Plant Science Exam 2
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Which of the following describes an herbaceous perennial plant?
Lives for more than two years and is not woody
The GROUND tissue of a plant is:
all tissue which is not vascular or dermal
Tissue which consists of living cells with thin primary cell walls, typically functioning in photosynthesis or storage is called___.
Parenchyma
Cell division, which results in new growth in plants, occurs at localized regions called___.
meristems
Where is the secondary cell wall found in a plant cell?
Between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall
Root hairs are ___.
Elongated epidermal cells
Which meristem replaces cells crushed and sloughed off from the root tip during growth?
Apical
In a eudicot primary root cross section, the tissue between the epidermis and the endodermis is called the __.
cortex
The water-proof band of suberin found around the cell walls of the endodermis of roots is called the ___.
Casparian strip
Sugar beets from which table sugar is extracted are
storage roots
What is the function of guard cells?
Regulate the size of stomatal pores
Of the terms below, which is the incorrect description of leaf arrangements of a stem?
Combined
Where do the leaves of most plants have a greater density of stomata?
On the underside of the leaf
How are vascular bundles arranged in a monocot stem?
They are scattered throughout the stem
A difference between herbaceous stems and woody stems are:
lateral meristem growth
What is a rhizome?
A horizontal underground stem
Which of the following terms apply to water movement in plants?
cohesion, adhesion, and root pressure
Guttation represents morning dew on plants
-True or false?
False
In an herbaceous eudicot stem, the pith is located:
towards the inside of the vascular bundles
Stems function in:
Internal transport, growth, and structural support
An egg cell fertilized by a sperm cell results in a single diploid cell called a(n) __.
Zygote
What are the characteristics of bat-pollinated flowers?
Dull white petals, strong fruity scent, night-blooming
Which of the following is a simple fruit with several fused carpels?
Tomato
How do the sperm get to the egg in angiosperms (flowering plants)?
They are carried by the pollen tube
What is the ovule-bearing reproductive unit of a flower?
carpel
Which of the following structures develops into a seed?
ovule
What flower structure develops into a fruit?
ovary
Name the nutritive tissue formed in the developing seed following fertilization of the polar nuclei.
Endosperm
The absorption of water by a seed prior to germination is called ____.
Imbibition
Name the type of fruit derived from a single flower with many free carpels
Aggregate
Flowers pollinated by insects are usually:
yellow or blue
The secondary xylem is also known as:
wood
Which of these is not capable of secondary growth?
monocots
The generative cell in pollen, produces 1 sperm cells
True or false?
False (produces 2)
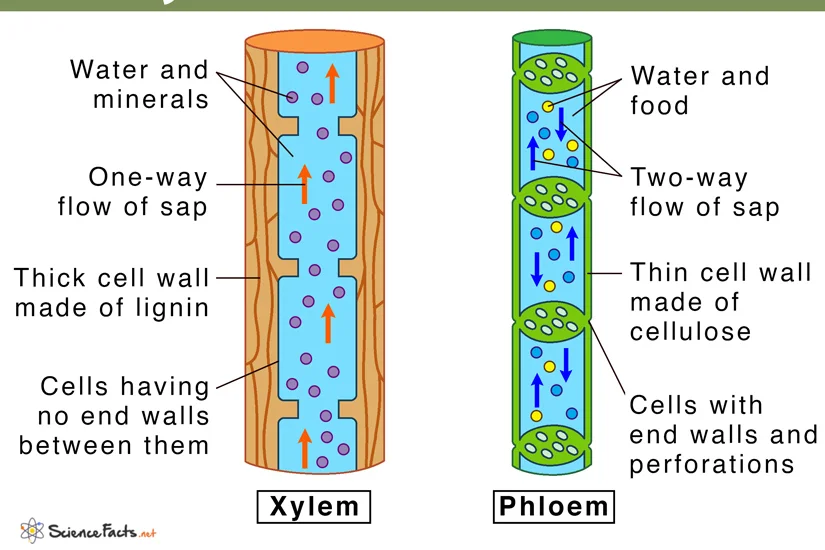
Xylem and phloem make up the:
vascular tissue system
Which process requires MEISOSIS?
sporophyte —> spores
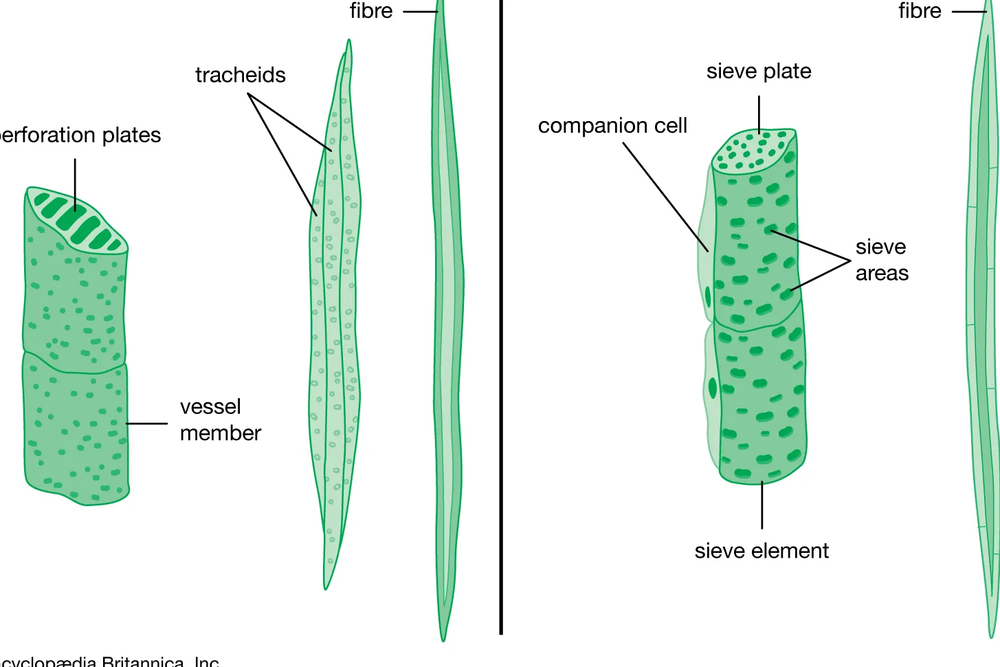
Tracheids and vessel elements are both____ and part of the __
dead ; xylem
Pollen contains:
a tube cell and generative cell
Which of these cells have no nucleus?
sieve tube elements
How many megaspores survive? (after the ovule undergoes meiosis)
1
The MAIN function of the meristem is:
cell division
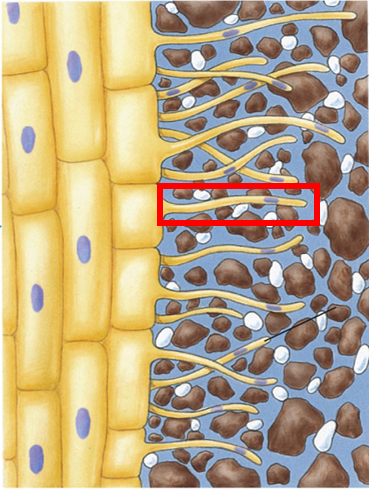
The red highlighted box in the image shows ___, they are extensions of _____ cells.
root hairs; epidermal
Which of the below do only MONOCOT roots have?
pith
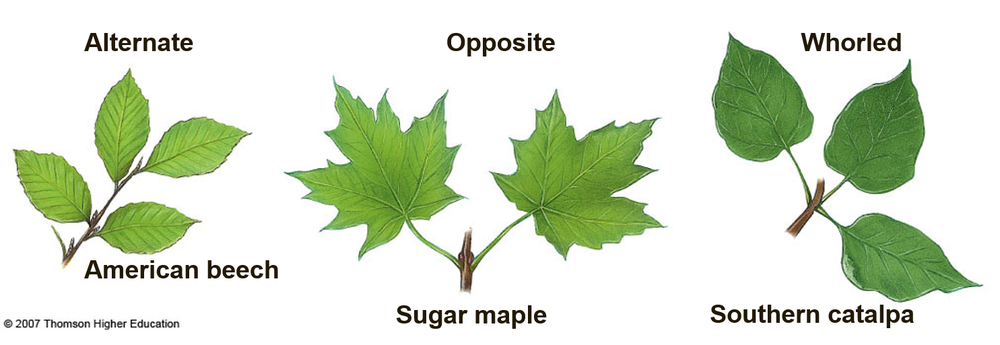
This picture compare different leaf ___.
arrangements
Osmosis is the driving force for __ transport.
sugar
Fruits produced from ONE flower containing several carpels are __
aggregate fruits
Guard cell opening is triggered by:
blue light
Periderm is also known as _____ and is made by the ___.
outer bark; cork cambium
Which of theses forces does help water move upward?
root pressure, adhesion/cohesion, and transpiration
Sugar transport requires active transport
True or false?
True
Which of these is the male part of a flower?
anther
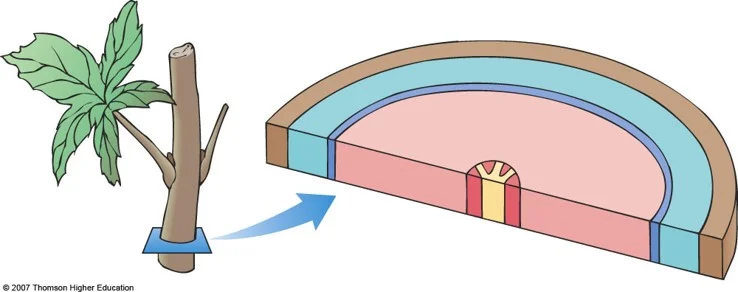
What is the dark blue region?
vascular cambium
The central cell is fertilized and becomes ____, its ploidy is ___
endosperm; 3n
DICOT stems have a ___ arrangement of vascular bundles and _____ have a pith
radial; do
A flower that is white and blooms at night is most likely pollinated by:
bats
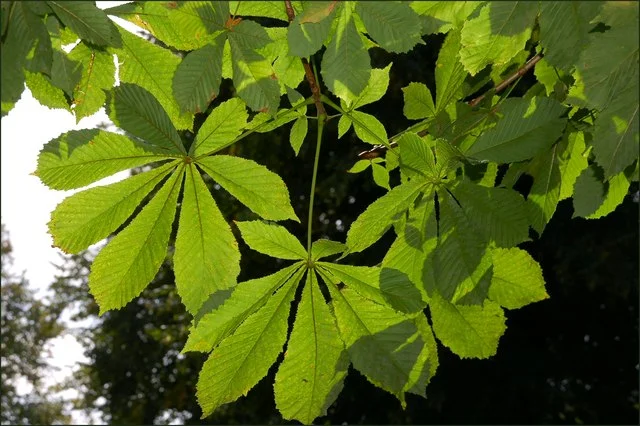

In this photo, the leaf form is ___, the arrangement is _____.
palmately compound; whorled
Ovules mature into ___, ovaries mature into ___.
seeds; fruit
Fruits produced from fused carpels from MANY flowers are:
multiple fruits
Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells make up:
ground tissue system
A root is not uniform along its length but has distinct zones. Starting at the tip, these zones are which of the following?
Root cap -----> apical meristem ------> zone of elongation ------> zone of maturation/root hairs
The leaf of poison ivy has three leaflets attached to the end of the petiole. This leaf is:
palmately compound
Which of the following is the order in which flower parts are attached to the receptacle, from lowest to highest?
Sepals ----> petals ----> stamens ----> carpels
Root hairs are part of the
epidermis
The vascular bundles of herbaceous eudicot stems are
arranged in a ring around the pith
In plants with secondary growth, the "wood" is
the secondary xylem
Special openings at the tips of leaf veins through which liquid water is exuded are -------.
hydathodes.
How do the sperm get to the egg in angiosperms?
They are carried by the pollen tube.
A fruit developing from a single flower with many separate ovaries, such as a blackberry is called____.
aggregate
The leaf abscission zone is
at the base of the petiole