chem topic 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is electrolysis?
decomposition by electricity (a chemical method)
test for chloride ions
dissolve solid sample in water
add excess dilute nitric acid
followed by silver nitrate solution
white ppt (AgCl) formed
1. add acidified silver nitrate solution
2. white ppt (AgCl) formed
test for water
turns dry blue cobalt (II) chloride paper pink
flame test steps
cleaned platinum wire is put into conc. HCl (aq)
dipped into solid sample
heated in non-luminous (blue) flame
flame colour is recorded
explain the principle of the distillation process
when sea water is heated, water vapor escapes and passes through the condenser
vapour is cooled by cold water flowing around the condenser
water vapour condenses to form liquid water
saturated solution
a solution containing the maximum amount of solute at a certain temperature
crystallisation
a method used to separate a dissolved solid (solute) from a solution
saturated solution is obtained by heating the solution to evaporate some of the solvent
large crystals form upon slow cooling of saturated solution (the solubility of the solid in the solvent decreases with decreasing temperature)
what is fractional distillation?
a method used to separate a mixture of miscible liquids which have different boiling points
steps of fractional distillation of liquid air
air is filtered and purified (removes CO2, dust, water vapour, etc.)
purified air is cooled and compressed (repeatedly) to -200 °C
liquid air at -200 °C is introduced at the lower part of the fractionating tower /column
liquid air is slowly warmed and gases are collected one by one
uses of oxygen gas
respiration
supports combustion of fuels
uses of carbon dioxide gas
raw material for photosynthesis
dry ice (solid CO2) is used to provide a low temperature for different purposes (storing ice cream)
make fire extinguishers as it does NOT support combustion and is DENSER than air
used in soft drinks
use of helium gas
to fill balloons and airships as it is chemically inert and lighter than air
hydrogen gas is not used as it is explosive / flammable
use of neon gas
make neon light signs as it emits red light at a high temperature
use of argon gas
to fill up space in a light bulb to prevent oxidation of the metal (tungsten)
uses of nitrogen gas
to make ammonia (NH3) which is then used to make fertilisers
provides a chemically inert environment (food is packaged in gaseous nitrogen to increase shelf life)
liquid nitrogen provides a low temperature to store biological samples (cells) and freeze food
physical properties
appearance
colour
odour
solubility
density
melting point
boiling point
viscosity
electrical conductivity
thermal conductivity
uses of NaOH (aq) from electrolysis of brine
soap
bleaching solution
waste water treatment
uses of Cl2 (g) from electrolysis of brine
bleaching solution
sterilisation of drinking water
HCl (g)
HCl (aq)
uses of H2 (g) from electrolysis of brine
fuel
NH3 (g)
HCl (g)
HCl (aq)
chalk — formation, hardness, uses
sea animals with dried shells, shells fall to sea bed and built up a deposit, under high temperature and pressure deposit is converted to chalk after millions of years
hardness: soft
uses: white pigment in paper, plastics, paints
limestone — formation, hardness, uses
under high temperature and pressure, CHALK is converted to LIMESTONE
hard
cement, concrete
marble — formation, hardness, uses
under much higher temperature and pressure, chalk OR limestone is converted to marble
hardest
monuments, floors, materials for construction
action of water on calcium carbonate // CaCO3 (s)
no reaction / insoluble
action of acids on calcium carbonate // CaCO3 (s)
HCl (aq)
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) —> CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
HNO3 (aq)
CaCO3 (s) + 2HNO3 (aq) —> Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
action of heat on calcium carbonate // CaCO3 (s)
decomposes upon heating to give white calcium oxide // CaO (s) and carbon dioxide
tests for calcium and carbonate in calcium carbonate
calcium ion
flame test which gives a brick red flame
carbonate ion
addition of dilute HCl, after which effervescence occurs and turns limewater milky due to formation of insoluble calcium carbonate
if excess CO2 is bubbled into the milky suspension, mixture turns clear again
also, can heat the solid in a test tube and put a burning splint into the tube. flame extinguishes as CO2 which is decomposed on heating does NOT support combustion
the lime cycle
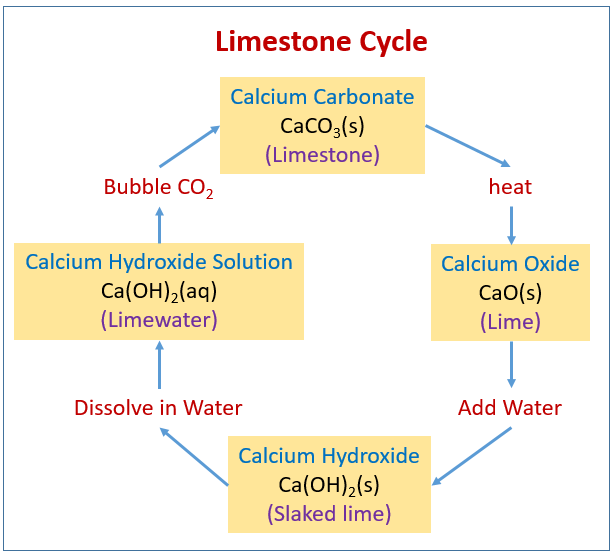
weathering
the process by which rocks are broken down into smaller particles by physical and chemical processes
(natural processes such as wind, water, and temperature changes)
erosion
when rocks are broken down and the particles are carried away by water, wind and gravity
examples of physical processes causing weathering
change in temp
causes repeated cooling and expansion of rocks
cracks are formed on rocks
water gets into those cracks
and freezes into ice at low temperature, causing further expansion and cracking of the rocks
examples of chemical processes causing weathering
normal rain water is acidic (pH 5.6)
carbonic acid formed when CO2 dissolves in rain water
carbonic acid reacts with calcium carbonate to form water soluble calcium hydrogencarbonate which is broken down
acid rain
also causes breaking down of calcium carbonate
calcium carbonate decomposes slowly at elevated temperature
forming calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
carbonate + acid
CO2 ; effervescence
calcium carbonate + dilute HCl reaction
CaCO3 + HCl —> calcium chloride + H2O + CO2
how to separate insoluble from soluble in a mixture?
shake a mixture of X and Y with water
filter the mixture using a funnel with filter paper and the residue is X
evaporate the filtrate and the solid formed is Y