STRUCTURAL EFFECTS ON ACIDITY pt2
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
INDUCTIVE EFFECT
Shift in electron density through charge polarization transmitted through
sigma (σ) bonds.
pi
_ bonds are involved in resonance
Electron-withdrawing groups
stabilizes conjugate base
Electron-donating groups
destabilizes conjugate base
-F, -CO2H, (benzene ring), -Cl, -CO2R, (N with + charge and two lines), -Br, -C(=O)-, (S with + charge and two lines), -I, -CN, -OR, -NO2, -OH, -SO2-, -N(with two lines), (two lines with double bond), -SR, (two lines with triple bond), -SH
Electron-withdrawing groups 20
-O-
-CH3
-CO2-
Electron-donating groups 3
Electron-withdrawing groups
Electron attracting
Electron-donating groups
Electron repelling
inductive electron
_withdrawal stabilizes the base
ELECTRON WITHDRAWING SUBSTITUENT
ACIDITY INCREASES AS YOU ADD _
STERIC EFFECT
Results from the presence of bulky groups
STERIC EFFECT
Results to congestion and twisting of bonds
Steric
*_ hindrance rather than inductive effect (AT TIMES)
F (STRONGER EWG, MORE EN TOO) INDUCTIVE EFFECT
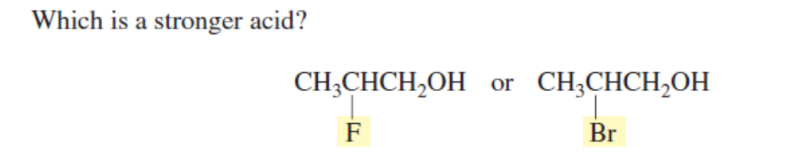
2,2- (SUSBTITUENTS ARE NEARER THE ACETIC HYDROGEN)
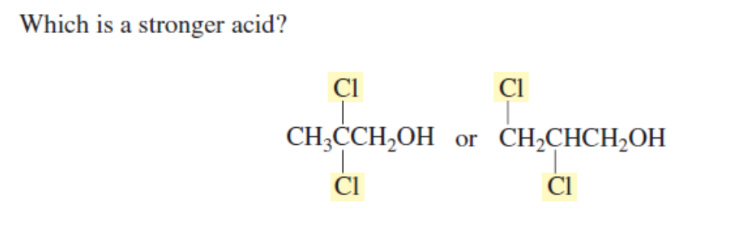
INDUCTIVE EFFECT
DISTANCE BETWEEN EW AND ACIDIC H DECRESEASES EW EFFECT
FIRST (EWG IS STRONGER)
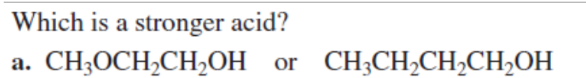
SECOND (EN)
Which is a stronger acid?
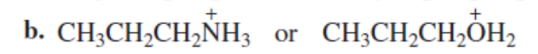
SECOND
Which is a stronger acid?

SECOND
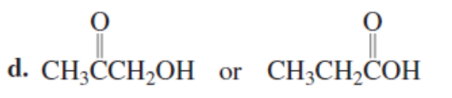
acid
Resonance in the acid stabilizes and weakens the _.
acid
Resonance in the conjugate base stabilizes the conjugate base and strengthens the _.
acidity
Delocalization of charge in the conjugate base anion increases _.
conjugate base anion
Delocalization of charge in the _ increases acidity.
inductive electron
Two factors cause the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid to be more stable than the
conjugate base of an alcohol:
◦ First, _ withdrawal:
pi electron
Two factors cause the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid to be more stable than the
conjugate base of an alcohol:
◦ Second, _ delocalization/resonance:
ACID
IF CB IS UNSTABLE; _ IS VERY WEAK
SECOND (IT HAS 3 RESONANCE FORMS)
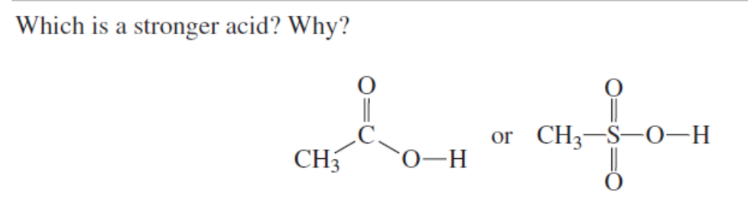
ACIDITY
INDUCTIVE EFFECT INCREASES _
HYBRIDIZATION
ELECTRON WITHDRAWING IS VIRTUE WITH ITS _
CANNOT DELOCALIZE WITH AROMATIC RING
hybridization
Inductive effect due to _ INCREASES ACIDITY
ACIDITY
Inductive effect due to hybridization INCREASES _
ACIDITY
Resonance WEAKENS _
ortho
Steric effect due to substituents in the _ position prevents resonance.
resonance
Steric effect due to substituents in the ortho position prevents _.
stability of acid
Decreased resonance decreases _ and INCREASES ACIDITY.
ACIDITY
Decreased resonance decreases stability of acid and INCREASES _.
resonance
Decreased _ decreases stability of acid and INCREASES ACIDITY.
Ortho position
Meta position
Para position
POSITIONS 3
Ortho position
electron-withdrawing effect + steric effect → stabilizes anion,
destabilizes acid and increases acidity
steric effect
Ortho position:
electron-withdrawing effect + _→ stabilizes anion,
destabilizes acid and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
anion
Ortho position:
electron-withdrawing effect + steric effect → stabilizes _,
destabilizes acid and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
acid
Ortho position:
electron-withdrawing effect + steric effect → stabilizes anion,
destabilizes _ and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
acidity
Ortho position:
electron-withdrawing effect + steric effect → stabilizes anion,
destabilizes acid and increases _
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
Meta position
electron-withdrawing effect → stabilizes anion and increases
acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
electron-withdrawing effect
Meta position
_ → stabilizes anion and increases
acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
anion
Meta position
electron-withdrawing effect → stabilizes _ and increases
acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
acidity
Meta position
electron-withdrawing effect → stabilizes anion and increases
_
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
Para position
electron-withdrawing effect + resonance → stabilizes anion,
destablilizes unionized acid and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
electron-withdrawing effect
Para position
_ + resonance → stabilizes anion,
destablilizes unionized acid and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
resonance
Para position
electron-withdrawing effect + _ → stabilizes anion,
destablilizes unionized acid and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
anion
Para position
electron-withdrawing effect + resonance → stabilizes _,
destablilizes unionized acid and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
unionized acid
Para position
electron-withdrawing effect + resonance → stabilizes anion,
destablilizes _ and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
acidity
Para position
electron-withdrawing effect + resonance → stabilizes anion,
destablilizes unionized acid and increases _
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
acid
Resonance form of _ is unfavorable – electron-withdrawing group close to a positive charge
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
positive
Resonance form of acid is unfavorable – electron-withdrawing group close to a _ charge
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
Resonance form of acid is unfavorable – electron-withdrawing group close to a
positive charge
electron-withdrawing effect
Ortho position
_+ steric effect → stabilizes anion,
destabilizes acid and increases acidity
Electron-withdrawing group on benzoic acid
Ortho position
steric effect > electron-donating effect → destabilizes acid
and increases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
steric effect
Ortho position
_ > electron-donating effect → destabilizes acid
and increases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
electron-donating effect
Ortho position
steric effect > _ → destabilizes acid
and increases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
acid
Ortho position
steric effect > electron-donating effect → destabilizes _
and increases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
acidity
Ortho position
steric effect > electron-donating effect → destabilizes acid
and increases _
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
Meta position
electron-donating effect → destabilizes anion and decreases
acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
electron-donating effect
Meta position
_ → destabilizes anion and decreases
acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
anion
Meta position
electron-donating effect → destabilizes _ and decreases
acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
acidity
Meta position
electron-donating effect → destabilizes anion and decreases
_
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
Para position
electron-donating effect + resonance → destabilizes anion,
stabilizes acid and decreases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
electron-donating effect
Para position
_+ resonance → destabilizes anion,
stabilizes acid and decreases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
resonance
Para position
electron-donating effect + _ → destabilizes anion,
stabilizes acid and decreases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
anion
Para position
electron-donating effect + resonance → destabilizes _,
stabilizes acid and decreases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
acid
Para position
electron-donating effect + resonance → destabilizes anion,
stabilizes _ and decreases acidity
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
acidity
Para position
electron-donating effect + resonance → destabilizes anion,
stabilizes acid and decreases _
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
Resonance form of acid is favorable – electron-donating group close to a positive
charge
favorable
Resonance form of acid is _ – electron-donating group close to a positive
Electron-donating group on benzoic acid
Ortho position
– steric effect > resonance effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
steric
Ortho position – _ effect > resonance effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
resonance
Ortho position – steric effect > _ effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
Meta position
– inductive effect (no resonance forms involving carboxyl group)
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
inductive; carboxyl
Meta position – _ effect (no resonance forms involving ——- group)
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
Para position
– resonance effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
resonance
Para position – _ effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
Ortho position
_ – steric effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
steric
Ortho position – _ effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
Meta position
_ – inductive effect (no resonance forms involving carboxyl group)
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
carboxyl
Meta position – inductive effect (no resonance forms involving _ group)
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
Para position
_ – resonance effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
resonance
Para position – _ effect
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance
benzoic acid
Substituents on _ that can participate in resonance in the
ortho position
resonance
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in _ in the
ortho position
ortho
Substituents on benzoic acid that can participate in resonance in the
_ position
intramolecular H bonding
_+ steric effect > resonance effect
steric
intramolecular H bonding + _ effect > resonance effect
resonance
intramolecular H bonding + steric effect > _ effect
Phenol
PI ELECTRON DELOCALIZATION/
RESONANCE ex
Ortho and Para
_ 2positions – resonance effect → stabilizes phenoxide ion
and increases acidity
Nitro group on phenol
resonance
Ortho and Para positions – _ effect → stabilizes phenoxide ion
and increases acidity
Nitro group on phenol
phenoxide ion
Ortho and Para positions – resonance effect → stabilizes _ and increases acidity
Nitro group on phenol
acidity
Ortho and Para positions – resonance effect → stabilizes phenoxide ion
and increases _
Nitro group on phenol