Gen Bio Exam 1
1/59
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
scientific method
observation, hypothesis, experiment, research, analyze, conclude
characteristics of living species
reproduction, heredity, homeostasis
ionic bonds
oppositely charged atoms with different electronegativities are electrostatically attracted to each other
covalent bond
sharing of an electron pair between two atoms
hydrogen bonds
hydrogen atom bonds to a strongly electronegative atom
weakest to strongest atoms
hydrogen, covalent, ionic
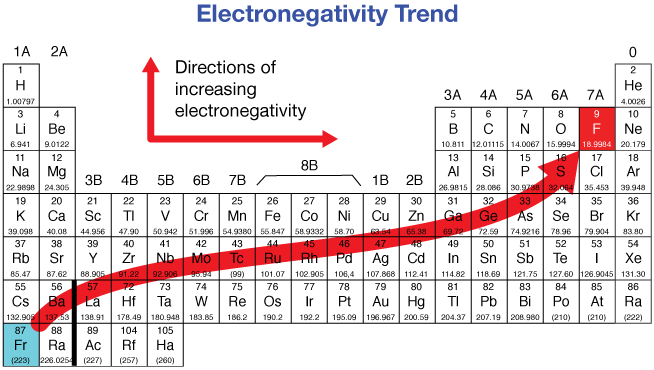
electronegativity scale
increase from left to right across the periodic table, decrease from top to bottom within a group
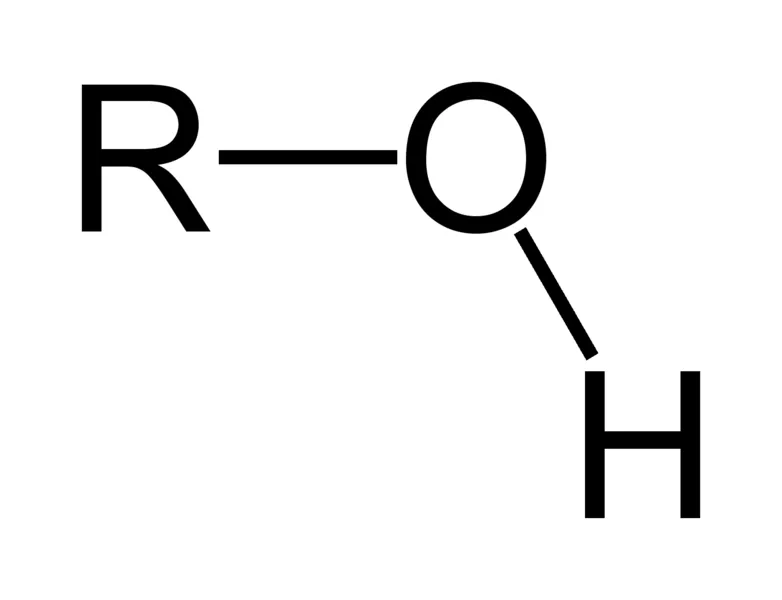
hydroxyl
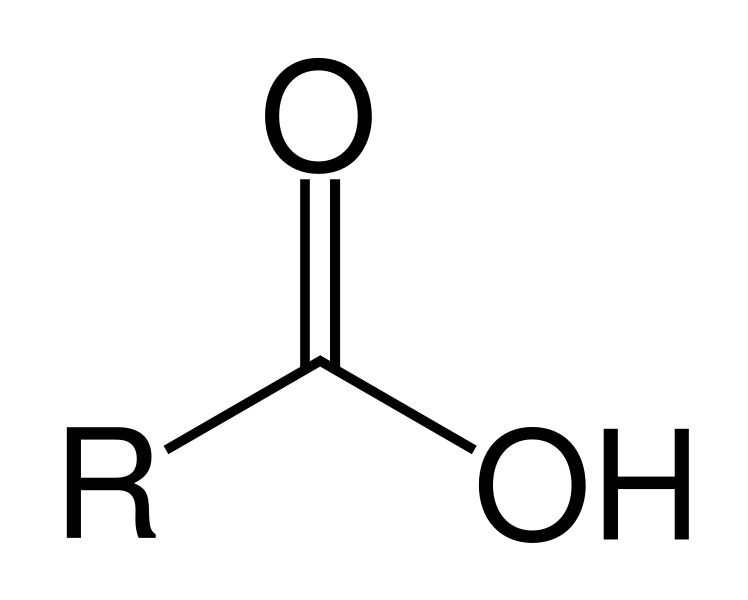
carboxyl
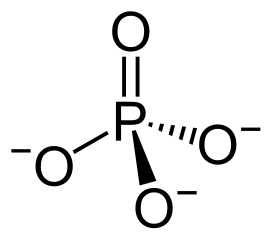
phosphate
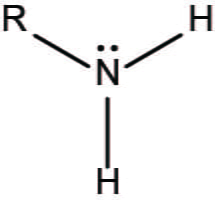
amino
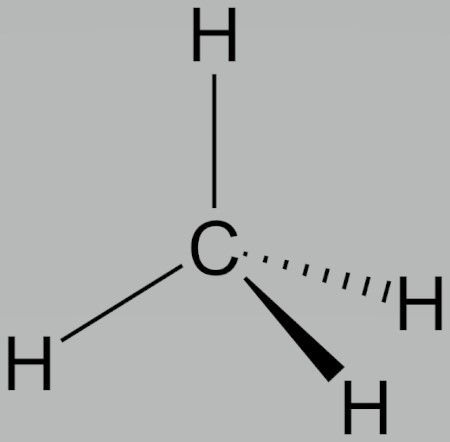
methyl
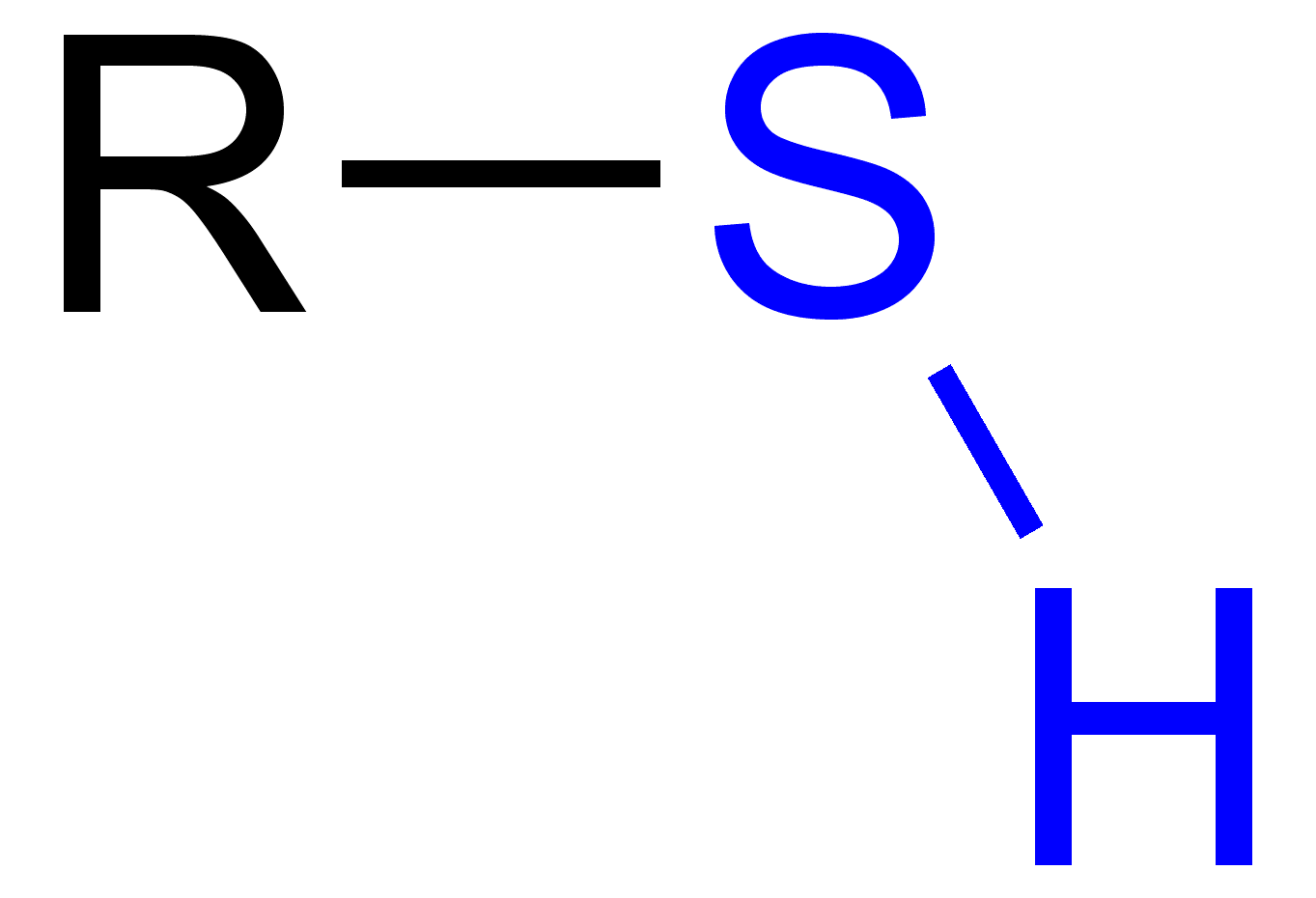
sulfhydryl
polar covalent bond
covalent bond that occurs when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons unequally
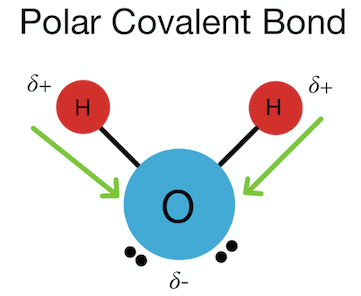
which atom has a partial charge in a polar covalent bond
the atom with the lesser electronegativity
polar molecules interactions with water
molecules with partial or full charges, interact with water's dipoles and dissolve in it
nonpolar molecules interactions with water
don't interact well with water and can't form hydrogen bonds with water
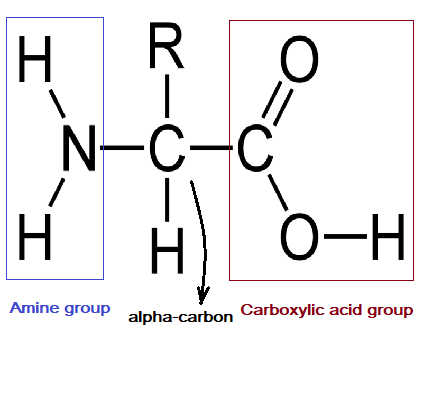
general structure of an amino acid
a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group and an organic side chain
side chains in amino acids
polar amino acids have side chains that interact with water, while nonpolar amino acids do not
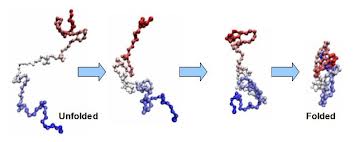
polypeptide chains 3D folding near water
protein folding; polar amino acid side chains gather on the outside to interact with water, while nonpolar amino acid side chains form a tightly packed hydrophobic core
phospholipids
they have a polar head which is hydrophilic and two non-polar tails made of fatty acids which are hydrophobic
phospholipid bilayers
formed by two layers of phospholipids coming together, with the hydrophilic heads facing outward and the hydrophobic tails facing inward
membrane proteins
functions include communication, cell signaling, cell division, transport, adhesion
integral membrane proteins
located directly within the lipid bilayer, such as receptors and ion channels
peripheral membrane proteins
not directly located in the lipid bilayer but associated with the membrane indirectly, generally by interactions with integral membrane proteins
prokaryotic cells
absence of a nucleus, organelles, or a cytoskeleton.
eukaryotic cells
possesses a clearly defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
plasma membrane functions
protects the cell, regulates the transport of materials, provides structural support, and allows interaction with other cells through its proteins
plasma membrane makeup
semipermeable membrane that separates the inside of a cell from its external environment, mainly made up of the phospholipid bilayer
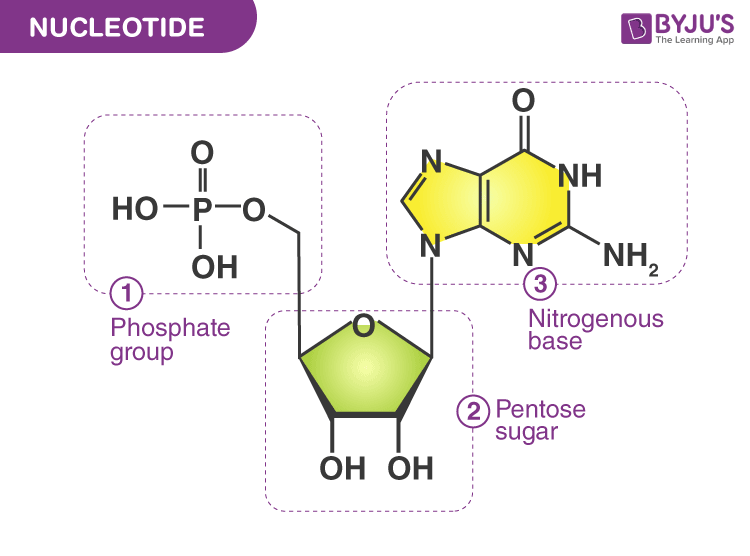
structure of nucleotides
consists of a nitrogenous base, a five carbon sugar, and a phosphate group.
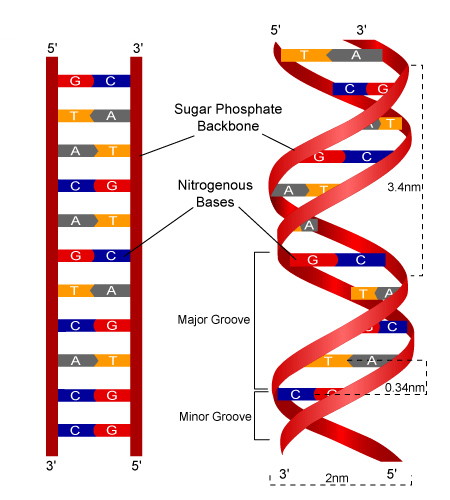
structure of DNA
“backbone” made of alternating sugar and phosphate groups, the inside is made up of nucleotide bases and connected by hydrogen bonds between.
double stranded DNA molecule replication template
ensures that each dividing cell receives an identical DNA copy, each strand from the parent dictates which strand it will be on in each new daughter strand
DNA vs RNA
DNA is double-stranded while RNA is usually single-stranded. Sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, where RNA contains ribose. DNA uses the base of thymine whereas RNA uses uracil.
mRNA
messenger RNA; carries the protein blueprint
tRNA
transfer RNA; carries amino acids
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; makes up ribosomes
RNA
ribonucleic acid; carries DNA’s genetic info to ribosomes, binds to DNA through complementary base pairing
nucleus
double membrane-bound organelle that stores, retrieves, and duplicates genetic information
mitochondrion
organelle that constantly undergoes fission and fusion; energy-associated; “powerhouse of the cell”
cell wall
outermost layer of the eukaryotic cell; protects plasma membrane
cytoskeleton
network of interlinking protein filaments, aids in cell shape, organization, and movement
lysosome
the cell’s “garbage disposal”, breakdown of proteins
ribosomes
present in eukaryotic cells for protein synthesis
rough endoplasmic reticulum
covered in ribosomes on its surface, produces proteins which are folded
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
stores lipids and steroids
exon
coding sequences
intron
noncoding sequences
promoter
DNA sequence where proteins bind to initiate transcription
transcription
the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence.
translation
the sequencing of a mRNA molecule to a sequence of amino acids