Telomerase and Aging
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What happens when telomeres reach critically short lengths in cells without telomerase?
Cells stop proliferating and enter permanent / irreversible cell cycle arrest (cell senescence).
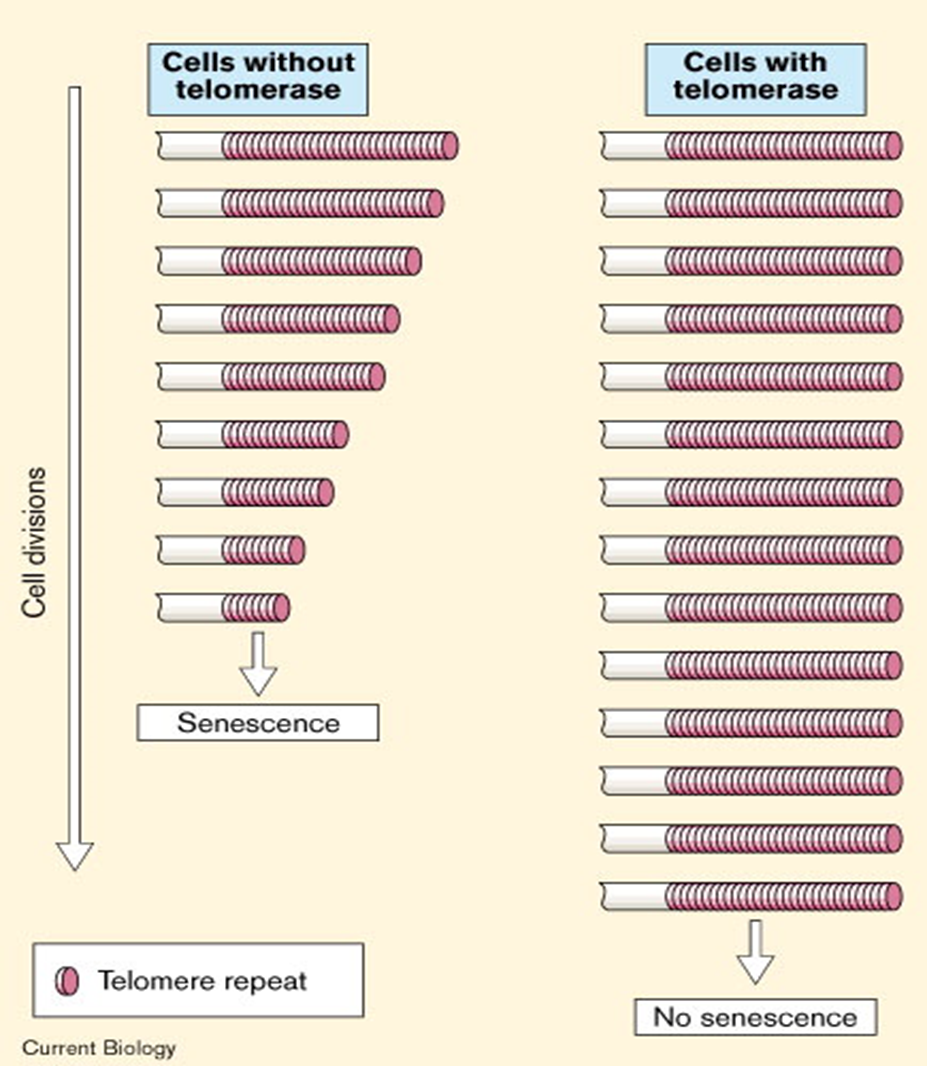
senescence can act as __________
tumor suppression mechanism
Hayflick limit is
maximum number of times a normal somatic cell can divide before it stops dividing and enters a state of cellular senescence.
a form of cellular aging
immortal cell have
high telomerase activity that maintains telomere length allowing unlimited divisions and preventing senescence
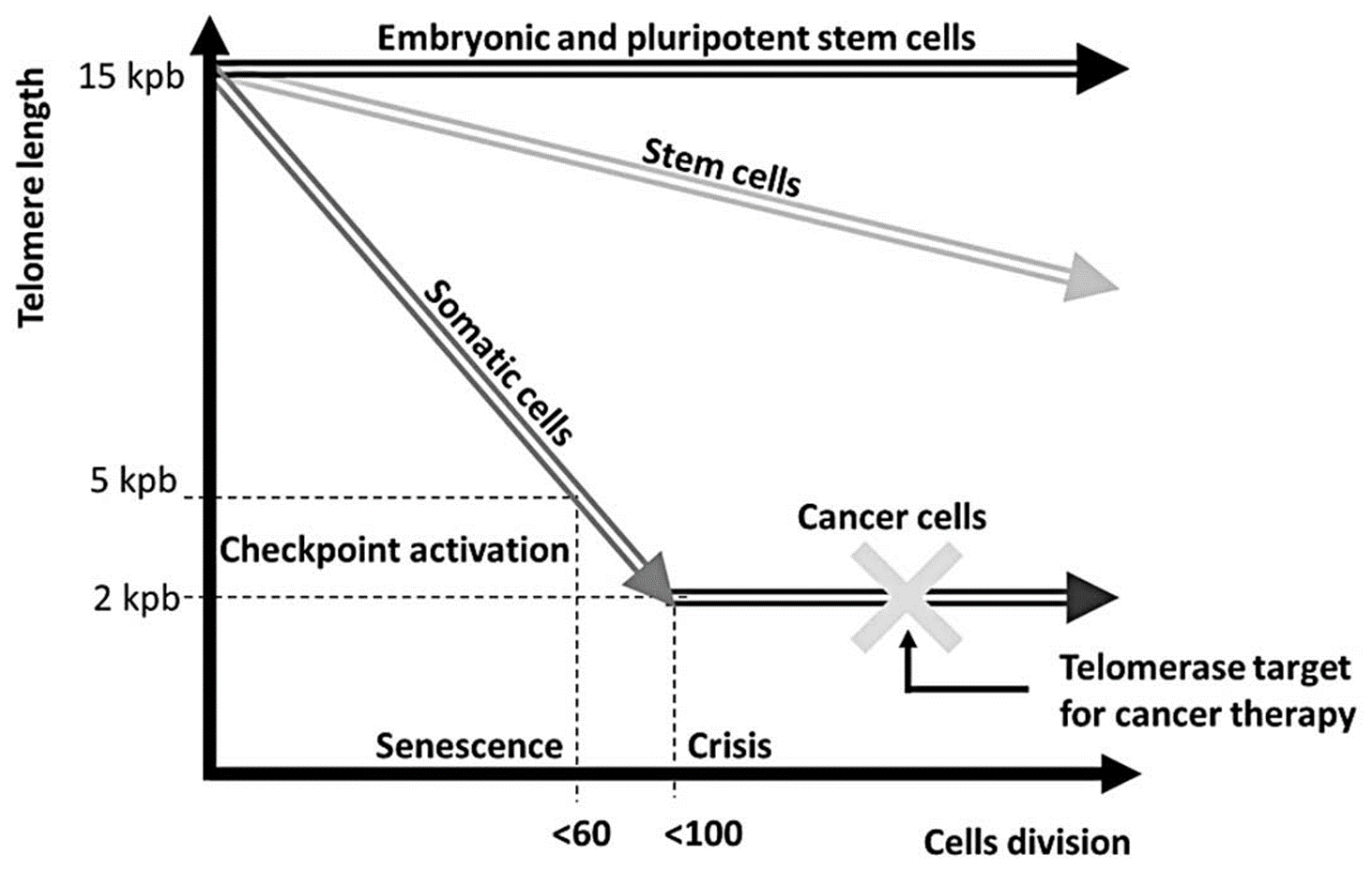
Telomere length and telomerase activity___________
varies in different cell types of an organism
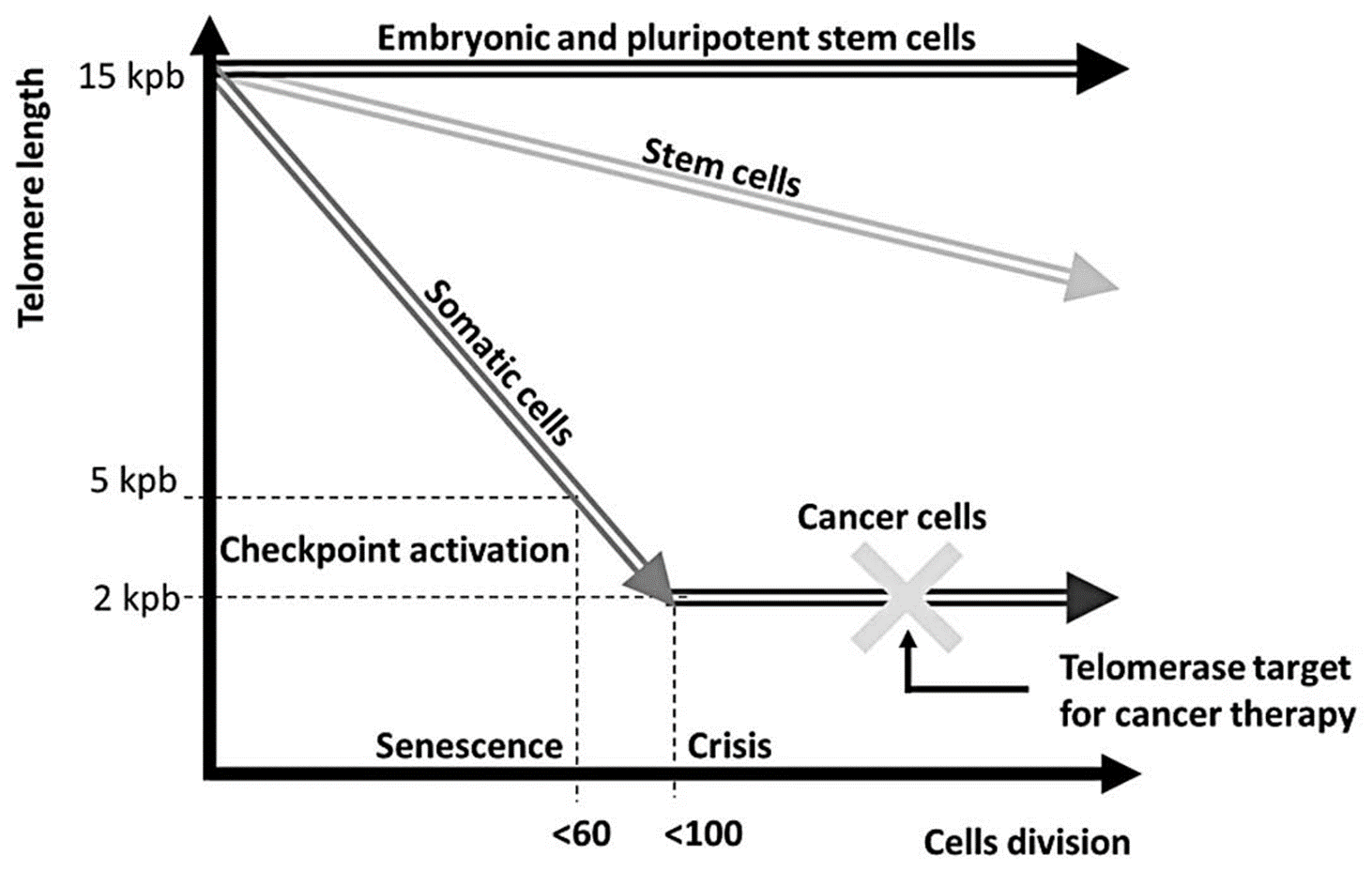
Embryonic and pluripotent stem cells have
high telomerase activity → maintain telomere length
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): Found in the inner cell mass of a blastocyst during early embryonic development.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): Somatic cells reprogrammed to a pluripotent state in vitro.
Germ Cells: Precursors to sperm and eggs, maintaining high telomerase activity to protect telomeres for reproductive purposes.
Tissue Stem Cells have
medium telomerase activity → gradual decrease in telomere length
Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs): Found in the bone marrow, responsible for generating blood cells.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Found in various tissues like bone marrow, fat, and umbilical cord, involved in tissue repair.
Satellite Cells: Muscle stem cells that aid in muscle repair and regeneration.
Telomerase Activity:
embryonic and pluripotent stem cells → high telomerase activity to maintain indefinite proliferation
tissue stem cells → lower telomerase activity to balance repair and cancer suppression.
Progenitor and differentiated cells → typically exhibit negligible telomerase activity, leading to gradual telomere shortening and eventual senescence.
progenitor and differentiated cells have
low/absent telomerase activity → senescence
Differentiated Cells / Specified Cells (progenitor)
Fibroblasts: Cells that produce collagen and extracellular matrix in connective tissues.
Keratinocytes: Skin cells forming the epidermis, with limited capacity for division.
Hepatocytes: Liver cells with some regenerative ability but low telomerase activity.
Senescence of tissue stem cells may contribute to __________
aging
TERC mRNA of telomere knockout result in
defects in tissue homeostasis
infertility increases with generation → germ line stem cell apoptosis
Diskeratosys Congenita like phenotypes: due to limited tissue stem cell proliferation
other disease due to poor telomere maintenance / premature aging
defective closure of neural tube
small size / atrophy of the intestine
abnormal skin pigmentation
defective skin/nail/hair regeneration
bone marrow failure
death
TERT (protein component) Over expressed Mice
Live longer
higher incidence of cancer
revealed that balance between cancer and telomere length
What factors, aside from telomerase and telomere length, contribute to organismal aging?
Epigenetic changes and spurious transcription.
Accumulation of mutations due to replication errors and other challenges.
Changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) or cellular composition of the stem cell niche.
Altered signals disrupting cell-cell communication.
Endocrine signals (e.g., differences between young and old blood).
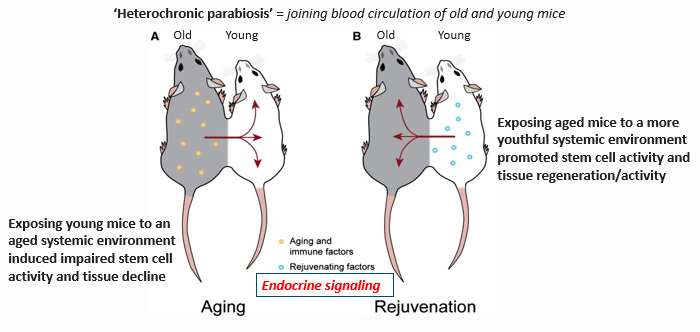
What role do circulatory factors play in aging and stem cell decline?
Circulatory factors, including endocrine signals, affect the systemic environment:
Aging blood introduces inflammatory and immune factors that impair stem cell function.
Young blood provides rejuvenating factors that promote regeneration.
What are the primary hallmarks of aging and their impact?
cause cellular damage:
Genomic instability (mutations)
Telomere attrition (shortening of telomeres)
Epigenetic alterations (modifications to gene expression)
Loss of proteostasis (protein function)
What are the antagonistic hallmarks of aging, and how do they respond to damage?
responses to damage:
Deregulated nutrient-sensing (Metabolic imbalances)
Mitochondrial dysfunction (Energy deficits)
Cellular senescence (irreversible arrest of the cell cycle)
What are the integrative hallmarks of aging, and what do they result in?
culminate in aging phenotypes:
Stem cell exhaustion → decline in the function, number, or regenerative capacity of stem cells over time causing Reduced tissue regeneration, aging, increased disease risk
Altered intercellular communication (dysregulated signaling) → Inflammaging, impaired tissue function, cancer progression
Telomerase activity process
telomerase recognizes the telomere repeat sequence located at the end of chromosomes
Telomerase with its integral RNA template adds additional telomere repeats
Primer attaches to the added telomere region
polymerase alpha completes the lagging strand
Telomere is
Repetitive nucleotide sequence that caps the ends of linear chromosomes → thousands of TTAGGG
attracts telomerase to the chromosome ends
constitutive heterochromatic (condensed) region that is a devoid of genes
Telomerase is
Enzyme that elongates telomeres, synthesizing the repetitive nucleotide sequences found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
carries its own RNA template → used to add multiple copies of the same repetitive DNA sequence to the lagging strand template
DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides to the _______ an existing polynucleotide chain
3’ end
DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA from 5’ to 3
What Are Regenerative Tissues?
Cells that require frequent cell turnover or repair to maintain their function throughout life.
stem cells dependent to replenish lost or damaged cells.
Skin
Intestinal lining
Bone marrow
Liver
** NONE OF THESE ARE STEM, IPS, OR GERM CELLS
These will gradually die
what are proliferating tissues
tissues in which cells are actively dividing (proliferating) to support growth, maintenance, or repair