Non-AI Alterations in Digestive Function
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Anticholinergic
class of antiemetic drugs that block the action of acetylcholine ex. Scopolamine
Antihistamine
inhibits the physiological effects of histamine. Ex dimenhydrinate (Gravol), diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Antihistamine
Dimenhydrinate is a ___________ drug
Neuroleptic
reduce nervous tension by depressing nerve functions *prochlorperazine (Stemetil)
Neuroleptic
Prochlorperazine (Stemetil) is a __________ drug
Prokinetic agents
a class of drugs that promote the passage of ingested material in the gastrointestinal tract. *metoclopramide (Maxeran)
Prokinetic agent
Metoclopramide (Maxeran) is a __________
Pro-Kinetic Agents
a class of drugs that promote the passage of ingested material in the gastrointestinal tract. *metoclopramide (Maxeran)
Serotonin blockers
inhibit the action of serotonin Ex. ondansetron (Zofran)
Bulk-Forming
Class of laxative. High fibre, absorbs water to increase bulk. Distendeds bowel to initiate reflex bowel activity.
Bulk-Forming
Psyllium is a type of ________ laxative
Emollient
Class of laxatives that are stool softeners and lubricants. Promote more water and fat in the stools. Lubricate the fecal material and intestinal walls
Hyperosmotic
Class of laxatives that increase fecal water content resulting in bowel distention, increased peristalsis, and evacuation
Hyperosmotic
Glycerin is a type of ___________ laxative
Hyperosmotic
Lactulose is a type of ___________ laxative
Saline
Laxative that increases osmotic pressure within the intestinal tract, causing more water to enter the intestines Result: bowel distention, increased peristalsis, and evacuation. Ex. magnesium sulfate, magnesium hydroxide. Indicated for constipation, removal of helminths and parasites, diagnostic and surgical bowel preparation.
Stimulant
Class of laxative that increases peristalsis via intestinal nerve stimulation. Examples include castor oil, senna (Senekot), cascara, bisacodyl (Dulcolax), Ex-lax. Most likely of all laxatives to cause dependence. Indicated by acute constipation, diagnostic and surgical bowel preparation.
Bulk-Forming
Side effects of _____ laxatives include Impaction, fluid overload
Emollient
Side effects of _____ laxatives include skin rashes, decreased absorption of vitamins
Hyperosmotic
Side effects of _____ laxatives include abdominal bloating, rectal irritation
Saline
Side effects of _____ laxatives include magnesium toxicity (with renal insufficiency), cramping, diarrhea, Increased thirst
Stimulant
Side effects of _____ laxatives include nutrient malabsorption, skin rashes, gastric irritation, rectal irritation
Large Volume
Diarrhea that is indicated by increase in water or secretions or both. Usually a result of sickness
Small Volume
Diarrhea that is indicated by excessive intestinal motility, inflammation, irritation
Motility
Diarrhea that is caused by surgical resection or bypass
Steatorrhea
(Fat in stools) more common of malabsorption syndromes
Absorbents
Class of antidiarrheals that coat the walls of the GI tract. Bind to the causative bacteria or toxin, which is then eliminated through the stool. Examples include Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) activated charcoal. *Decrease the absorption of many medications, cause increased bleeding time when given with anticoagulants.
Anticholinergics or Antispasmodics
Class of antidiarrheals that decrease intestinal muscle tone and peristalsis of GI tract, slowing the movement of fecal matter. Ex. Atropine
Intestinal Flora Modifiers
Class of antidiarrheals that include bacterial cultures of Lactobacillus (normal bacterial flora of GI tract) Creates an unfavorable environment for overgrowth of fungi and bacteria and supply missing bacteria to the GI tract, suppressing the growth of diarrhea-causing bacteria. Useful when antibiotic therapy has killed normal bacterial flora in GI tract. Ex. L. acidophilus
Opiates
Class of antidiarrheals that decrease bowel motility and relieve rectal spasms. Decrease transit time through the bowel, allowing more time for water and electrolytes to be absorbed. Examples: diphenoxylate (Lomotil)
Imodium
loperamide (_______) is the only opiate antidiarrheal available OTC.
Upper GI bleeding
Bleeding from the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. Often caused by bleeding ulcers
Lower GI bleeding
Bleeding from the jejunum, ileum, colon colorectum - can be caused by polyps, inflammatory disease, cancer, or hemorrhoids
Hematemesis
blood in vomitus
Hematochezia
bright blood from rectum
Melena
dark, tarry stools
Occult bleeding
slow chronic blood loss in stool, found by guaiac test, results in iron deficiency anemia
Peptic Ulcers
Ulcers originating in the lower esophagus, duodenal, gastric
Gastric Ulcers
Ulcers that develop adjacent to acid-secreting mucosa. _____ ulcers are an abnormality that increases the mucosal barrier’s permeability to hydrogen ions. Tend to be more chronic compared to peptic ulcers.
Duodenal Ulcers
More frequent than other types of peptic ulcers. Major cause is infection with H. pylori, along with hypersecretion of acid and pepsin combined with inadequate secretion of bicarbonate
Duodenal Ulcers
Pathology and treatment of ___________ includes chronic intermittent pain in epigastric area. Pain beginning 30m->2h postprandial. Pain relieved rapidly with use of antacids. In elderly, first symptom may be perforation or bleed. Need to regulate secretion of acid
Antacids
Acid controlling agents that promote gastric mucosal defense mechanisms. Cause secretion of mucus, bicarbonate, prostaglandins (prevent activation of proton pump). Reduce pain associated with acid-related disorders by raising pH
Aluminum Salts
Antacid that has constipating effects, often used with magnesium to counteract constipation.
Magnesium Salts
Antacid that commonly causes diarrhea; usually used with other agents to counteract this effect. Dangerous when used with renal failure—the failing kidney cannot excrete extra ________, resulting in accumulation
Calcium Salts
Antacid that may cause constipation, result in kidney stones, rebound hyperacidity with prolonged use
Sodium Bicarbonate
Highly soluble antacid, buffers the acidic properties of HCl. Quick onset, but short duration. Produces gas and belching. May cause metabolic alkalosis. Sodium content may cause problems in clients with HF, hypertension, or renal insufficiency ie: Alka seltzer
Antacids
_______ can cause numerous drug interactions by lowering the ability of other drugs to be absorbed into the body, increasing stomach pH, increasing urinary pH (increased secretion of acidic drugs, decreased secretion of basic drugs).
H2 antagonist
Reduces acid secretion by blocking histamine at the receptors of acid-producing parietal cells leading to suppressed HCL production.
H2 antagonist
Cimetidine (Tagamet) is an example of a _________
H2 antagonist
Ranitidine (Zantac) is an example of a __________
H2 antagonist
Indications for ________ include GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease), PUD (Peptic Ulcer Disease), Erosive esophagitis, Adjunct therapy in control of upper GI bleeding, Pathological gastric hypersecretory conditions.
H2 antagonist
Side effects of ________ include headaches, lethargy, confusion, diarrhea, urticaria, sweating, flushing.
Proton Pump Inhibitors
___________ results in achlorhydria - ALL gastric acid secretion is blocked. Drugs include lansoprazole (Prevacid), omeprazole (Losec).
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Indications for __________ include GERD maintenance therapy, erosive esophagitis, short-term treatment of active duodenal and benign gastric ulcers, treatment of H. pylori–induced ulcers
Proton Pump Inhibitor
Pantoprazole is the only _________ medication available for parenteral administration.
Pyloric Obstruction
Narrowing or blocking of opening between stomach and duodenum. Acquired obstruction caused by peptic ulcer disease (more often duodenal ulcers) or carcinoma. Pt becomes more distressed postprandial and later in the day. Develops anorexia and weight loss. Copious vomiting several hours after eating
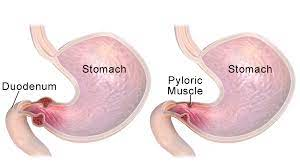
Intestinal Obstruction
anything that prevents normal flow of chyme through intestine. Mechanical blockage, functional obstruction d/t lack of motility
Ulcerative Colitis
Chronic condition causing ulceration of colonic mucosa, usually in rectum and sigmoid colon. Often people between 20-40. Causes are dietary, infectious, genetic and immunologic.
Crohn’s Disease
Inflammatory disorder that can affect any part of the GI tract (mouth -> anus) Risk factors and causes same as ulcerative colitis. Begins in intestinal submucosa and spreads to mucosa and serosa, most common site is ileocolon. May skip areas or be limited to one side of colon. Inflammation may extend into lymphoid tissue. Fistulae may form in perianal area or extend into bladder. No specific symptoms except irritable bowel for several years. Diarrhea most common sign. Look for weight loss and lower abd pain. May be protein, vitamin B12, D, folic acid and calcium deficiencies. Anal manifestations in 30%. At risk for carcinomas of small intestine obstruction, fistulae, abscess formation and blood loss are complications
Appendicitis
Inflammation of vermiform appendix, projection of apex of cecum. Most common surgical emergency of the abdomen Exact cause is controversial, may arise from obstruction ->bacterial infection. May become hypoxic, ulcerates, gangrene may develop. Look for epigastric or periumbilical pain - vague ->increasing over 3-4 hours. Right lower quadrant pain associated with extension of inflammation. N&V, anorexia, fever is common. Serious complications include perforation, peritonitis, and abscess formation. Rebound tenderness, elevated WBC and C-reactive protein. Antibiotics and appendectomy tx of choice
Maldigestion
failure of chemical process of digestion to take place - often caused by deficiencies of enzymes necessary for digestion.
Malabsorption
failure of intestinal mucosa to absorb digested nutrients - results from mucosal disruption caused by gastric or intestinal resection, vascular disorders, or intestinal disease
Exogenous Obesity
obesity caused by too much ingestion
Endogenous Obesity
obesity caused by inherent metabolic problems
Hyperplastic Fat Cells
Increase in the number of fat cells
Hypertrophic Fat Cells
Increase in the size of fat cells
Anorexia Nervosa
as many as 1% of women are adolescent girls. Risk factors include genetic, familial, biologic, psychologic, and social factors. Associated with sexual assault, elderly are experiencing it associated with depression, anxiety and personality disorders. Absence of three consecutive periods
Bulimia Nervosa
Self induced vomiting, laxatives, fasting to oppose the effect of binge eating or excessive exercise. 2 binge eating episodes per week for at least 3 months. Teeth become affected due to acid and eventually tracheoesophageal fistula. Rectal bleeding from laxative use
Hepatitis A
Usual mode of transmission is fecal-oral route. Can be spread by transfusion of infected blood. Spreads rapidly in crowded, unsanitary conditions. Person-person contamination through daycares. Incubation period 4-6 weeks, most contagious from 14 days before symptoms to 3 months post symptoms. Antibodies develop 4 weeks post infection, IgG levels remain high for several years.
Hepatitis B
Transmitted through infected blood, body fluids, needles. Incubation period of 6-8 weeks. Levels of IgG antibodies rise more slowly and remain elevated for years
Hepatitis C
causes most cases of post transfusion hepatitis. RNA virus. Uses a screen for all blood products. Is a risk factor for chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and carcinoma. non curable
Chronic Hepatitis
Persistence of CM and liver inflammation after HAV, HBV (most common), and HCV. Liver function tests remain abnormal >6/12
Cholelithiasis
The presence of gallstones in the gallbladder. Affects about 20% of the population over 40 years of age. More prevalent in women. Unlocalized abdominal discomfort. Eructation. Intolerance to certain foods. In clients with severe pain, cholecystectomy is recommended
Cholecystitis
Acute or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder. Acute cholecystitis is usually caused by a gallstone that cannot pass through the cystic duct. There is RUQ pain of the abdomen and N&V, eructation, flatulence. Diagnosis by ultrasound. Treatment is usually surgery
Acute pancreatitis
Usually due to damage of the biliary tract by alcohol, trauma, infection, or certain drugs. Characterized by severe abdominal pain (epigastric) radiating to the back, fever, anorexia, N&V, jaundice.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Similar to the acute form. In alcohol abuse, there is scarring of the smaller pancreatic ducts. Abdominal pain, N&V, steatorrhea due to decreased pancreatic enzymes. Diabetes mellitus may develop due to decreased pancreatic insulin production.