TOGAF
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
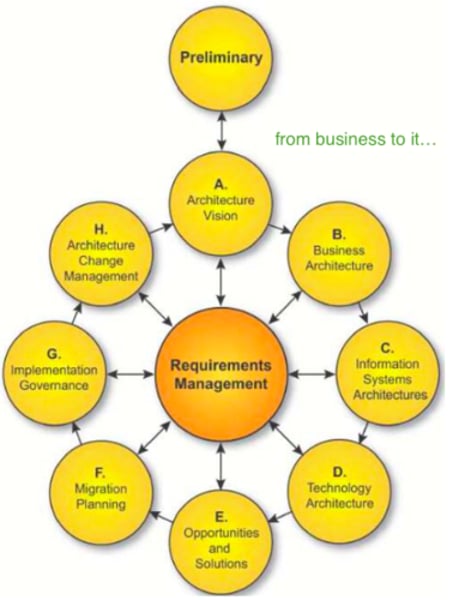
What is ADM?
Architecture Development Method
Phase A of ADM
Architecture Vision
Name all phases of ADM
As depicted
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/TOGAF-92-Phases-and-Artifacts_fig1_338353469
What is BDAT
BDAT -
Business architecture,
Data&Application architecture,
Technology architecture
Last ongoing phase?
Requirements management. Phase ongoing
Architecture Capability Framework?
Sets KPIs, plans, budgets
What is a deliverable in TOGAF?
Documentation of the Architecture. It is discussed with customer and validated.
A powerpoint - is not a deliverable.
What is an Architectural artifacts in TOGAF?
Architectural artifacts are created in order to describe a system, solution, or state of the enterprise.
Catalogs, Matrices, Diagrams.
"environment" of a system
Is the context determining the setting and circumstances of all influences upon a system. The environment of a system includes developmental, technological, business, operational, organizational, political, economic, legal, regulatory, ecological, and social influences.
What is Capability in TOGAF?
Ability that an organization, person, or system possess.
Business Capability
A particular ability, that a business may possess or exchange to achieve a specific purpose.
Application Architecture
A description of the structure and interaction of the applications as
groups of capabilities that provide key business functions and manage the data assets.
Architectural style
The combination of distinctive features related to the specific context within
which architecture is performed or expressed; a collection of principles and characteristics that steer
or constrain how an architecture is formed.
What is Architecture according TOGAF
The STRUCTURE of components,
their inter-RELATIONSHIPS,
and the PRINCIPLES and GUIDELINES
governing their DESIGN and EVOLUTION over time.
Architecture Building Block
A constituent of the architecture model that describes a single
aspect of the overall model.
Architecture Continuum
A part of the Enterprise Continuum. A repository of architectural
elements with increasing detail and specialization
Architecture Development Method
The core of the TOGAF framework. A multi-phase,
iterative approach to develop and use an Enterprise Architecture to shape and govern business
transformation and implementation projects.
Architecture Domain
The architectural area being considered. The TOGAF framework has
four primary architecture domains: business, data, application, and technology.
Architecture Framework
A conceptual structure used to plan, develop, implement, govern,
and sustain an architecture.
Architecture governance
The practice of monitoring and directing architecture-related work.
Architecture Principle
A qualitative statement of intent that should be met by the architecture.
Architecture View
A representation of a system from the perspective of a related set of
concerns.
Architecture Viewpoint
A specification of the conventions for a particular kind of architecture
view.
Architecture Vision
A succinct description of the Target Architecture that describes its business
value and the changes to the enterprise that will result from its successful deployment. It serves
as an aspirational vision and a boundary for detailed architecture development.
Artifact: An architectural work product that describes an aspect of the architecture.
Artifact in TOGAF
An architectural work product that describes an aspect of the architecture.
Baseline
A specification that has been formally reviewed and agreed upon, that thereafter
serves as the basis for further development or change and that can be changed only through
formal change control procedures or a type of procedure such as configuration management.
Building Block
A (potentially re-usable) component of enterprise capability that can be
combined with other building blocks to deliver architectures and solutions.
Business Architecture
A representation of holistic, multi-dimensional business views of:
capabilities, end-to-end value delivery, information, and organizational structure; and the
relationships among these business views and strategies, products, policies, initiatives, and
stakeholders.
Business Capability
A particular ability that a business may possess or exchange to achieve
a specific purpose.
Business governance
Concerned with ensuring that the business processes and policies
(and their operation) deliver the business outcomes and adhere to relevant business regulation.
Capability
An ability that an organization, person, or system possesses.
Concern
An interest in a system relevant to one or more of its stakeholders.
Course of Action
Direction and focus provided by strategic goals and objectives, often to
deliver the value proposition characterized in the business model.
Data Architecture
A description of the structure and interaction of the enterprise's major types
and sources of data, logical data assets, physical data assets, and data management resources.
Deliverable
An architectural work product that is contractually specified and in turn formally
reviewed, agreed, and signed off by the stakeholders.
enterprise
The highest level (typically) of description of an organization and typically covers
all missions and functions. An enterprise will often span multiple organizations.
Foundation Architecture
Generic building blocks, their inter-relationships with other building
blocks, combined with the principles and guidelines that provide a foundation on which more
specific architectures can be built.
gap
A statement of difference between two states.
governance
The discipline of monitoring, managing, and steering a business (or IS/IT
landscape) to deliver the business outcome required.
Information
Any communication or representation of facts, data, or opinions, in any medium or
form, including textual, numerical, graphic, cartographic, narrative, or audio-visual forms.
Information Technology
1. The lifecycle management of information and related technology used by an organization.
2. An umbrella term that includes all or some of the subject areas relating to the computer industry.
34 │ Copyright © 2018
Course Book | TOGAF® 9 Training Course: Level 1 and 2 Combined
Training content licensed to alexander.friesen@siemens.com, issued on 29-01-2021, edition 2021 by Digicomp Academy AG
3. A term commonly assigned to a department within an organization tasked with provisioning
some or all of the domains described in (2) above.
4. Alternate names commonly adopted include Information Services, Information Management,
et al.
logical architecture
An implementation-independent definition of the architecture, often grouping related
physical entities according to their purpose and structure.
Metadata
Data about data, of any sort in any media, that describes the characteristics of an
entity.
Metamodel
A model that describes how and with what the architecture will be described in a
structured way.
Method
A defined, repeatable approach to address a particular type of problem.
Modeling
A technique through construction of models which enables a subject to be
represented in a form that enables reasoning, insight, and clarity concerning the essence of the
subject matter.
objective
A time-bounded milestone for an organization used to demonstrate progress towards
a goal.
reference Model
An abstract framework for understanding significant relationships among the
entities of [an] environment, and for the development of consistent standards or specifications
supporting that environment.
repository
A system that manages all of the data of an enterprise, including data and process
models and other enterprise information.
https://circle.visual-paradigm.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/storing-files-into-architecture-repository-768x355.png
requirement
A statement of need that must be met by a particular architecture or work
package.
service
1. A repeatable activity; a discrete behavior that a building block may be requested or otherwise
triggered to perform.
2. An element of behavior that provides specific functionality in response to requests from
actors or other services.
solution Architecture
A description of a discrete and focused business operation or activity
and how IS/IT supports that operation.
solution Building Block
A candidate solution which conforms to the specification of an
Architecture Building Block.
strategic Architecture
A summary formal description of the enterprise, providing an organizing
framework for operational and change activity, and an executive-level, long-term view for
direction setting.
Target Architecture
The description of a future state of the architecture being developed for
an organization.
Technology Architecture
A description of the structure and interaction of the technology
services, and technology components.
Transition Architecture
A formal description of one state of the architecture at an architecturally
significant point in time.
Value stream
A representation of an end-to-end collection of value-adding activities that create
an overall result for a customer, stakeholder, or end user.
Examples of Requirements:
Business requirements represent the high-level objectives of the organization or the customer who requests the system
User requirements describe user goals or tasks that the users must be able to perform with the product
..
Example:
"The system should be able to encrypt communication"
Examples of Architecture-Principles
Data is an Asset: Data is an asset that has value to the enterprise and is managed accordingly.
Data is Shared: Users have access to the data necessary to perform their duties; therefore, data is shared across enterprise functions and organizations.
Data is Accessible: Data is accessible for users to perform their functions.
Data Trustee: Each data element has a trustee accountable for data quality.
Data Security: Data is protected from unauthorized use and disclosure.
Technology Independence: Applications are independent of specific technology choices and therefore can operate on a variety of technology platforms.
Ease-of-Use: Applications are easy to use. The underlying technology is transparent to users, so they can concentrate on tasks at hand.
TOGAF Guidelines what are they for?
Guidelines include adapting the ADM to deal with a number of usage scenarios and applying the ADM across the Architecture Landscape
Guidelines for the ADM The guidelines for adapting the ADM are as follows:
- Applying ITERATIONS to the ADM: This guideline describes the concept of iteration and lists the potential strategies that can be used for applying iterations to the ADM. The iterations help to manage the complexity of implementing the ADM.
- Applying the ADM Across the Architecture Landscape: This guideline describes various types of architecture engagements that occur at different levels of the enterprise. Further, this guideline recommends how to implement these architecture engagement types.
TOGAF techniques - what are they for?
Techniques assist in the implementation of particular tasks in the ADM.
Techniques of the ADM
The techniques for applying the ADM are as follows:
- Architecture Principles — Architecture principles are general rules and guidelines for the
enterprise. These are used for deploying IT resources across the enterprise.
- Stakeholder Management — This technique describes the routine for managing various
stakeholders so as to gather their support for the architecture projects.
- Architecture Patterns — This technique describes various activities involved in using
architecture patterns.
- Gap Analysis — This technique is used for identifying the differences between the baseline and target architecture.
- Migration Planning Techniques — This set of techniques help in migration planning in Phases E and F.28
- Interoperability Requirements — This technique describes a procedure for determining
interoperability requirements.
- Business Transformation Readiness Assessment — This technique describes the procedure
for identifying business transformation issues.
- Risk Management — This technique provides the routine for managing risk during an
architecture or business transformation project.
- Capability-based Planning — This technique describes the routine of capability-based
planning.
Additional guidelines and techniques are available in the TOGAF Library (for example, guidelines and
techniques for Business Scenarios)
The TOGAF Library (https://publications.opengroup.org/togaf-library) includes an evolving list of documents
providing suggestion and guidance for the application of the TOGAF framework within specific context
How many parts of TOGAF do exist? Name them
six parts:
1 introduction
2 Arch Development Method ADM
3 ADM Guidelines and Techniques
- GUIDELINES gives you iterations in ADM,
- TECHNIQUES give you help for particular tasks: stakeholder management, arch patterns, gap analysis, migration planing, risk management
4 Arch Content Framework-https://pubs.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf91-doc/arch/chap36.html
Describes arch-work products:
Deliverables,
made of artefacts (tables, matrices)
describing building blocks
5 Arch Continuum and Tools - discusses appropriate taxonomies and tools to categorize and store the outputs of architecture activity
6 Arch Capability Framework - This part discusses the organization, processes, skills, roles, and responsibilities required to establish and operate an architecture function
"Architecture work" documents
REQUEST of architecture work (from Preliminary)
Project Background: Description of requests made by the sponsoring organization underlying the need for architecture work.
Summary of Request: A brief description of the changes required to achieve. Think about the problems to be solved by developing an architecture. You may also include the rationale and the objectives of changes.
Organization Sponsors: Sponsors are identified and appointed to ensure that the rest of the architecture development activities have resources to proceed and to clear support of the business management.
Business Imperative
- Business Mission Statements
- Business Goals
- Strategic Plans of the Business
- Changes in the Business Environment
- Purpose of Architecture Work
Success Criteria
Project Timeframe
Constraints
-------------------------------------
-------------------------------------
STATEMENT of Architecture work (from all other phases)
Architecture Objectives
List and describe the objectives that need to be fulfilled by the target architecture.
Stakeholders
Risks and Assumptions
Architecture Project Plan and Schedule
Review and confirm the architecture project plan and schedule.
-------------------------------------
-------------------------------------
Architecture DEFINITION document (from technology architecture phase)
This document describes the baseline and target technology architecture, and gap analysis for your project. It contains the core architectural artifacts created during a project.
How many main iterations exist in TOGAF,
which can be sub-devided
4:
Preliminary - ArchVision:
Name "Arch Capability Iteration"
Business Arch - Migration planing
Name "Arch Development Iteration"
Oportunities and Solution - Migration Planing
Name "Transition Plan Iteration"
Name "Arch Governance"
Arch Governance - Change Management
Viewpoint library
A collection of the specifications of architecture viewpoints contained in the
Reference Library portion of the Architecture Repository.
ADM Preliminary objectives
Determine the architecture capability desired by the organization
Establish the architecture capability
ADM Preliminary Inputs
EXTERNAL INPUTS:
TOGAF framework
Other major relevant frameworks
NON ARCH INPUTS:
Board Strategies
Board business plans
Business strategies
Business principles
Business goals
Business drivers
IT strategy
ADM Preliminary Outputs
REQUEST FOR architecture WORK
Organizational Model of Enterprise architecture
Tailored architecture framework
Architecture governance framework
Architecture principles
Reference to Inputs.
Requirements Management steps
Baseline Requirements
Monitor requirements
Identify changed requirements
Record prios
Outputs of Requirement Management step
Requirement Spec Revised
Assumptions
Guidelines
Success Measures
Constraints
App Service contracts
Requirement Impact assessment
What is the impact of changed requirements?
What are Objective of the Architecture Vision phase
Create an aspirational vision of architecture.
Get an approval of architecture work.
What are inputs of the Architecture Vision phase?
External to enterprise:
- architecture reference materials
Non-arch inputs:
- REQUEST FOR architecture WORK
- business principles
business goals,
business drivers
Arch inputs:
- org. model
- arch. framework incl. principles
- architecture documentation
what are OUTPUTS of the Architecture Vision phase
- APPROVED statement of work
- refined statements of business principles, goals, drivers
- arch principles
- Capability assessment
- Tailored arch framework
- arch. vision including
-- problem desribtion
-- objective of statement of arch work
-- summary views
-- business scenario
-- refined key high-lvl stakeholder requirements
- draft arch. definition document incl
- baseline business, data, application and tech. architecture 0.1
- target business, data, application and technology arch 0.1
- communication plan
- additional content populating the arch repository
The OBJECTIVES of the Business Architectures Phase
- Develop TARGET BUSINESS ARCHITECTURE
describing how the enterprise needs to operate to achieve the business goal and respond to
strategic drivers set out in the ARCHITECTURE VISION,
in a way that addresses the request for Architecture Work and stakeholder concerns
- identify candidates Arch. Roadmap components
based upon gaps between the Baseline and Target Business Architecture
The INPUTS of business Architecture Phase
External
- arch reference materials
Non-arch inputs:
- REQUEST FOR architecture WORK
- business principles
business goals,
business drivers
- capability asessment
- communications plan
Arch-inputs:
- org. model
- tailored arch. framework
- arch. principles
- enterprise continuum
- arch. repository
- arh VISION
- draft arch. definition document
The OUTPUTS of BUSINESS ARCHITECTURE VISION
- refined statements of business principles, goals, drivers
- statement of architecture work
- validated business principles, business goals, business drivers
- arch. principles
- draft ARCHITECTURE DEFINITION document containing content updates
- DETAILED BASELINE business architecture version 1.0
- DETAILED TARGET BUSINESS ARCHITECTURE, version 1.0
- Views corresponding to selected viewpoints addressing key stackeholder CONCERNS
Draft architecture requirements specification, including
- gap analysis
- technical requirements
- updated business requirements
Business architecture components of an architecture roadmap
Objectives of Information Architecture Systems Architecture
- Develop the target information systems (Data and Application)
- Identify architecture roadmap components
The INPUT of the Info System Architecture
EXTERNAL reference materials
- Architecture reference materials
Non Architecture input:
- Request for architecture work
- capability assessment
- communication plan
Architecture inputs:
- Architecture VISION
- BUSINESS architecture COMPONENTS of an architecture roadmap
- Organization model for enterprise architecture
- tailored architecture framework
- Data and Architecture principles
- statement of architecture work
- Architecture repository
- draft architecture definition
- draft architecture requirement spec
The OUTPUT of the Info System Architecture
- INFORMATION System COMPONENTS of an architecture MAP
- validated statement of Arch Work
- validated (or new) data and application principles
- draft architecture definition document, containing content updates
-- baseline data and app architecture
-- target data and app architecture
- Draft architecture requirements specification, including content updates in
-- GAP ANALYSIS results
-- relevant technical requirements
-- constrains of the technology architecture
-- updated business requirements
-- updated data and application requirements
Objectives of Technology Architecture
- Develop the target technology architecture
- Identify the roadmap components for candidate architecture
INPUTS of Technology Architecture
EXTERNAL reference materials
- Architecture reference materials
- Product information on candidate products
NON Architectural inputs
- Request for architecture work
- capability assessment
- communication plan
Architecture inputs:
- Architecture VISION
- BUSINESS, DATA and APPLICATION ARCHITECTURE COMPONENTS (of an architecture roadmap)
- Organizational model
- tailored architecture framework
- technlogy principles
- statement of architecture work
- architecture repository
- draft architecture definition document
- draft architecture REQUIREMENT SPECIFICATION
OUTPUTS of Technology Architecture
- TECHNOLOGY ARCHITECTURE COMPONENTS (of an architecture roadmap)
- Draft architecture REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION specification, including content updates (The Architecture Requirements Specification provides a quantitative view of the solution, stating MEASURABLE CRITERIA, KPIs that must be met during the implementation of the architecture.)
- GAP ANALYSIS results
- requirements output from Phases B and C
- Updated technology requirements
- Draft architecture DEFINITION specification, including content updates
- BASELINE TECHNOLOGY architecture, version 1
- TARGET TECHNOLOGY architecture, version 1
- technology architecture views
- Statement of Architecture work
- validated technology principles or new technology principles ( if generated)
objectives of OPPORTUNITIES AND SOLUTIONS
ROADMAP - Generate the initial complete version of the architecture ROADMAP
Determine whether an incremental approach is required and if so identify TRANSITION ARCHITECTURES that will deliver continuous business value.
Define the overall Solution Building Blocks to finalize the Target Architecture based on the Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs).
INPUTS Opportunities and Solutions
EXTERNAL reference materials
- Architecture reference materials
- Product information on candidate products
NON Architectural inputs
- PLANING METHODOLOGIES
- Request for architecture work
- capability assessment
- communication plan
Architectural inputs
- CANDIDATE architecture ROADMAP components from Phases B,C and D
- Organizational model for Enterprise Architecture.
- Governance models and frameworks.
- Tailored architecture framework.
- Statement of architecture work.
- Architecture vision.
- Architecture repository.
- Draft architecture definition document.
- Draft architecture requirements specification.
- Change requests for existing programs and projects.
STEPS for Opportunities and Solutions
Review and consolidate gap analysis results from Phases B to D.
Identify transition architectures
Identify and group major work packages.
Formulate implementation and migration strategy
Confirm readiness and risk for business transformation
OUTPUTS of Opportunities and Solutions
Architecture roadmap, including
- Identification of transitions architectures, if any
- Implementation recommendations:
-- Criteria measures of effectiveness
-- Risk and Issues
-- Solution Building Blocks
- Implementation and migration plan version 0.1, including
What is a transition architecture?
Shows the formal description of one state of the architecture at a particular point of time.
Reflects the progress towards target architecture from the baseline architecture.
Can be developed more than once during the architecture development cycle.
Describes the specifics of the increments implemented to reach the target architecture state
OBJECTIVES of migration planing
- finalize the architecture ROADMAP and supporting implementation and migration plan
- ensure that the implementation and migration plan is COORDINATED WITH ENTERPRISE APPROACH
of MANAGING and implementing CHANGE
in the Enterprise overall change portfolio
- ensure that the business value and cost of work
packages and transitions architectures is UNDERSTOOD
by key STACKEHOLDERS
INPUTS of MIGRATION PLANING
- Architecture ROADMAP
- Implementation and migraiton plan version 0.1
Also
Architecture reference materials
Request for architecture work
Capability assessment
Communications plan
Organizational model for Enterprise Architecture
Governance models and frameworks
Tailored architecture framework
Statement of architecture work
Architecture vision
Architecture repository
Draft architecture definition document
Draft architecture requirements specification
Change requests for existing programs and projects
Business and IT capability assessment
STEPS of migration planing phase
- assign a BUSINESS VALUE to each work package
- estimate resource requirements, project TIMING, availability or delivery vehicle.
- prioritize the migration projects
through the conduct of a COST or BENEFIT assessment and RISK validation
OUTPUTS of the Migration Planning Phase
- Detailed implementation and migration plan v 1.0
- implementation governance model
Also
Finalized architecture definition document.
Finalized architecture requirements specification.
Finalized architecture roadmap.
Reusable architecture building blocks.
Requests for architecture work for a new iteration of the ADM cycle, if any.
OBJECTIVES of implementation governance
- Ensure conformance with the TARGET ARCHITECTURE by implementation projects
- Perform appropriate architecture governance functions for the solution and any implementation-driven architecture change requests.
OBJECTIVES of the Architecture Change Management (Permanent) Phase
- Ensure that the architecture LIFECYCLE is MAINTAINED
- Ensure that the architecture GOVERNANCE framework is executed
Enterprise-Repository - what are the blocks in there?
- Architecture-Repository
-BLOCKS IN DIFFERENT QUESTION, CAUSE TOO MANY
Supporting blocks, supporting architecture repository:
- Solution Repository
- Only one "Solution building blocks"
- (Business) Requirements Repository
- Strategic requirements
IMHO strategic goals.
- Segment requirements
IMHO goals arised from segments
- Capability requirements
IMHO capability requests. Like Features, mayby arised from tactical goals.
Wander, whether those requirements do overlap?
https://pubs.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf91-doc/arch/chap41.html#tagfcjh_97
Architecture Repository - what are the building blocks within?
- Architecture Metamodel
- - Architecture Methiods-ADM adopted for Enterprise
- - Content Metamodel - classification, aka. technical, business
- Reference Library
- - organization reference materials
- Architecture Landscape, structured accord. to requirements
- - strategic architectures
- - segment architectures
- - capability architectures
- Standard Information Base
- - Business Standards
- - Data Standards
- - Application Standards
- - Technology Standards
- Governance Log (controlled by Architecture Board)
- - Decision Log
- - Compliance Assesments
- - Capability Assessments
- - Project Portfolio
- - Performance Measurement
- - Calender?
- Architecture capability
- - Skills repository
- - Organization structure
- - Architecture charter
TRM(Technical Reference Model)
TRM together with SIB (Standards Information Base) is
part of the FOUNDATION architecture.
Based on which a more specific solution
can be developed.
High level its made of 3 levels
- Application
- Application Platform - Application Platform in the TOGAF TRM is a single, generic, conceptual entity. From the viewpoint of the TOGAF TRM, the Application Platform contains all possible services.
The Application Platform for a specific Target Architecture will typically NOT be a SINGLE entity, but rather a combination of different entities for different, commonly required functions, such as desktop client, file server, print server, application server
- Communication Infrastructure - provides the basic services to interconnect systems. Internet.
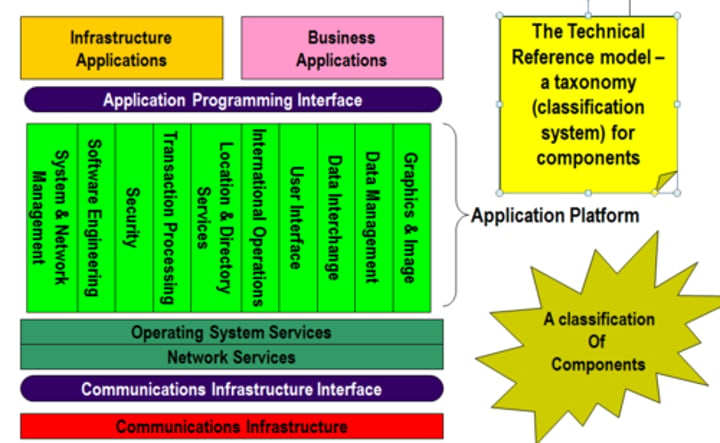
(III-RM) Integrated Information Infrastructure Reference Model
An application focused FOUNDATION ARCHITECTURE,
based on the TRM (technical reference model) subset.
enterprise continuum (architecture continuum, solutions continuum)
https://sparxsystems.fr/resources/gallery/diagrams/architecture/arc-togaf-enterprise-continuum.html
ARCHITECTURE CONTINUUM
classification of architectures of different levels
1. foundation architectures
2. common system architectures
- industry Architectures
3. industry architecture
3. organizations architecture
SOLUTION CONTINUUM
represents the IMPLEMENTATION of architecture from architecture continuum at the right level.
1. products and services
2. system solutions
3. industry solutions
4. organization solutions
Architecture continuum
guides
Solution continuum
Business Scenarios
TECHNIQUE, used to capture the business needs at the beginning of ADM,
mostly during the Architecture Vision phase.