Topic 9 -Analytical (tests for ions)
1/69
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What are simple cations composed of?
just 1 type of atom, they are metal ions
Na+, Mg2+, Al3+
What are the 2 types of test for simple cations?
1) Flame test
2) Adding aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH (aq)
When is the flame test specifically used?
This is used to identify metal ions usually when they are part of a solid salt
What is the method for a Flame test?
Dip a nicrome wire into concentrated hydrochloric acid (to clean the wire)
Dip this into the sample of the solid you wish to test.
Place the wire into a blue or non-luminous flame and observe the colour produced
In the flame test what colour will the splint turn when a compound with K+ (potassium ion) has been put on the nicrome wire?
Lilac
In the flame test what colour will the splint turn when a compound with Na+ (sodium ion) has been put on the nicrome wire?
yellow
In the flame test what colour will the splint turn when a compound with Li+ (lithium ion) has been put on the nicrome wire?
red
In the flame test what colour will the splint turn when a compound with Ca2+ (calcium ion) has been put on the nicrome wire?
red- orange
In the flame test what colour will the splint turn when a compound with Cu2+ (copper ion) has been put on the nicrome wire?
green - blue
When is the reaction with NaOH test specifically used?
When identifying the cations when they are in solution of their salts
What is the method to identify cations when they are in a solution of their salts?
Take a sample of the metal ion, in solution (if it is as solid sample, then you must dissolve it in water first)
Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution
Record the colour of the precipitate
If the precipitate is white then excess sodium hydroxide solution is added to see if the precipitate dissolved in excess
What observation did you make after adding NaOH (aq) to Cu2+?
A blue precipitate formed
What observation did you make after adding NaOH (aq) to Fe2+?
A dirty green precipitate formed
What observation did you make after adding NaOH (aq) to Fe3+?
A red/ brown precipitate formed
What observation did you make after adding NaOH (aq) to Al3+?
A white precipitate formed
so we needed to add excess NaOH,
which makes the precipitate dissolve
What observation did you make after adding NaOH (aq) to Ca2+?
A white precipitate forms
so we needed to add excess NaOH
which made no change
The reactions to test for the presence of cations in solutions are examples of what type of reaction?
Precipitate reactions
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between NaOH and Cu2+?
Cu2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) —> Cu(OH)2 (s)
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between NaOH and Fe2+?
Fe2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) —> Fe(OH)2 (s)
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between NaOH and Fe3+?
Fe3+ (aq) + 3OH- (aq) —> Fe(OH)3 (s)
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between NaOH and Al3+?
Al3+ (aq) + 3OH- (aq) —> Al(OH)3 (s)
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between NaOH and Ca2+?
Cu2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) —> Cu(OH)2 (s)
What type of cation is ammonium?
A complex cation
How is ammonium a complex cation?
It is a group of atoms, covalently bonded together, with a positive charge on the whole molecule
What type of ionic salts does ammonium form? Give examples
)negative ions. E.g Ammonium sulphate (NH4)2SO4, ammonium chloride NH4Cl
What is the method for the test for the presence of ammonium ions?
1) Add sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq)
2) Test the gas given off with damp red litmus
3) The red litmus turns blue (because ammonium is given off)
Why does the red litmus paper turn blue when sodium hydroxide solution is added to an ammonium ion?
Because the sodium hydroxide and ammonium ion have reacted to form ammonia gas - so it is the ammonia that is the alkaline gas that turns the red litmus blue.
What is the ionic equation for the reaction of ammonium ions(NH4+) with hydroxide ions(OH-)?
NH4+(aq) + OH- (aq) → NH3(g) + H20
What is the test for ammonia?
Damp red litmus turns blue
What type of water should only be used in the analysis tests ? and why?
Distilled / Deionised water because it contains no dissolved ions so you would avoid contamination or false positives
What is the test for Cl- ?
Add a few drops of nitric acid* followed by silver nitrate solution
What is the test for Br-?
Add a few drops of nitric acid8 followed by silver nitrate solution
What is the test of I-?
Add a few drops of nitric acid followed by silver nitrate solution
What is the test for SO42-?
Add a few drops of hydrochloric acids* followed by barium chloride solution
What is the test for CO32-?
Add dilute hydrochloric acid, collect the gas given off and pass it through limewater
What is the result for the test for the anion Cl-?
A white precipitate forms
What is the result for the test for the anion Br-?
a cream precipitate forms
What is the result for the test for the anion I-?
a yellow precipitate forms
What is the result for the test for the anion SO42-?
a white precipitate forms
What is the result for the test for the anion CO32-?
Limewater turns cloudy?
Why is the nitric acid added before the silver nitrate, and the hydrochloric acid before the barium chloride?
In order to get rid of any unwanted ions, carbonate and hydroxide ion, that would also give a white precipitate.
What type of reaction is the one between
-Cl-, Br-, I- and silver nitrate
-SO42- and barium chloride solution?
A precipitation reaction
What type of reaction is the one between CO32- and dilute hydrochloric acid?
A neutralisation reaction
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between Cl- and AgNO3?
Cl- (aq) + Ag+(aq) → AgCl(s)
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between Br- and AgNO3?
Br-(aq)+Ag+ (aq) → AgBr(s)
What is the ionic equation for the reaction between I- and AgNO3?
I- (aq) + Ag+ (aq) → AgI(s)
What is the symbol equation for the reaction between a sodium ion and barium chloride? (use sodium sulphate)
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 → 2NaCl (aq) + BaSO4(s)
What is the ionic equation fore the reactions between a sodium ion and barium chloride? (use sodium sulphate)
SO42- (aq) + Ba2-(aq) → BaSO4(aq)
What is the symbol equation for the reaction between a carbonate ion and hydrochloric acid? (use calcium carbonate)
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq)+ CO3(g)+ H20 (l)
What is the ionic equation fore the reactions between a carbonate ion and hydrochloric acid? (use calcium chloride)
CO3(s) + 2H+ (aq) → CO2(g) + H2O (l)
What type of reaction is he occurring in the test for carbonate ions?
Neutralisation reaction
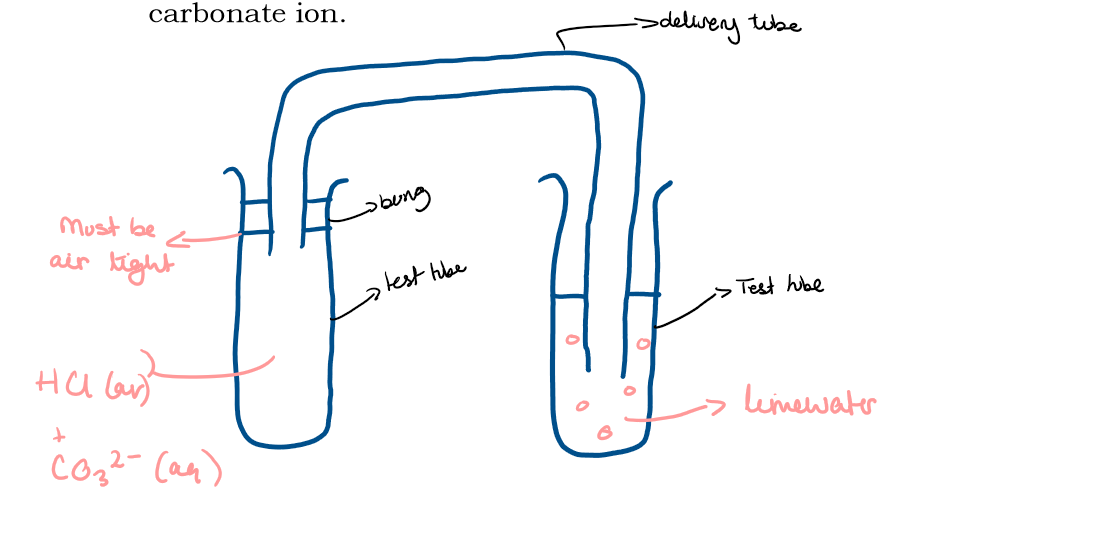
Draw and label the equipment that would be used to collect the gas and pass it through line water in the test for the presence of carbonate ion
What is the method to identify unknown positive ions?
Using a dropping pipette, fill a test tube to a depth of about 2cm with one of the five unknown solution
Using a different dropping pipette, add a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution to the tube. Hold the test tube near the top and shake the bottom gently from side to side to mix its contents
Observe and record the colour of the precipitate produced
If a white precipitate is obtained in step 3, add more sodium hydroxide a until the test tube is about half full. Observe and record whether precipitate disappears to leave a colourless solution.
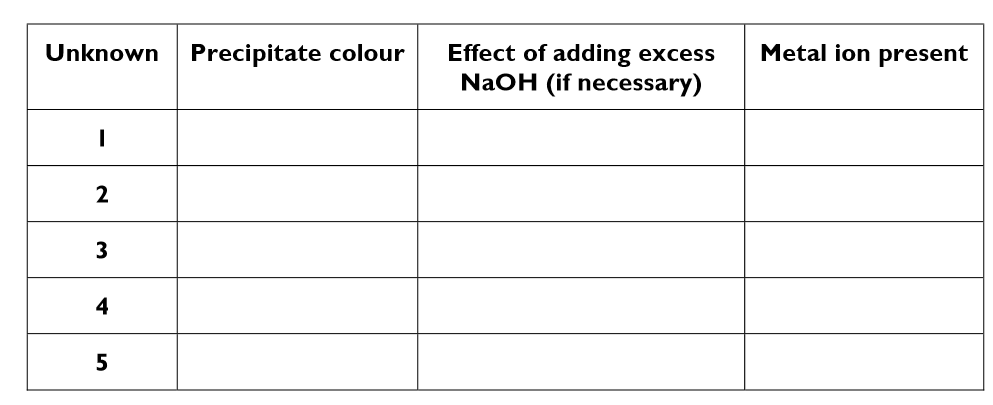
fill in the results table for the investigation to identify positive ions
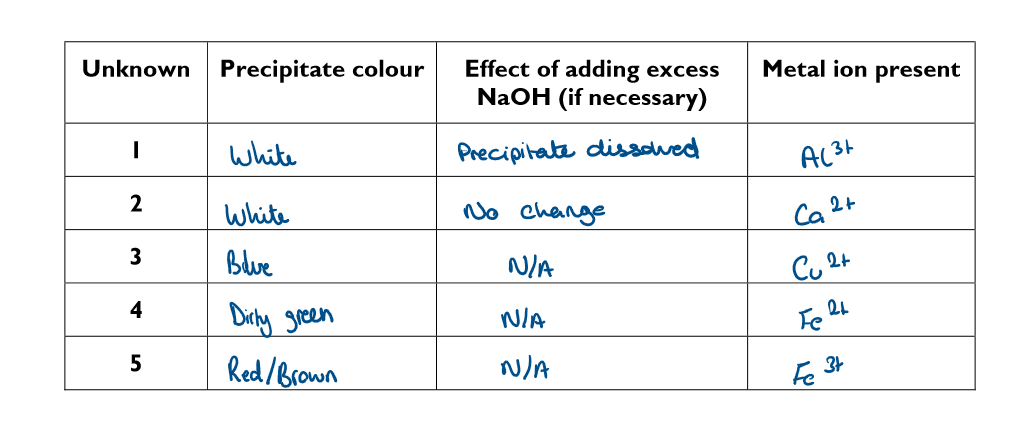
Based of your results from the investigation to identify unknown positive ions… Explain why step 4 of the method is necessary to identify certain metal ions in solutions
So you can identify between Al3+ and Ca2+ as they both have a white precipitate
Based of your results from the investigation to identify unknown positive ions… Explain why all the metal ion solutions were made using distilled water, not tap water
Because tap water contains dissolved ions which could interfere with the results and give a false positive
Based of your results from the investigation to identify unknown positive ions…
Another solution containing a cation goes not produce a precipitate with NaOH, but does produce an alkaline pas. Suggest the formula of the cation present
NH4+
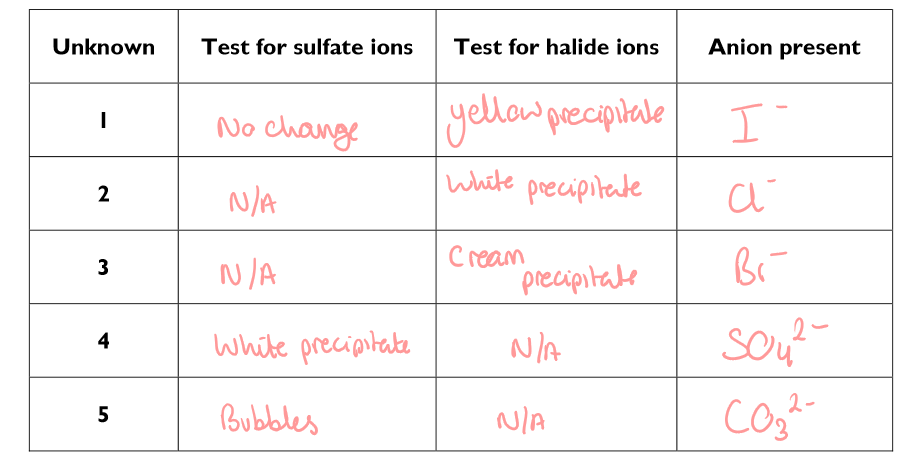
What is the method to identify negative ions?
Fill a test tube to a depth of about 2cm with one of the unknown solutions
Carry out a test for sulphate ions. Also look for bubbles (and so the presence of carbonate ions) when you acidify the solution with dilute nitric acid or dilute hydrochloric acid
Once you have identified solution containing sulphate or carbonate anions, test the remaining solutions to find out if they contain halide ions. No solution should contain a mixture of anions
Based on your results form the investigation to identify negative ions…
Silver carbonate and barium carbonate are insoluble solids. Suggest explanations as to why dilute acids are added to the test solution when using barium chloride or silver nitrate.
To react with the carbonate ion first, so the silver carbonate precipitate and barium carbonate precipitate do not form to give a false result
Based on your results form the investigation to identify negative ions…
Suggest what extra step you would have to take if the ‘unknown’ compound to be testes was provided as a solid rather than a solution?
Dissolve the solution in distilled water
Fill in this results table for the investigation to identify negative ions
What are the limitations to the analysis techniques methods we have used (such as observing colours of flames or of a precipitate)?
time
human perception (subjective)
lack of accuracy
Give an example of an instrumental method?
Calorimetry
Give 3 advantages of instrumental method
Improved accuracy: less contamination, so results are closer to the ‘real’ value.
Improved sensitivity: only small amounts are needed for analysis, so resources are saved
Faster
How does a Flame Photometer work?
The coloured light form a vapourised sample can be split to produce an emission spectrum. This is a series of lines, that look a bit like a barcode.
The position of the lines can be used to compare and identify an unknown.


Na+ and Li+
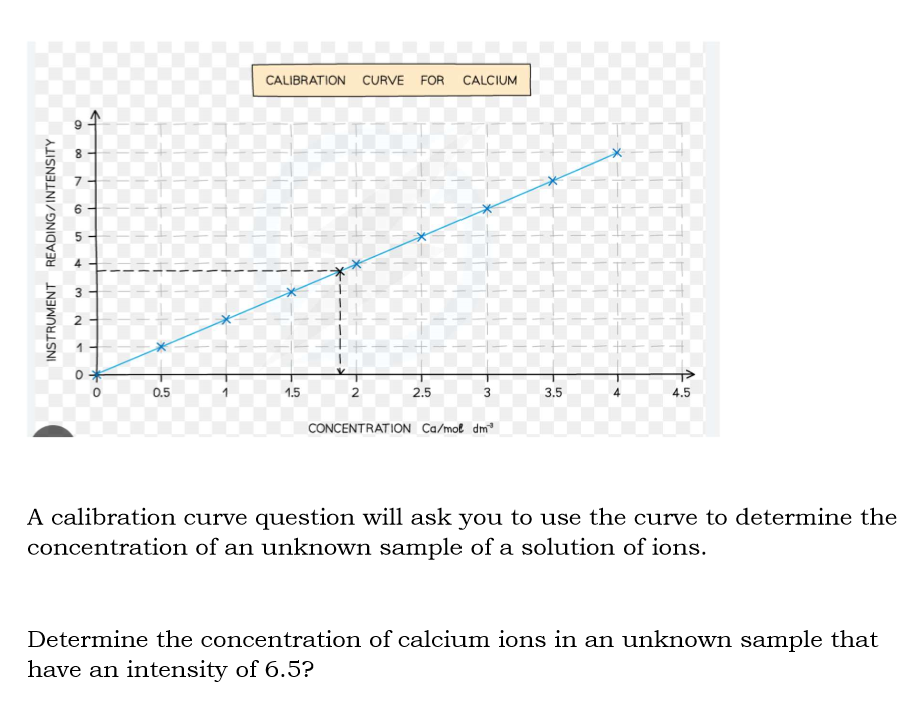
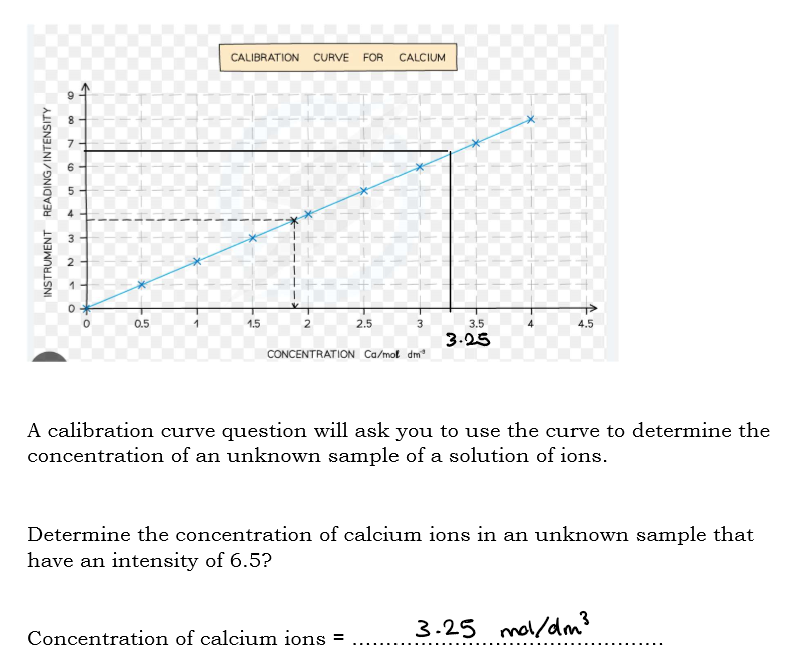
What are calibration curves for a flame photometer used to do?
a calibration curve for flame photometers is used to determine the concentration of specific ion in a solution by measuring the intensity of the light emitted during flame.
The light intensity readings for each known standard are plotted
What is the y-axis in a calibration curve?
Intensity of light emission measured by the flame photometer
What is the x-axis in a calibration curve?
concentration of ions in the standard solution