8.3: Regulation of transcription and translation
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is a transcription factor?
Proteins which regulate transcription of specific target genes in eukaryotes by binding to specific DNA base sequences on promoter regions, either activating or repressing the transcription of a particular gene
What is transcriptional regulation?
The control of gene expression by preventing or promoting the transcription of DNA into RNA, usually through transcription factors binding to promoter regions
How is transcription regulated using transcription factors?
Transcription factors move from the cytoplasm to the nucleus
They bind to DNA at a specific DNA base sequence on a promoter region
This stimulates/inhibits transcription of target genes by helping or preventing RNA from binding
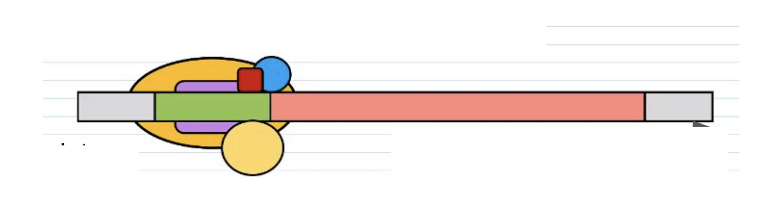
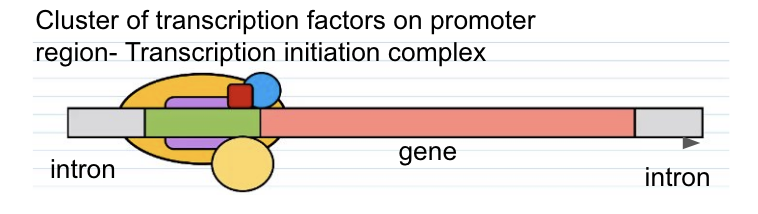
Label the diagram
Cluster of transcription factors on promoter region- transcription initiation complex
Intron
Gene
How does oestrogen initiate transcription?
Oestrogen diffuses directly across the phospholipid bilayer as it is a lipid-soluble steroid hormone
In the cytoplasm, oestrogen binds to a receptor site on a specific transcription factor, forming an oestrogen-receptor complex
This causes a conformational change of the DNA binding site of the transcription factors
The oestrogen-receptor complex diffuses from the cytoplasm into the nucleus
It then binds to a specific DNA base sequence on the promoter region of a target gene
This stimulates transcription of target genes by forming mRNA by helping RNA polymerase to bind
Therefore the gene is transcribed and expressed
Why does oestrogen only affect target cells?
Other cells do not have oestrogen receptors
What is epigenetics?
Changes to DNA that alters the expression of genes without changes to the base sequences of DNA, which can be inheritable or caused by environmental changes
What is the epigenome?
All possible chemical modifications of DNA and histone proteins that regulate gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence
What is heterochromatin?
Tightly packed chromatin associated with histones
It is silenced as it cannot be accessed by RNA polymerase and transcription factors
What is euchromatin?
Loosely bound chromatin associated with histones
It can be expressed as it is more accessible to RNA polymerase and transcription factors
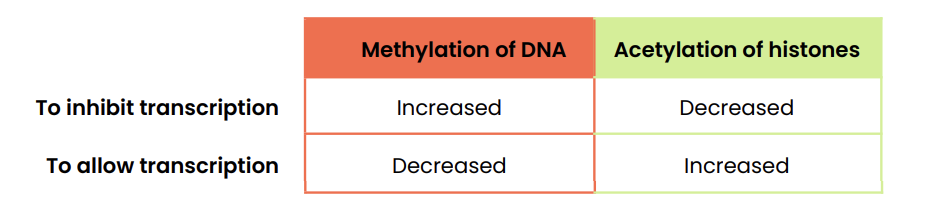
Summarise the epigenetic control of gene expression in eukaryotes
To inhibit transcription: DNA methylation increased, Histone acetylation decreased
To allow transcription: DNA methylation decreased, Histone acetylation increased
How can methylation inhibit transcription?
Methyl groups are added to DNA at specific locations (CpG) sites by methyltransferase
CpG sites is where cytosine is next to guanine in the DNA chain
DNA methylation prevents transcription factors from binding to the DNA, so RNA polymerase cannot bind so gene cannot be transcribed
So transcription is always inhibited
(Methyl groups can also be removed in demethylation so effect would be in reverse)
How can acetyl groups promote transcription?
Acetyl groups are added directly to the lysine amino acid on histones by acetyl coenzyme A
Acetylation neutralised the positive charge of lysine, reducing attraction between DNA and histones
So histones bind to DNA less tightly, becoming euchromatin
This stimulates transcription factors and RNA polymerase to bind to promoter regions
So genes are transcribed
(Acetyl groups can also be removed in deacetylation so effect would be in reverse)
What is RNA interference?
Inhibition of translation of mRNA produced from target genes, by RNA molecules such as siRNA
This inhibits expression of a target gene
Describe the regulation of translation by RNA interference
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) is incorporated into a protein, forming an RNA induced silencing complex (RISC)
siRNA is synthesised as double stranded RNA with one strand incorporated
Single stranded siRNA within the RISC binds to target mRNA with a complementary base sequence
This leads to hydrolysis of mRNA into fragments which prevents ribosomes from binding
Preventing translation of target mRNA into a protein
Why is RNAi sequence-specific?
siRNA binds only to mRNA with a complementary base sequence