RADR 2401 Exam 3 - Ch. 11: Cranium
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
How many cranial bones are there?
8
What are the (8) cranial bones?
frontal, R/L parietal, R/L temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid
What (2) areas are the cranial bones separated into?
Calvarium (skullcap) and Floor
What (4) cranial bones make up the calvarium?
Frontal, Right & Left Parietal, Occipital
What (4) cranial bones make up the cranial floor?
Right & Left Temporal, Sphenoid, Ethmoid
What are the (2) main portions of the frontal bone?
Squamous (vertical) and Orbital (horizontal)
What is the raised prominence of the frontal bone between the eyebrow just above the bridge of the nose?
Glabella
What is the name of the slight depression above each eyebrow?
The Supraorbital groove (SOG)
What is the name of the superior rim of each orbit?
Supraorbital Margin
What is the name of the small opening within the SOM?
Supraorbital Notch
What are the names of the large, rounded prominences above the SOG?
Fronteal tuberosities (eminences)
What (4) bones do the frontal bone articulate with?
Right/Left parietals, sphenoid, and ethmoid
The lateral walls of the cranium and part of the roof are formed by what (2) bones?
Right/ Left Parietal
The widest portion of the entire skull is located between what structures?
Parietal Tubercles (eminences)
What (5) bones do the parietal bones articulate with?
frontal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid, and opposite parietal
What bone forms the inferoposterior portion of the skullcap?
Occipital bone
What is the name of the portion of the occipital bone that forms most of the back of the head?
Squamous portion
What is the name of the prominent bump at the back of the head?
Occipital protuberance or inion
What is the name of the opening at the base of the skull?
Foramen magnum
What are the names of the (2) lateral oval processes on the foramen magnum?
Occipital condyles or condylar portions
What do the occipital condyles articulate with? What joint is made there?
Atlas (C1); atlantoccipital joint
What (6) bones do the occipital bone articulate with?
R/L parietal, R/L temporal, sphenoid, and atlas (C1)
What is the name of the anterior arch of the temporal bone?
Zygomatic arch
What are the (3) sections of each temporal bone?
Squamous (upper), Mastoid (middle; posterior to EAM), and Petrous (most inferior/posterior)
What are the (3) alternative names to the petrous portion of the temporal bone?
Petrous pyramid, pars petrosa, petromastoid portion
The petrous ridge corresponds to the level of what external landmark?
TEA
Each temporal bone articulates with what (3) cranial bones?
Parietal, occipital, and sphenoid
What cranial bone forms an anchor for the rest?
Sphenoid
What is the name of the central depression of the sphenoid?
Sella turcica
What is the name of the posterior portion of the sella turcica?
Dorsum Sellae
What is the name of the shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae?
Clivus
The sella turcica and dorsum sellae are best demonstrated on what projection?
Lateral
What bones do the Sphenoid articulate with?
All 7 cranial bones
What is the name of the small upper portion of the ethmoid bone?
Cribiform plate
What is the name of the superior projection of the cribiform plate ethmoid bone?
Crista Galli
What is the name of the major portion of the ethmoid plate?
Perpendicular plate
What (2) bones do the ethmoid articulate with?
Frontal and sphenoid
What suture separates the frontal bone from the 2 parietal bones?
Coronal suture
What suture separates the 2 parietal bones?
Sagittal suture
What suture separates the 2 parietals from the occipital?
Lambdoidal suture
What suture is formed by the inferior junctions of the 2 parietal bones with their respective temporal bones?
Squamosal suture
What is the name of the junction at the anterior end of the sagittal suture?
Bregma
What is the name of the junction at the posterior end of the sagittal suture?
Lambda
What is the name of the junction at the posterior end of the sphenoparietal suture?
Pterion (right or left)
What is the name of the junction where the squamosal and Iambdoidal sutures meet?
Asterion (right and left)
At what age do fontanels close completely?
18 months
The bregma in an adult is what fontanel in an infant?
Anterior fontanel
The Lambda in an adult is what fontanel in an infant?
Posterior fontaneI
The Right Pterion in an adult is what fontanel in an infant?
Right sphenoid fontanel
The Left Pterion in an adult is what fontanel in an infant?
Left sphenoid fontanel
The Right asterion in an adult is what Fontanel in an infant?
Right Mastoid fontanel
The Left asterion in an adult is what fontanel in an infant?
Left Mastoid fontanel
Cranial sutures do not ossify completely until what age?
Mid to late 20s
What is the name for the small, irregular bones that can develop in adult sutures?
Sutural or wormian bones
What is a skull fracture?
Disruption in the continuity of the skull
What is a linear fracture?
Skull fracture that appears as a lucent line that lies at a right angle to the axis of the bone
What is a depressed fracture?
When a bone fragment is separated and depressed into the cranial cavity
What is a basal skull fracture?
Fracture through the temporal bone
What modality is used to differentiate epidural and subdural hemorrhaging?
CT
What is multiple myeloma?
Condition where one or more bone tumors originate in the marrow
What is multiple myeloma contraindicated for?
lodinated contrast
What is paget disease (osteitis deformans)?
Disease that begins as a stage of bony destruction followed by repair; gives a "cotton wool" appearance
What is an acoustic neuroma?
Tumor on the acoustic nerve
What is the term for an average head shape? What is the width?
Mesocephalic; The width is 75-80% of the length
What is the term for a broad, short head? What is the width?
Brachycephalic; 80% or higher than the length
What is the term for a long, narrow head? What is the width?
Doliocephalic; Less than 75% of the length
The petrous pyramids in a mesocephalic head form how much of an angle to the MSP?
47 degrees
The petrous pyramids in a brachycephalic head form how much of an angle to the MSP?
Greater than 47 degrees (54 approx.)
The petrous pyramids in a doliocephalic head form how much of an angle to the MSP?
Less than 47 degrees (40 approx.)
What is the ridge of bone that extends across the forehead directly above each eye?
The superciliary ridge (arch)
What is the groove above the superciliary arch?
The Supraorbital groove (SOG)
What is the landmark at the junction of the 2 nasal bones and the frontal bone?
Nasion
What is the midline point of the upper lip and septum?
Acanthion
What is the lower posterior angle on the jaw?
Gonion
What is the technical name of the chin?
Mentum
What is the junction where the eyelids meet near the nose?
Inner canthus
What is the lateral junction of the eyelids?
Outer canthus
What is the superior rim of the bony orbit of the eye?
Supraorbital Margin (SOM)
What is the inferior rim of the bony orbit of the eye?
Infraorbital Margin (IOM)
What is the opening of the external ear canal?
external auditory (acoustic) meatus (EAM)
What is the center of the EAM?
Auricular point
What is the line between the glabeIla and EAM?
Glabellomeatal line (GML)
What is the line between the outer canthus and EAM?
orbitomeatal line (OML)
What is formed by connecting the IOM to the EAM? What is the degree of angulation between this and the OML?
Infraorbitomeatal line (IOML); 7 degrees
What is the line between the acanthion and the EAM?
Acanthiomeatal line (AML)
What is the line between the mentum and the EAM?
Mentomeatal line (MML)
What is the line from the junction of the lips to the EAM?
Lips-Meatal Line (LML)
What connects the glabella to a point on the anterior aspect of the alveolar process of the maxilla?
Glabelloalveolar line (GAL)
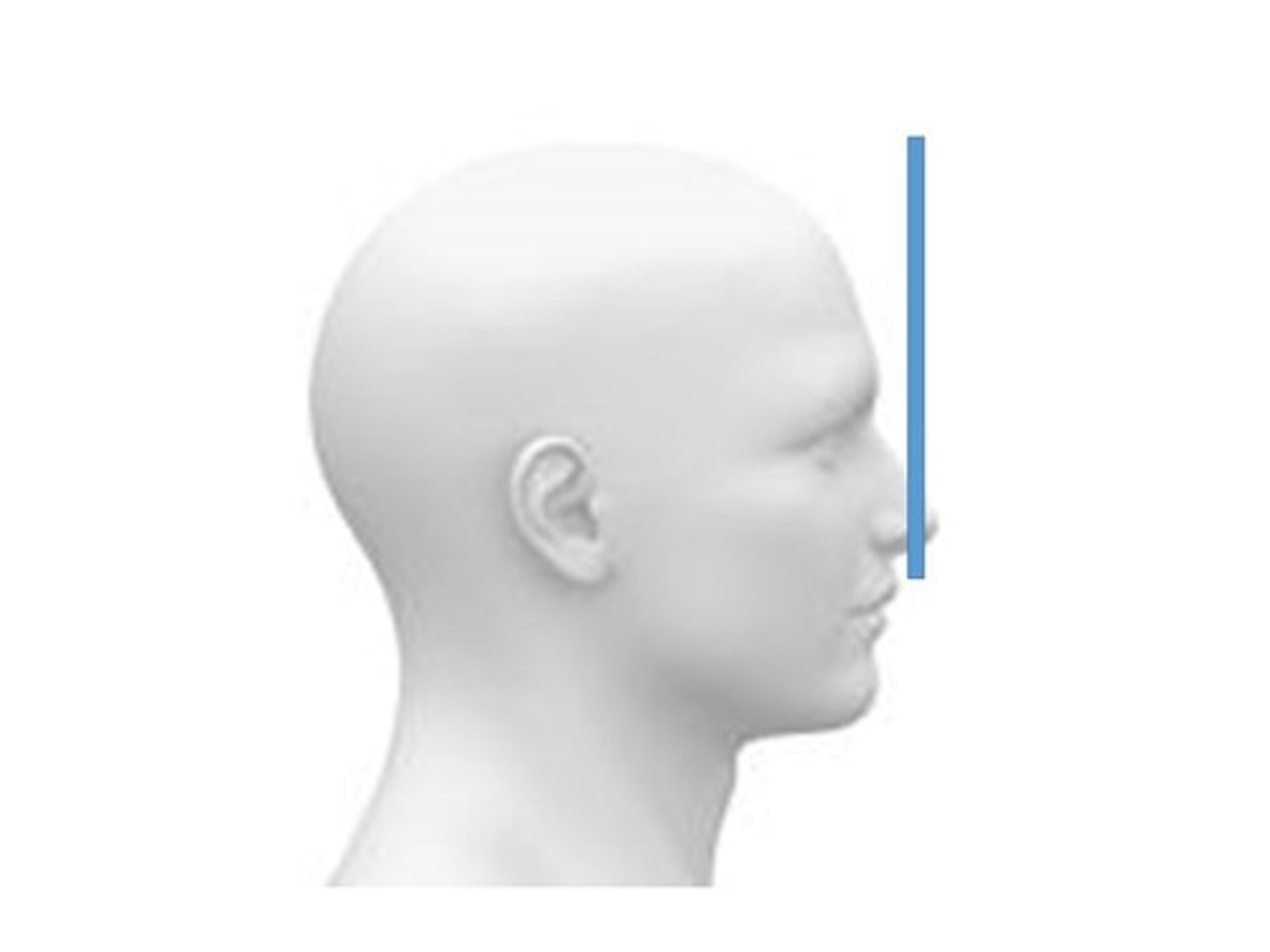
What is the line that connects the pupils?
Interpupillary Line (IPL)
What are the (5) common positioning errors?
Rotation, tilt, excessive flexion, excessive extension, incorrect CR angle
What are the (2) most common positioning errors?
Rotation and Tilt
When doing a PA Skull, why should the CR be parallel to the OML?
So the petrous pyramids can be projected directly into the orbits
When doing a waters (parietoacanthial) projection, why is the chin raised?
So the petrous pyramids are projected just below the maxinary sinuses
What is the order of a skull series?
AP Axial (Townes), R/L Lateral, PA 0 degree or caldwell 15 degree, SMV
What is osteomyelitis?
Localized infection of bone marrow
What is the name for the external portion of the ear?
Auricle (pinna)
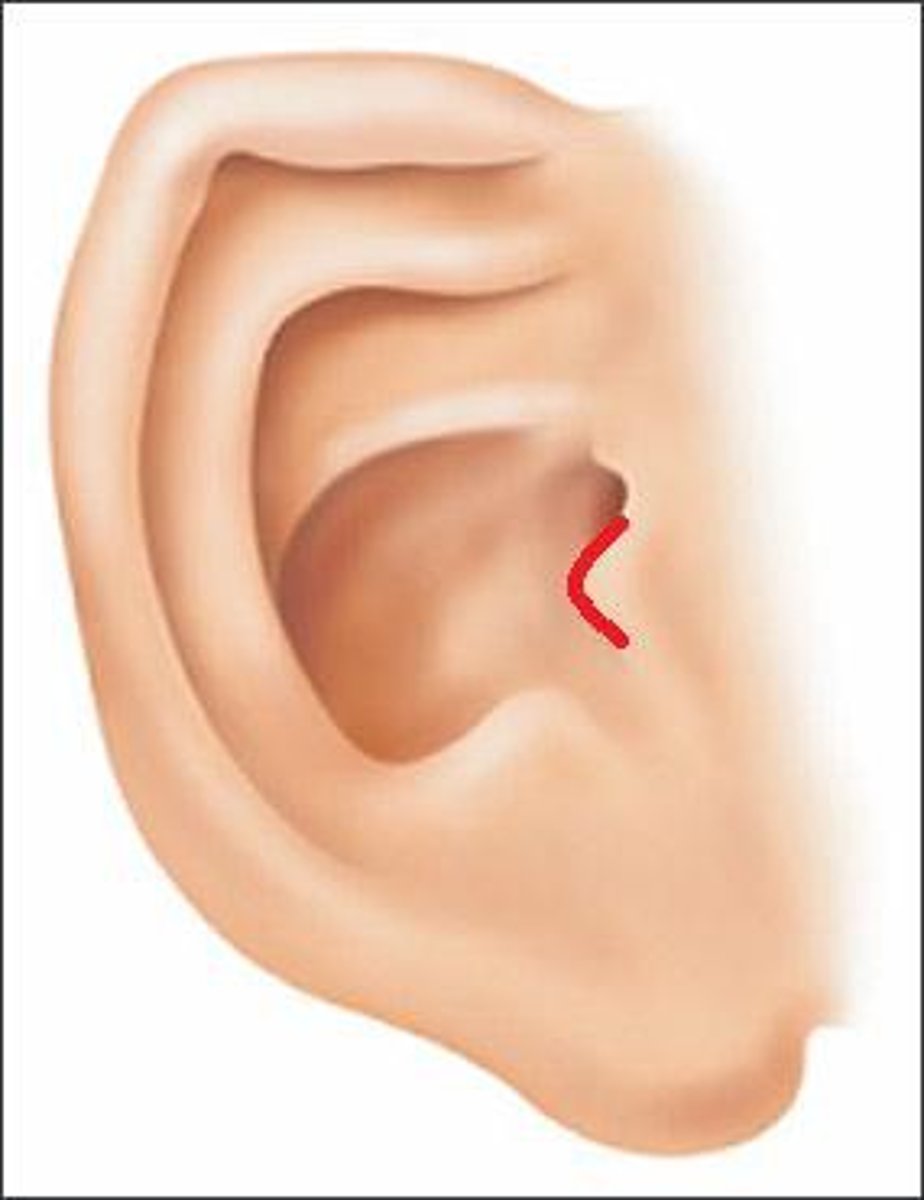
What is the name of the small cartilaginous flap that covers the opening of the ear?
What is the kVp range for cranium projections?
75-95
What is the name for the AP Axial skull projection?
Towne
What is the IR size, patient positioning, and SID for the Towne method?
10x12 portrait; Patient in erect or supine position will depress chin so OML is perpendicular to the IR, CR will have a 30 degree caudad angle and be centered to 2.5 inches above the glabella to pass through the base of the occipital. 34 inch SID (86 cm).