oil and gas, part 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
define fossil fuels:
fuel made up of ancient plants and animals (i.e. dead organic matter that is used for energy resources)
what are some examples of a fossil fuel:
coal
oil
natural gas
true or false: energy is the capacity to perform work or transfer heat:
true
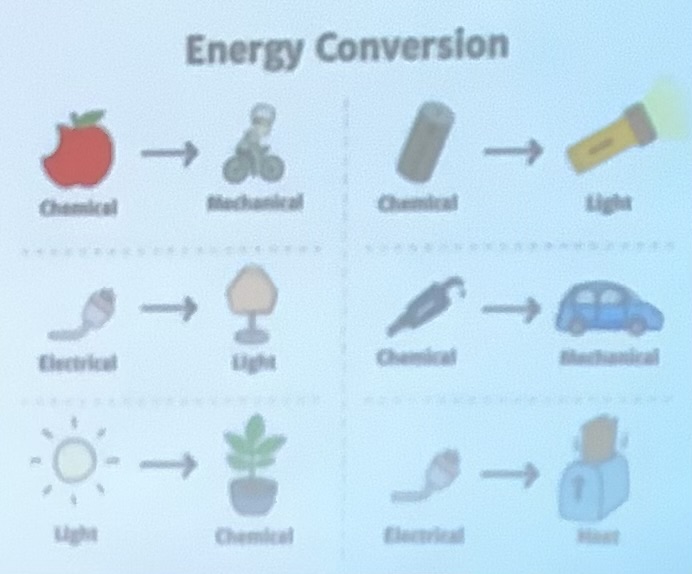
what are some examples of energy conversion?
electrical, mechanical, digestion
flashlight
fan
photosynthesis
which of these past environments would likely create coal: deserts, swamps, deep sea, or all of the above?
swamps
what is the term used to describe crude oil and natural gas?
petroleum
true or false: if oil is buried below 15,000ft, it has the chance to turn into natural gas?
true (gas window)
what are the major types of fossil fuels, typically called conventional fuel?
coal, oil, and natural gas
energy sources are critical for___
almost all facets of life, ranging from food production to construction
what % of the energy consumed by humans comes from fossil fuels?
83%
true or false: the world has a vast supply of cheap oil
false. the world is running out of cheap oil
define energy:
energy is the capacity to perform work or transfer heat
define work:
work involves moving an object (mass) some distance against a given force (work = mass x distance)
define electrical energy:
movement of electrons through a conductor
define chemical energy:
energy stored in chemical bonds
define thermal (heat) energy:
the vibration of atoms
define kinetic (mechanical) energy:
object in motion
define potential energy:
stored energy
define nuclear energy:
energy that holds the nucleus together
define radiant (light) energy:
electromagnetic energy that travels in waves
define energy conversion:
one form of energy can convert to another
what are some examples of energy conversion?
plugging in a a fan
burning wood
photosynthesis
why do we care about energy efficiency:
if fossil fuels run out, we need to make the most out of what we have
we want our gallons of gas to go as far as possible because of how expensive gas costs
true or false: for every $1 you spend on gasoline, 75 cents is lost to heat
true :(
what was one of the first and primary forms of energy used by humans?
the sun
what was the second form of energy used by humans?
fire
humans then transitioned to ___
domesticating animals for work
__ energy was harnessed to perform mechanical processes
wind
__ was used to power engines
steam
what then became the primary energy source?
fossil fuels
oil consumption greatly increases around___
1900 because cars and the combustion engine had just been invented and were better than steam engines
in the 1940’s, oil overtakes coal and becomes the dominant source for energy. why is this?
mostly due to oil bing a liquid, it is safer and easier to transport. also due to its energy density, so you get more out of it for every unit that you burn
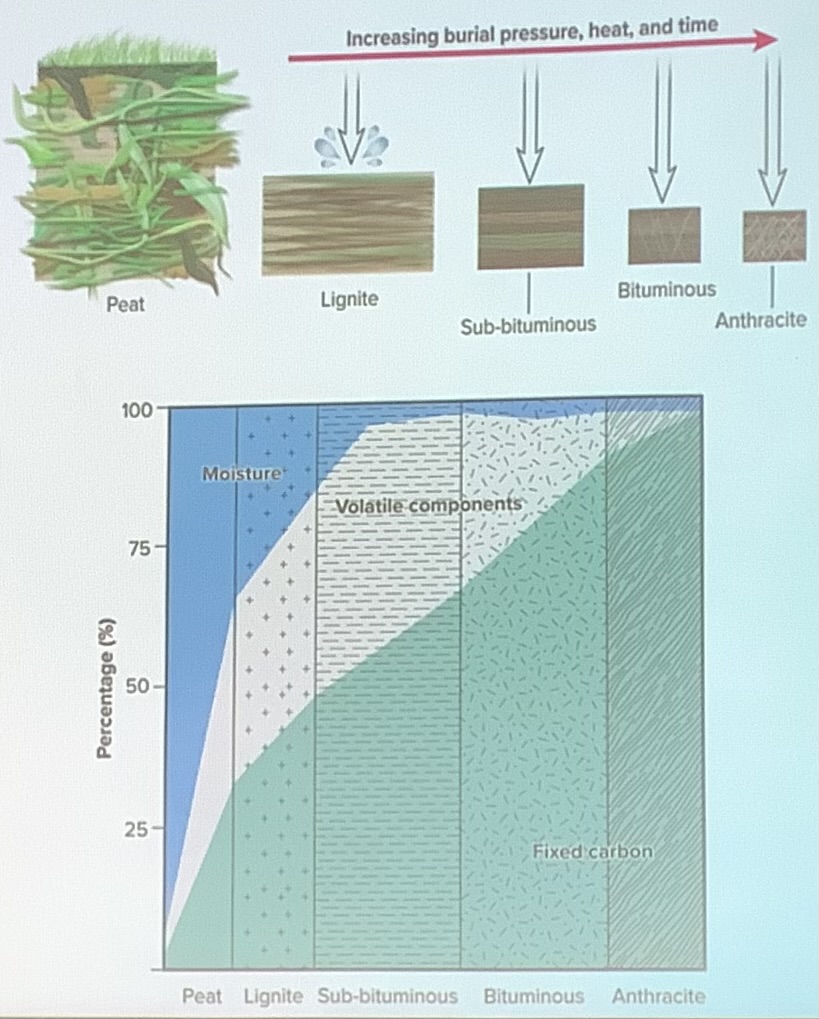
define coal:
a biochemical sedimentary rock composed of partially altered, compressed remains of plants
coal seams can range from inches in thickness to over ___ in thickness
100 feet
how does coal form?
a swamp environment with ample plant matter must be present
this swamp must be inundated for an extended period of time
due to water, free oxygen decreases and microbial activity slows down
more and more plant material accumulates
plant material becomes buried and subject to heat and pressure as the burial depth increases over time
as pressure and temperature increase, different versions of coal start to develop. as a result the carbon content increases