1.4 Explain common networking ports, protocols, services, and traffic types
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
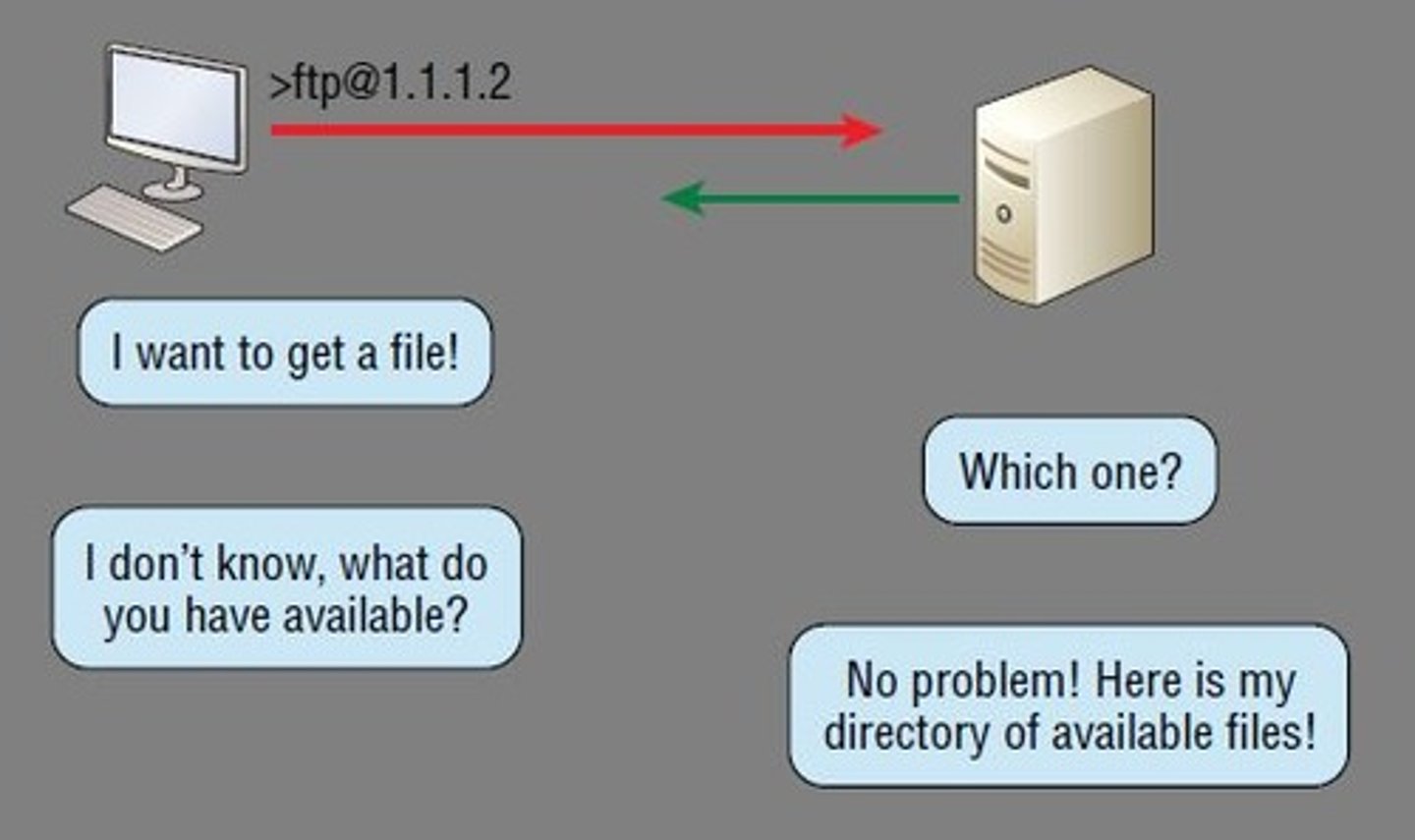
FTP
File Transfer Protocol
A communications method for transferring data between computers on the Internet
tcp Port 20 (data transfer)
tcp Port 21 (command and response)
SFTP
Secure File Transfer Protocol
A secure protocol used to transfer files from one device to another over a network uses SSH (Secure Shell)
tcp port 22
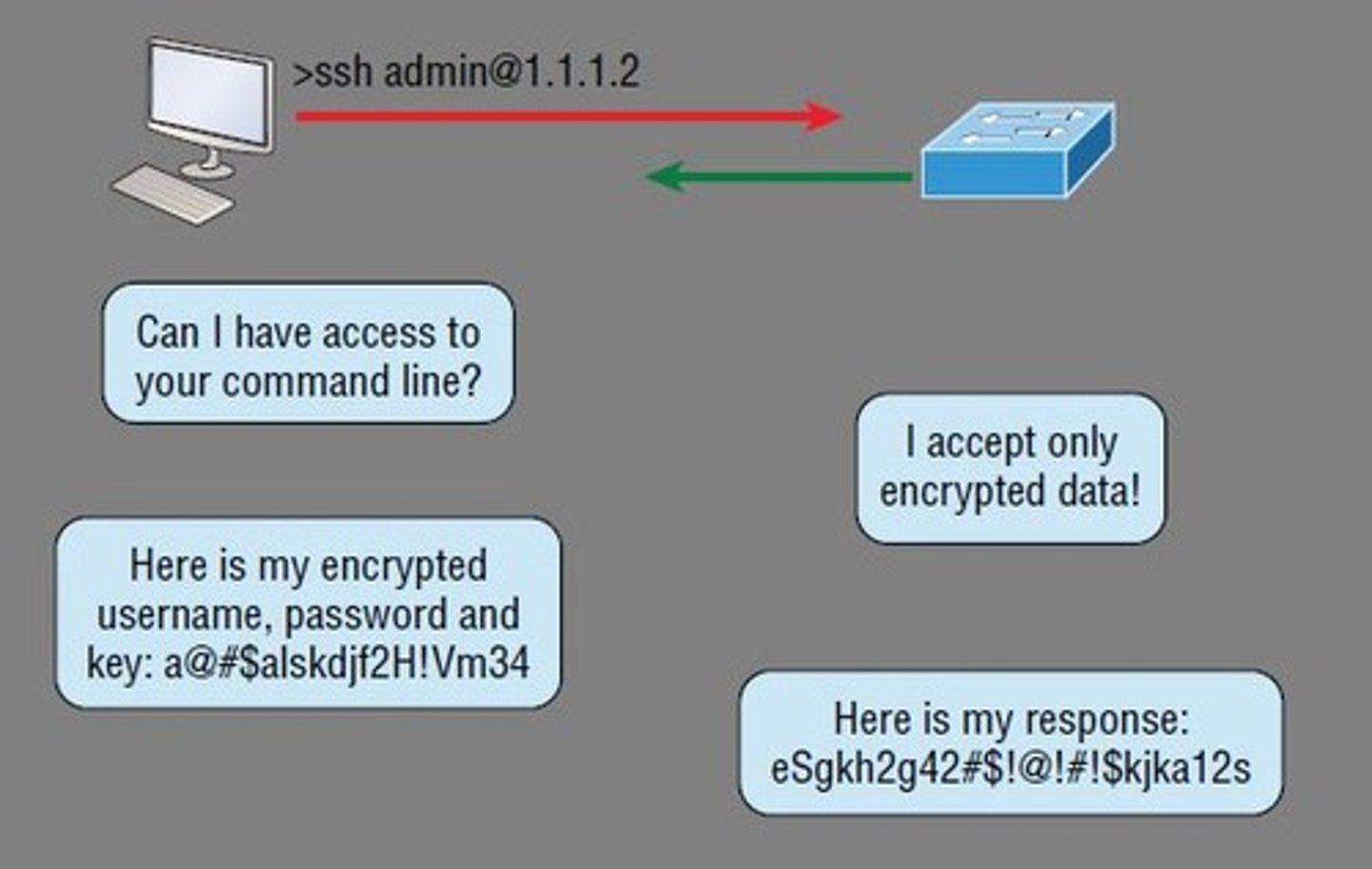
SSH
Secure Shell
a cryptographic network protocol that provides a secure channel over an unsecured network
Ex: can replace Telnet or FTP using SFTP
tcp port 22
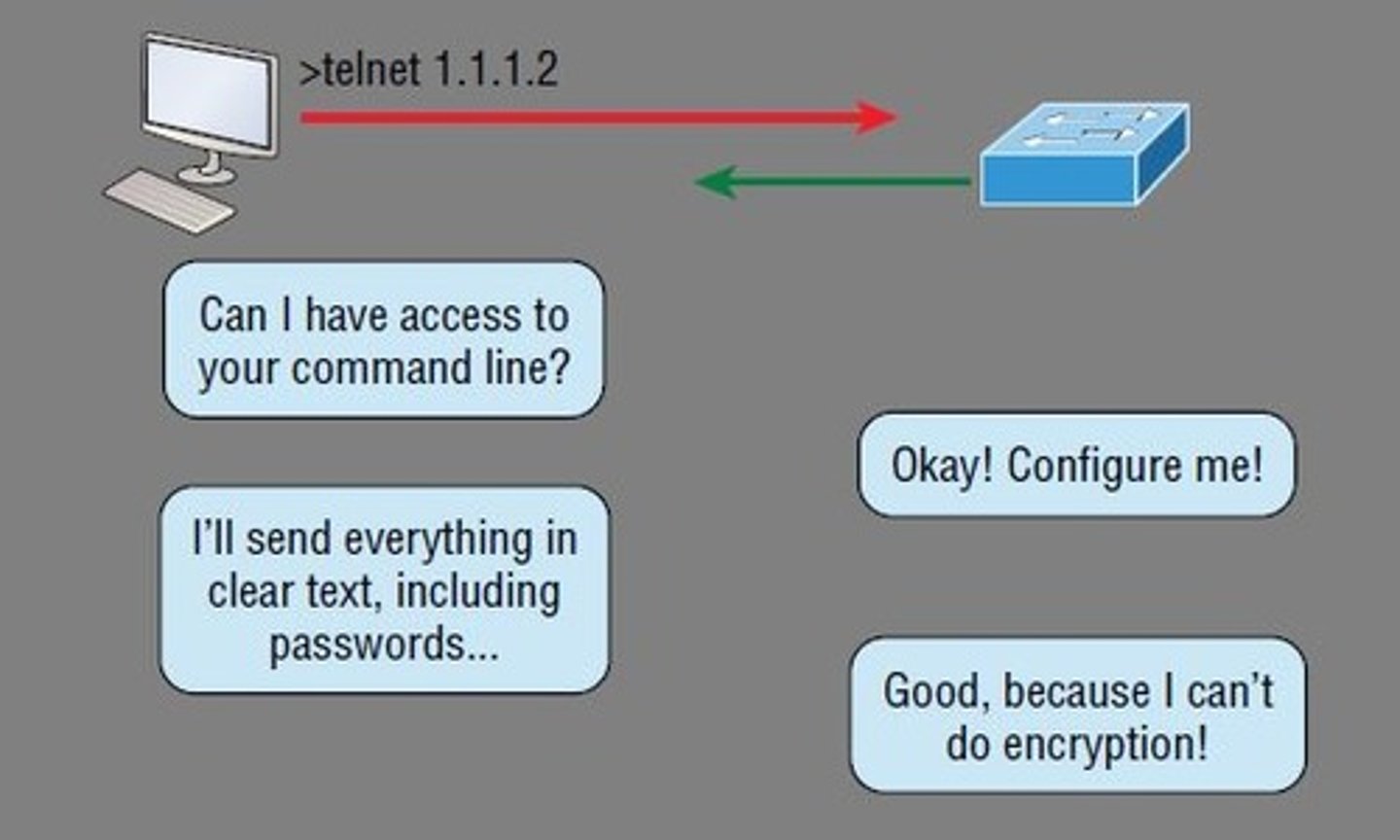
Telnet
network protocol that enables users to remotely access and control a computer or network device via a command-line interface
heavily insecure
TCP port 23
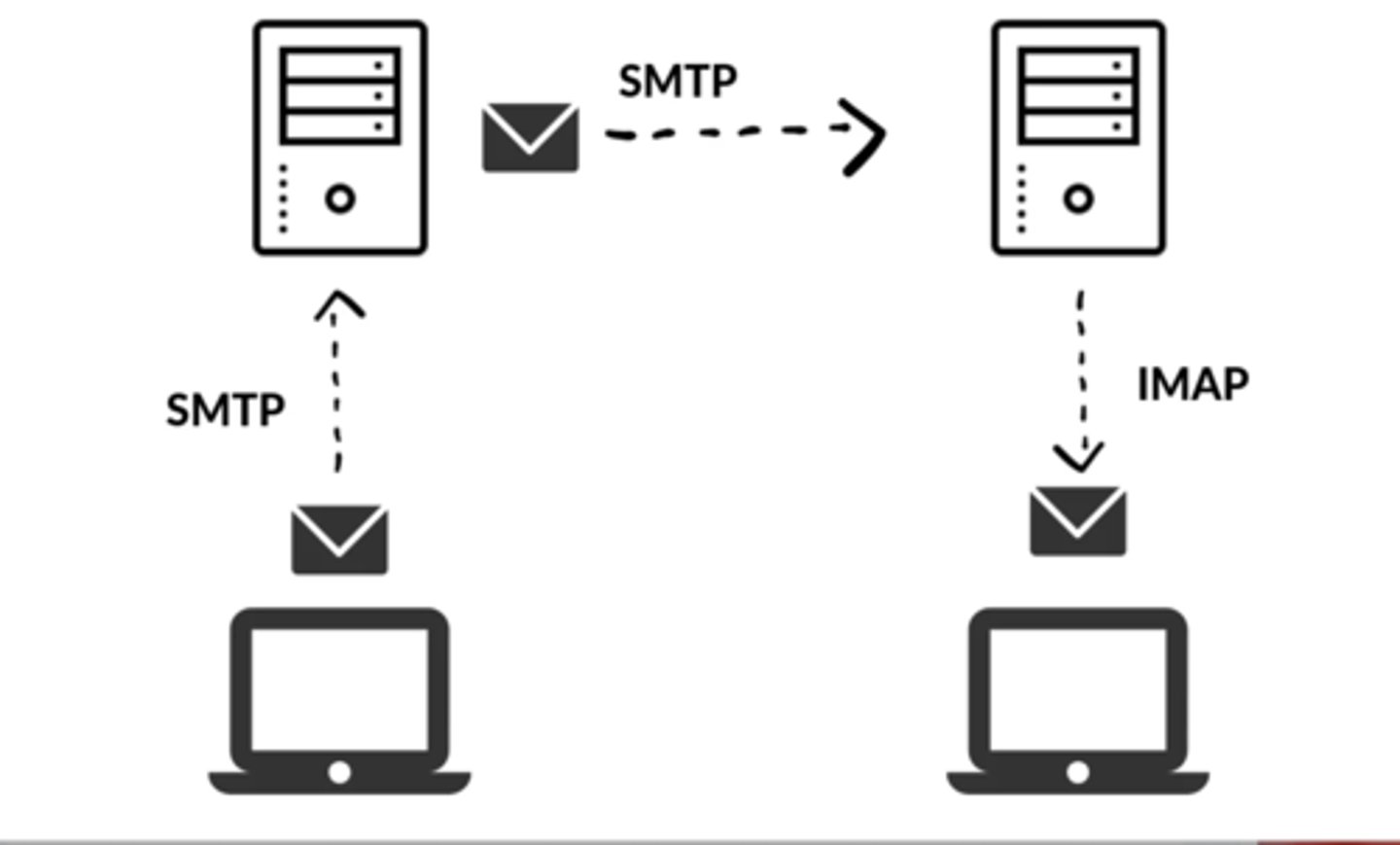
SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
standard protocol for email transmission across the Internet.
tcp port 25
DNS
Domain Name System
like the internet's phone book — it translates names like google.com into IP addresses that computers use to find each other.
TCP or UDP port 53
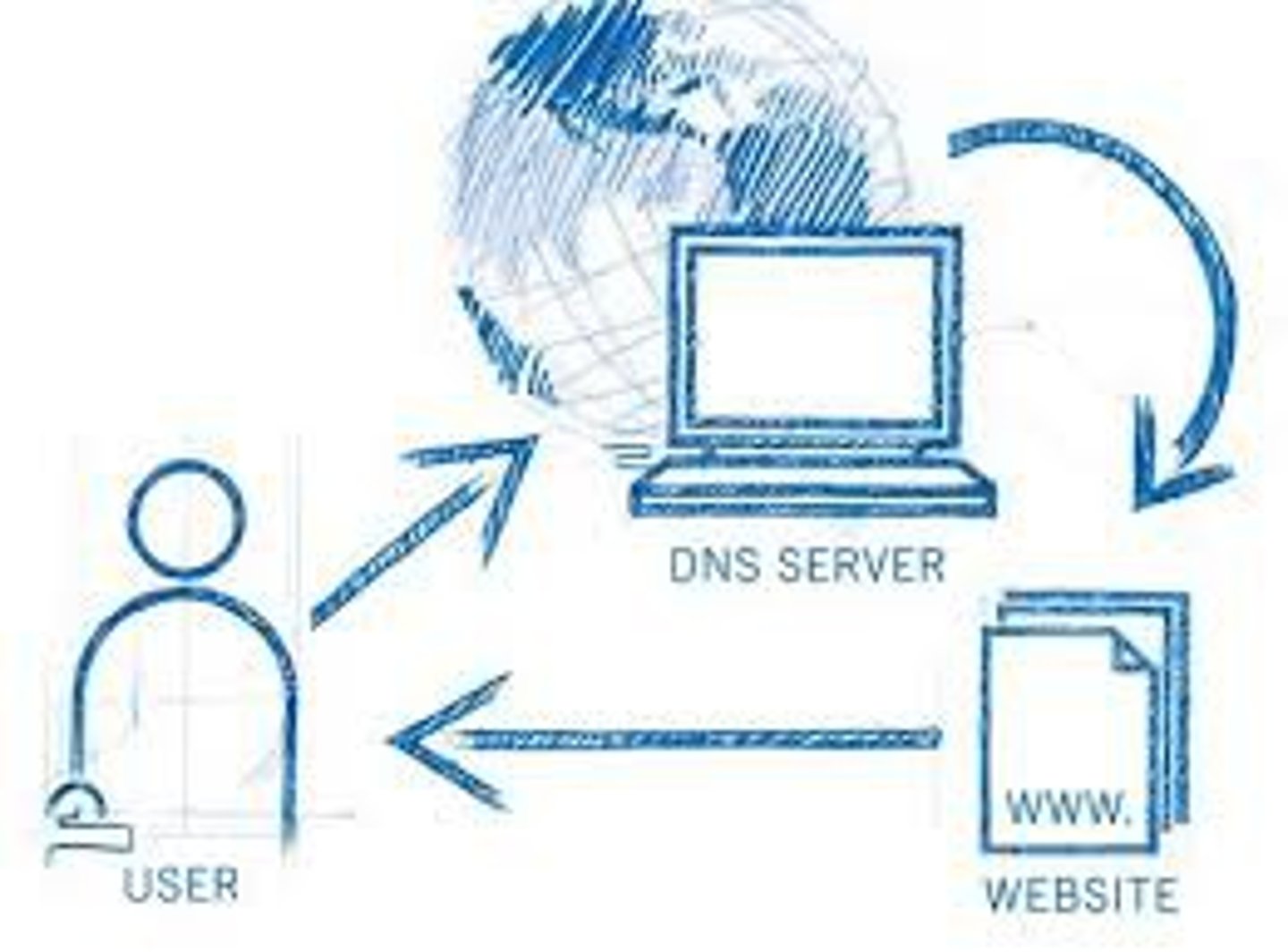
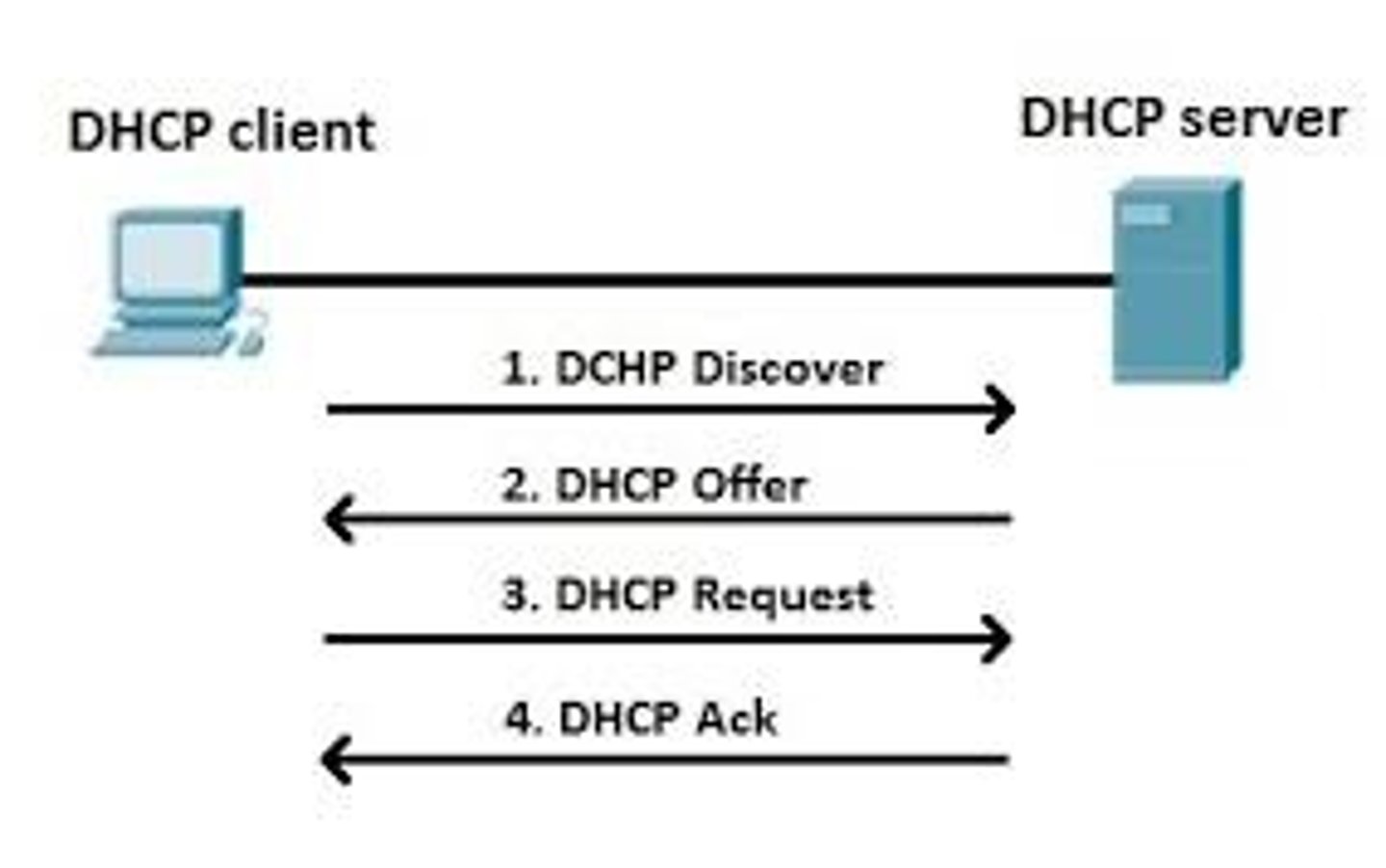
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dynamically assigns IP address information (for example, IP address, subnet mask, DNS server's IP address, and default gateway's IP address) to network devices.
UDP port 67/68
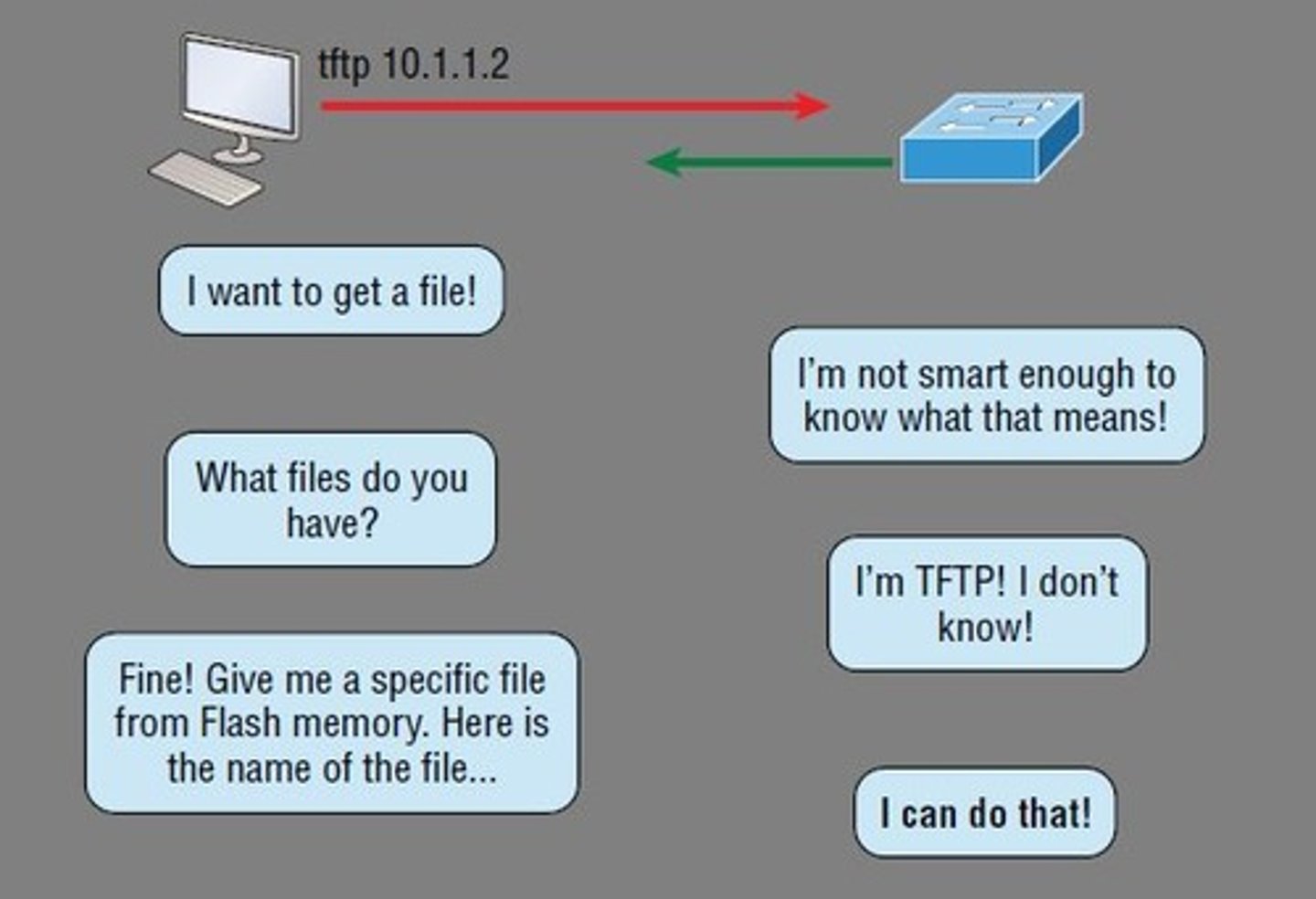
TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol
simple, lock-step, file transfer protocol with no authentication, used for transferring files smaller in size.
UDP port 69
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
a protocol for computers to request and share the pages on the Internet
TCP port 80

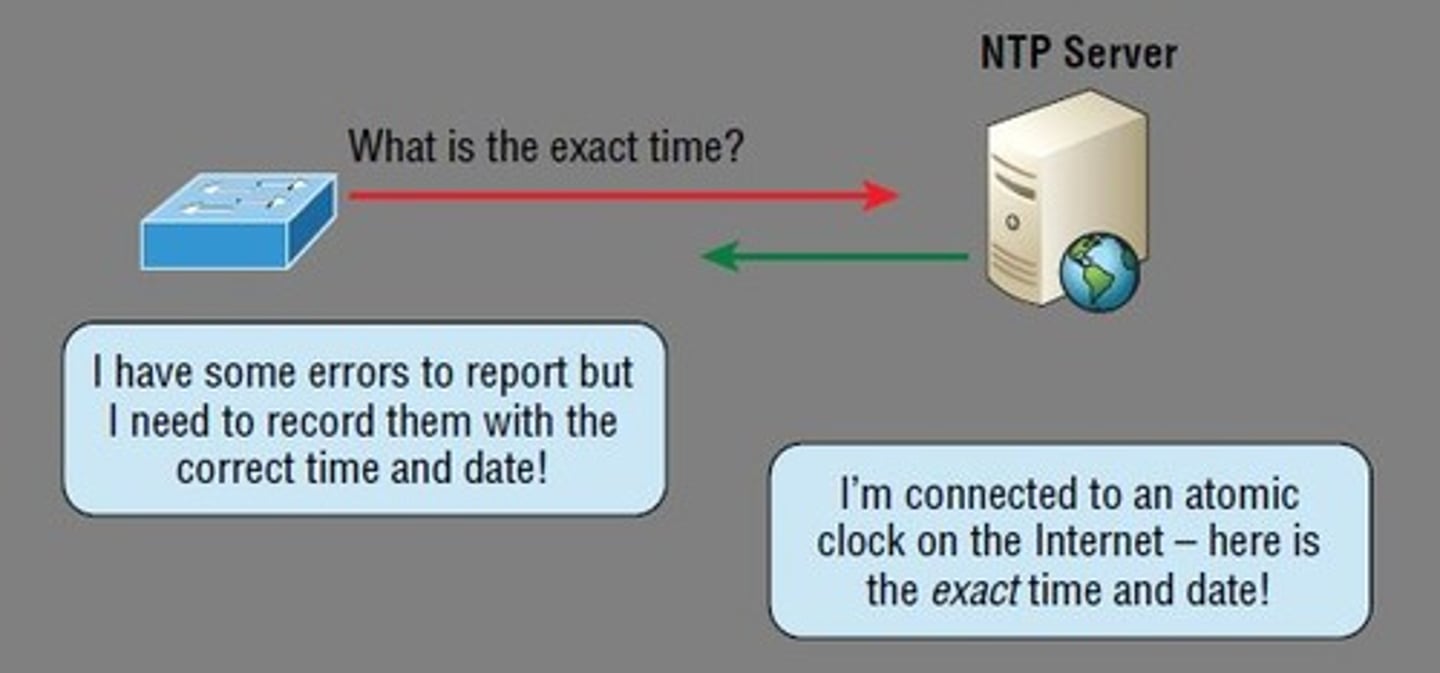
NTP
Network Time Protocol
Used to synchronize clocks of computers over a network.
UDP port 123
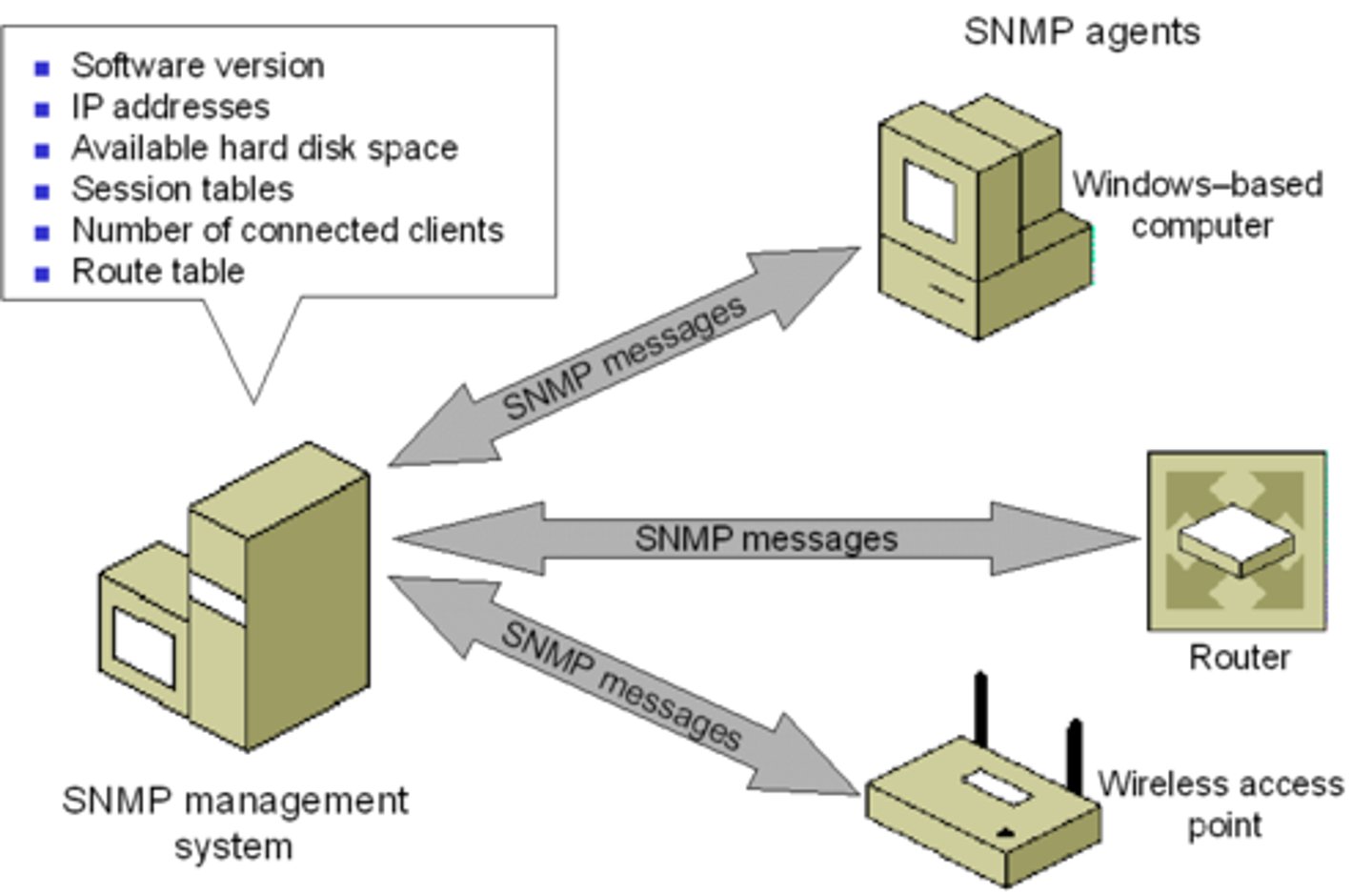
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
widely used internet standard protocol for monitoring and managing network devices.
use only v3 (encrypted and secure), not v1 v2
UDP port 161/162
LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
a protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network.
TCP port 389
HTTPS/SSL
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) [Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)]
originally using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), is the secure version of HTTP, used for secure communication over a computer network.
TCP port 443
Secure Sockets Layer
a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a Web server and a browser, ensuring that all data passed between them remains private.
Not used today
HTTPS/TLS
TLS encrypts the communication, ensuring a secure and authenticated connection between the browser and the website
tcp port 443
TLS
Transport Layer Security
standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between web servers and browsers.
replaces SSL
SMB
Server Message Block
network communication protocol that allows devices on the same network to share files, printers, and other resources
primarily used on Windows to share files
TCP port 445
Syslog
used to configure and manage system logging, which collects and stores log messages from network devices.
udp port 514
SMTPS
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Secure
method for securing SMTP communications between email servers and clients.
uses an encryption layer to enhance the security of data being transferred during email communications.
TCP port 587
LDAPS
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol over SSL
providing a secure method of accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network.
TCP port 636
Structured Query Language (SQL) Server
SQL Server, a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft, uses TCP port 1433 for client connections.
TCP port 1433
RDP
Remote Desktop Protocol
Microsoft protocol that enables remote connections to other computers, primarily running Windows operating systems.
TCP port 3389
SIP
Session Initiation Protocol
a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, modifying, and terminating real-time sessions that involve video, voice, messaging, and other communications applications and services.
Ex. VoIP
TCP port 5060/5061
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol
used for network diagnostics and error reporting (e.g., ping, traceroute).
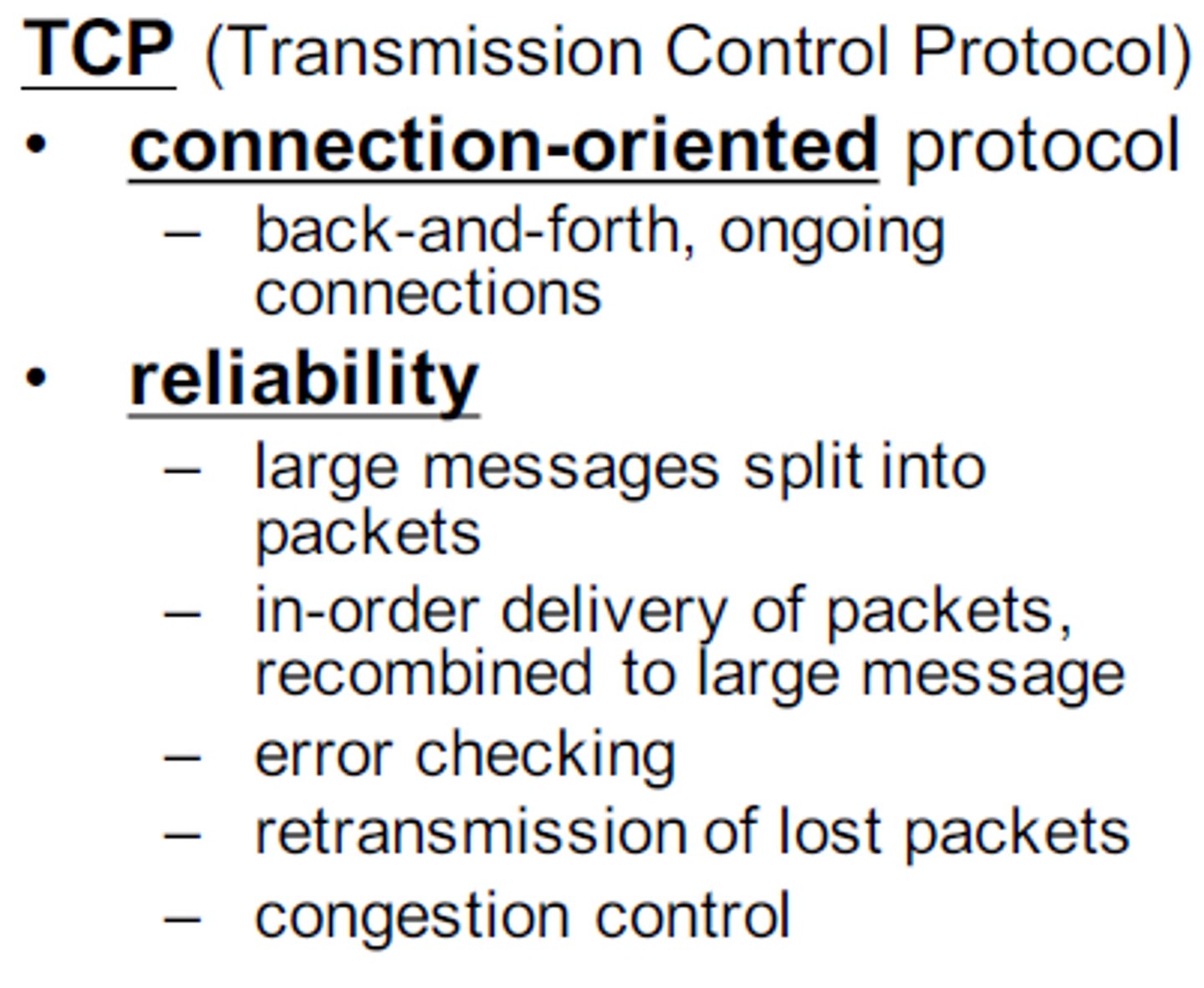
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of packets on the internet.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
a connectionless protocol that allows the transmission of data without establishing a prior connection between the sending and receiving hosts.

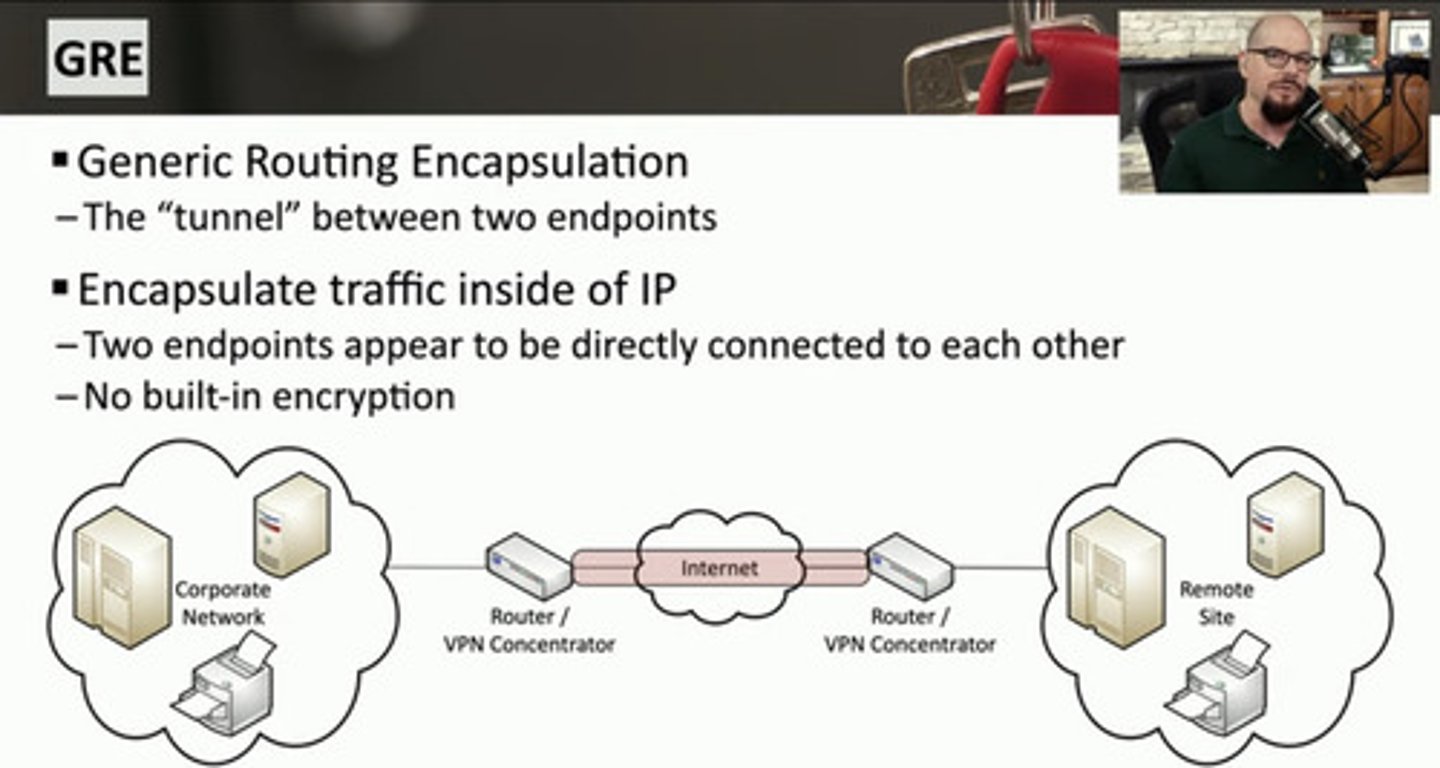
GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation
a tunneling protocol used to encapsulate various network protocols for transport over IP networks.
IPSec
Internet Protocol Security
a suite of protocols that encrypt, authenticate, and ensure the integrity of IP traffic. Commonly used in VPNs.
AH
Authentication Header
An IPSec component that provides integrity & authentication
ESP
Encapsulating Security Payload
An IPSec component that provides the same services as AH but also provides encryption when sending data.
IKE
Internet Key Exchange
a protocol used to set up a secure, authenticated communication channel between two parties.
Ex: VPN
udp port 500
Unicast
a one-to-one form of communication where data is sent from one source to one specific destination identified by a unique IP address.
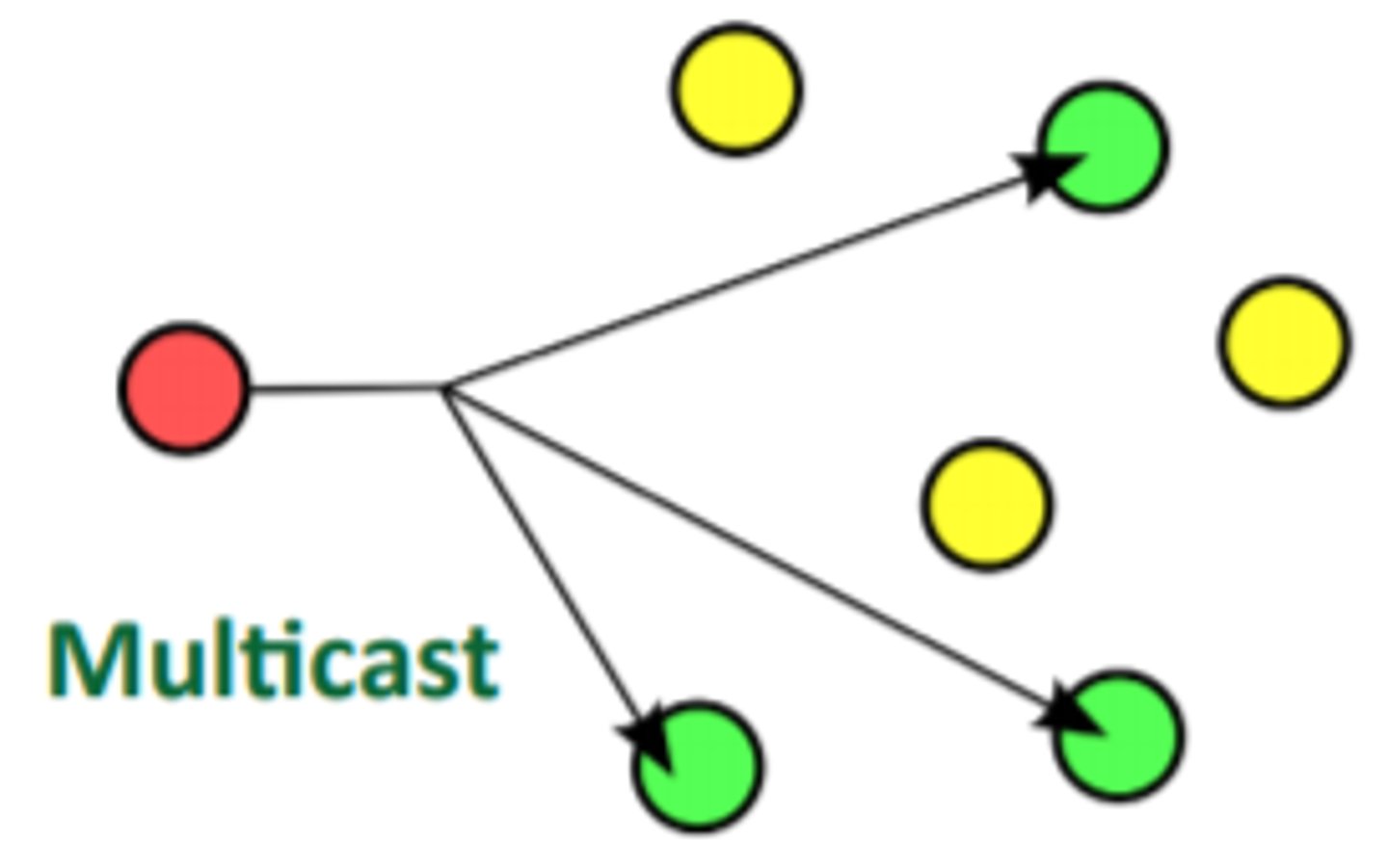
Multicast
data is sent from one or more sources to multiple destinations simultaneously over a network
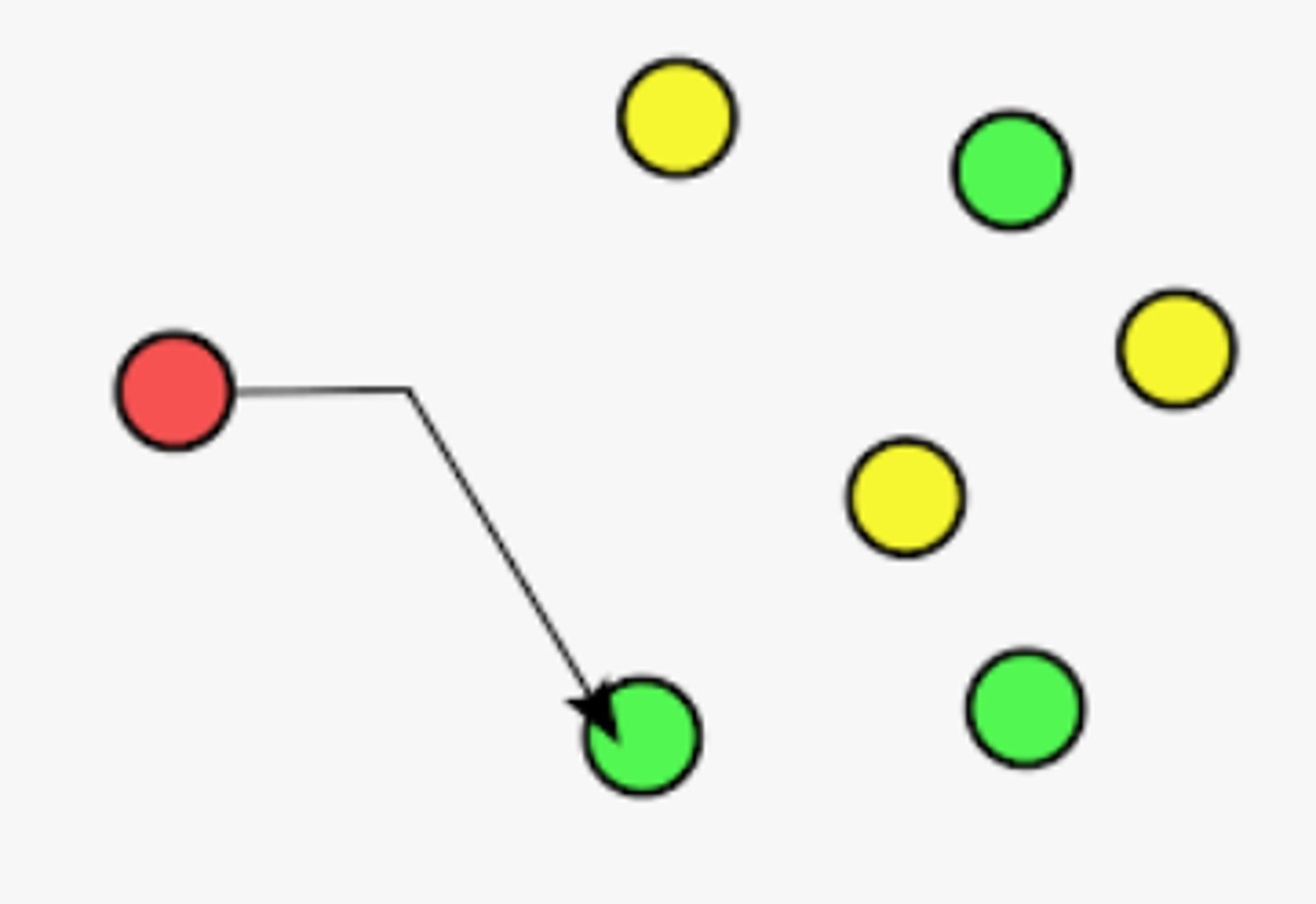
Anycast
data is sent to the nearest or best destination as determined by routing protocols, from among multiple potential destinations sharing the same address.
Broadcast Dom
communication method where a message is sent from one sender to all potential receivers within a network segment.