skeletal system
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
cranial/rostral
towards head
caudal
towards tail
dorsal
towards spine
towards belly
ventral
cranial (in terms of limbs)
front of limb above carpus and tarsus
caudal (in terms of limbs)
back of limb above carpus and tarsus
proximal
moving towards spinedis
distal
moving away from spine
dorsal
front of limb below carpus and tarsus
palmar
back of limb below carpus (think palm)
plantar
back of limb below tarsus (think planting feet)
sagittal (plane)
divides dog into left and right portions
median (plane)
middle sagittal plane; medial (inner) vs lateral (outer)
transverse (plane)
divides body into cranial and caudal portions
dorsal (plane)
divides dog into ventral and dorsal portions
transverse axes of rotation
sagittal plane motion that occurs around an axis of rotation that is directed mediolaterally
ventrodorsal axes of rotation
dorsal plane motion that occurs around an axis of rotation that is directed ventrodorsally
craniocaudal axes of rotation
transverse plane motion that occurs around an axis of rotation that is directed craniocaudally
varus
abnormal turn in a limb towards midline
valgus
abnormal turn in a limb away from midline
superficial
close to surface of body
deep
far away from surface of body
flexion
movement of bones so that angle of joint between them is decreased, results in a folding or shortening of limb
extension
bones move so that angle of joint between them is increased and limb is stretched out or lengthened; extension beyond 180 is over extension
abduction
movement of a part away from median plane or axis
adduction
movement toward median plane or axis
circumduction
movement of a part when outlining surface of a cone
rotation
movement of a part around its long axis, very limited in domestic animals
pronation
rotation of forearm and carpus so that palmar surface turned downward
supination
rotation of forearm and carpus so that palmar surface turned upward
protraction
to advance a limb forward as in walking
retraction
to move a limb backward as in walking
axial
located or directed towards an axis
abaxial
located or directed away from an axis
perissodactyle
animal with an odd number of toes
artiodactyle
animal with even number of toes
axis consists of
skull, ribcage, vertebral
appendicular consists of
everything else
There are 2 parts to the intervertebral discs. The (2 words) ______ is the tougher outer layer that acts like a ligament to hold the IVD in place. The (2 words) ______ consists of a gel-like substance that helps provide cushioning between the vertebrae.
manubrium
xiphoid process
What is the main metacarpal bone found in the cannon bone in horses?
metacarpal III
In what way is the bovine tibia/fibula unique compared to the other species?
Only the head of the fibula is present and it is fused to the tibia
Which of these are major differences between canine's and horse's/cow's axial skeleton?
Horses and cows have horizontal transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae
Horses have a split (bifid) spinous process on their axis
Horses have 18 ribs
What is a unique anatomical feature you can find on the equine femoral head?
fovea capitis
In what location does the femoral head have contact with the pelvis?
Acetabulum
The atlas, the 2nd cervical vertebrae, has a tall spinous process while the axis, the 1st cervical vertebrae, has long transverse processes. They connect together via the dens.
false
Which species has a caudal and cranial greater trochanter on the femur?
equine
Which bones in the equine tarsus are fused?
1st and 2nd tarsals
In dogs and cats, what does the fusion of the spinous processes in the sacrum make up?
Median sacral crest
How many ribs are not attached to the sternum in cows?
5
There are 2 specialized sternebrae in the sternum. The (1 word) ______ is at the cranial end and is a major attachment point for several muscles. The (2 words) ______ is at the caudal end and is an attachment point for the diaphragm. The cartilage on this sternebrae disappears over time.
annulus fibrosus
nucleus pulposus
In the dog, which carpal bone(s) found on the palmar aspect (bones specifically on the same side as bottom of foot) of the carpus?
accessory carpal
1st carpal
In what section of the vertebral column do all the species we have discussed have the same number of vertebrae?
cervical
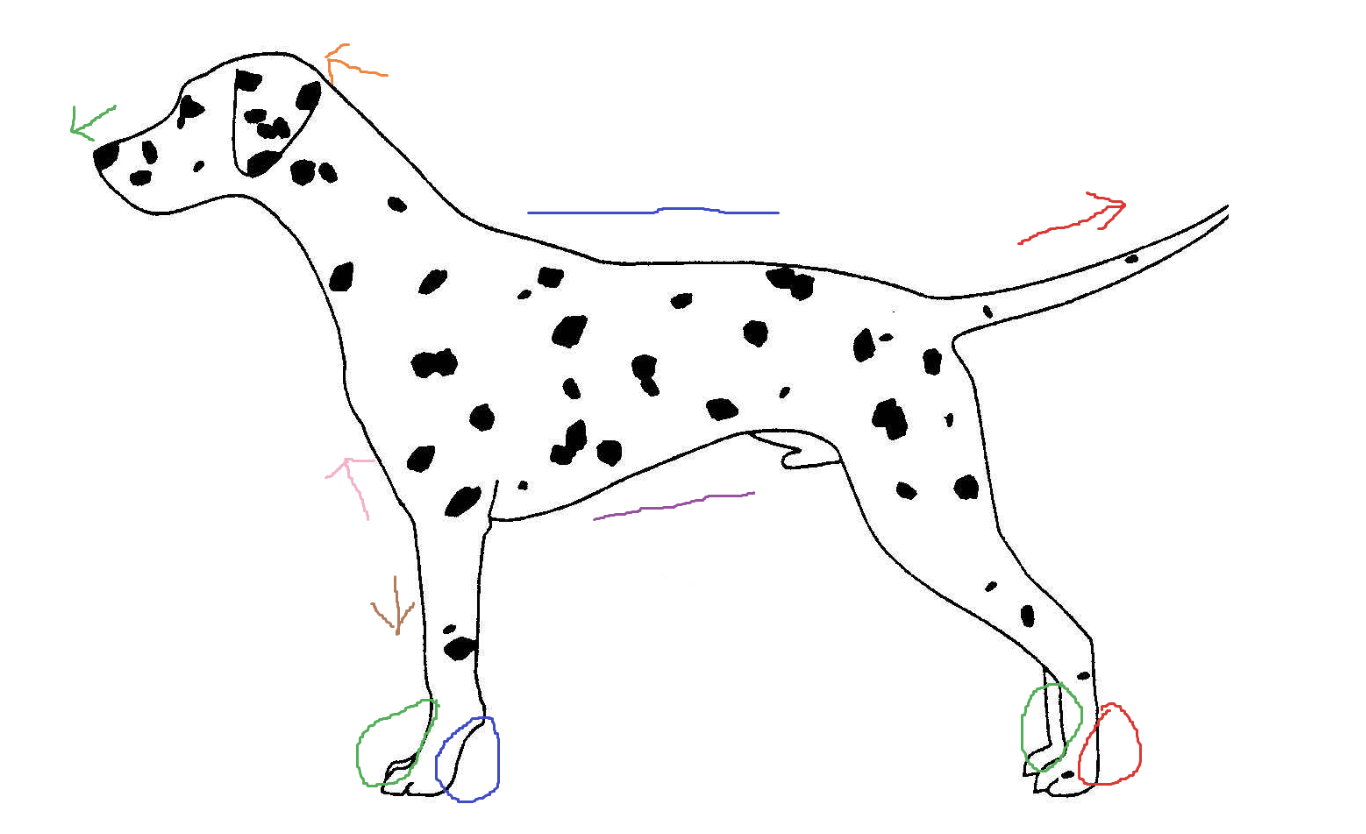
Blue circle
palmar
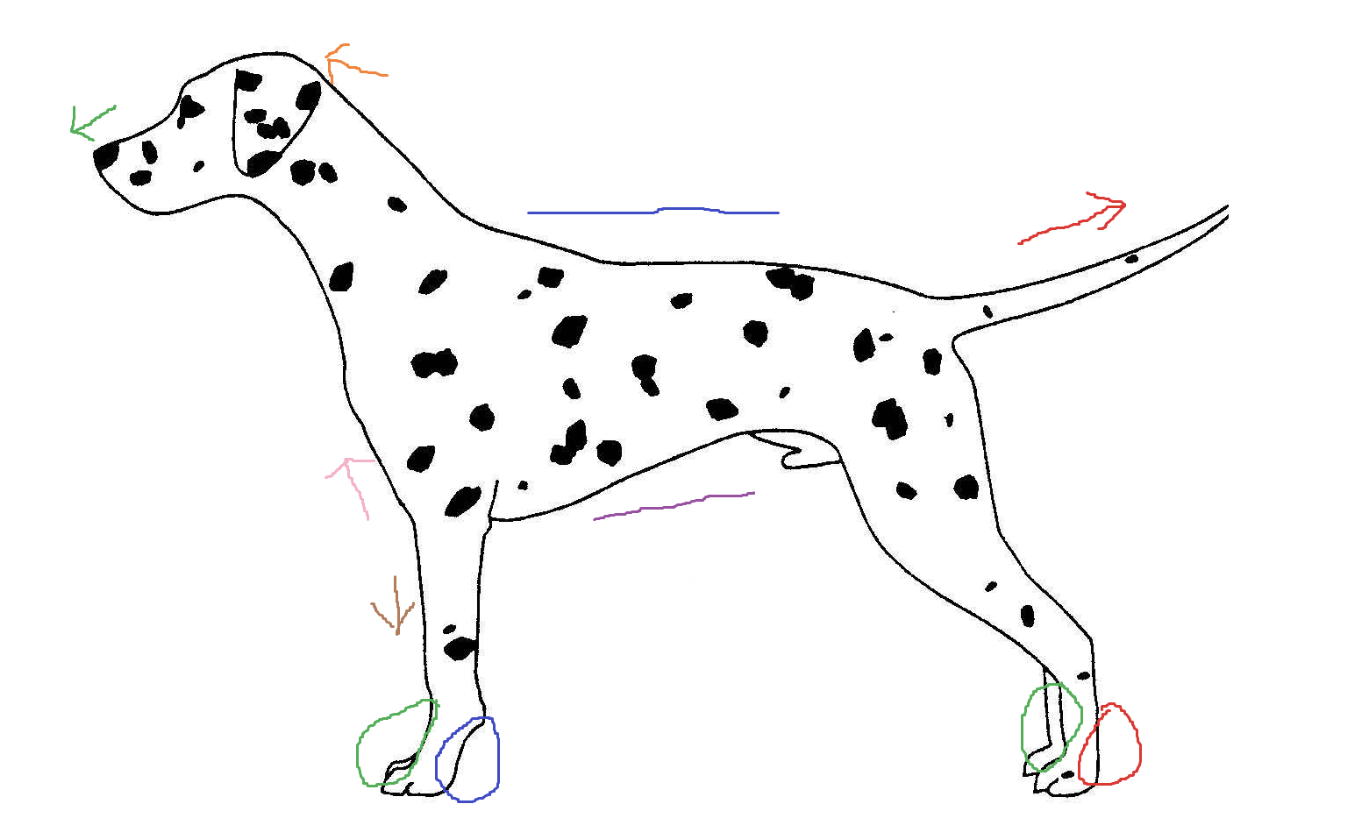
Red arrow
caudal
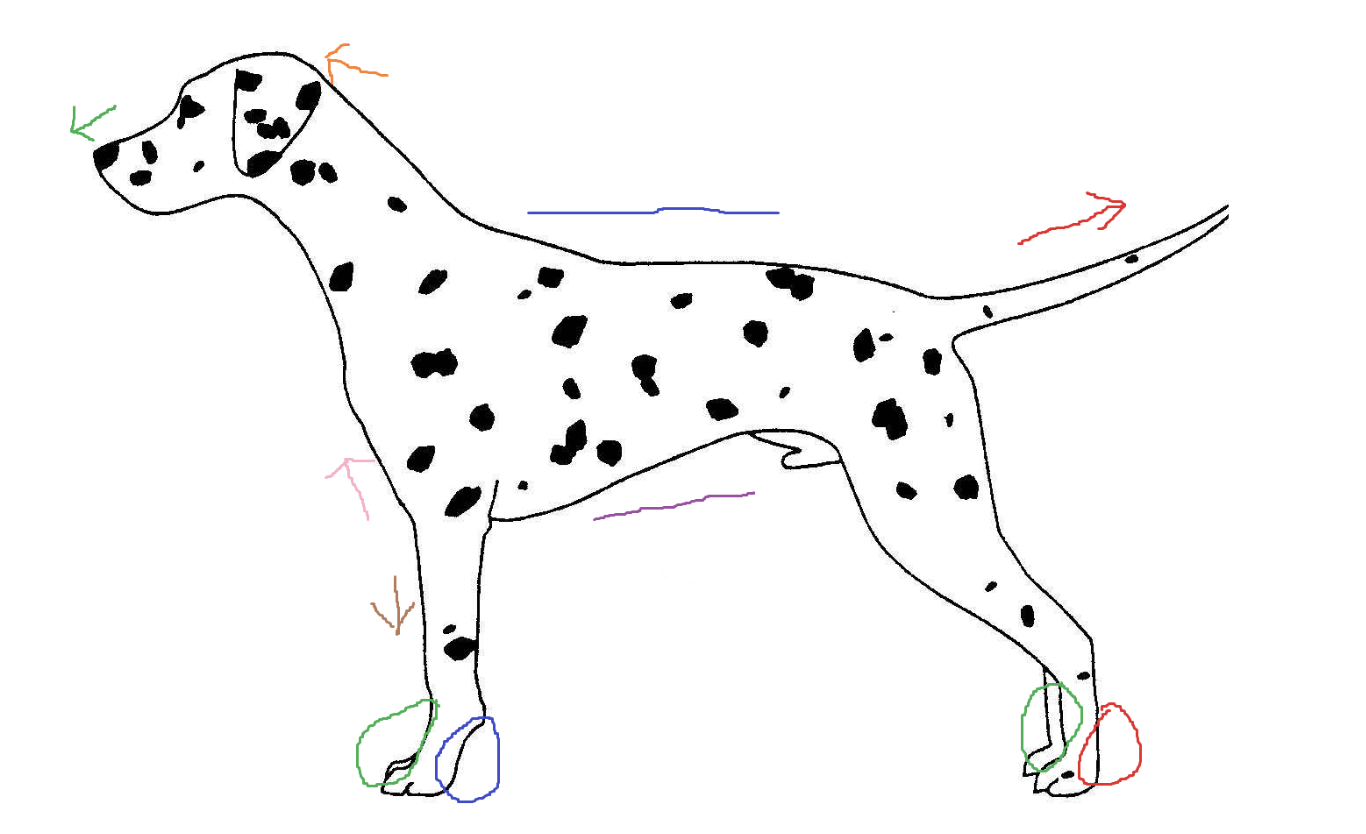
Green arrow
rostral
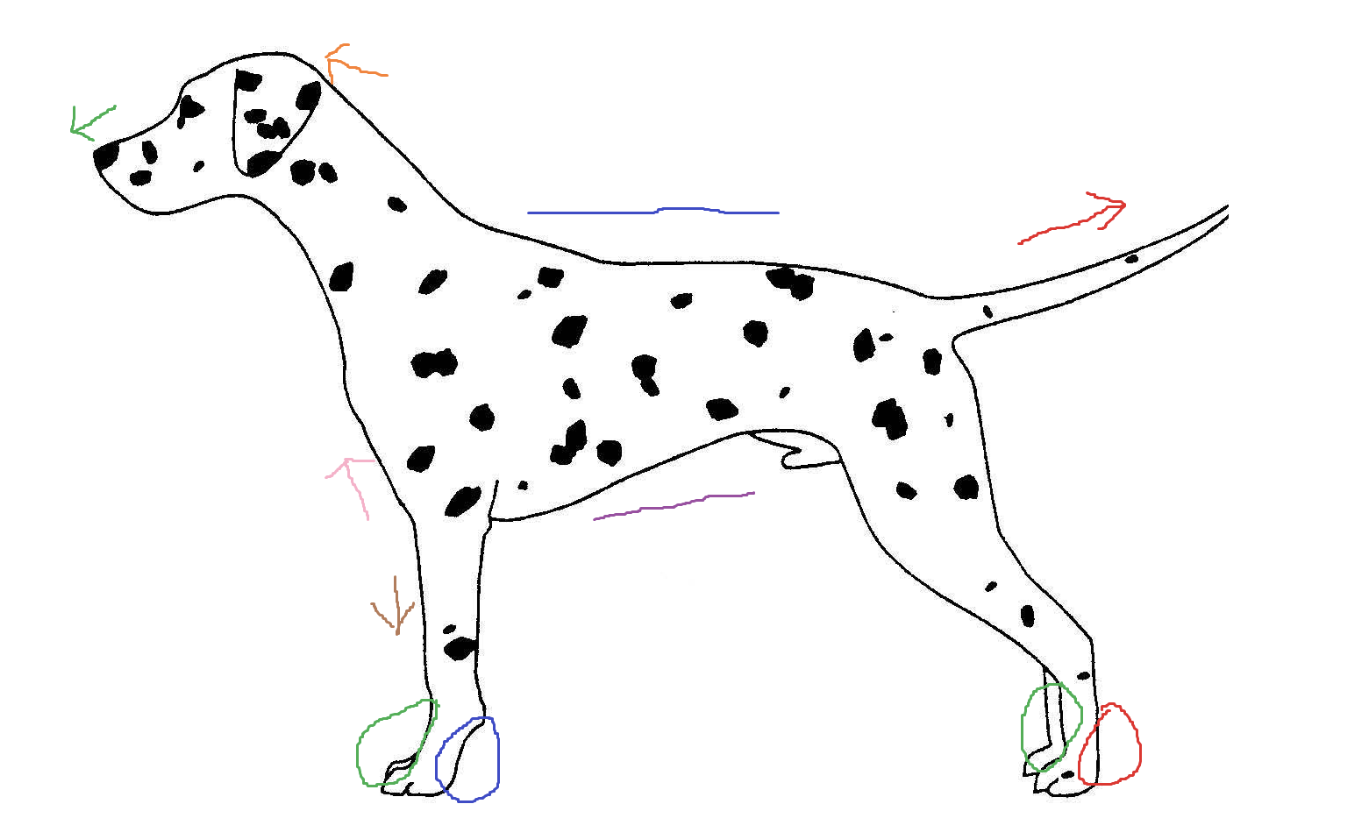
Blue line
dorsal
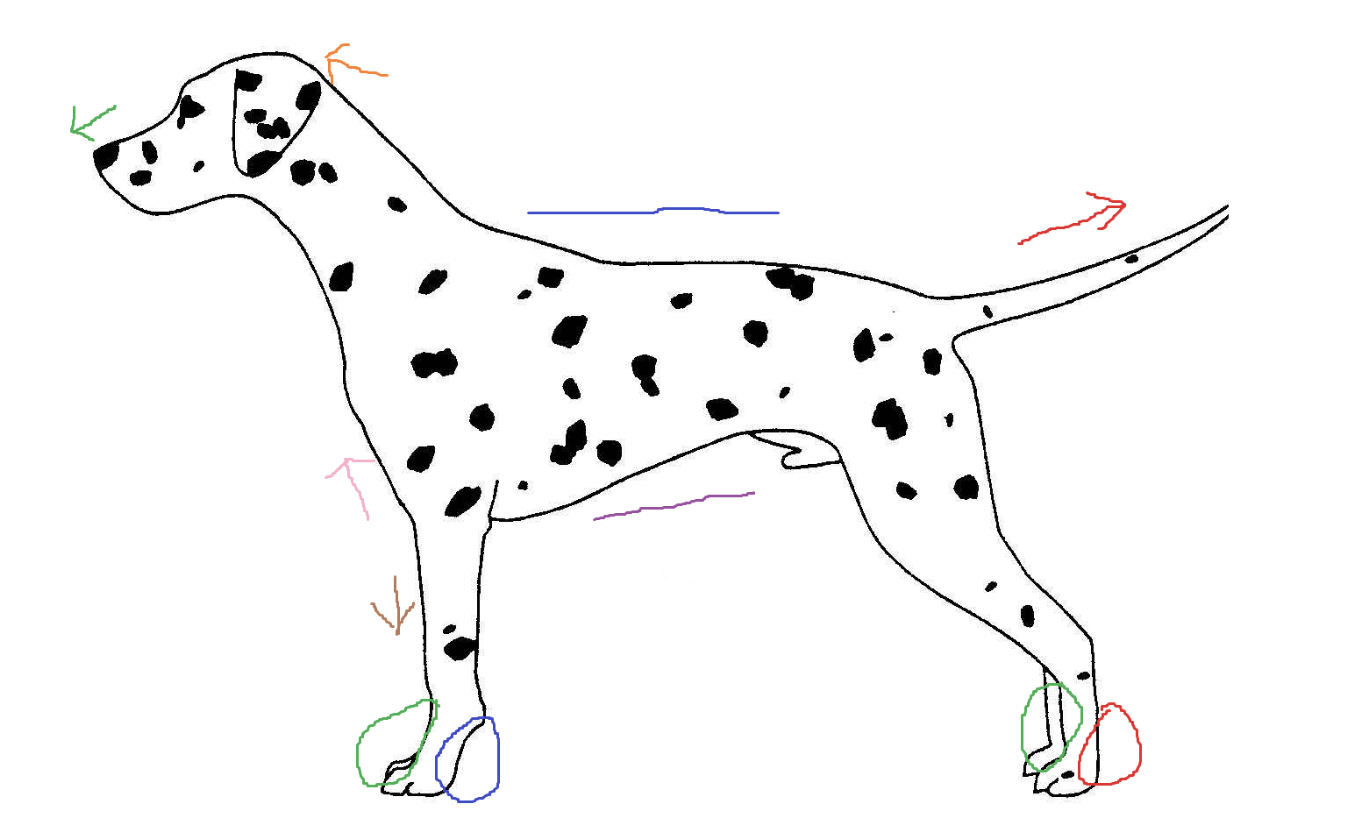
Green circle
dorsal
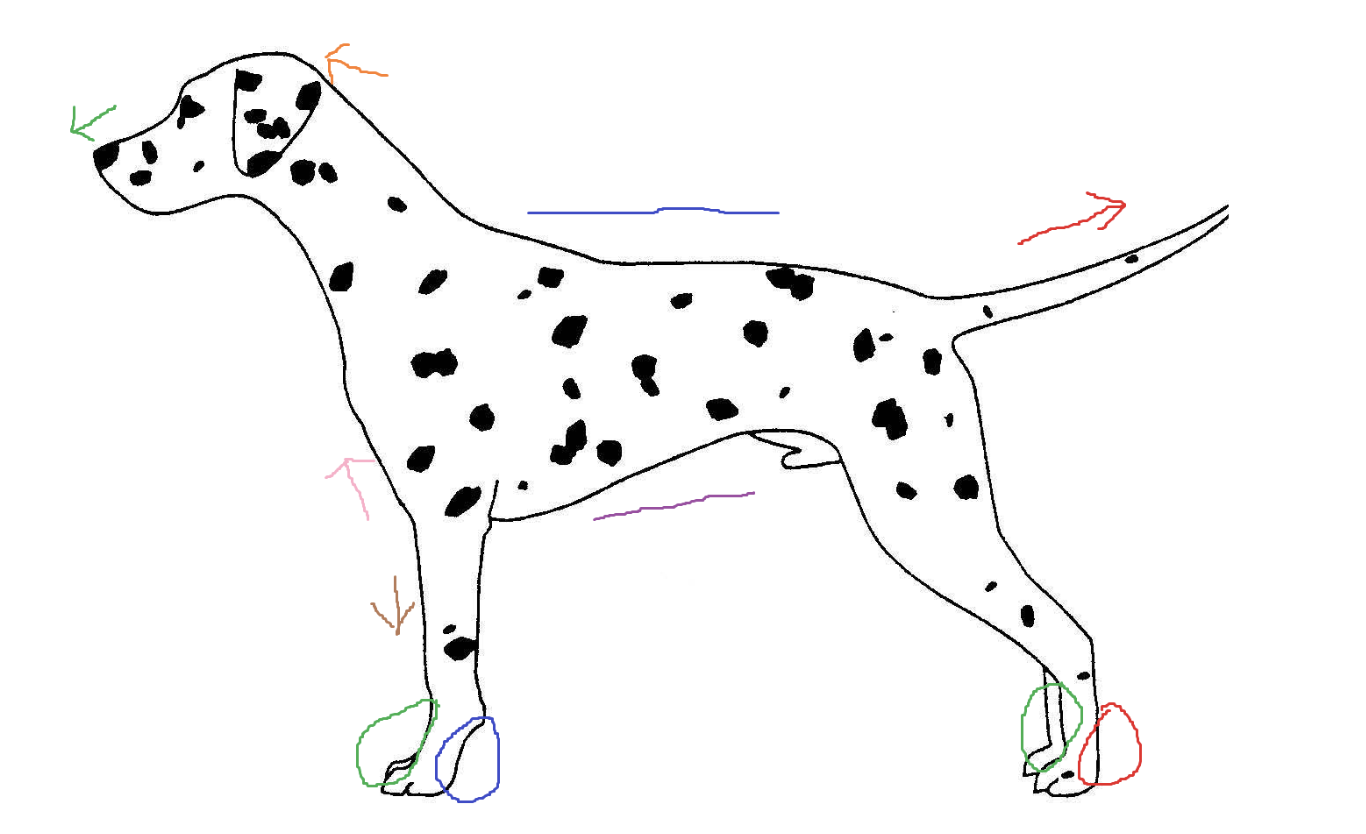
Purple line
ventral
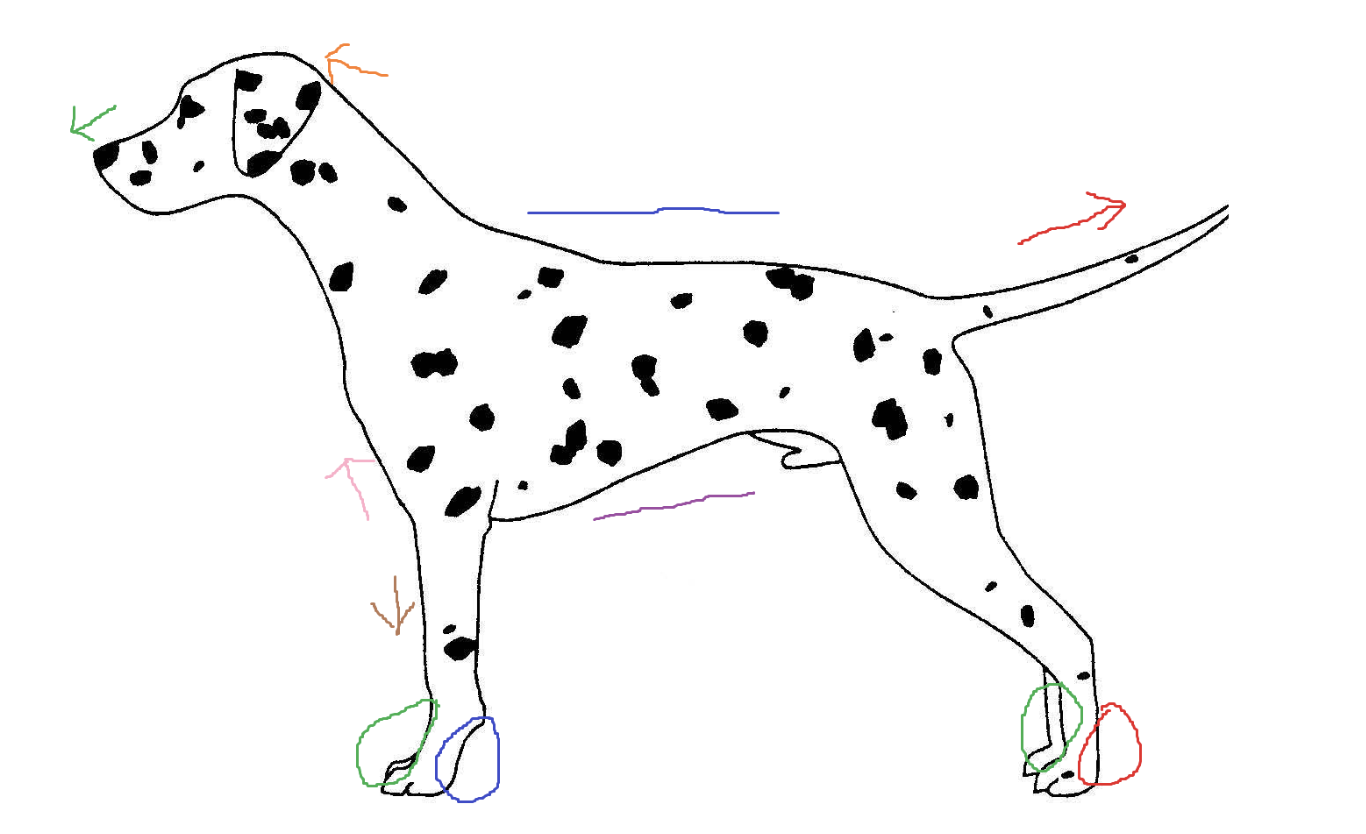
Brown arrow
distal
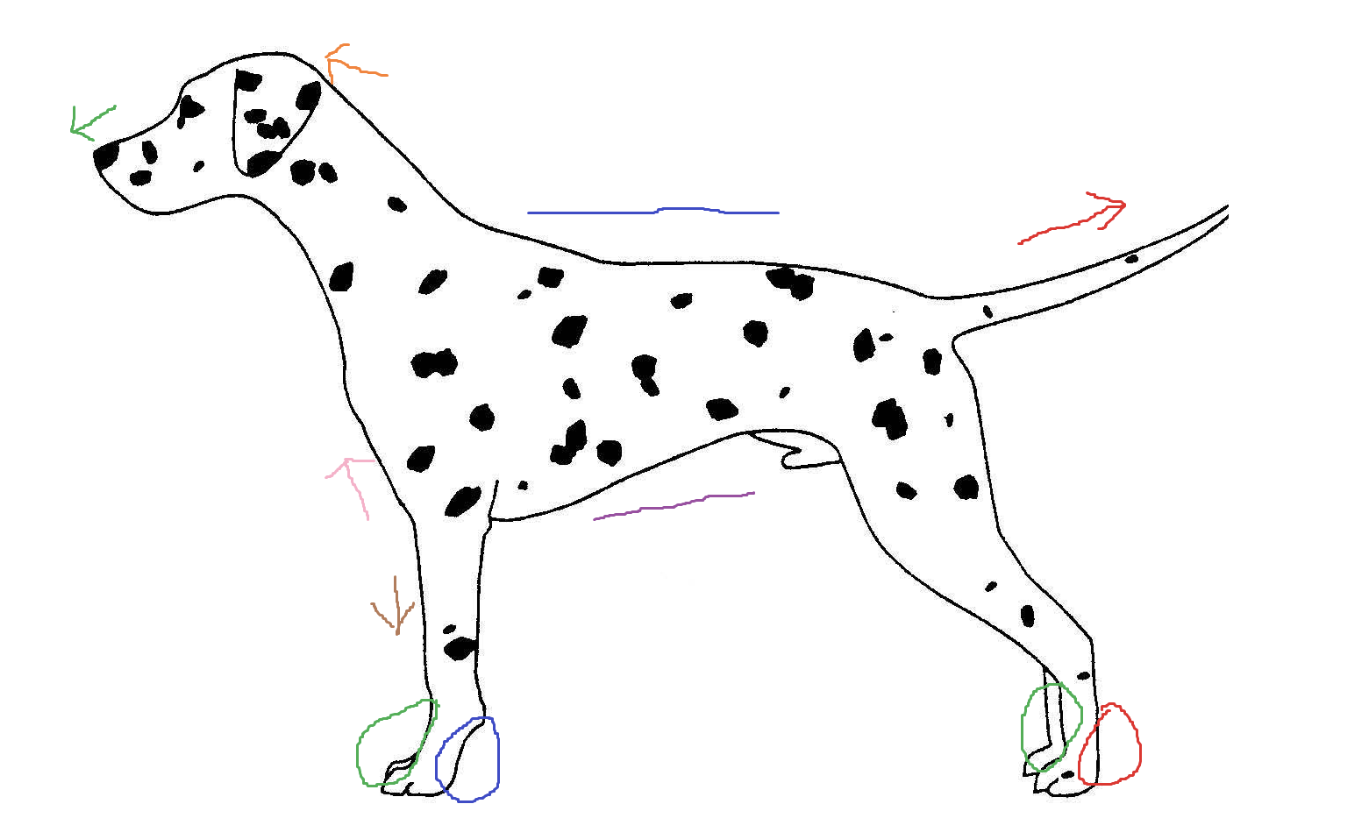
Orange arrow
cranial
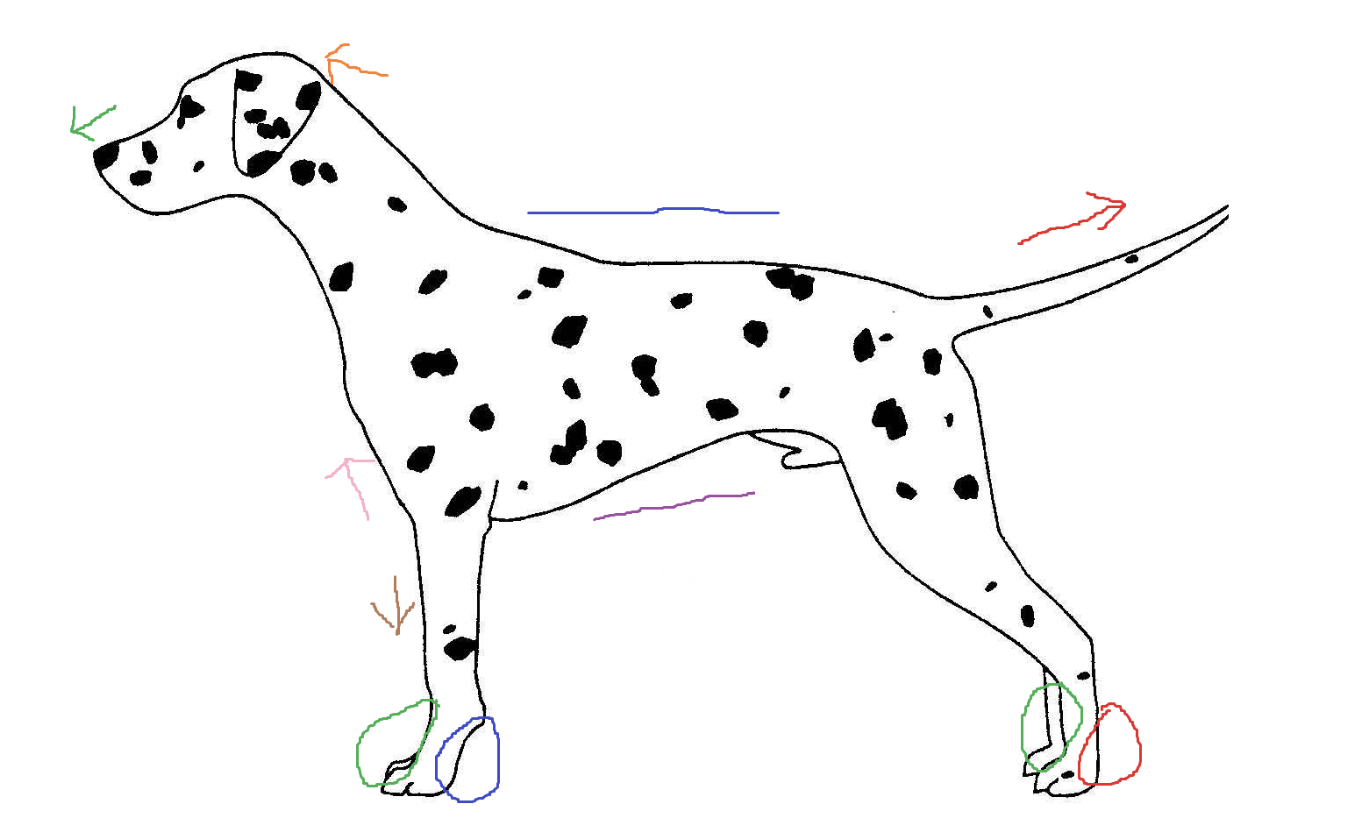
Pink arrow
proximal
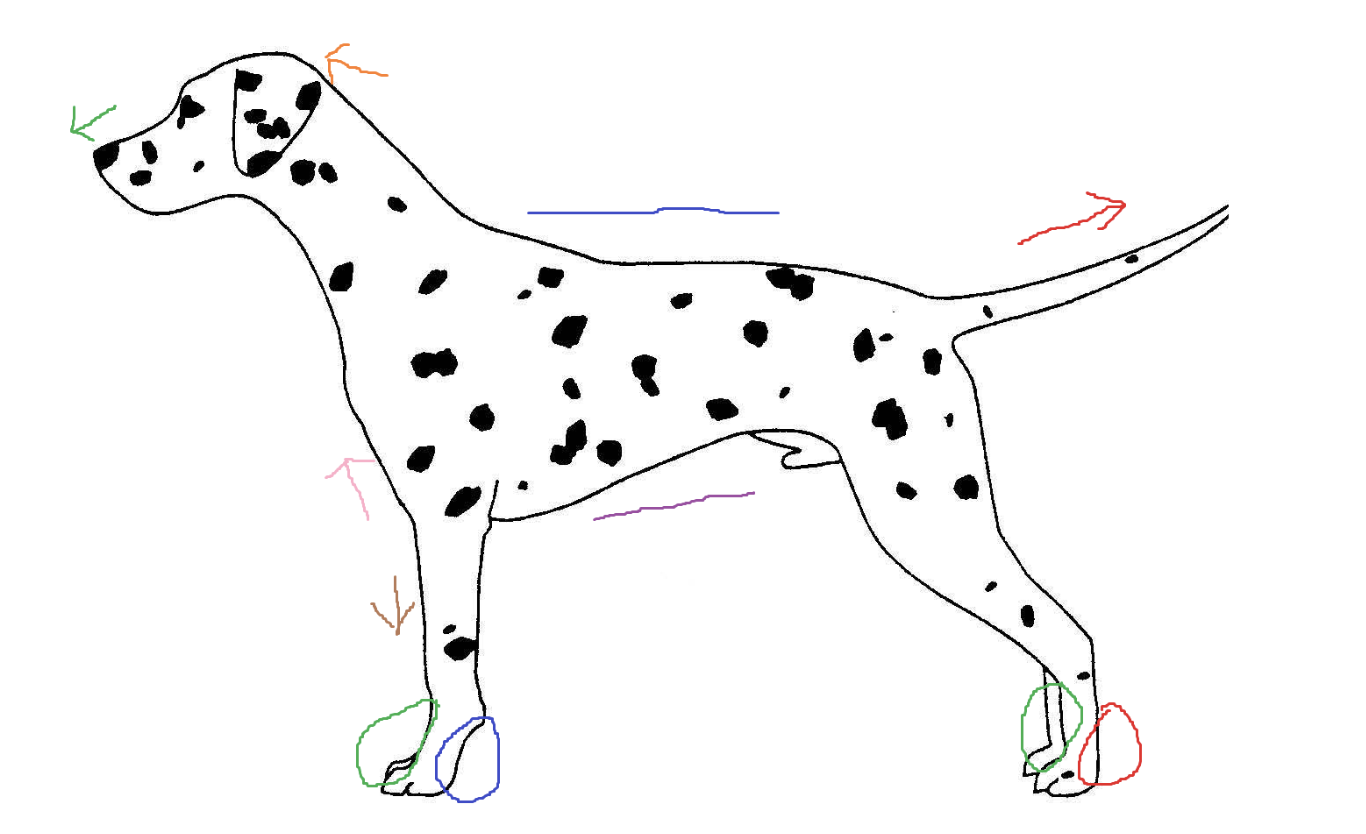
Red circle
plantar