resp. - care of pt w pulmonary embolism
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
focus on nursing CARE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
oxygen therapy
admin of O2 at concentration greater of room air
boost % that pt is taking in
goal: increase O2 availability to lungs/tissue
reduces effort of breathing
reduces cardiac stress
low-flow
room air and supplemental oxygen
inconsistent or unknown O2 concentration
delivery options: traditional nasal cannula, mask (simple, partial rebreather, non-rebreather)
high-flow
total inspired air (meet or exceed demand)
precise O2 concentration
delivery options: venturi mask, high flow nasal cannula, mechanical ventilation
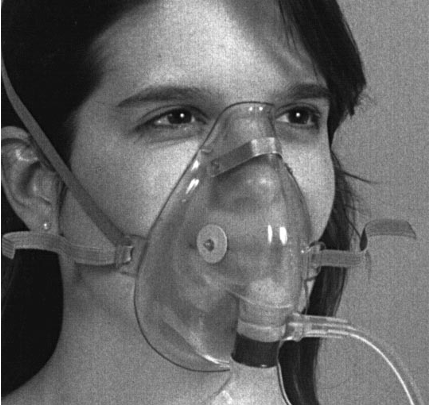
non-rebreather
one-way valves - only getting new air, exhale out old (think name)
O2 reservoir → bag
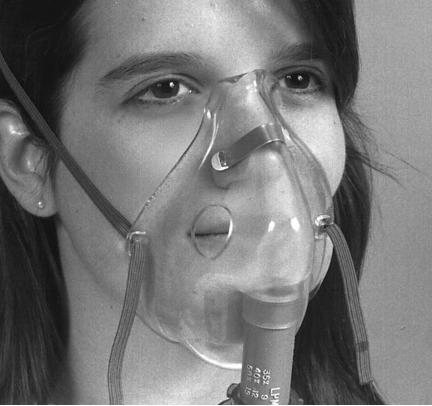
venturi mask
v for valve, open
not reservoir, but open gaps for room air
emergency use of oxygen
nurses can apply low flow w/o order
nasal cannula, simple mask, partial rebreather, non-rebreather
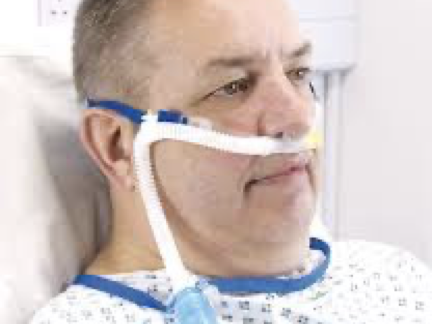
high flow oxygen therapy
newer form
meets or exceeds inspiratory flow demand
must be heated and humidified for comfort (irritating to nasal passages)
no built-in monitoring capabilities → freq. assessment needed
oxygen toxicity - manifestations
from too much oxygen
headaches, substernal discomfort, dyspnea, alveolar atelectasis, paresthesia, restlessness, anxiety, fatigue, malaise, confusion, refractory hypoxemia
oxygen toxicity - assess
chest tightness, respiratory rate, breath sounds, O2 sat, numbness/tingling of extremities, activty lvl, general attitude, change in mentation
oxygen toxicity - intervention
monitor O2 flow, total therapy time
assess w change in therapy, initiated at correct dose
PEEP
positive end-expiratory pressure: maintains airway pressure above atmospheric airway pressure at end of expiration; may be used w either spontaneous or mechanical ventilation
CPAP
continuous positive airway pressure - maintains positive airway pressure throughout whole respiratory cycle; used w spontaneous ventilation
BiPAP
bilevel positive airway pressure
similar to CPAP, noninvasive
two lvl of pressure - w higher pressure during inhalation
used for COPD, sleep apnea, pneumonia
use of PEEP/CPAP/BiPAP
helps prevent micro atelectasis
maintains slight positive lung pressure
maintain slightly expanded lung tissue
allows lower % of oxygen to be effective
positive and expiratory pressure
pt education - oxygen therapy
maintain therapy at prescribed settings
notify physician of
frequent headaches, increased anxiety, blue tinge, drowsiness, new confusion, restlessness
change in established breathing pattern - slow, shallow, difficult, irregular
safety
pt education - safety precautions
no open flames, combustible products
exercise care w electrical devices, use explosion-proof plugs
storage: cart or collar cylinder, avoid bumping them, post “no smoking”, keep in well ventilated area
therapy - examine
whole patient, monitor VS + color for cyanosis
respiratory retraction, nasal flaring
false or low oxygen saturation reading: cold extremities or fingers
hypothermia or hypovolemia
false high: anemia, CO reading
incentive spirometer - use
exhale (breathe out) normally and then:
mouthpiece in mouth + close lips tightly around
inhale slowly and deeply through mouthpiece
when you cannot inhale any longer, remove mouthpiece and hold breath for at least 5 seconds
exhale normally
pulmonary embolism
an embolus that clogs an artery (or arteries) in pulmonary vascular system
pulmonary emboli - vascular problem
blood flow obstructed → poor lung perfusion of lung tissue
originate in venous system, in left heart if affecting brain
pulmonary emboli - respiratory response
air gets into lungs but enough oxygen can’t get into obstructed blood stream → SOB
pulmonary emboli - basic dx
chest X-ray: dilated pulmonary artery
spiral CT scan
EKG: sinus tachy, r heart strain
d-dimer: rules out blood clot
VQ scan - perfusion is issue
pulmonary emboli - gold standard
pulmonary angiogram (arteriogram)
dye injected through cath treaded through vena cava into R side of heart
allows for direct visual of obstruction, assessment of perfusion deficit
pulmonary emboli - risk factors [START EDITS]
Age 50+
Venous stasis
Prolonged immobility
Hypercoagulability
Previous history of thrombophlebitis
Damage to vessel walls
Orthopedic surgery
Hip>knee for PE
Certain disease states: heart disease, trauma, postoperative, diabetes mellitus, COPD
Other conditions: pregnancy, post-partum, supplemental estrogen, birth control pill, obesity, constrictive clothing
pulmonary emboli - consequences
death can result only 1 hour from onset
pulmonary emboli - priorities
early recognition of clinical pic, early treatment
pulmonary emboli - human response
non-specific, non-diagnostic
anxiety, fear
chest pain
cough - may have bloody sputum
crackles, rub near area of embolus
sudden dyspnea - when clot lodges
syncope, tachycardia, tachypnea, diaphoresis
pulmonary emboli - chest pain
Sudden, pleuritic; substernal
May become worse with deep breaths, coughing, eating, bending, or stooping
Worsens with exertion but won't recede with rest
prevent PE - NI
Identify presence of risk factors
Early ambulation
Reposition frequently
Active/passive leg exercises
AE hose/SCDs
Change IV sites according to best practices
Patient/family education
Avoid prolonged sitting, legs and feet in dependent position, knees crossed, adequate hydration, wear AE hose/SCDs, etc.
Recognize PE clinical presentation
PE - emergency NI: independent
Vital Signs
Assess lung sounds
Assess respiratory rate/effort
Administer O2: Low flow systems
High Fowler’s position
EKG: Dysrhythmia, R-side failure
PE - emergency: with orders NI
Establish IV access
Labs: H&H, electrolytes, d-Dimer
Medications: Morphine, Sedation, Anti-anxiety
PE - emergency medical management
Protect airway
Manage pain/anxiety
Confirm diagnosis
Pharmacology: Thrombolytic, Anticoagulation (i.e. heparin, warfarin)
Surgery: Transvenous catheter embolectomy for major/massive PE, Implantation of umbrella filter (Greenfield or IVC filter)
Post PE - post-embolectomy or umbrella
Routine post-op care
Assessment, activity/ROM, AE/SCDs, C/T/DB, skin/incision care, hydration, O2 prn
Post-PE: NI
Monitor labs: PT/INR/PTT, platelets
Monitor pulmonary parameters
Monitor respiratory effort
Evaluate all assessment data against previous data
Intervene as appropriate
Alert PCP
Document
Patient/family education
PE: patient education
Anti-coagulant medication
Importance of
Labs as ordered, Dosing as ordered
Safety: S/S of bleeding – joints, brain; OTCs, Alert of HCPs
Self care
Notify MD if/when…
Post-op
Activity
Incision care
Notify MD if/when…
Post-PE: patient education
Alert all future HCP of PE history
Stay active; get out of bed as soon as possible after illness
On long car or plane trips, take breaks/walk at least every 2 hours
Change positions often
Do leg exercises if you are on bed rest
Don’t cross your legs
Get immediate medical attention for….