IGSCE Biology - Plant Nutrion, Gas Exhange and Transport
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H20 → C6H1206+6O2
Glucose is turned into:
Starch - storage
Sucrose - movement around the plant
cellulose - cell walls
Function of chloroplast
contains chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment
It absorbs light energy to make food in the process of photosynthesis
Chlorophyll traps the energy from the sun and uses it to turn water and carbon dioxide into sugars for the plant
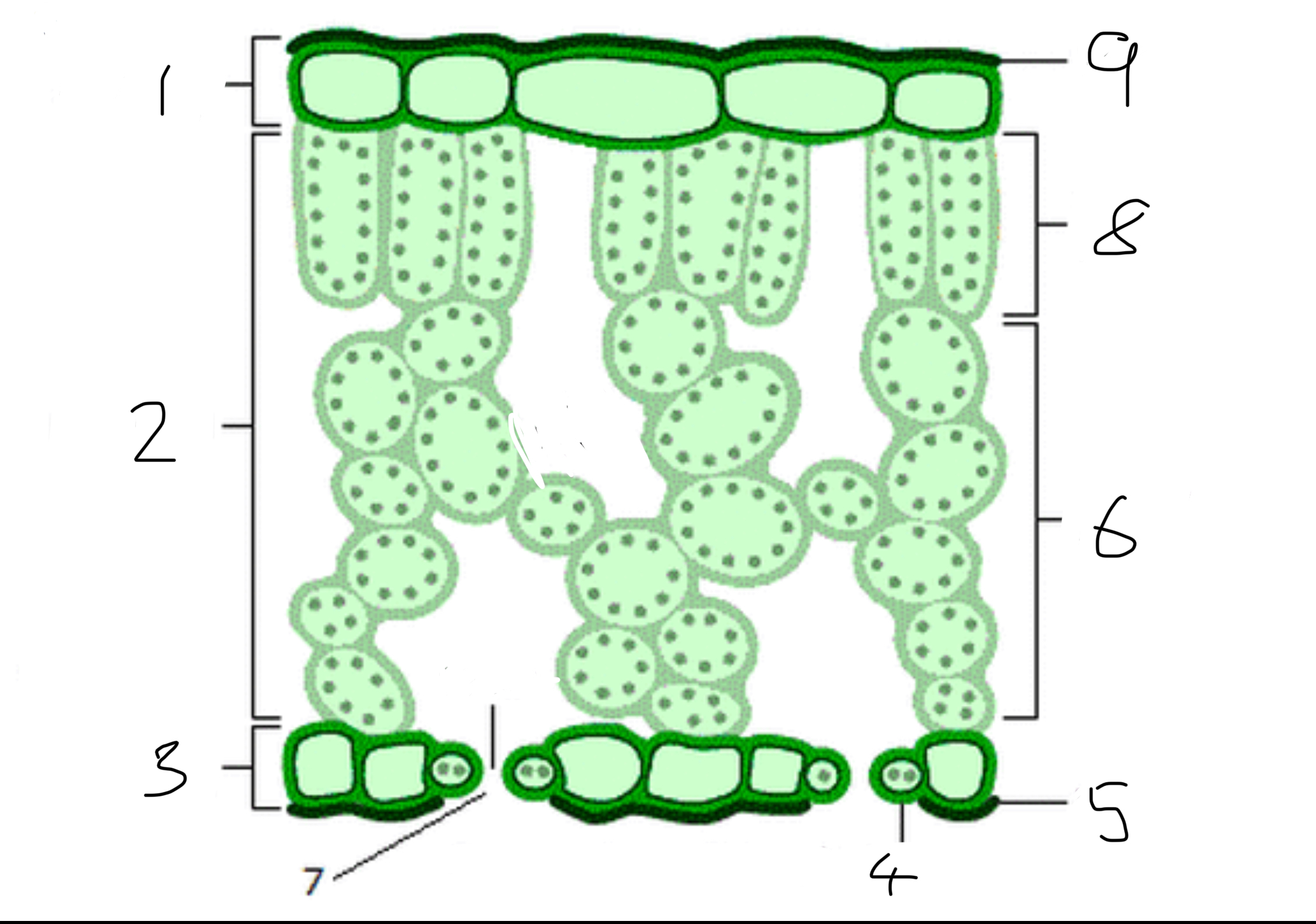
Label the diagram
Upper epidermis
Mesophyll
Lower epidermis
Guard cells
Wax cuticle
Spongy mesophyll
Stomata
Palisade mesophyll
Wax cuticle
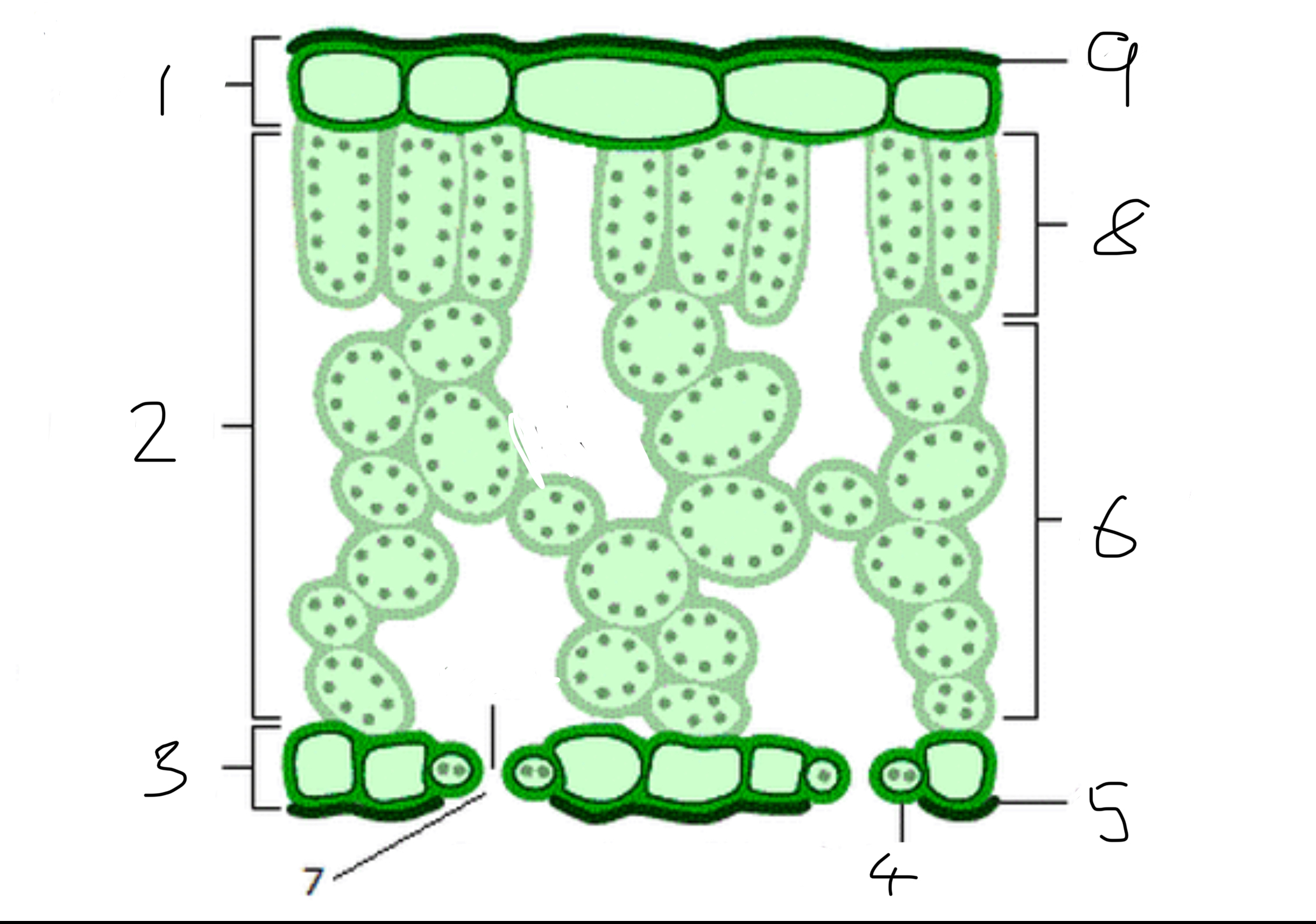
How is the leaf adapted for it function?
the palisade layer is packed full of lots of chloroplast for photosynthesis
The lead has a transparent upper epidermis to key light through to the palisade layer
Broad shape to increase surface area to catch more light
Leaf is thin to allow rapid diffusion for gas exchange
Air spaces in the spongy mesophyll to allow for gas exchange
Lots of stomata to allow for gas exchange
Guard cells control if the stomata is open or closed
The wax cuticle reduces water loss by evaporation
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Light intensity - higher the intensity, faster the rate of photosynthesis.
Amount of CO2 - more CO2 = faster rate of photosynthesis
Temperature - higher temperature = faster rate of photosynthesis. Temperature affects the enzymes controlling photosynthesis. However, at a certain point the temp. may cause the enzymes to denature
Mineral ions needed by plants
Nitrate ions - contains nitrogen for amino acids and proteins.
Magnesium ions - needed for chlorophyll (leaves green) so they can make glucose.
Practical: testing green leaf for starch
Leaf in water for 1 min
Turn off Bunsen burner
Place leaf into test tube with ethanol for 10 min
Leaf on petri dish and cover with iodine solution
The leaf should go black
Practical: how does light effect photosynthesis?
fill 4 tubes with hydrogencarbonate indicator
Place pondweed in 2 test tubes
Cover one pondweed tube with tin foil and one without pondweed with tin foil
Shine bright light on tubes
Pond weed in light= photosynthesis > respiration = takes up CO2 → alkaline conditions = purple
No pondweed in light=control to show indicator doesn’t change in light
Pondweed in dark=respiration>photosynthesis = lots of CO2 → acidic conditions = yellow
No pondweed in the dark = control
Understand gas exchange in relation to respiration
During the night, oxygen enters the lead and CO2 leaves the leaf. This is to help the leaf respire and because the leaf does not photosynthesise in the night.
Understand gas exchange in relation to photosynthesis
During day, more CO2 enters the leaf than oxygen because, on average, the leaf photosynthesis more than it respires.
Understand how the structure of the leaf is adapted
leafs are broad → large surface area
Thin → short distance for gas to travel
Air spaces in spongy mesophyll → lets gases move easily between cells
Stomata lets gases like O2 and CO2 in and out the leaf
Stomata close in the dark to stop CO2 from entering when they cant photosynthesise
Role of stomata
close in dark to stop CO2 entering
Open in light to let CO2 enter
Stomata also close when water supplies from the roots dry up
If CO2 concentration increases, hydrogen-carbonate indicator
Goes from orange to yellow
If CO2 concentration decreases, hydrogen-carbonate indicator
Goes from orange to purple
Phloem
Transports sugars, like sucrose and amino acids from where they’re made, in the leaves, to other parts of the plant
Translocation
The movement of food substances around the plant
Xylem
Carry water and mineral salts from the roots up the shoots to the leaves in the transpiration system
Roots
The cells on the roots grow into long ‘hairs’ which stick out into the soil
There are millions of these ‘hairs’ giving the roots a large surface area for the absorption of water and minerals
Transpiration
caused by the evaporation and diffusion or water from the plants surface, mostly in the leaf.
This causes a shortage of water in the leaf, so more water is drawn up from the rest of the plant in the xylem
This means that more water is drawn up from the roots, and so there is a constant transpiration stream of water throughout the plant
How is the rate of transpiration effected?
Light intensity
the brighter the light, the greater the rate of transpiration. When stomata are closed, very little water can escape
Temperature
warmer it is, the faster transpiration happens. Due to energy of water particles increases so diffusing quicker
Wind speed
higher wind speed = faster rate of transpiration. Due to wind sweeping water vapour away and keeping a low water concentration maintained
Humidity
drier = faster transpiration. Due to low concentration of water outside the leaf.