Ventilation
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Mediastinum
area in the thorax, between the lungs where the heart, large blood vessels, trachea and oesophagus lie
Pleural membranes (2)
epithelial membrane lining the thoracic wall and lungs
very thin membrane
Pleural cavity
sealed compartment
Parietal (=wall) pleura location
=costal
lines the inside of the thoracic wall
Visceral (organ) pleura ‘location’
covers surface of the lungs
Cross-section of the thorax (photo)
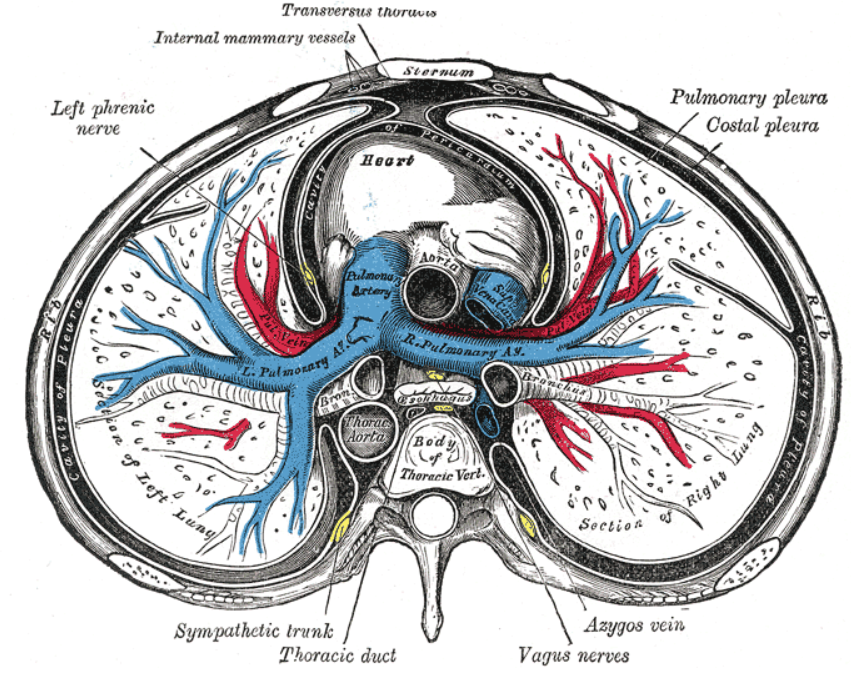
Intrapleural Space (5)
Both pleura continuously forming a potential space between them - FLUID
maintains negative pressure:
air from outside flow into the lungs
during inhalation chest, lungs expands → creates a pressure difference
air flows into the conducting zone to the terminal bronchioles and alveoli
Intrapleural pressure
subatmospheric
potential space
small air in the intrapleural space
parietal pleura function (4)
Secrete FLUID
serves as a lubricant
forms from the blood capillaries
drains in the lymphatics
lubricant definition
a substance used to reduce friction between two surfaces in contact, allowing them to move smoothly over one another
Transpulmonary / transmural pressure (2)
Intrapleural space pressure:
lower than that in the lungs
Low p pulls the lungs outwards
Higher pressure in the lungs what does it do?
pushes the lungs outwards against the chest wall
Pneumothorax (2)
air leaks between the lungs and the chest wall in the intrapleural space
pressure ↑s → the lung collapses
Pneumothorax caused by (2)
spontaneous (no obvious cause)
injury
Pneumothorax treatment
Chest drains - to remove air out
Chest drains used for (4)
post-op
trauma
to drain pleural effusion
pneumothorax
Pleuritis
inflammation of the pleural membranes with an increase of fluid in the intrapleural space (Painful with breathing)
Pleuritis caused by (5)
viral or bacterial infections of the pleura
lung infections (pneumonia)
cancer
autoimmune conditions:
SLE (Systemic lupus erythematosus)
RA (rheumatoid arthritis)
Pleural Effusion
Increase in fluid between the lungs, causing pressure on the lungs and difficulty with breathing (May be painless)
Pleural Effusion caused by (7)
Heart failure
kidney and liver disease
inflammatory conditions
Pleuritis
Pneumonia
Tuberculosis
Lupus
inflammatory conditions
in which inflammatory fluid is increased
Air flow into the lungs depends on (4)
Pressure gradient
Physical properties of the lung
Airways resistance
Volume changes
Physical properties of the lung in ventilation (4)
Compliance of the lung
Elasticity
Surfactant
Surface Tension
Compliance (4)
=distensibility
The change in lung volume per change in pulmonary pressure
Lung compliance is changed in conditions
lung fibrosis: where there is infiltration of connective tissue proteins which decrease lung compliance
inspiration
Elasticity (3)
refers to the tendency of the lungs to return to their initial size after being distended, aiding expiration by facilitating the collapse of the lungs
bc/ elastin proteins present in lung tissue
allows respiration
elastic tension is counteracted by
intrapleural pressure
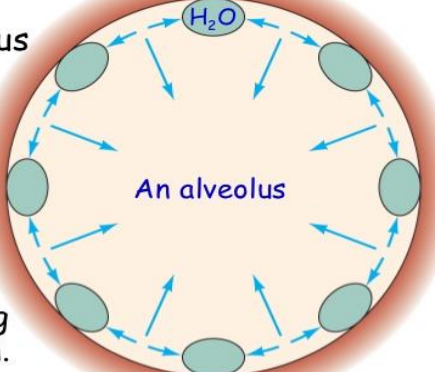
Surface Tension (7)
The lungs secrete and absorb fluid, leaving a thin film on the alveolar surface
the thin film of fluid has a surface tension
the film squeezes the alveolus → produce recoil
pulls the alveoli inward → increasing the tendency to cause the lungs to collapse → increases the pressure of the air inside the alveolus
allows alveolus to resist expansion
coat pulmonary surfactant → prevents alveoli from collapsing from this tension
lining fluid
Insuffiecient pulmonary surfactant produce
newborn respiratory distress syndrome
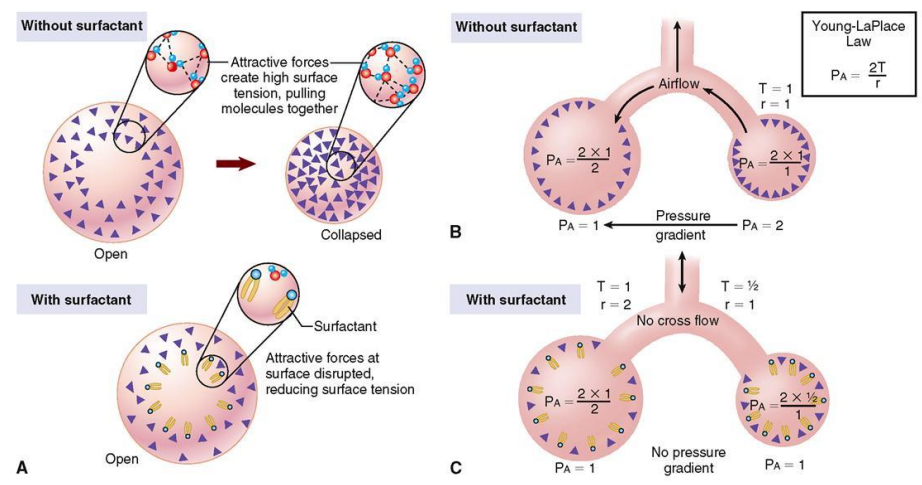
Surfactant (5)
= Surface Acting Agent
Secreted by Type II alveolar cells
Consists of Phospholipids and hydrophobic surfactant proteins
primarily phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylglycerol
It is interspersed between the H2O molecules at the water-air interface, reducing the H bonds between the H2O molecules at the surface, reducing the surface tension
Effect of surfactant on smaller alveoli (3)
improves as the alveoli get smaller during expiration
due to the increase in concentration
preventing the alveoli from collapse
Type I alveolar cells secretes
Epithelial cells
Airways resistance
Determined by airway diameter
Pressure Gradient
Air moves in and out of the lungs as a result of the pressure differences created by changes in the lung volumes
Air flow (2)
Directly proportional to the pressure difference induced by changes in lung volume
Inversely proportional to friction resistance
Boyles’ Law (2)
P1V1 = P2V2
If the size of a container is reduced → the collisions between the gas molecules and the walls become more frequent → the pressure ↑
Inspiration pressure (2)
Alveolar pressure ↓ as the volume ↑
Air flows into the lungs
Expiration pressure (2)
Alveolar pressure ↑ as the volume ↓
Air is pushed out of the lungs
Cystic Fibrosis (3)
inherited, genetic condition
the lung fluid is viscous (thick and sticky) - difficult to clear
The higher surface tension affects lung function - making it more difficult to expand
Premature Babies
Immature lungs –lack of surfactant
Factors affecting airways resistance (5)
Length of conducting system (constant)
Viscosity of air (usually constant but may be slightly altered by humidity and altitude)
Diameter of Airways (main determinant)
Upper airways – physical obstruction, mucus, spasm
Bronchioles constriction/dilatation
Anatomy and Structure of the Bronchial Tree and lobules of the Lung (7 + photo)
Trachea
Right + left primary bronchi
Secondary bronchi 2x left, 3x right
Bronchioles
Terminal bronchioles
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveoli
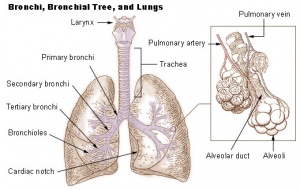
Gas exchange location
At Respiratory bronchioles + Alveoli
Airways of the lower respiratory tract
are kept open by cartilage and smooth muscle
Cartilage - Lower Respiratory Tract (3)
found down to the small bronchi
In the trachea they are C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
In the bronchi the cartilage takes the form of plates
Smooth muscle - Lower Respiratory Tract (2)
found from the trachea down to the bronchioles
In asthma the smooth muscle contracts narrowing the lumen of the bronchial tree, causing obstruction to air flow
Bronchi and bronchioles are made from
elastic tissue
Physiological changes in bronchial airways diameter - Airways Resistance (5)
Bronchoconstriction
Bronchodilation
Sympathetic Influence
Salbutamol
Bronchoconstriction (4)
Narrowing of the airways
Caused by:
Parasympathetic stimulation via muscarinic receptors
Histamines and leukotrienes (allergens)
Bronchodilation
Occurs when CO₂ levels in expired air ↑
Sympathetic Influence (2)
no direct sympathetic nerve control of the airways
epinephrine (adrenaline) from the bloodstream can cause bronchodilation by stimulating β2 receptors
Salbutamol
a β2 receptor agonist that mimics epinephrine, causing bronchodilation and reducing airway resistance
Obstructive Lung Disease (5)
External pressure from enlarged thyroid gland other masses
Physical obstruction of bronchial lumen
fx.: tumours, inhaled foreign bodies
Narrowing of airways from smooth muscle spasm or inflammation
fx.: asthma
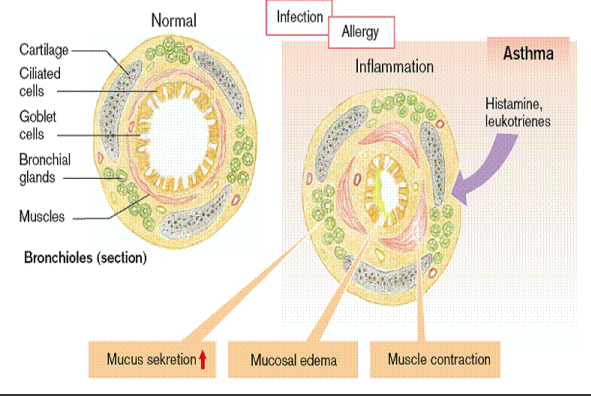
Restrictive Lung Disease (photo)