Semisolid Dosage Forms: Ointments, Creams, and Gels
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Semisolid
Not pourable; retains shape until force applied.
Ointment
Semisolid form with <20% water, >50% hydrocarbons.
Cream
Emulsion of oil and water, often used topically.

Gel
Semisolid system with a jelly-like consistency.
Paste
Thick semisolid, often used for protective barriers.
Plaster
Semisolid adhesive used for topical applications.
Lotions
Liquid preparations for topical application, often soothing.
Occlusive
Forms a barrier to retain moisture in skin.
Emollient
Softens skin or soothes irritation in membranes.
Oleaginous Base
Insoluble in water, greasy, and occlusive.
Absorption Base
Absorbs water without changing consistency significantly.
Water-removable Base
Oil-in-water emulsion, water washable and non-greasy.
Water-soluble Base
No oleaginous components, completely water washable.
Levigation
Mixing powder with liquid to reduce particle size.
Petrolatum
Semisolid hydrocarbons from petroleum, used as ointment base.
White Petrolatum
Decolorized petrolatum, considered more esthetically pleasing.
Yellow Ointment
Contains yellow wax and petrolatum; greater viscosity.
White Ointment
Contains white wax and white petrolatum; bleached.
Emulsifiable Base
Anhydrous base allowing incorporation of aqueous solutions.
Emulsion Base
W/O emulsion that allows additional aqueous solutions.
Dermabase™
O/W emulsion, soluble in water, non-greasy.
Hydrophilic Ointment USP
Water-soluble, non-occlusive, and lipid-free.
Vaseline
Common name for petrolatum, used in ointments.
Unibase®
Water-removable base, non-greasy and water washable.
Hydrophobic Barrier
Prevents moisture evaporation from skin.
Oleaginous
A base with high oil content.
Absorption Ointment
Base that can absorb water.
Water/Oil Emulsion
Emulsion with water dispersed in oil.
Oil/Water Emulsion
Emulsion with oil dispersed in water.
Water-miscible
Able to mix with water.
Ointment Bases
Foundations for ointment formulations.
Hydrophilic
Having affinity for water.
Hydrophobic
Having low affinity for water.
Spreadability
Ease of spreading the ointment.
Washability
Ability to be washed off easily.
Stability
Resistance to changes over time.
Drug Release Potential
Rate at which drug is released.
Occlusiveness
Ability to form a barrier on skin.
Uses of Ointments
Includes protectants and emollients.
Examples of Ointments
Includes Aquaphor and Eucerin.
Incorporation Method
Mixing components until uniform.
Fusion Method
Melting components together for ointment.
Levigating
Reducing particle size before mixing.
Hydrous
Containing water in the formulation.
Anhydrous
Free from water content.
Hydrolytic Degradation
Decomposition due to water interaction.
Lipophilic Drugs
Drugs with high affinity for lipids.
Absorption Bases
Bases that absorb water and drugs.
Fusion
Process of melting components to create ointments.
Medicated Ointments
Ointments containing active medicinal ingredients.
Microbial Content
Limits on microbial presence in topical applications.
Antimicrobial Preservatives
Substances like methylparaben preventing microbial growth.
Minimum Fill
Net weight or volume verification of filled containers.
Packaging Requirements
Specific containers for storage and labeling of ointments.
Viscosity
Measurement of a fluid's resistance to flow.
In Vitro Drug Release
Testing drug release from formulations in controlled conditions.
Hydrophilic Creams
Creams that attract water, easier to wash off.
Lipophilic Creams
Creams that repel water, more greasy texture.
Preparation of Creams
Involves heating lipid and aqueous phases separately.
Gels
Jellylike dispersions of particles in liquid vehicles.
Gelling Agents
Substances like carbomer that create gel structures.
Two-Phase Gel
Gel with distinct particles, thixotropic properties.
Single-Phase Gel
Homogeneous gel with no distinct particle boundaries.
Syneresis
Shrinkage of gel due to liquid expulsion.
Swelling
Increase in gel volume by liquid absorption.
Imbibition
Liquid uptake without volume increase in gel.
Bentonite Magma
5% bentonite used as a suspending agent.
Aluminum Hydroxide Gel
Gel used as an antacid, contains aluminum oxide.
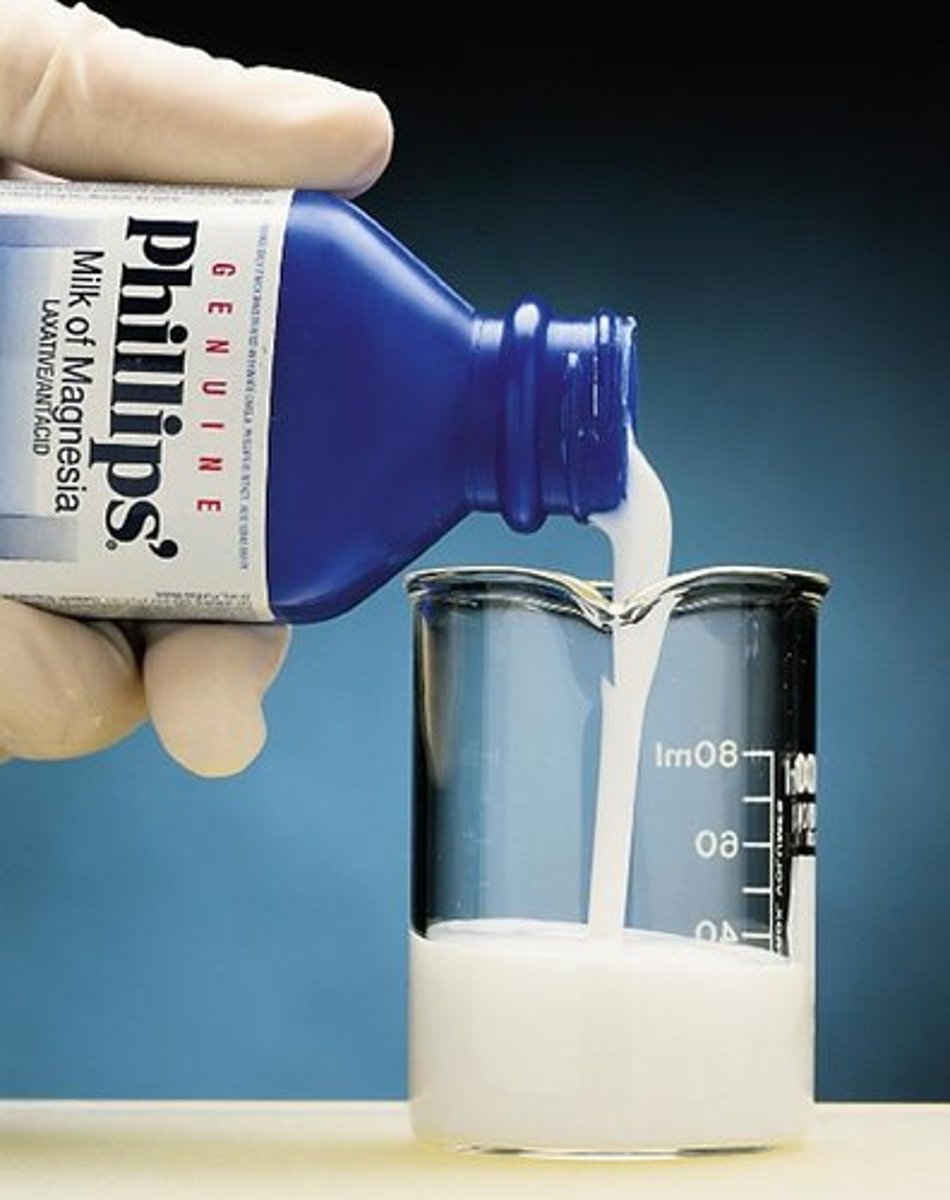
Milk of Magnesia
Magnesium hydroxide suspension used as an antacid.

Pastes
Stiffer semisolids with 20-50% solid material.
Cooling Process
Stirring during cooling ensures uniform ointment consistency.
Topical Administration
Application of formulations to skin or mucous membranes.
Zinc oxide paste
Used to protect and soothe skin.
Plasters
Adhesive masses for prolonged skin contact.
Salicylic acid plaster
Used for removal of corns.
Volatiles in lotions
> 50% of lotion volume is volatile.
Viscosity of lotions
Low enough to be poured easily.
Cooling sensation
Occurs as lotion evaporates on skin.
Glycerogelatins
Plastic masses for long-term skin contact.
Composition of glycerogelatins
Contains 15% gelatin, 40% glycerin, 35% water.
Zinc gelatin
Used for treating varicose ulcers.
Semisolid formulations wheel
Visual representation of topical formulations.
Ointments
Semisolids for topical application, systemic effects.
Creams
Emulsions with varying water content.
Packaging of semisolids
Jars, tubes, or syringes for topical products.
Contamination risks
Ointments and creams can harbor bacteria.
Preservatives in semisolids
Include parabens, phenols, and sorbic acid.
Transdermal preparations
Deliver drugs through skin for systemic effects.
Ophthalmic preparations
Include ointments and gels for eye use.
Rectal preparations
Ointments, creams, and gels for rectal use.
Vaginal preparations
Include creams and creamlike foams.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Bacteria that can contaminate semisolids.
Staphylococcus aureus
Another bacterium posing contamination risk.