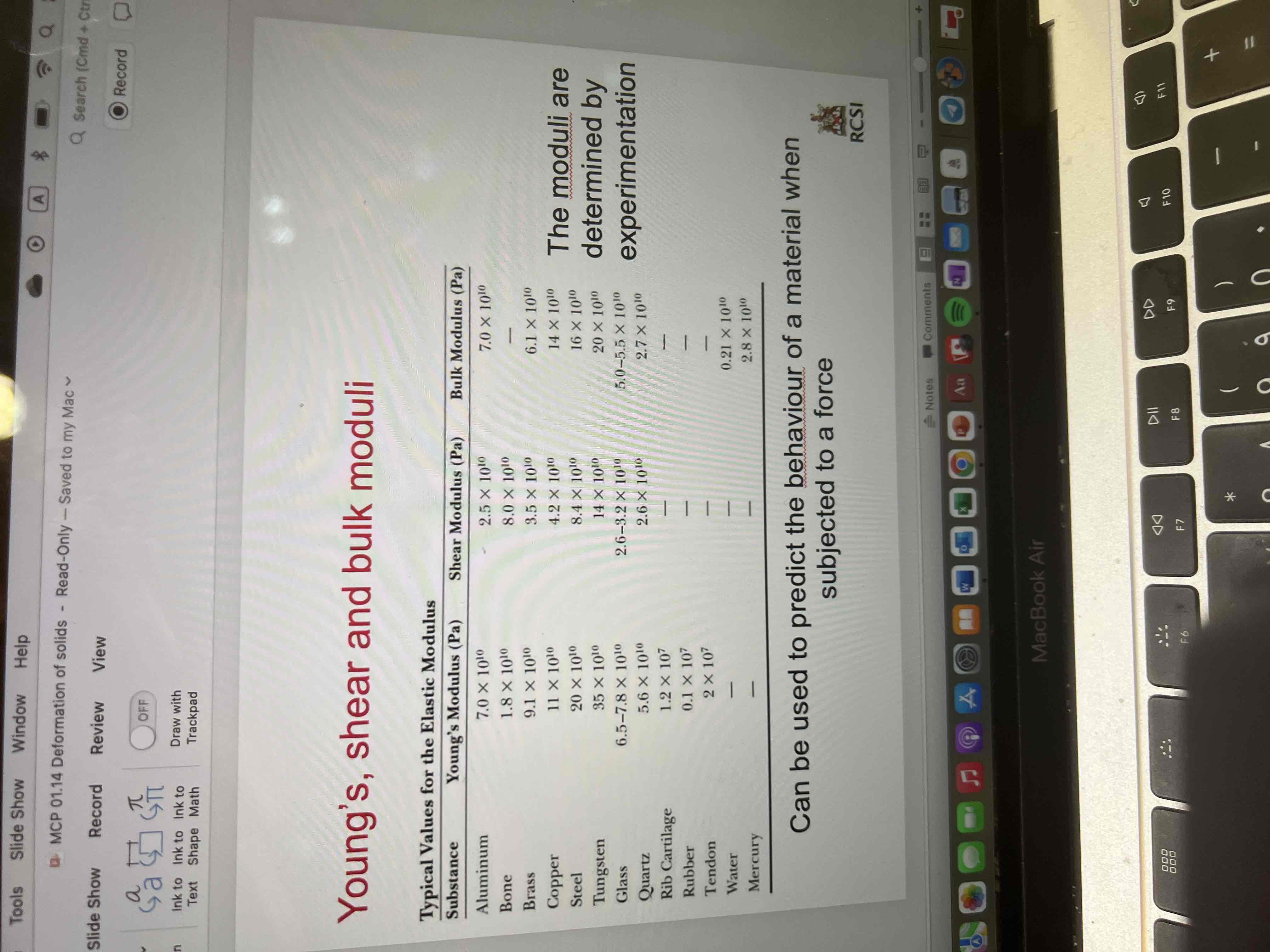
Young’s, shear and bulk moduli
Can be used to predict the behavior of a material when subjected to a force
Strain question

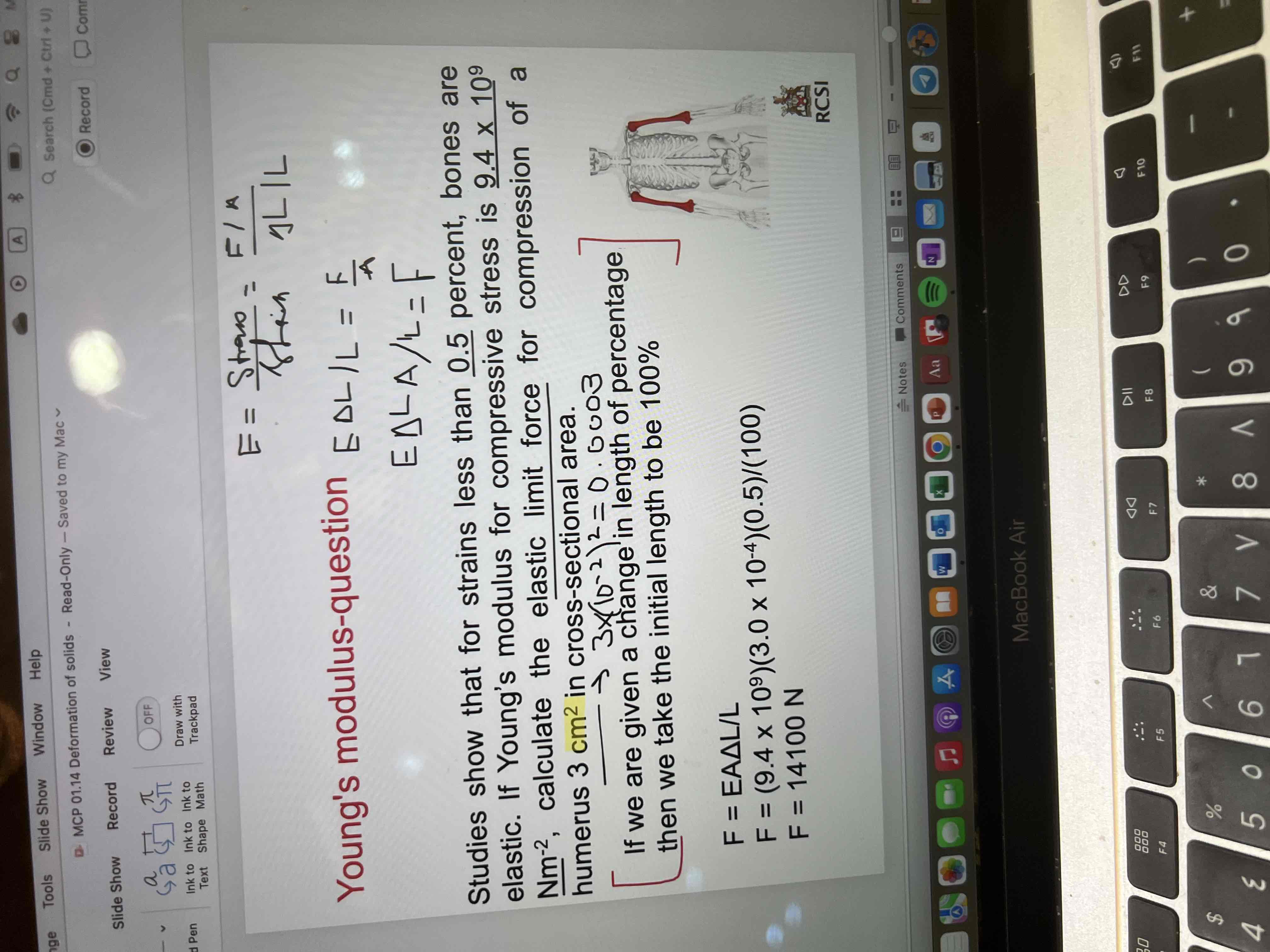
Young’s modulus question