Unit 9- Renal Anomalies (Elie)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is agenesis?
Absence of a kidney, failure to form
What is Dysgenesis?
Defective embryonic development of kidney
What is Supernumerary?
Complete duplication of renal system
What is a Pseudotumor?
Overgrowth of cortical tissue mistaken for mass
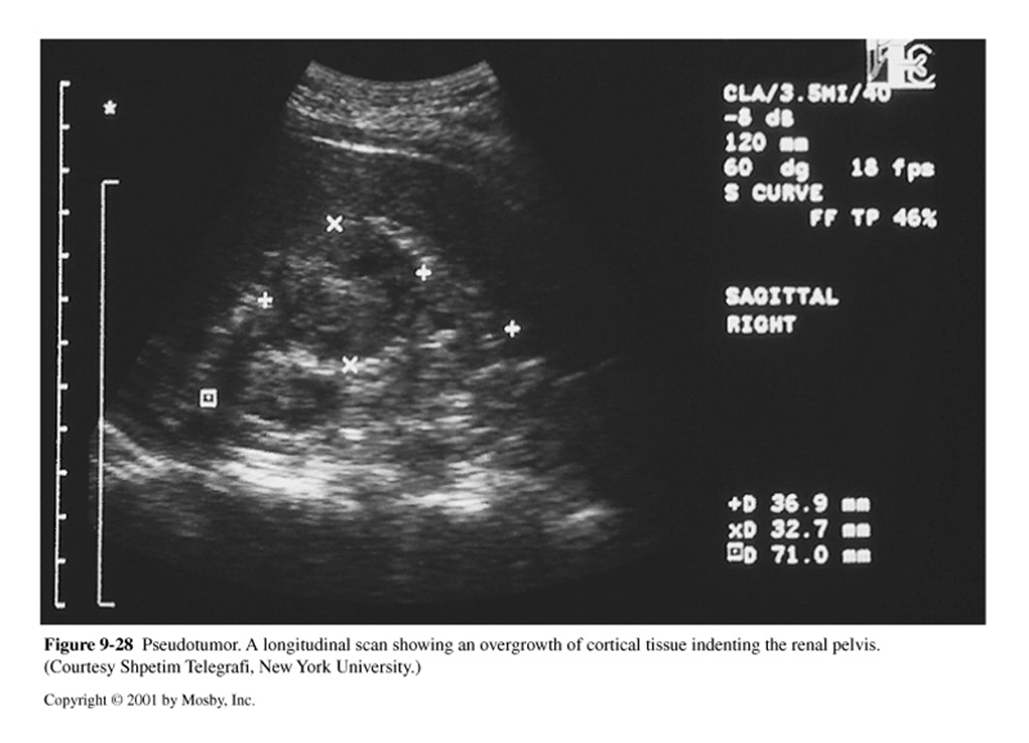
What is this image showing?
Pseudotumor
Agenesis is considered______
Rare
Agenesis US appearance:
Verify no small, nonfunctioning kidney present
Enlargement of remaining kidney
What is renal hypoplasia?
Incomplete development
Normal, just smaller than normal
With renal hypoplasia, you want to differentiate from?
Atrophy
Secondary to: pyelonephritis or renal artery stenosis
What is the variant Duplex Collecting System?
Bifid Renal Pelvis
Duplication of renal pelvis with 1 ureter
A duplex collecting system can be ________ or ________
Complete or Incomplete
What is the appearance of a duplex collecting system?
Complete confirmed with 2 ureteral jets on same side of bladder
Enlarged kidney, smooth borders
Central sinus separated by appearance of normal parenchymal tissue
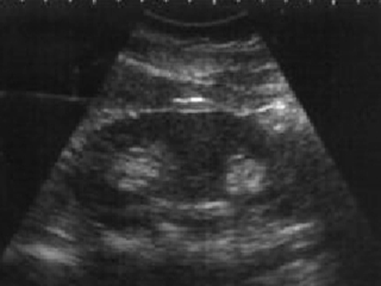
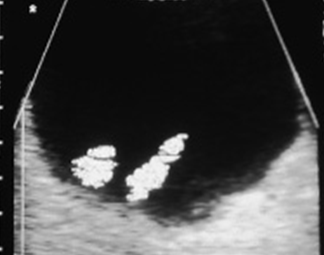
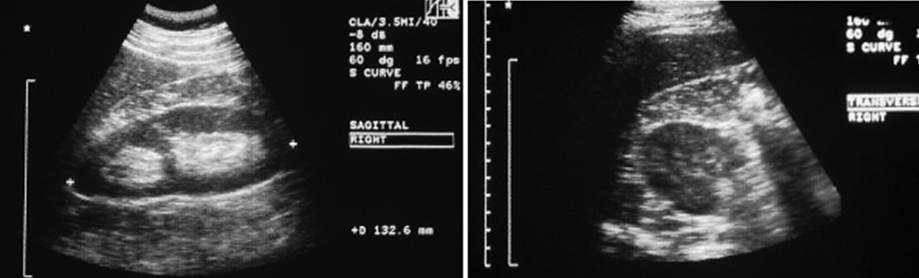
What are these images showing?
Duplex Collecting System/ Supernumerary
What is a Pelvic Kidney and what is it associated with?
“Ectopic Kidney” - inferior
Kidney not in renal fossa
Associated with: vesicoureteral reflux & abnormal extrarenal pelvis
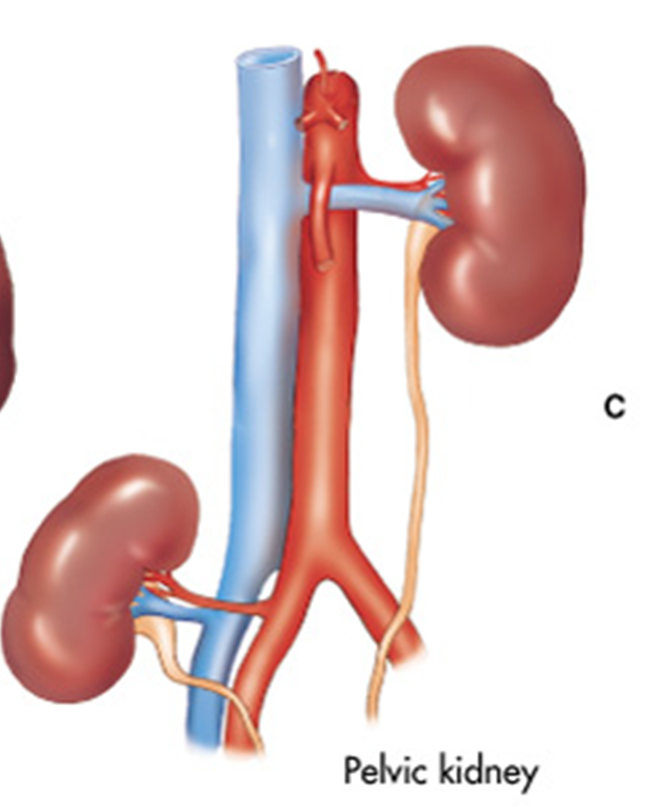
What is this showing?
Pelvic Kidney
What is Crossed Renal Ectopia?
Both kidneys found on same side (Rt > Lt)
What percentage of a crossed renal ectopia are fused?
85-90%
What is the incidence of crossed renal ectopia?
1 in 1,000-1,500
In a Crossed renal ectopia the ureterovesical junctions are in what positions?
Normal positions
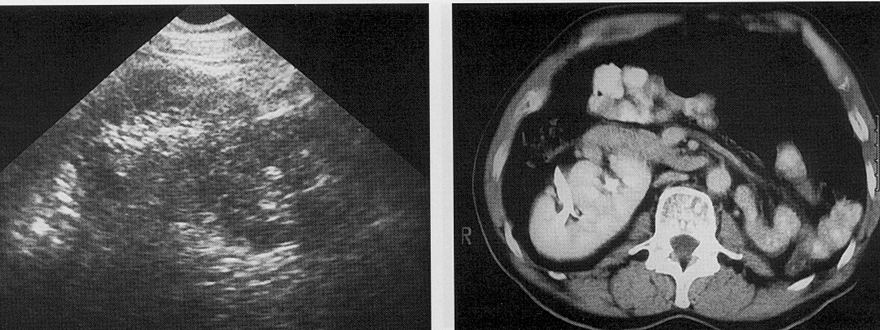
What are these images showing?
Crossed Renal Ectopia
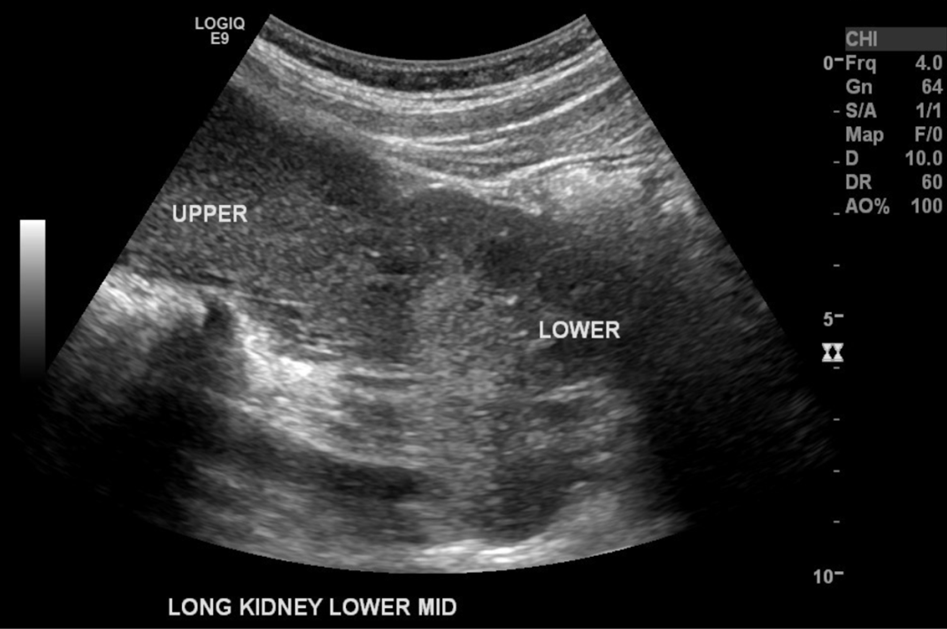
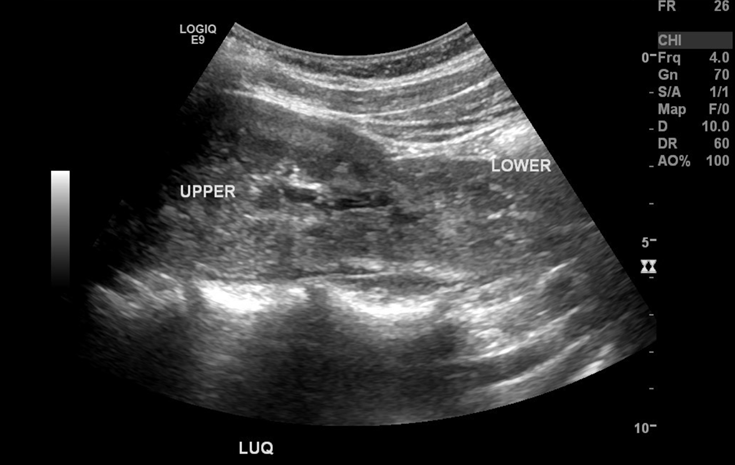
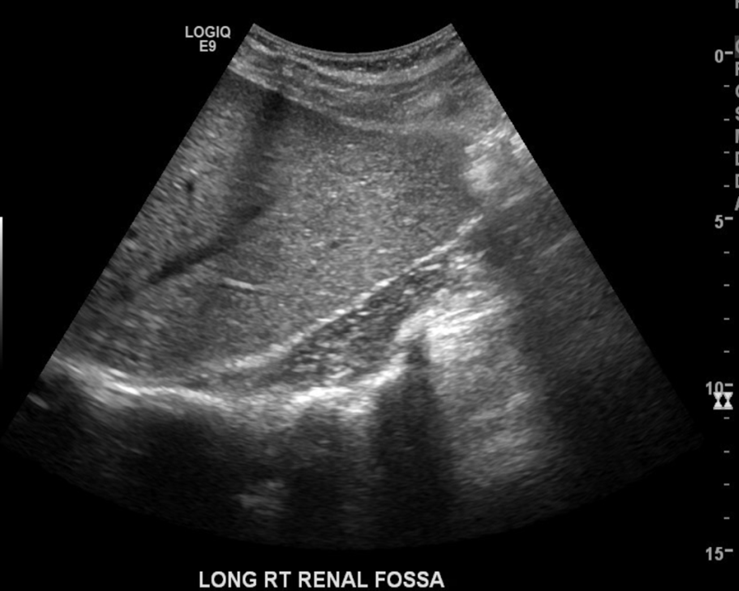
What are these images demonstrating?
Crossed Renal Ectopia
What is a horseshoe kidney?
Fusion of lower polar regions
Where are horseshoe kidneys located?
Located more inferiorly than normal
Pelves located ventrally
Closer to spine
Isthmus of kidney is anterior to spine, Aorta & IVC
What other pathologic conditions are associated with a horseshoe kidney?
Kidney malrotation
Urolithiasis
UPJ Obstruction
Pyelocaliectasis
Anomalous extrarenal pelvis
Infection
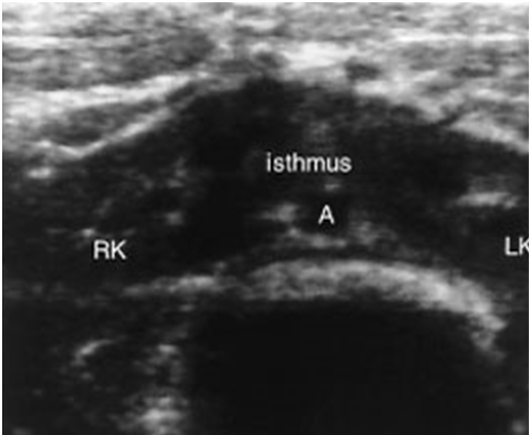
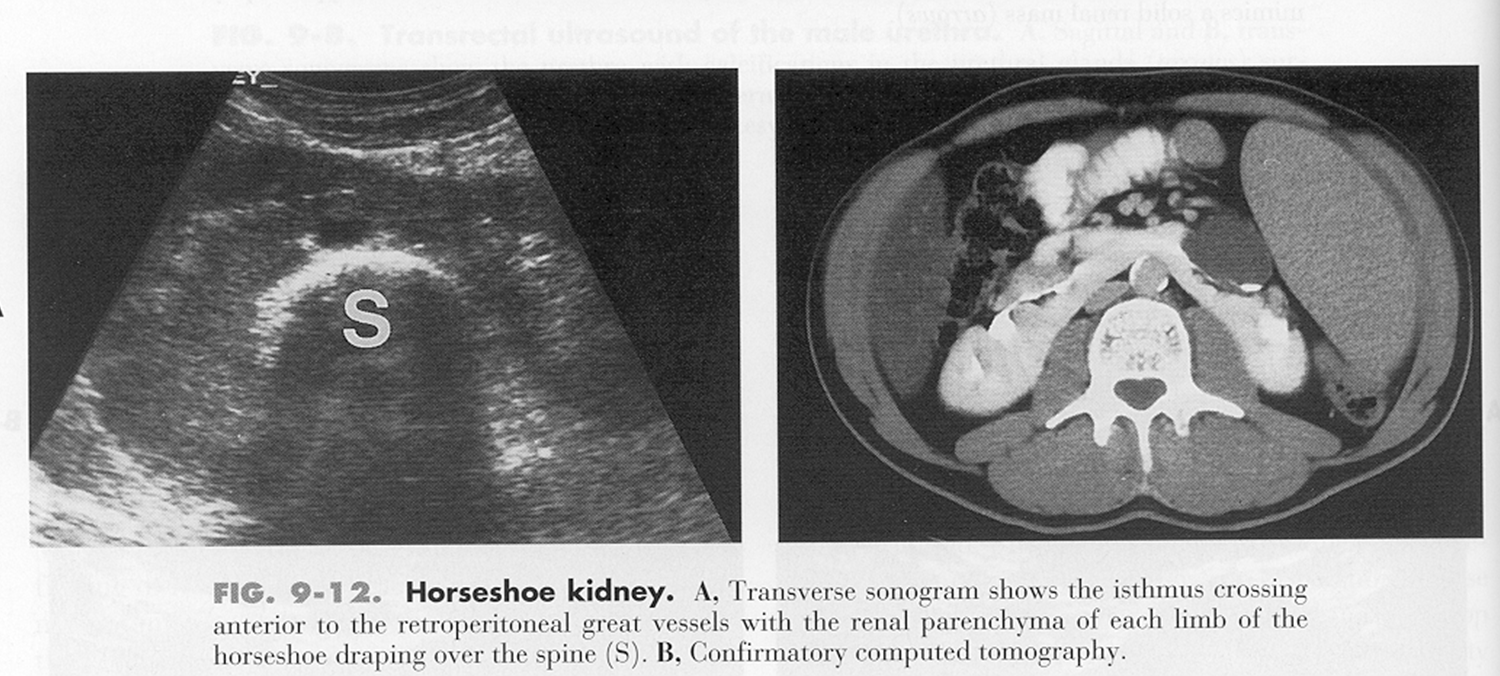
What are these images showing?
Horseshoe Kidney
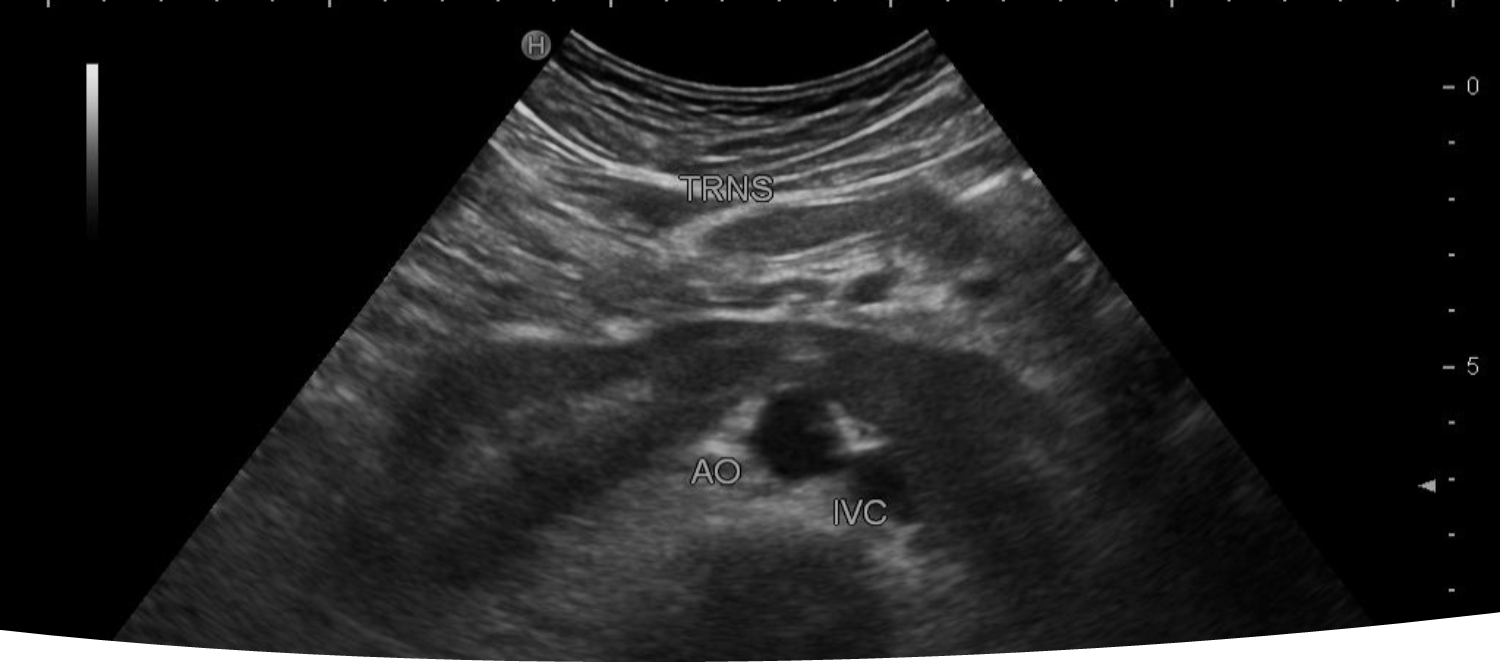
What is being shown in the image above?
Transverse image of the right and left kidney showing the inferior poles connected and crossing anterior to the IVC and Aorta.
What is the responsibility of the sonographer before an exam?
Review a patient’s chart & previous exams (US, X-ray, CT, MRI, IVP, Lab work) & gather adequate patient history
What does the sonographer scan and evaluate?
Size & shape of kidneys
Location of mass lesion
Look for distortion of renal or ureter structure
Look for stones or gas within kidney
Look at surrounding structures
US appearance of a Cystic Renal Mass?
Smooth, thin well-defined border
Round or oval
Sharp interface between cyst & renal parenchyma
Anechoic
Increased Posterior enhancement
US appearance of a Solid Renal Mass?
Irregular borders
Low-level echoes
Poor through transmission
Increased Attenuation
US appearance of a Complex Renal Mass?
Mixed echogenicity
Necrosis
Hemorrhage
Calcification
Abscess
Characteristics of both cystic & solid
What are all the aspirations of renal masses?
Simple Cyst (I)
Mildly complex cyst (II)
Mildly complex (IIF)
Indeterminate lesion (III)
Malignant lesion (IV)