Honors Bio Ecology Unit Terms
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Biosphere
living organisms together with their environment. biospheric
Biome
n area classified according to the species that live in that location.
Ecosystem
a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Community
organization and functioning of communities, which are assemblages of interacting populations of the species living within a particular area or habitat.
Population species
a group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area.
Habitat
the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
Niche
The job an organism does in it’s habitat
Biotic
relating to living organisms
Abiotic
relating to nonliving organism
How does energy flow through the ecosystems
Food chains
Example of competition
two male birds of the same species might compete for mates in the same area. is an example of what?
Symbiosis
interaction between two different organisms living in close physical association, typically to the advantage of both.
Predation
the preying of one animal on others.
Carrying capacity
The maximum number of individuals the enviorment can support with the provided resources
Limiting factors to a population
food, water, living space, and disease.
Dependant limiting factors
disease, competition, and predation, resources
Independent limiting factors
food or nutrient limitation, pollutants in the environment, and climate extremes, including seasonal cycles such as monsoons
Threats to biodiversity
Climate change, pollution, habitat loss, overexploitation of species and invasive species
biological magnification
the rise or increase in the contaminated substances caused by the intoxicating environment.
Why is biodiversity important
Biodiversity is essential for the processes that support all life on Earth, including humans.
Why is biodiversity useful for humans?
Humans depend upon biodiversity for survival, such as for the foods we eat, medicines we use to stay healthy, and materials we wear or use to build our homes.
Describe some current issues relating to environmental concerns
air pollution (20-public median of 76% say this is a big problem), the loss of forests (74% median) and extinction of plant and animal species (67% median).
Why is human interferance a big problem with major ecosystems
Human activities have led to various environmental issues that affect ecosystems, climate, and biodiversity. Pollution from industrial emissions, transportation, and agriculture has contaminated air and water, adding health risks to humans and wildlife.A
five examples of declining biodiversity
changes in land and sea use; direct exploitation of organisms; climate change; pollution; and invasive species.
Population
A group of organisms/species sharing the same space/enviorment at a specific time
Lag Phase
Dependent on the reproductive
Exponential growth
number of births exceeds the number of deaths. Unlimited resources. Birth rate>death rate
Logistical Growth
The entire graphed line (Lag phase+ exponential growth+carrying capacity) Birth rate=death rate. Limited resources, Carrying capacity
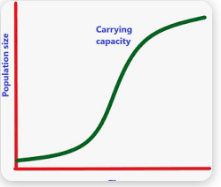
Logistical Gowth Graph
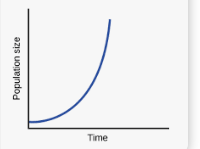
Exponential Growth graph
Competition relationship
One species increases while the other decreases
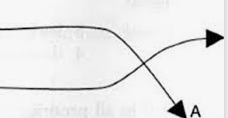
Competition Graph
Commensalism relationship
One species benefits while the other is unaffected
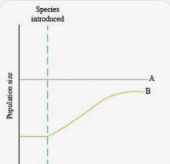
Commensalism Graph
Predator/Prey relationship
As one species benefits or decreases the other one benefits or decreases. Same pattern @ different times.
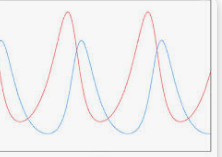
Predator prey graph
Mutualism relationship
Both species benefits same pattern at about the same time.
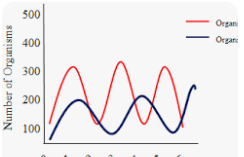
Mutualism Graph
Parasitic Relationship/ Parasitism
One species benefits while the other species is negatively affected
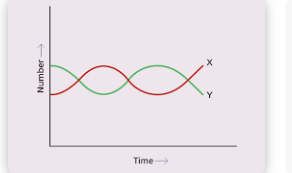
Parasitism Graph
Parasitism explanation
Parasite increases→host decreases→parasite decreases→host increases