Comprehensive Guide to Labor, Delivery, and Postpartum Nursing Care
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What marks the beginning of the first stage of labor?
Regular uterine contractions.
What is the endpoint of the first stage of labor?
Full cervical effacement and dilation.
What are the three phases of the first stage of labor?
Latent phase, active phase, and transition phase.
What characterizes the latent phase of labor?
Cervical dilation from 0 to 3 cm with irregular contractions.
What occurs during the active phase of labor?
Cervical dilation from 4 to 7 cm with more intense contractions.
What is the transition phase in labor?
Cervical dilation from 8 to 10 cm, often associated with significant discomfort.
How is the first stage of labor defined according to the new guidelines?
Divided into two phases: latent phase and active phase.
What does the active phase of labor begin at?
6 cm of cervical dilation.
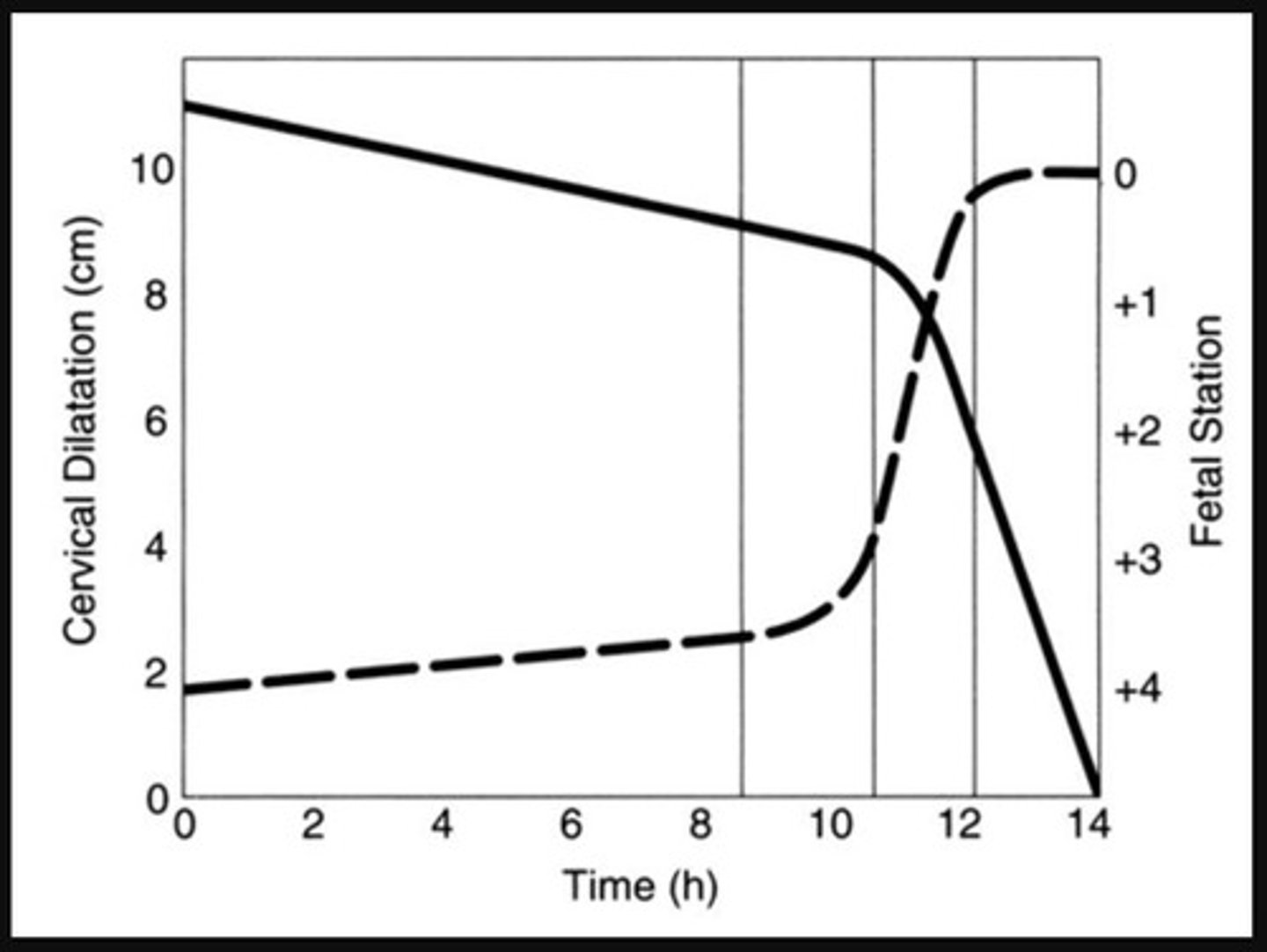
What is Friedman's Labor Curve used for?
To show the relationship between cervical dilation and descent in labor.
What should be assessed to determine if a woman is in true labor?
Contractions and cervical changes.
What is the Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA)?
A law ensuring that a woman is considered in true labor until a qualified provider determines otherwise.
What is the significance of the cervical examination during labor?
To assess cervical effacement, dilation, and fetal descent.
What is assessed during the admission to the labor unit?
Admission data, prenatal data, and psychosocial factors.
What factors should be considered regarding the psychosocial assessment of a laboring woman?
History of sexual abuse, use of substances, and cultural beliefs.
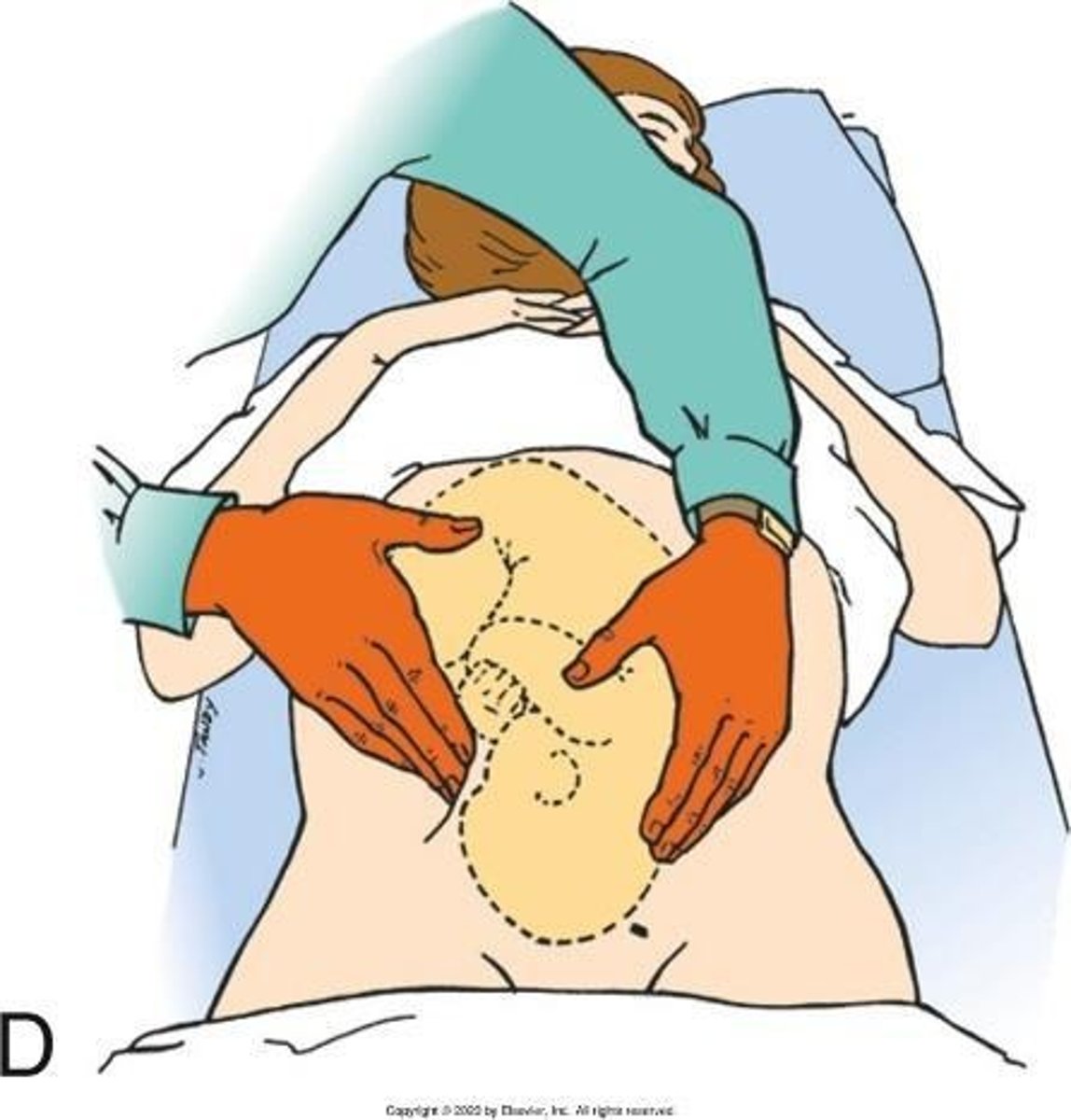
What are Leopold Maneuvers used for?
To assess fetal position and presentation through abdominal palpation.
What laboratory tests are typically performed upon admission in labor?
Urinalysis, complete blood count (CBC), and HIV testing.
What is the purpose of Group Beta Streptococcus (GBS) testing?
To determine if antibiotics are needed to prevent infection during labor.
What should be monitored for signs of infection during labor?
Maternal temperature and vaginal discharge.
What is the role of the nurse in determining true labor?
To perform assessments and examinations to evaluate cervical changes.
What is the importance of assessing fetal heart rate (FHR) during labor?
To monitor fetal well-being and response to labor.
What should be done if a woman is not dilating enough during the active phase?
Augment labor with oxytocin or prepare for a cesarean section.
What is the significance of understanding cultural factors in labor?
To provide culturally competent care and respect the woman's preferences.
What is the recommended action if membranes rupture during labor?
Assess for cervical changes and monitor for signs of infection.
What is the recommended approach for managing pain during labor?
Discuss pain management options with the patient and assess their preferences.
What is the typical duration of the latent phase of labor?
Can last for days or even weeks.
What should be assessed regarding uterine contractions?
Frequency, intensity, and duration.
What is the significance of the 'bloody show' during labor?
It indicates cervical changes and the onset of labor.
What should be monitored for patients with vaginal discharge during labor?
Monitor temperature and start antibiotics if necessary.
What is a key nursing intervention regarding physical care during labor?
Avoid keeping pads on; use chucks and towels for cleanliness.
What is the recommended oral intake during labor?
Provide ice chips and clear fluids as ordered by the doctor.
What should be done regarding intravenous intake during labor?
Always have an IV running, especially for those with a birth plan.
How often should a patient void during labor?
At least every 2 hours to keep the bladder empty.
What is the significance of maintaining a full bladder during labor?
A full bladder can prevent the baby's head from descending properly.
What should be prepared for in case of active labor?
Have oxygen and an ambu bag ready for the baby.
What is the recommended position for a laboring mother?
Avoid lying on the back; ambulation is encouraged.
What are the two phases of the second stage of labor?
Latent phase (calm with passive descent) and Active phase (urge to push).
What is the Ferguson reflex?
The urge to bear down during labor.
What is the purpose of the closed-glottis pushing technique?
It helps manage hypertension during labor.
What is the purpose of an episiotomy?
To facilitate delivery and prevent tearing.
What should be observed during the second stage of labor?
Fetal heart rate, contractions, and maternal position.
What are the advantages of an upright position during labor?
It promotes descent of the fetus and can shorten labor.
What is the role of the support partner during labor?
To assist with comfort measures and maintain the mother's position.
What should be done if a patient experiences intense pressure in the rectum during labor?
Inform the doctor as it indicates the baby is putting pressure on the rectum.
What is the significance of ambulation during labor?
It can help the baby descend and facilitate labor progress.
What is a common practice regarding maternal positioning during labor?
Encourage positions that utilize gravity to aid in descent.
What is the purpose of using a birthing ball during labor?
To help maintain a squatting position and facilitate pelvic relaxation.
What should be done if the mother has an epidural?
Use bed exercises and change positions frequently.
What is the recommended action if a patient has a bulging perineum?
Prepare for imminent birth and monitor closely.
What is the role of the midwife during the second stage of labor?
To observe fetal heart rate and contractions, and assist with delivery.
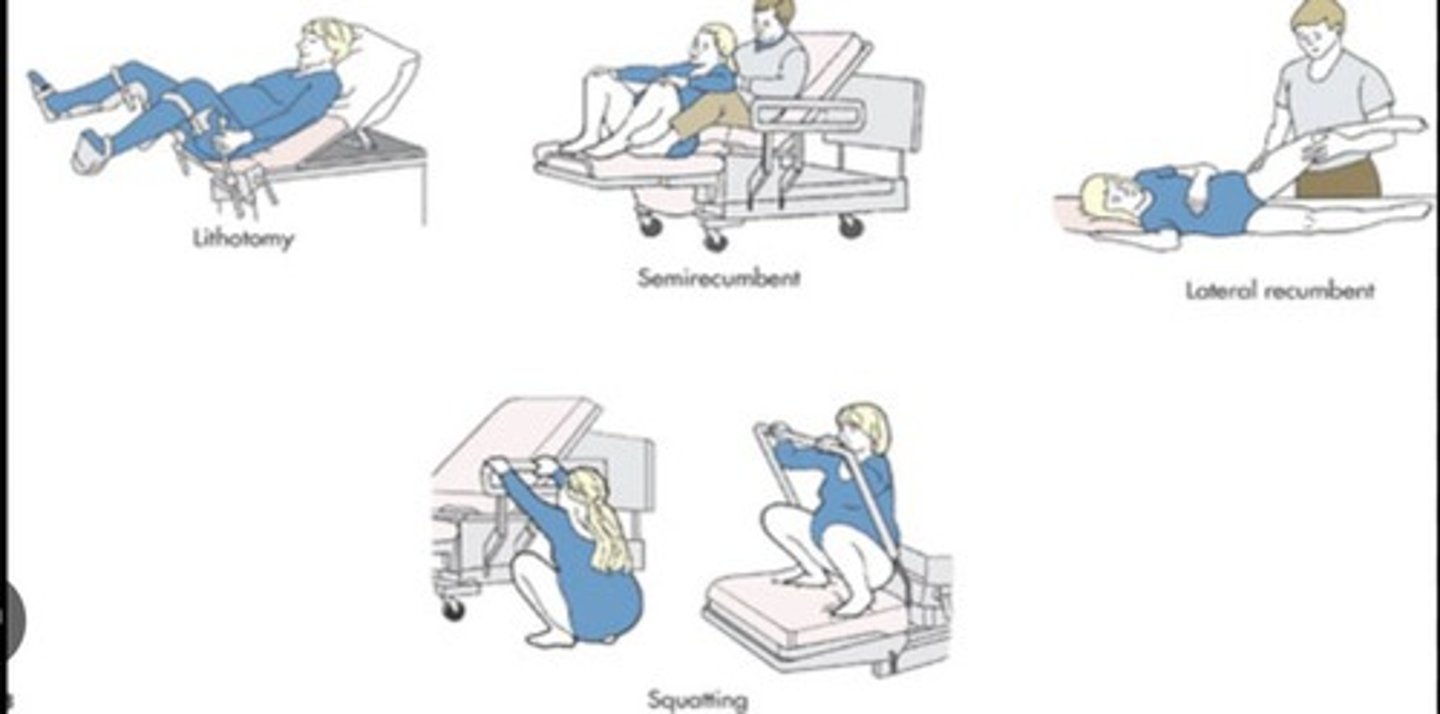
What is the main position for birth in western medicine?
The delivery room or birthing room, typically with the mother on her back.
What is the lithotomy position?
A position where the mother is lying on her back with legs raised and supported, commonly used during childbirth.
What is vertex presentation?
The position where the baby's head is down and presents first during delivery.
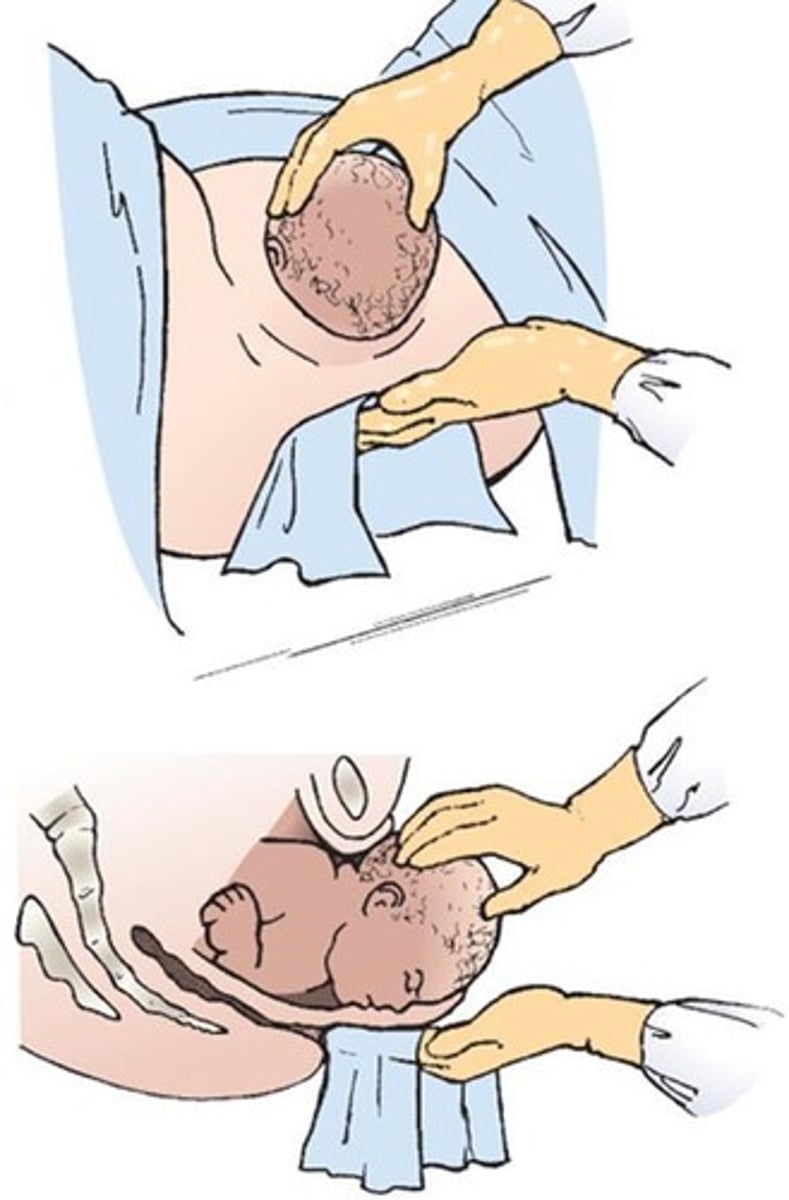
What is the Ritgen maneuver?
A technique used to assist in the delivery of the baby's head to prevent it from getting stuck.
What is a nuchal cord?
A condition where the umbilical cord is wrapped around the baby's neck.
What is fundal pressure and when is it contraindicated?
Fundal pressure involves applying pressure to the abdomen to assist delivery; it is contraindicated in cases of shoulder dystocia.
What is the purpose of immediate assessments after birth?
To ensure the baby is stable, including putting ID bands on the baby and performing the APGAR assessment.
What is skin-to-skin care?
A practice where the newborn is placed directly on the mother's chest to promote bonding and regulate the baby's temperature.
What is a lotus birth?
A practice where the umbilical cord remains attached to the placenta until it naturally separates from the baby.
What are the cardinal movements of labor?
Engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation, and expulsion.
What is delayed cord clamping?
A practice where the umbilical cord is not clamped for at least 30-60 seconds after birth to allow for blood transfer to the newborn.
What is the significance of cord blood banking?
It allows for the collection of stem cells from the umbilical cord for potential future medical use.
What are the four degrees of perineal lacerations?
First degree: skin and vaginal mucosa; Second degree: fascia and muscles; Third degree: external anal sphincter; Fourth degree: through the rectal mucosa.
What is an episiotomy?
An incision made in the perineum to enlarge the vaginal outlet during delivery.
What are the signs that the placenta has separated?
Gush of blood, lengthening of the umbilical cord, and vaginal fullness.
What is the third stage of labor?
The stage from the birth of the baby until the placenta is expelled.
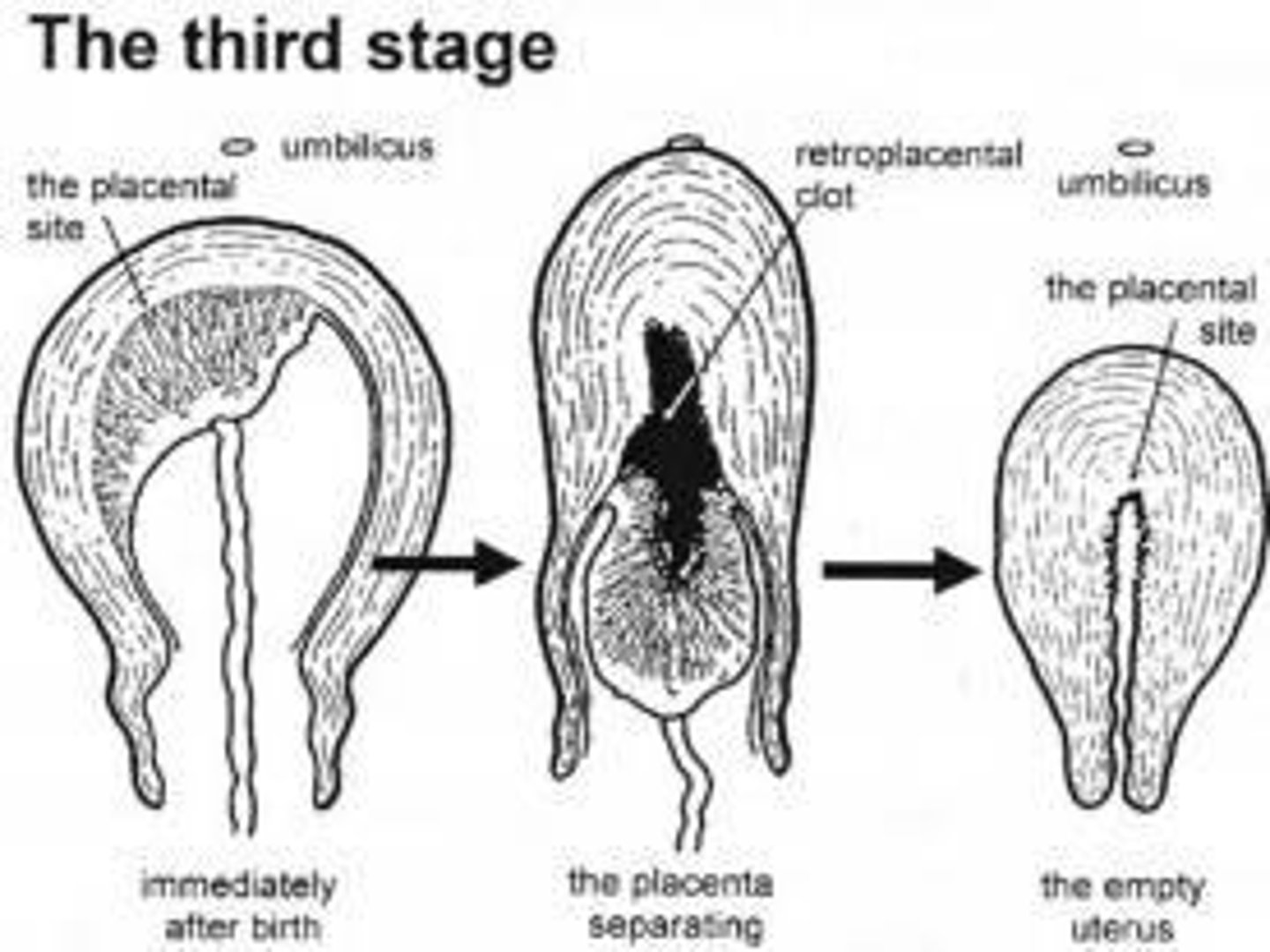
What are the nursing care responsibilities during the third stage of labor?
Monitor for signs of separation, administer oxytocic medications, examine the placenta, and provide emotional support.
What is the fourth stage of labor?
The period following the expulsion of the placenta, lasting until the mother is stable, usually within the first hour.
What are common risk signs during the fourth stage of labor?
Hypotension, tachycardia, excessive bleeding, and a noncontracting uterus.
What is the purpose of fundal massage after delivery?
To promote uterine contraction and prevent excessive bleeding.
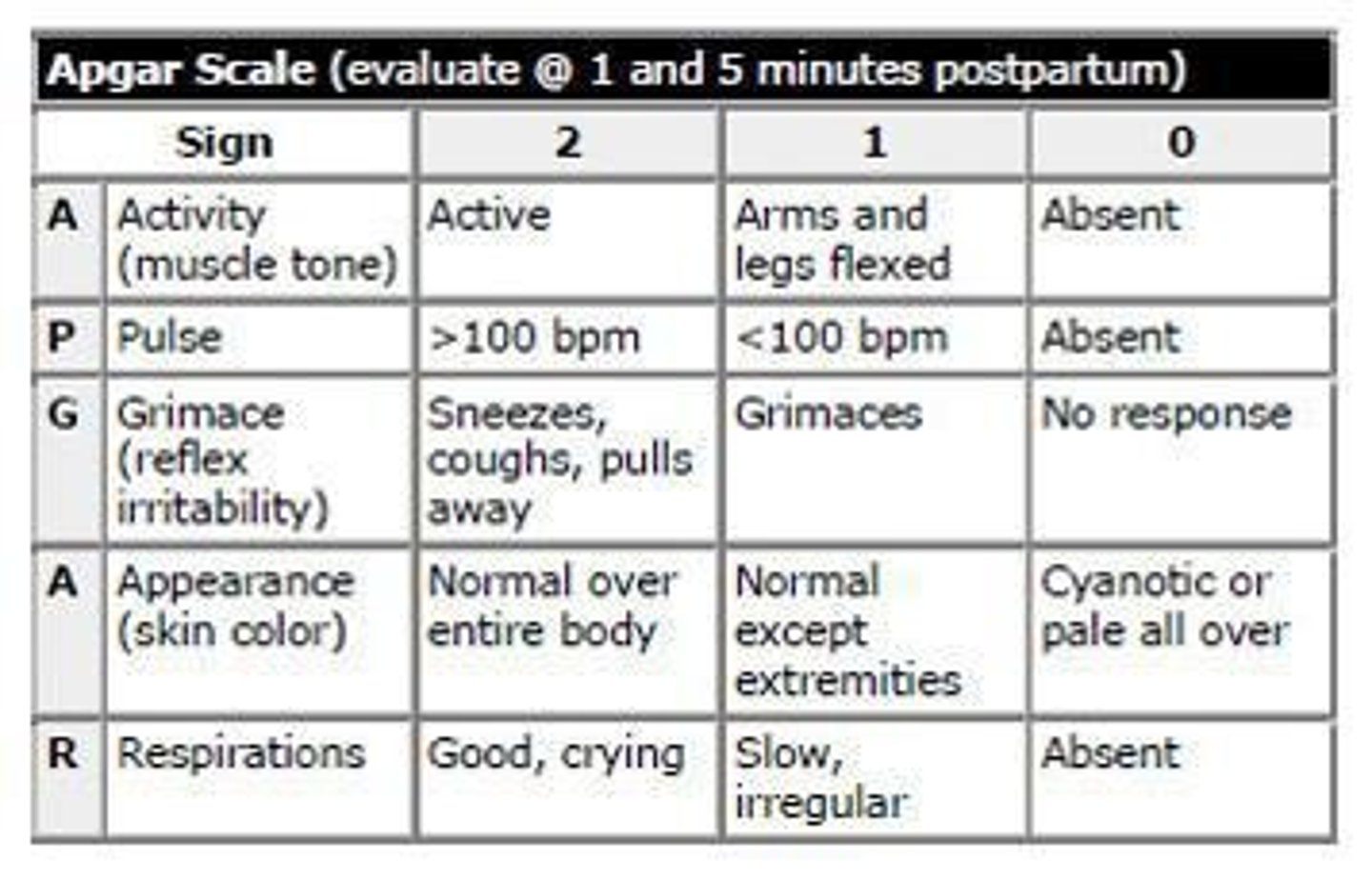
What is the APGAR score?
A quick assessment of the newborn's health based on Appearance, Pulse, Grimace response, Activity, and Respiration.
What is the importance of monitoring vital signs and urine output in postpartum care?
To ensure the mother is stable and to identify any complications early.
What should be done if a mother experiences excessive bleeding postpartum?
Perform fundal massage more vigorously and assess for uterine firmness.
What is the role of the Postanesthesia Recovery (PAR) unit?
To monitor women recovering from cesarean sections or regional anesthesia during childbirth.
What are the components of the PAR score?
Activity, respirations, blood pressure, level of consciousness, and color.
What is the significance of immediate newborn care?
To ensure the newborn's airway is clear, maintain warmth, and properly identify the baby.
What should be done if the newborn's APGAR score is low?
Continue monitoring and provide necessary interventions to stabilize the baby.