Biology 11- Arthropods
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Response of Crustaceans
Well-developed nervous system
Brain which consists of a pair of ganglia
Ventral neve cord connects the brain with the rest of the body
Simple sense organs (statocysts) and chemical receptors
Compound eye
feeding
Every mode of feeding and there is a great variation
Locusts: herbivores and will eat anything green
Carnivores like spiders, preying mantic, centipedes, eat other animals
Crabs and crayfish eat already dead animals
Parasitic ones may be external or internal (ticks, flea, lice)
Some area also filter feeders
respiration
Gills
Book gills and book lungs
Tracheal tubes
internal transport system
Well-developed heart pumps blood through an open circulatory system
Blood moves through spaces in the tissues called sinuses
Blood collects in a large cavity surrounding the heart, then re-enters the heart through small opening
movement
Well-developed muscle systems coordinated by the nervous system
Pull of muscles against the exo skeleton allows arthropods to beat their wings, walk, or swim
excretion
Undigested food becomes solid waste and leaves through anus
Nitrogen-containing waste from cellular metabolism are removed in different ways
Terrestrial arthropods use Malpighian tubules which removes waste from body sinuses, concentrate them, and add them to undigested food before it leaves the anus
Some may have excretory glands at the bases of their legs, instead of Malpighian tubules
Aquatic arthropods eliminate it through their heads (green glands)
Reproduction
Male produce sperm, female produce eggs
Fertilization takes place inside
Body plan
jointed appendages, segmented bodies, exoskeleton
ecological roles of other arthropods
Pollination
Production of honey, wax, silk
Recycle biological material to air in producing topsoil
Fomr symbiotic relationship with other organisms
Part of the food chain
3 main features of arthropods
tough exoskeleton, jointed appendages, segmented body
body plan of arthropods
external supporting structures made of chitin
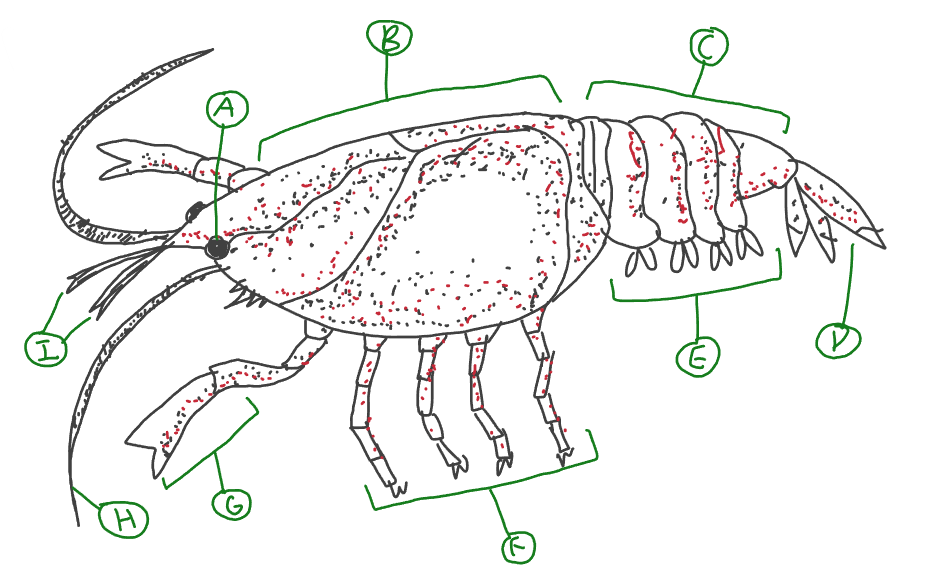
Label
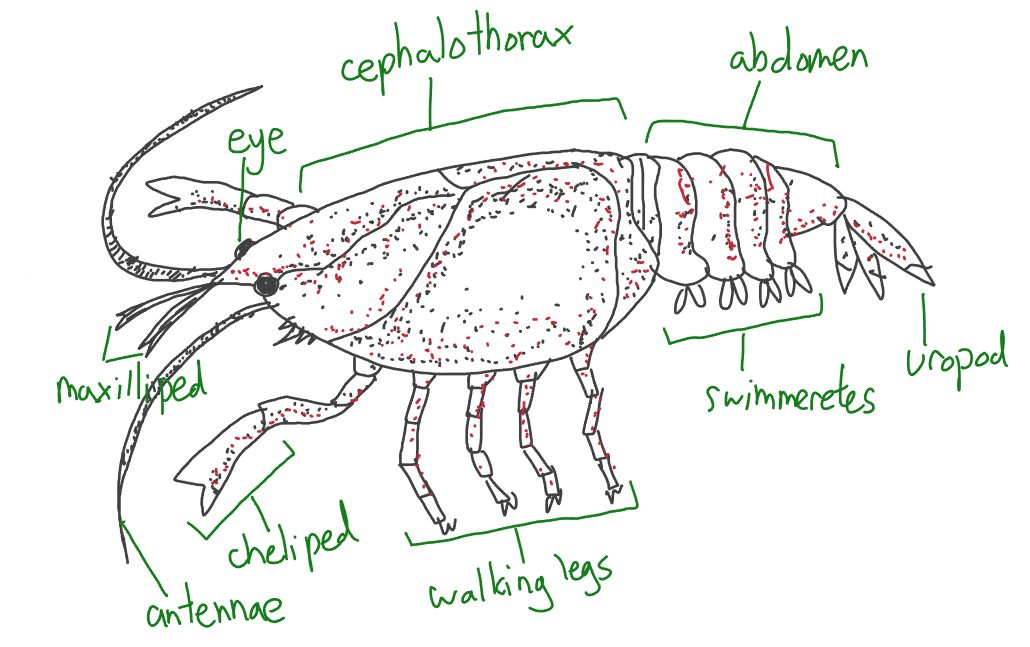
swimmerets
creates water currents, which bring oxygen to their gills and propels them backwards
uropod
used for swimming, steering, tail flipping
maxillipeds
mouth appendages that hold and bring food to the mouth
cheliped
defend itself and snare prey
antennae
tactile or touch receptors to gather information
green gland
excretion of liquid waste
carapace
large bumpy covering over the thorax used for protection
mandible
sturdy jaws around the mouth used for chewing
gastric mill
second set of internal "teeth" used to grind food in stomach
3 subphyla of arthropoda
Uniramia- centipedes, millipeds, all insects
Chelicerate- spiders, ticks, scorpians
crustacea- lobsters, crabs