Neurobiology unit 1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
dendrite
neurites convey information toward cell body (receives information)
soma
sell body of neuron (contains nucleus) integrates info, is also the metabolic center
axon
neurites convey info away from soma, sometimes over long distances (sending info)
synaptic terminal
ouput of neuron, passed along to target
convergence
number of inputs to a single neuron; reflects ability to integrate signals
divergence
number of targets innervated by one neuron
glia
non-neuronal cells, have no active electrical response, small, and have symmetrical branches;
They provide physical support, regulate extracellular env, and produce myelin
astrocytes
most numerous and diverse macroglia, surround blood vessels, migrate to site of neural injury and proliferate to aid in repairing damaged neural tissue
oligodendrocytes
predominate in white matter, extend multiple arms to myelinate multiple axons within the CNS, insulate cells in the CNS
microglia
survey the CNS to combat infection, infiltrate ones and scavenge for damage and infeciton
somatic nervous system
controls voluntary muscles and transmits info
sympathetic nervous system
arouses body to expend energy (fight or flight)
parasympathetic nervous system
calms body to conserve and maintain energy
PET scan
measures radioactive glucose in brain; acquires signals more slowly and approaches spacial resolution of fMRI
fMRI
measures neuronal activity in the brain by measuring rate of oxygenated to deoxygenated blood in brain; allows for good balance between spacial and temporal resolution
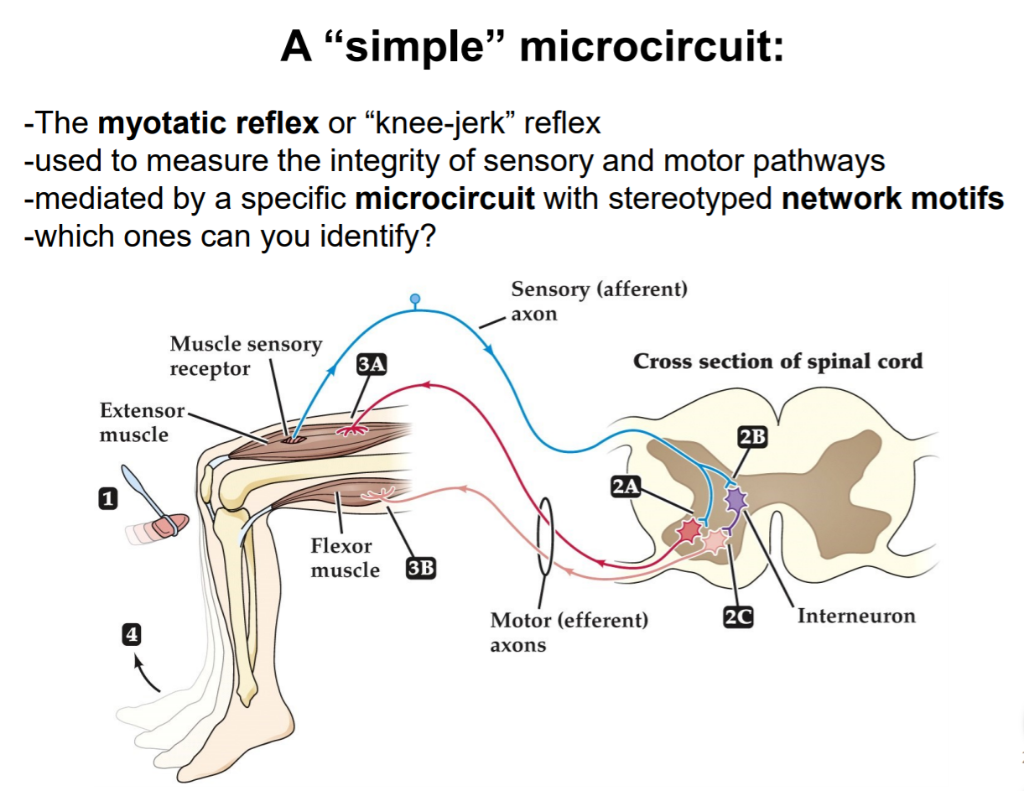
myotatic reflex cycle
hammer tap —> sensory neuron —> motor neuron (extensor) —> interneuron —> motor neuron (flexor) —> leg extends
anterograde tracer
maps connections from source to termination (soma —> down axon)
retrograde tracer
maps connections from termination to origin (up axon—> to soma)
tract tracing
brain mapping with high spacial resolution, produces lots of data and hypothesis, but is very invasive and time sensitive
DTI (diffusion tensor imaging)
brain mapping thatmeasures magnetic fields to calculate the diffusion of water molecules
maps the trajectory of axons
can be conducted in living humans and animals
amphipathic
the phospholipid structure is ______ (hydrophilic and phobic region)
hydrophilic head
part of phospholipid that contains the phosphate and charged group
hydrophobic head
part of phospholipid that contains the fatty acids
hydrophobic and small polar molecules
molecules that can passively move across the plasma membrane
diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium is reached
fluid mosaic
term to model the plasma membrane made of bilayer, proteins, and carbohydrates
integral membrane proteins
proteins that span the entire membrane
peripheral membrane proteins
proteins that do not span the entire membrane and are usually temporary
large polar molecules and ions
molecules that cannot pass through the membrane passively
facilitated diffusion
ion channels facilitate ions through the channel, or transport/carrier proteins
ion channels
allow ions to diffuse down the concentration gradient; can be selective or gated
transport/carrier proteins
allows large molecules to diffuse through membrane from area of high to low concentration
active transport
moves ions against their concentration gradient; require energy
Na+/K+ pump
makes a decrease in electrical charge inside the cell; for every 2 K+ pumped into the cell, 3 Na+ are pumped out
-70 mV
resting membrane potential is about _____
electrical potential
uneven distribution of charge forms basis for __________
electrochemical gradient
ion transporters moving ions across the plasma membrane create an ________; a reparation of charge across the membrane
ATPases
_____ create an ion concentration gradient and separation of charge, creating an electrical and chemical gradient which mediates ion movement
electrochemical gradient
the aggregate force of the chemical gradient and electrical potential which mediate ion movement; the net effect of the chemical and electrical gradient
resting potential
the result of ion concentration gradients and selective permeability
nernst equation
the voltage across a membrane that exactly counteracts the movement of ions from the side with high to the side with low concentration