5(a) Food Production using Microorganisms
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
How does yeast help make bread?
• Yeast uses the sugars to respire aerobically and then anaerobically to produce carbon dioxide which makes the dough rise.
• The gas bubbles expand further in the oven. The yeast is killed and any alcohol made by anaerobic respiration is evaporated off.
Fermentation
Anaerobic respiration by yeast
How do Bacteria help make yoghurt?
When you add Lactobacillus bulgaricus to milk, the bacteria use the lactose in the milk for anaerobic respiration. They produce lactic acid as a waste product which reduces the pH and gives the yoghurt its sour taste.
First step of Yoghurt production
All equipment is sterilised to kill other, unwanted bacteria. This prevents food poisoning and other diseases, contamination and competition with Lactobacillus bulgaricus for the lactose in the milk.
2nd step of yoghurt production
Pasteurisation of milk by heating it to 72 degrees for to kill other unwanted bacteria. This prevents contamination, food poisoning, diseases and competition with lactobacillus bulgaricus for the lactose in the milk.
3rd step of yoghurt production
Lactobacillus is added and incubated at 37-44 degrees(which is the optimum temperature for its growth and fermentation)for several hours.
4th step of yoghurt production
The bacteria ferment the lactose and converts it to lactic acid, lowering the pH which makes the milk solidify and gives it the sour taste.
5th step of yoghurt production
Thickened yoghurt is cooled to about 5 degrees.
6th step of yoghurt production
Flavours and fruits can be added.
Fermenters
Large containers where microorganism are grown in industry.
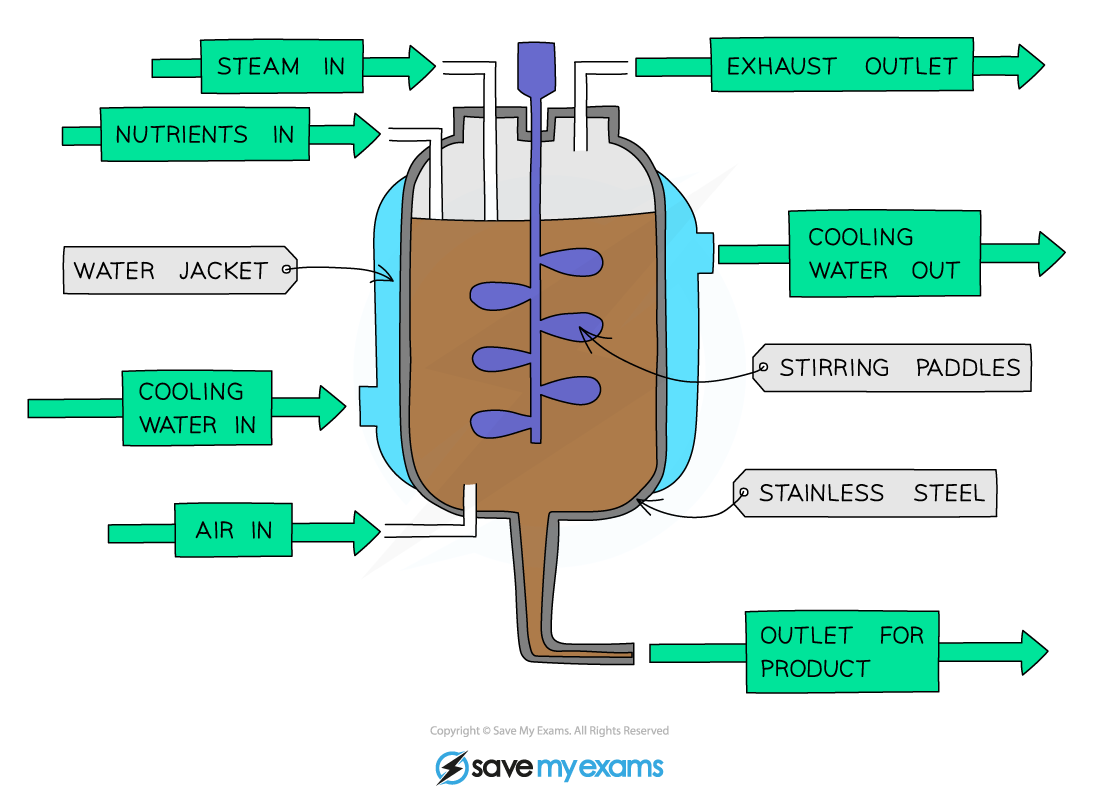
What conditions do the industrial fermenters control?
Aseptic (sterile) conditions
Nutrients and growth
Optimum temperature
Optimum pH
Oxygenation
Agitation
Why and how is aseptic condition controlled?
Fermenter is cleaned using steam to kill other, unwanted bacteria to prevent contamination, food poisoning, diseases and competition.
Why and how are nutrient conditions controlled?
Nutrients are needed for use in respiration to release energy for growth and reproduction of the organisms. Nutrients are added through the food inlet.
Why and how is the optimum temperature controlled?
An optimal temperature is maintained using a cooled water jacket, as reactions release heat. Optimum temperature needs to be ensured for enzymes so they do not denature when the temperature is too high, which would reduce the yield.
Why and how is optimum pH controlled?
The pH control reservoir adds acid or akali when needed to ensure an optimum pH for the enzymes and microorganisms are also sensitive to changes in pH which occur due to metabolic processes.
Why and how is oxygenation controlled?
Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration. Sterile air is pumped in at the bottom through the air inlet.
How is Agitation controlled?
Stirring paddles ensure that nutrients, oxygen, temperature and pH are evenly distributed throughout the fermenter. It also prevents the microorganisms settling off at the bottom so they get more exposure to the nutrients and oxygen.
How does the change in pH affect the protein found in milk?
The mixture coagulates(solidifies)and thickens, this causes the milk proteins to denature and turn into semi-solids.
Example of aerobic fermenters
The production of insulin by genetically engineered bacteria
The production of mycoprotein by fungi for vegetarian meat replacement products