Emotions Unit
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are emotions?
Whole-organism responses, involving…
Physiological arousal
Expressive behaviors
Conscious experience
What are the 3 components of emotion?
The 3 components of emotion are…
Physiological arousal is your body's reaction to stress, making things like your heart rate and hormones change.
Expressive behaviors are how you show your feelings through actions or body language.
Conscious experience is your awareness of thoughts and feelings or just the way you think.
William James & Carl Lange
This flash card is here so you know their full names. Their theory is presented later on in the study set.
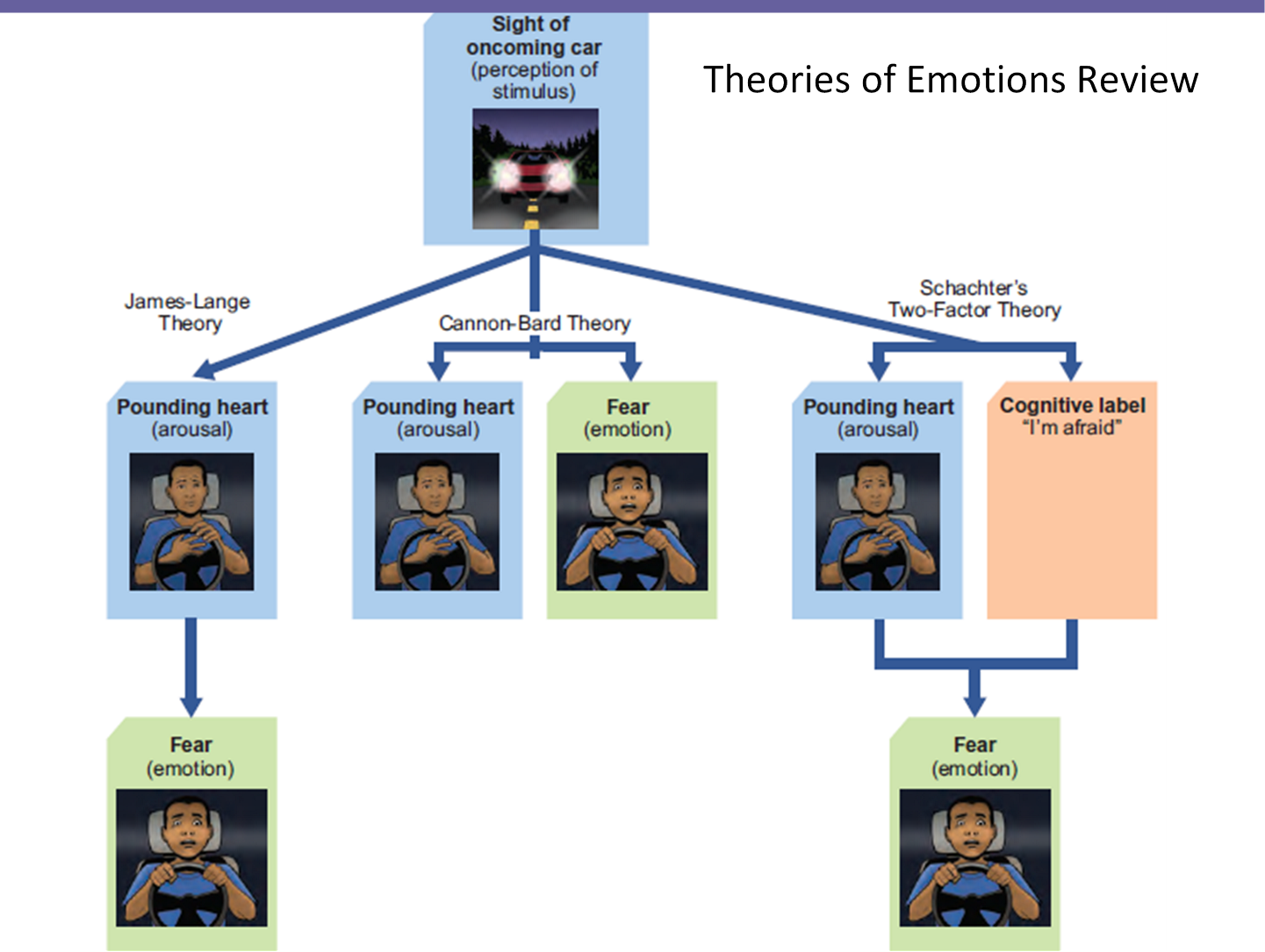
What is the James-Lange Theory?
Theory that because we are aware of physiological arousal, we experience emotion.
Fire alarm sounds
You start shaking.
You become aware of the shaking.
Then you realize this reaction as fear.
Walter Cannon & Philip Bard
This flash card is here so you know their full names. Their theory is presented later on in the study set.
What is the Cannon-Bard Theory?
The theory that physiological arousal and emotion occur at the same time.
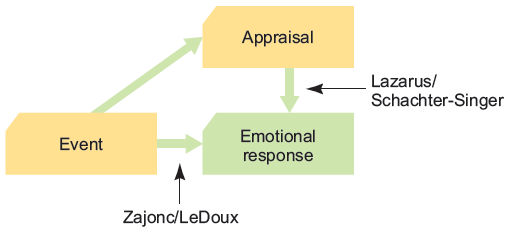
What is Cognitive Appraisal?
The way we determine a situation’s importance.
Stanley Schachter & Jerome Singer
This flash card is here so you know their full names. Their theory is presented later on in the study set.
What was the Two-Factor Theory?
To experience emotion, we must…
Be physiologically aroused.
Cognitively label the arousal.
A cognitive label is just the name you use for an emotion such as, anger, sadness, or disgust.
Luh Calm Example Photo
Luh Calm Picture Pt.2 for the guys
Who was Robert Zajonc?
Psychologist who concluded that emotion and cognition are separate.
Suggested that our interpretations of situations are sometimes slower than our emotional reactions. (before we know what we think about a situation, we know how we feel about it.)
What is the Amygdala?
The amygdala is a brain region that helps process and remember emotions, particularly fear and stress.
Who was Richard Lazarus?
Psychologist who concluded that some emotional responses do not require conscious thought.
But still involve some kind of unconscious cognitive appraisal.
What is Conscious Awareness and Unconscious Thinking?
Conscious awareness is being aware of your thoughts and feelings.
Unconscious thinking is thoughts and mental processes happening without your awareness.
Who was Barbara Fredrickson?
Psychologist who theorized that positive emotion has been under-researched.
Formulated the Broaden-Build Theory that helps people use happiness, safety and calm to improve mood and interactions with others.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
Division of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions.
Controls processes of:
breathing
blood pressure
digestion
Sympathetic (arousing) division.
Parasympathetic (calming) division.
What are your Sympathetic/Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Your Sympathetic Nervous System is…
The part of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to deal with perceived threats.
Fight / flight / freeze response.
Increased heart rate
Perspiration
Increased blood flow
Your Parasympathetic Nervous System is…
The part of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body.
Brings the body back down to a relaxed state.
Pupils contracting
Slowed heart rate
What is Nonverbal Communication?
Communicating feelings without words.
Facial expressions
Tone of voice
Hand gestures
Body language
How you communicate feelings/intentions through your physical movements and gestures.
What are Gender Effects?
Women are better at reading nonverbal communication of emotions.
Women tend to express emotions more than men do.
What is Power?
The first factor in interpreting nonverbal communications. (as in relation to a power dynamic to a boss to his employees)
What is Culture?
Culture is the second factor in interpreting nonverbal communication.
What are Display Rules?
The cultural rules governing how and when a person may express emotion.
Rules greatly vary from culture to culture.