peripheral nervous system - somatic and autonomic
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
ventral root
motor output from the spinal cord arising from neurons in ventral spinal cord. Axons leave via a ventral root and terminate on skeletal/smooth muscles
dorsal root
sensory input into dorsal spinal cord arising from neurons in the dorsal root ganglia
spinal nerves
combination of sensory and motor axons (ventral and dorsal roots)
somatic nervous system
responsible for carrying motor commands from the spinal cord to skeletal muscle and carrying sensory information from body wall/muscles back to spinal cord
responsible for producing contractions of skeletal (voluntary) muscles and processing sensory information that arrives as external stimulus
nerves
made up of axons of hundreds/thousands of individual neurons, made up of morphologically and functionally distinct types of axons
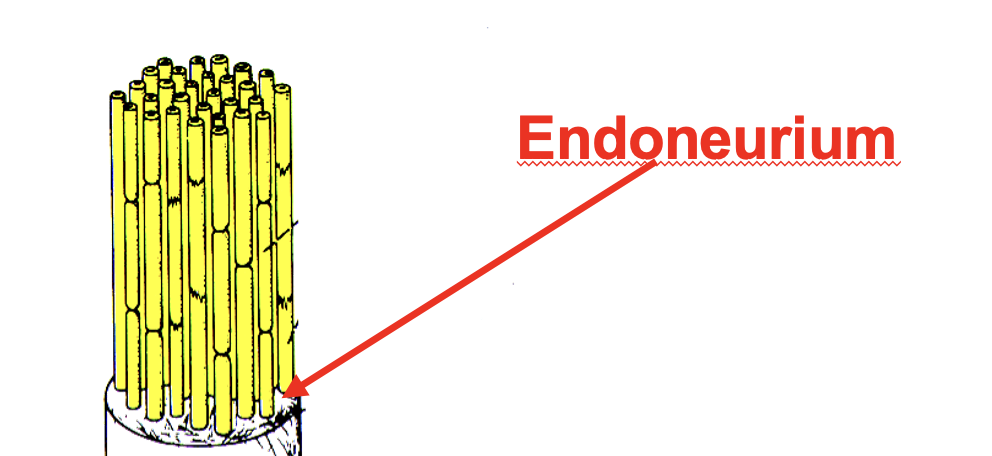
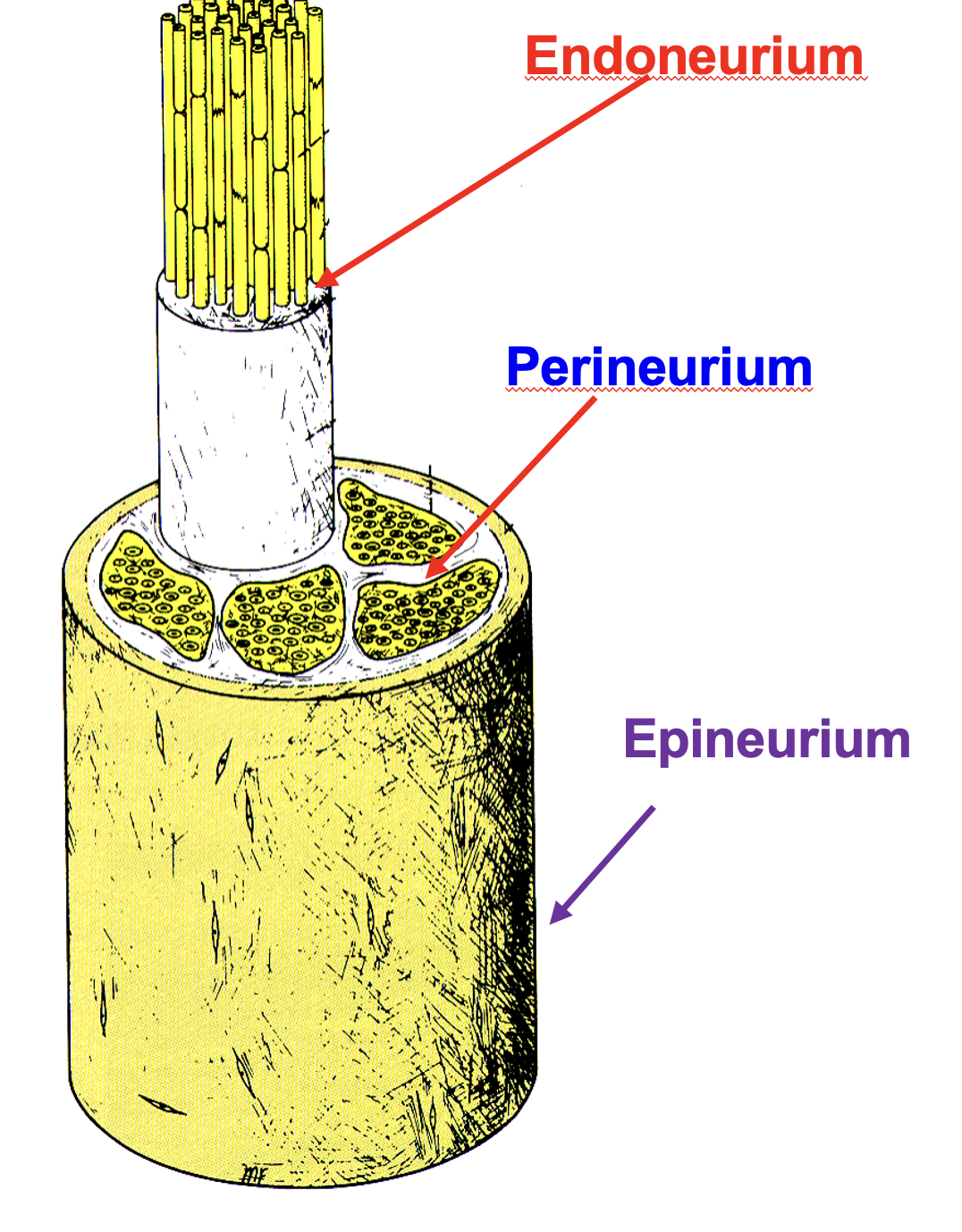
endoneurium
individuals axons are surrounded by connective tissue
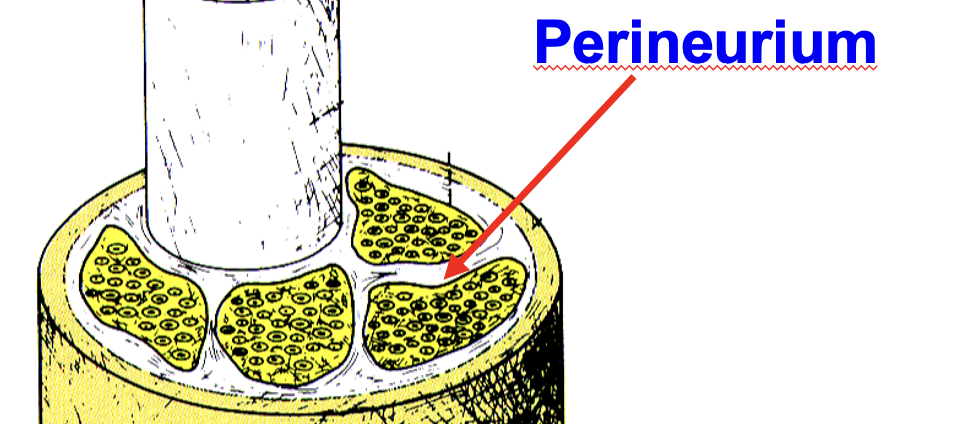
perineurium
multiple bundles are grouped together by this connective tissue sheath
epineurium
all bundles are enclosed by common thick external connective sheath
efferent
axons that conduct information away from the CNS; cell bodies located within the spinal cord
spinal somatic motor
outgoing axons carrying motor commands to skeletal muscles; large diameter and heavily myelinated
spinal visceral motor
ANS - outgoing axons carrying motor commands that are involved in innervating smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glandular tissue - small diameter and lightly myelinated
afferent
axons that conduct information towards the CNS, cell bodies are located in a dorsal root ganglion
spinal somatic sensory
axons that transmit sensory information from the body to the spinal cord; large diameter and heavily myelinated s
spinal visceral sensory
axons that transmit sensory information from organs to the spinal cord
cranial nerves
not formed from dorsal and ventral roots (not present in brainstem); some carry only motor info., some carry only sensory info., and some carry both sensory and motor info.
cranial somatic motor
skeletal muscles in head and neck
cranial visceral motor
ANS - glandular structures in head; smooth muscles in thorax and abdomen
cranial somatic sensory
axons that transmit sensory information from face, ear, oral cavity
cranial visceral sensory
axons that transmit sensory info. from internal organs to the brainstem
special sensory
cranial nerves - sensory information unique to head (vision, hearing, taste, smell, balance)
branchial motor
cranial nerves - unique voluntary muscles which have different embryological origin; these muscles are not derived from somites but rather from structures called pharyngeal arches
autonomic nervous system
portion of the nervous system that supplies motor and sensory innervation to structures not under voluntary control
sympathetic NS
prepare body for emergency; no stimulation in the digestion
parasympathetic NS
conserve and restore energy; maintain homeostasis; no parasympathetic connections in the periphery or head
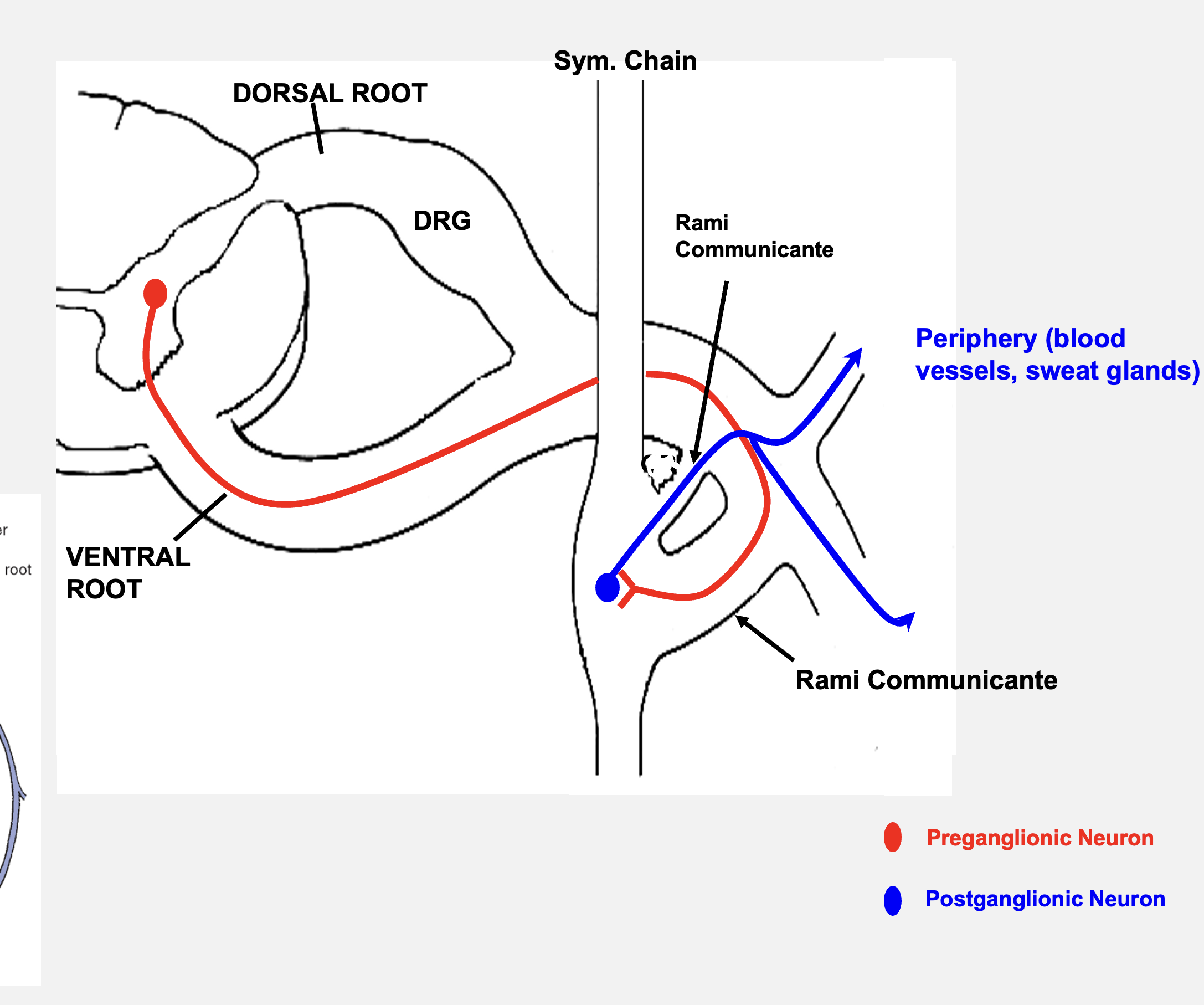
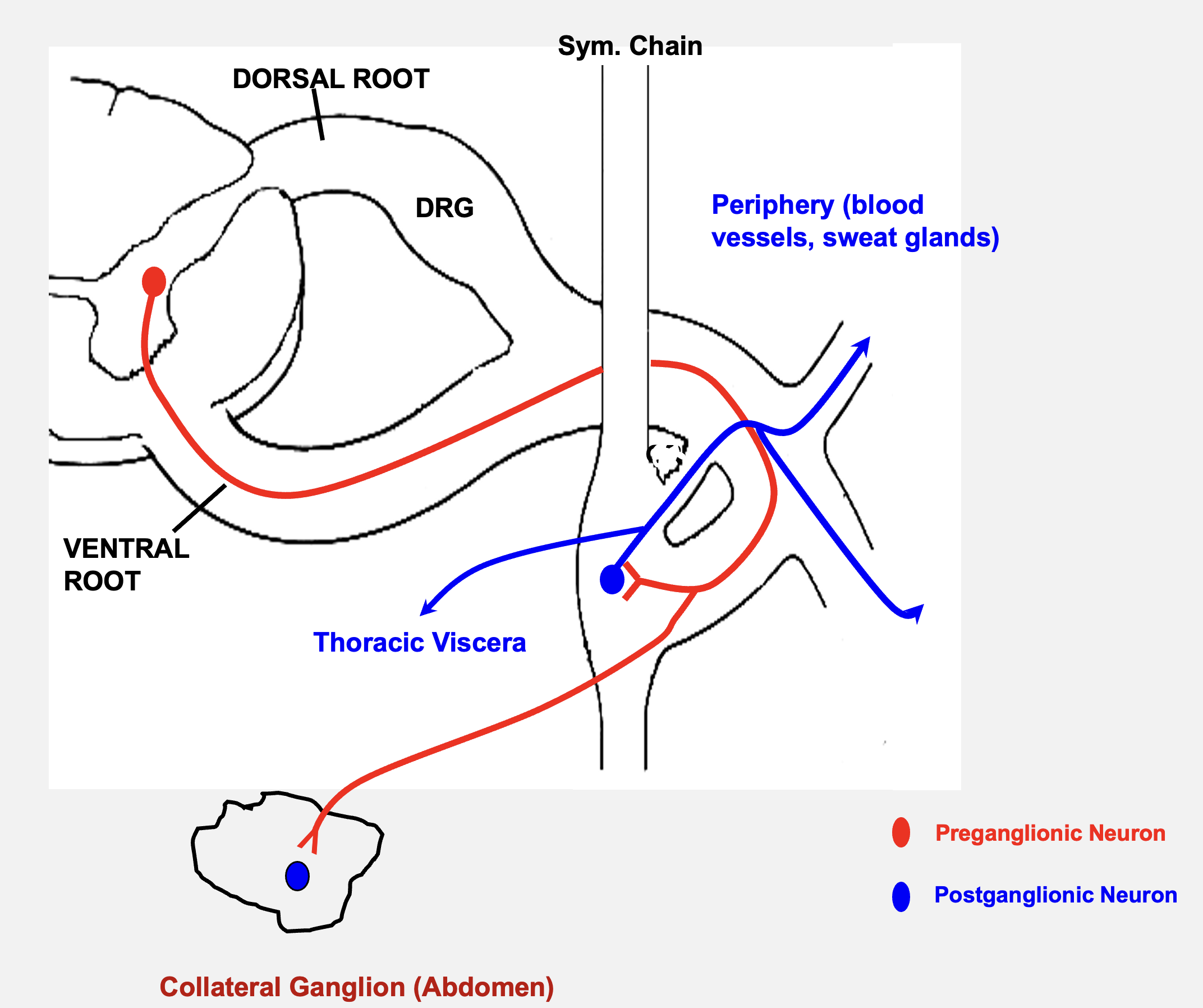
autonomic nervous system motor circuit
ANS requires 2 neurons to elicit a response in a target organ
pre-ganglionic neuron
1st neuron in ANS system; always located within the CNS
post-ganglionic neuron
2ns neuron in ANS system; always in a ganglia located in periphery
note: (not dorsal root ganglion - that area contains sensory info!)
sympathetic chain
collateral ganglion
location of sympathetic post-gangalionic neurons
sympathetic chain
bilateral para vertebral ganglia that is adjacent to vertebral column; extend from base of skull to coccyx
rami communicate
sympathetic chain ganglia are attached to adjacent spinal nerves by this feature
collateral ganglion
located around the abdominal aorta; houses post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons
between T1 and L2
pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons are located on the spinal cord between these two areas (thoracolumbar division = sympathetic nervous system)
pre-ganglion neuron
ventral root
sympathetic chain
rami communicante
post-ganglionic neurons
abdomen
collateral ganglia
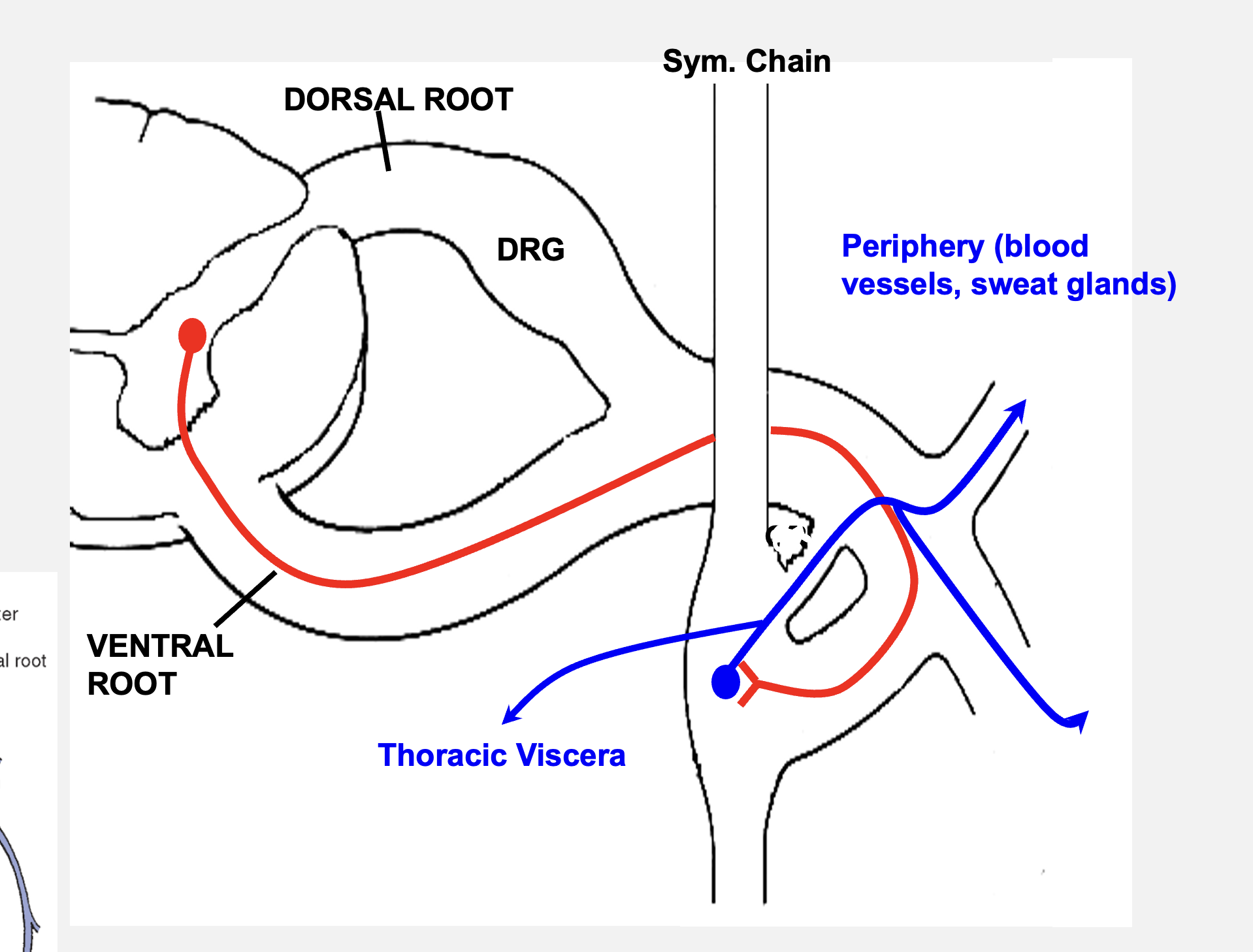
the axons of all BLANK BLANK leave the spinal cord via the BLANK BLANK and enter the BLANK BLANK via BLANK BLANK, where they synapse onto BLANK BLANK or continue to the BLANK to the BLANK BLANK
pre-ganglionic neurons
ventral root
sympathetic chain
rami communicante
post-ganglionic neurons
periphery
“run-the-chain”
the axons of all BLANK BLANK leave the spinal cord via the BLANK BLANK and enter the BLANK BLANK via BLANK BLANK, where they synapse onto BLANK BLANK at a DIFFERENT LEVEL, which re-enters the spinal nerve to reach target cells in the BLANK
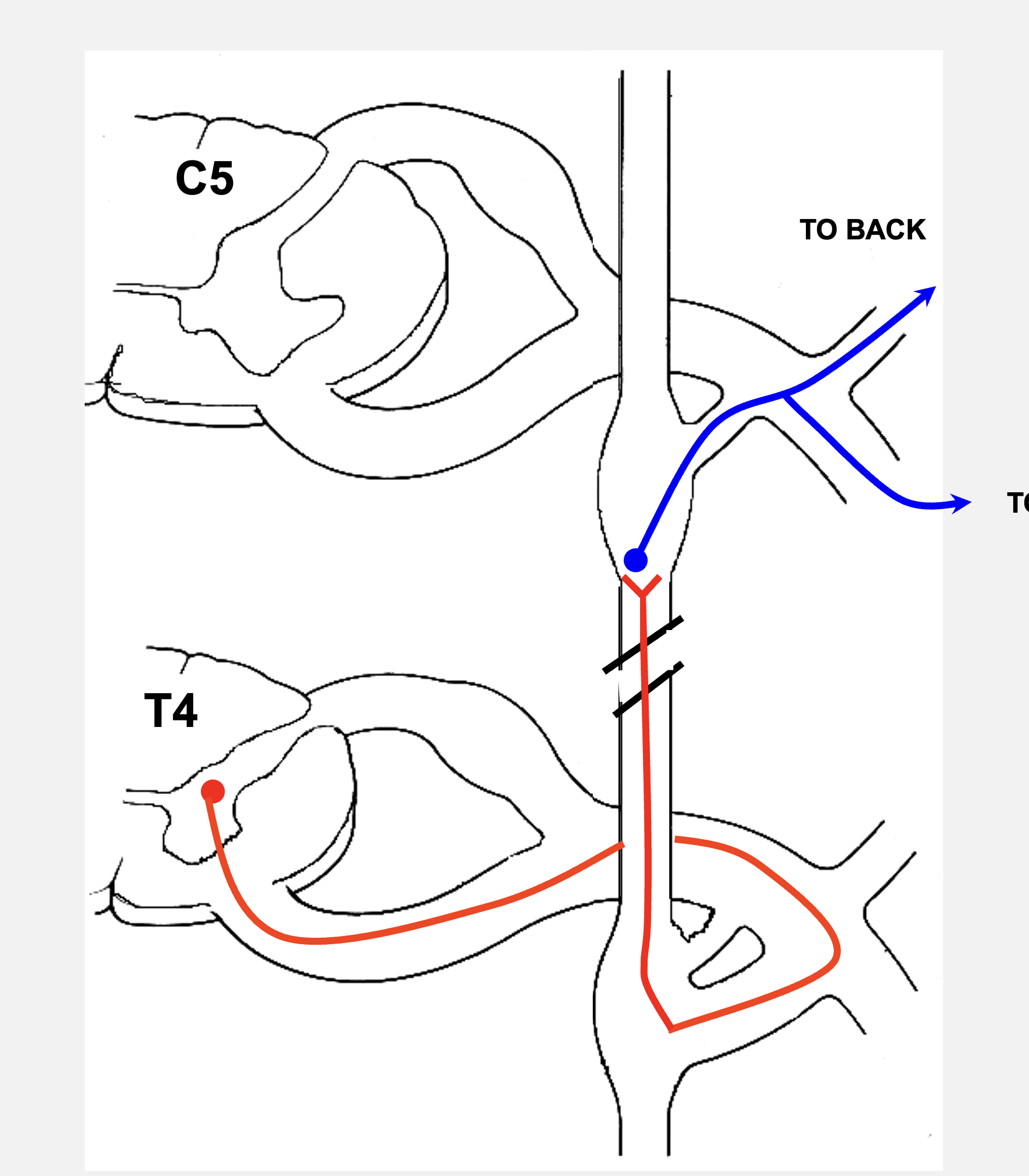
pre-ganglionic neurons
ventral root
sympathetic chain
rami communicante
rami communicante
collateral ganglion
abdomen
“abdominal viscera”
the axons of all BLANK BLANK leave the spinal cord via the BLANK BLANK and enter the BLANK BLANK via BLANK BLANK. The pre-ganglionic neurons branch off at BLANK BLANK and travel to the BLANK BLANK, which is located in the BLANK to innervate internal organs in that region
pre-ganglion neurons
ventral root
sympathetic chain
rami communicante
post-ganglionic neurons
thoracic
“thoracic viscera”
the axons of all BLANK BLANK leave the spinal cord via the BLANK BLANK and enter the BLANK BLANK via BLANK BLANK. The pre-ganglionic neurons synapse into BLANK BLANK here, which travel out of the sympathetic chain and travel to the BLANK region to innervate internal organs there
brainstem
sacral - between S2 and S4
pre-ganglionic PARASYMPATHETIC neurons are located here (craniosacral division = Para. NS)
location of post-ganglionic parasympathetic ganglia
in most areas, these neurons are located in walls of organ being innervated
distension/pressure in hollow organ
pain
sensory fibers innervating viscera relay information to the CNS about this:
ganglia in the head
sensory cells that give rise to axons that accompany the Parasympathetic nerves to viserca are located here
DRG
sensory cells that give rise to axons that accompany sympathetic nerves to viscera are located here
characteristics of visceral pain
not evoked by all viscera - not all viscera is innervated by sensory fibers
referred to body wall - convergence of viscerosensory and somatosensory fibers in central pain pathway
diffuse and poorly localized - few sensory fibers and extensive divergence in CNS