Photosynthesis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
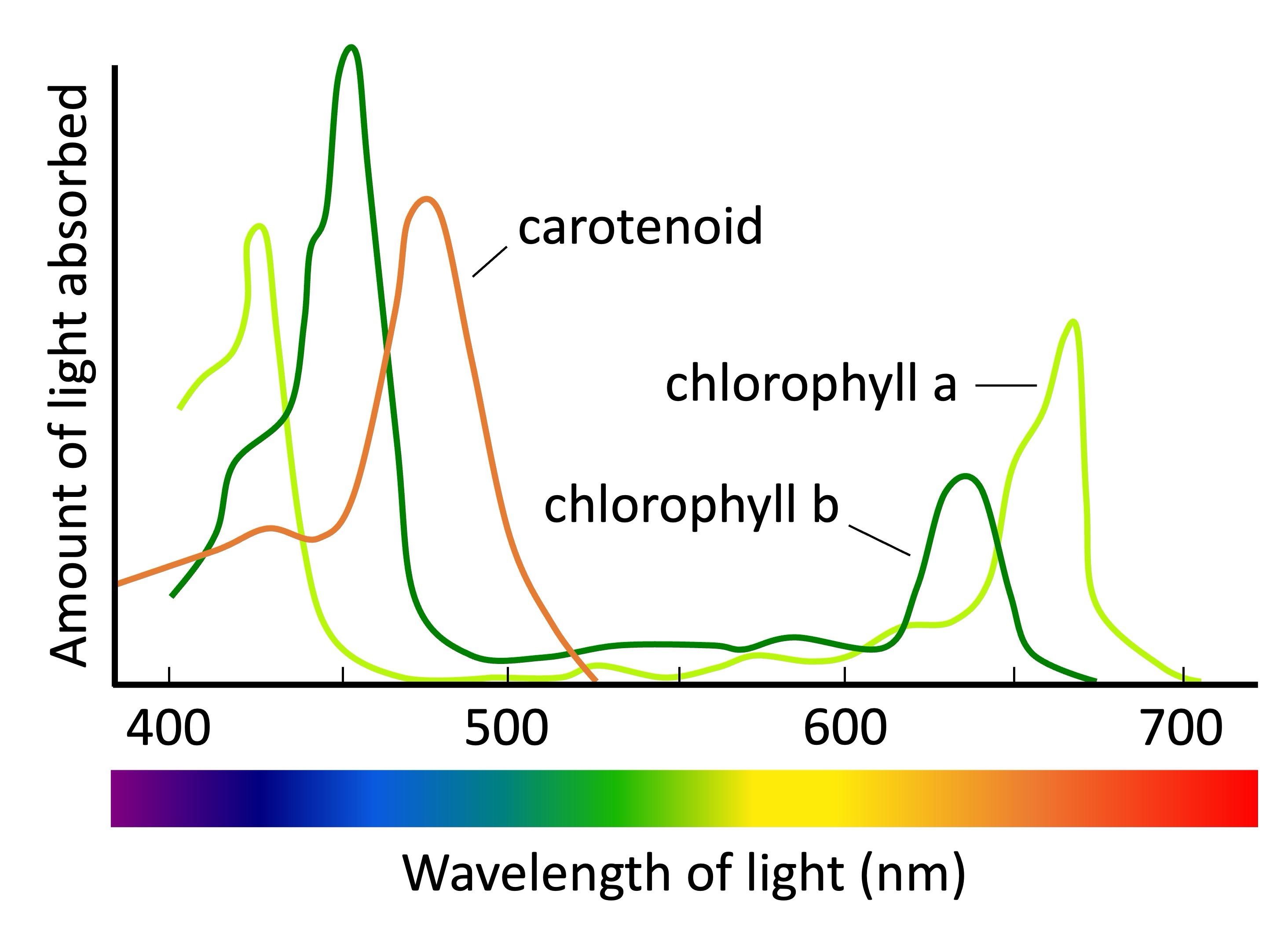
Absorption spectra
a plot of the amount of light energy of various wavelengths that a substance absorbs
used to determine a pigment’s wavelength
photosynthesis is dependent on the absorption of light by pigments
Action spectra
a plot of effectiveness of light energy of different wavelengths driving a chemical reaction
determined by the suspension of chloroplasts and measure the amount of o2 released by photosynthesis at different wavelengths
Engelmann’s experiment
used light microscope and glass prism to determine most effective wavelength in photosynthesis
placed algae and bacteria was only gathering around areas that most o2 was produced (site of photosynthesis)
large clusters of bacteria under red and purple wavelength
smallest cluster under green wavelength
Chlorophyll A
primary pigment
becomes oxidized during photosynthesis and donates an electron to an electron acceptor
located in the reaction centre
only absorbs blue and red light
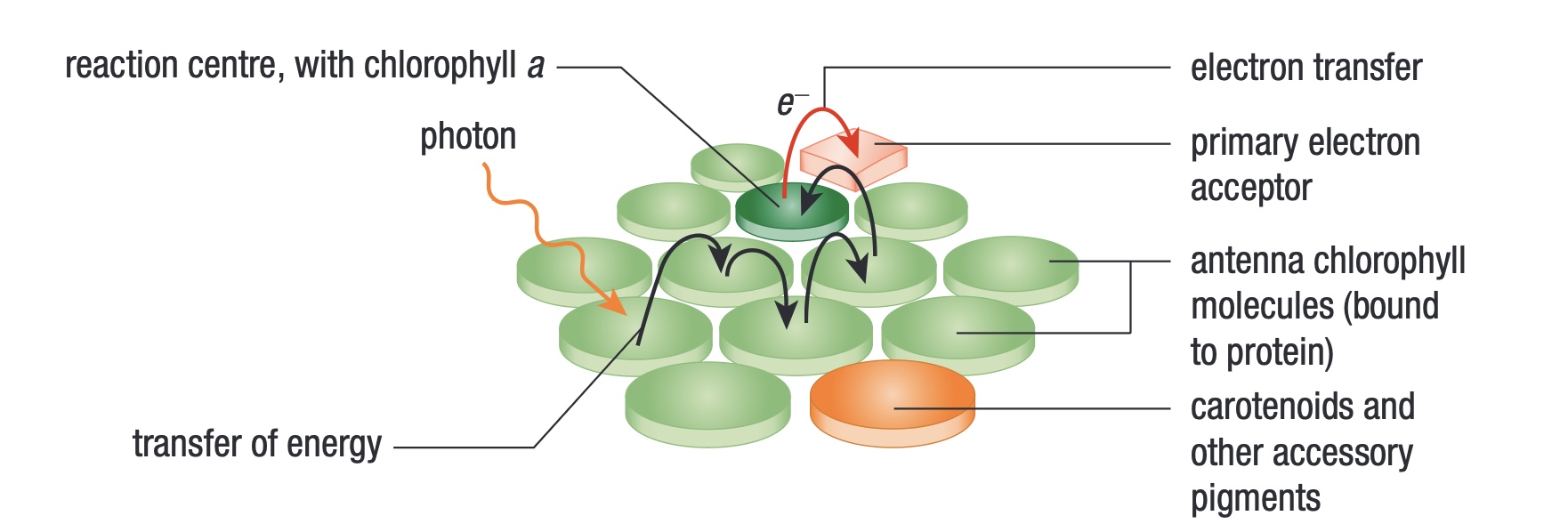
Chlorophyll b + carotenoids
accessory pigments
only absorb blue and green light
after light absorption: transfers excitation energy to chlorophyll A
Oxygen 18 experiment
O18 is a heavier isotope of O
wanted to find out if o2 produced came from Co2 or H2O
grew plants in an environment where water had O18 but Co2 did not
O2 given off had O18: O2 came from water
Light dependent reactions
first stage of photosynthesis
occurs in thylakoid membrane
photosystem I
contains specialized chlorophyll A molecules that absorb light at a wavelength of 70nm
excites electrons to a higher level which get passed to ferredoxin then to NADP→ NADPH
gets replacement electrons from photosystem II
photosystem II: photolysis
splits h2o into electrons, protons and O2
sun→ PSII absorbs light → splits H2O → boosts electrons → makes proton gradient→ helps make ATP → sends electrons to PSI
once electrons are boosted, they are passed along proteins like PQ in the thylakoid membrane
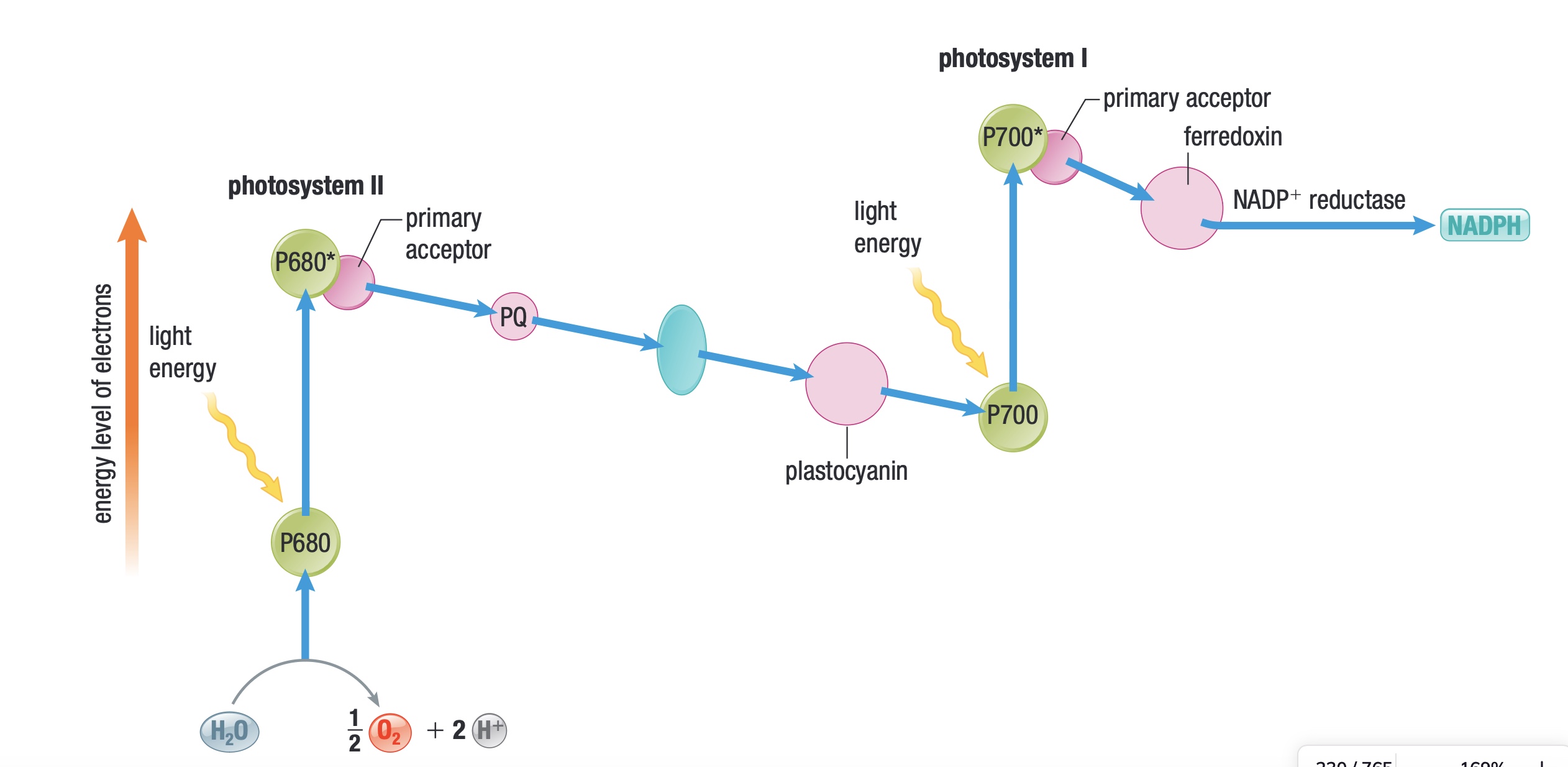
Z-Scheme diagram
Light hits PSII and boosts electrons
as electrons travel, they loose energy, lost energy is used to pump protons into thylakoid membrane, creating proton gradient
electrons arrive to PSI which boosts electrons
electrons are passed to ferrodoxin, then NADP+→ NADPH ( energy carrier)
Cyclic electron transport
PSI can function independently of PSII
electron transport of PSI to ferrodoxin is not followed by NADP+
instead, ferrodoxin donates electrons back to PQ
PQ is continually oxidized and moving protons across thylakoid membrane w/o PSII
results in ATP formation w/o oxidation of H2O of reduction of NADP+→ NADPH
occurs in thylakoid membrane
Light independent reactions
occurs in stroma of chloroplast
11 reactions to reduce co2 into sugar using NADPH
endergonic process
Phases of Calvin cycle
Carbon fixation
Reduction
Glucose synthesis
RuBP generation
Carbon fixation
conversion of carbon from inorganic → organic
inorganic Co2 reacts w/ RuBP→ 2 PGA
Reduction
3PGA is phosphorlyzed from hydrolysis of ATP and reduced by electrons of NADPH
reduces G3P
Glucose synthesis
6 G3P molecules produced, one is excessed
excess G3P combines with a second process (reverse of glycolysis)
RuBP generation
5 G3P molecules regenerate RuBP to restart cycle
fix another 3 molecules of Co2 to produce another G3P molecule
importance of Rubisco
is the enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction of Calvin cycle
catalyzes Co2 function in all autotrophs
provides source of organic carbon molecules
Rubisco “stupidity”
can accidentally bind to O2 instead of CO2
has low affinity for Co2
photorespiration
catalysts of O2 instead of Co2 by rubisco in RuBP which slows the Calvin cycle, consumes ATP and results in a release of carbon
C4 plants
found in hot and dry climates
minimizes photorespiration
C4 cycle
carbon fixation that plants use to increase [Co2] available for Calvin cycle reactins
co2 combines with 3-c molecules (PEP) to produce oxaloacetate
oxaloacetate reduced by malate by electrons produced by NADPH
malate enters bundle sheath cells that enters chloroplast and is oxidized to pyruvate which releases Co2
C3 vs C4
C4 has an additional energy requirement
additional ATP is easily met by cyclic light reactions
C4 has lower nitrogen demand due to less RuBP needed
CAM plants
same location, different time
metabolic pathway used mostly by succulent plants
process of CAM plants
Co2 accumulates at night and stored as malic acid
second phase happens in daylight, temp increases and stomate loses water and cuts of gaseous exchange with atmosphere
magic acid diffuses into cytosol where it is oxidized into pyruvate
pyruvate accumulates during the day and is converted back into malate at night
stomata
controlled gas exchange
small pores on leaf’s surface that can be opened and closed by guard cells
open during the day allowing Co2 to enter to be used for photosynthesis