Review Bio Final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
1
New cards
Eukaryotic cell
a cell that contains a nucleus
2
New cards
Rough ER
membrane bound space, studded with ribosomes, synthesis of proteins
3
New cards
Golgi apparatus
completes protein packages and ships proteins, stores protein
4
New cards
smooth ER
no ribosomes, synthesize lipids, stores calcium
5
New cards
lysosomes
cellular digestive system
6
New cards
peroxisomes
converts reactive oxygen species
7
New cards
centrioles
organizes microtubules
8
New cards
cytoskeleton
gives our cell their shape
9
New cards
endosymbiotic theory
How eukaryotic cell came to be
- one cell engulfed another
- plant cell engulfed another cell which was good at getting energy from the sun (chloroplasts)
- one cell engulfed another
- plant cell engulfed another cell which was good at getting energy from the sun (chloroplasts)
10
New cards
eukaryotic picture
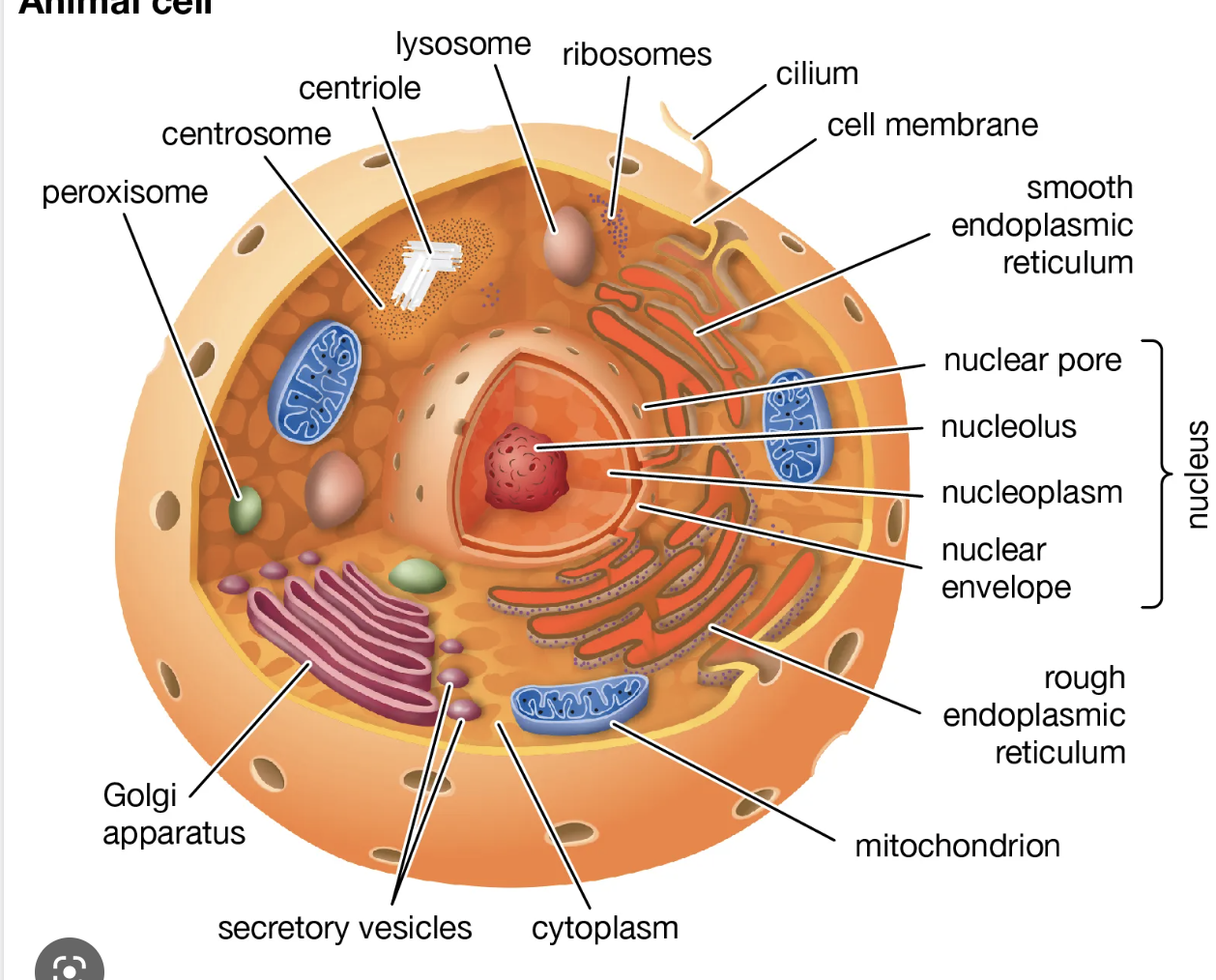
11
New cards
cell membrane
fluid mosaic model- within the membrane there is lipids and proteins
12
New cards
integral membrane protein
spans entire membrane, embedded in the membrane
13
New cards
peripheral membrane proteins
no exposed hydrophobic amino acid protein, on outer part of membrane
14
New cards
anchored proteins
tends to have a hydrophobic molecules covalently attached, anchored to membrane
15
New cards
structure of a phospholipid
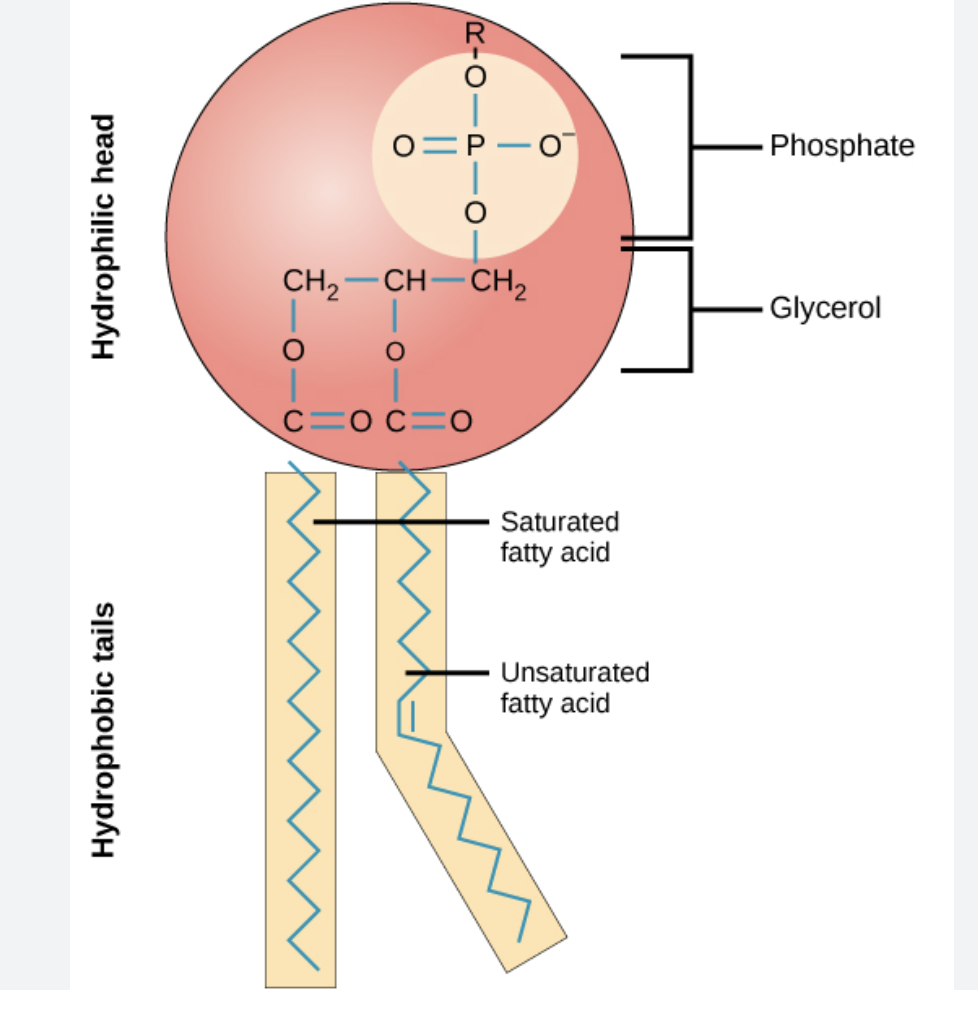
16
New cards
How does enzymes lower activation energy
1. orient substrates
2. induce physical strain
3. alter chemical charge of a substrate
2. induce physical strain
3. alter chemical charge of a substrate
17
New cards
orient substrate
putting molecules in the right position to bond them
ex: bonding two amino acids to form a peptide bond
ex: bonding two amino acids to form a peptide bond
18
New cards
induce physical strain
stretching bonds to be a able to produce chemical reactions
19
New cards
environmental enzyme regulation
temperature, pH
20
New cards
factors enzyme regulation
- inorganic ions
- co-enzymes- carbon containing molecule (ATP)
- prosthetic- permanently bound (heme)
- co-enzymes- carbon containing molecule (ATP)
- prosthetic- permanently bound (heme)
21
New cards
inhibitors
a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity
22
New cards
irreversible inhibitors
covalent bond with enzyme and shut off activity
23
New cards
competitive reversible inhibitors
compete for the same active site with a substrate
24
New cards
non-competitive reversible inhibitors
binds somewhere other than the active site and can change the shape of the active site
25
New cards
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
26
New cards
oxidation
loss of an electron
27
New cards
reduction
gain of an electron
28
New cards
how to enzymes help with energy release
energy is lost more slowly to heat (stair step method) each step is another enzyme and chemical reaction
29
New cards
two co-enzymes
-NAD+ -----> NADH
-FAD+ --------> FADH2
-FAD+ --------> FADH2
30
New cards
cellular respiration
glucose + O2 ------> CO2 + H2O
31
New cards
steps of cellular respiration
1. glycolysis
2. pyruvate processing
3. krebs cycle
4. electron transport chain
2. pyruvate processing
3. krebs cycle
4. electron transport chain
32
New cards
glycolysis energy investment phase
glucose is oxidized and an investment of two ATP molecules to result in 2 glyceraldehyd 3-phosphate and 2 ADP
33
New cards
glycolysis energy harvesting
4 ADP+ NAD+ (reduced)+ 2G3P ---> 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 ADP
34
New cards
ATP yielded from glycolysis
2 ATP
35
New cards
substrate level phosphorylation
taking a phosphate and adding it to something else (G3P--->ADP= ATP)
36
New cards
pyruvate processing
2 Pyruvate + 2 NAD+ + 2 CoA → 2 Acetyl-CoA + 2 NADH + 2CO2
-NAD+ is reduced to NADH
-NAD+ is reduced to NADH
37
New cards
krebs cycle
2acetylCoA + 6NAD+ + 2FAD + 2ADP --> 4Co2 + 6NADH + 2FADH2 + 2ATP
38
New cards
What does the Krebs cycle produce
4 ATP and lots of NADH
39
New cards
electron transport chain
a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation.
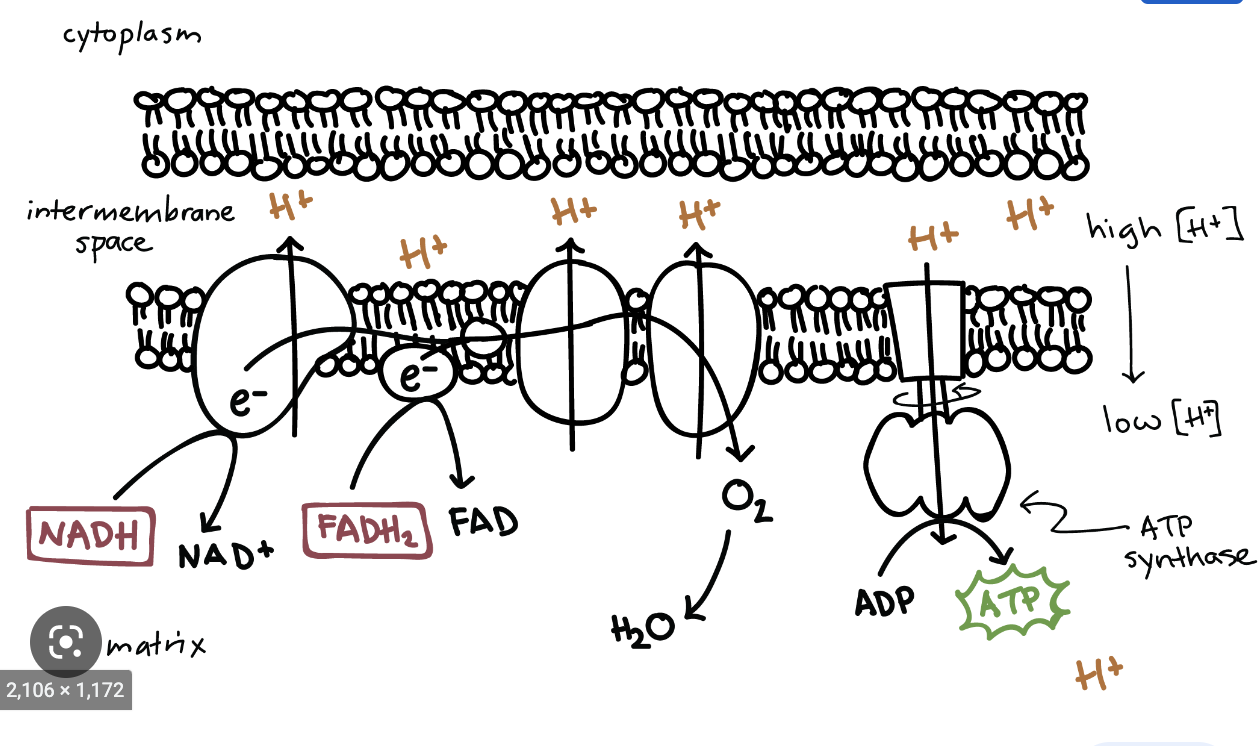
40
New cards
ATP synthase
a system that pumps hydrogen back into the cell through an ion gradient to create ATP from ADP+ Pi
41
New cards
how much ATP is yielded from electron transport chain
32 ATP
42
New cards
ATP yielded from cellular respiration
about 36 ATP
32 ATP from electron transport chain, 4 ATP from glycolysis
32 ATP from electron transport chain, 4 ATP from glycolysis
43
New cards
lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate converted to lactate (cheese, yogurt, buttermilk, sour cream)
44
New cards
alchohol fermentation
Pyruvate converted to acetaldehyde by pyruvate dehydrogenase
acetaldehyde converted to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase
occurs in some bacteria and fungi
loses CO2
acetaldehyde converted to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase
occurs in some bacteria and fungi
loses CO2
45
New cards
fermentation vs respiration
goal: covert glucose into energy
respiration: 32 ATP, needs oxygen
fermentation: 2 ATP, occurs when there is a lack of oxygen
respiration: 32 ATP, needs oxygen
fermentation: 2 ATP, occurs when there is a lack of oxygen
46
New cards
photosynthesis equations
light energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
47
New cards
light reactions
converts light energy into usable energy (ATP+ NADPH)
happens in the inner membrane of the chloroplasts in the stroma
happens in the inner membrane of the chloroplasts in the stroma
48
New cards
light independent reactions
uses ATP and NADPH and CO2 from light reactions to make carbohydrates
49
New cards
chloroplasts
where photosynthesis occurs, 2 membranes and has its own DNA
50
New cards
Non- cyclic electron transport chain
-occurs in the inner membrane of the chloroplast
- photosystem II absorbs so much light it gives electrons to another molecule (oxidizing agent) takes e- from H2O to make O2
- then given to photosystem I which is also absorbing light
- electron is eventually sent to where NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
- hydrogen is pumped back in through ATP synthase to produce ATP
- photosystem II absorbs so much light it gives electrons to another molecule (oxidizing agent) takes e- from H2O to make O2
- then given to photosystem I which is also absorbing light
- electron is eventually sent to where NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
- hydrogen is pumped back in through ATP synthase to produce ATP
51
New cards
cyclic transport chain
- only uses photosystem I
- e- always goes back to photosystem I
- can only produce ATP
- ATP synthase can still pump H+ back in to produce ATP
- e- always goes back to photosystem I
- can only produce ATP
- ATP synthase can still pump H+ back in to produce ATP
52
New cards
mitosis
cell division resulting in two daughter cells with the same DNA as the parent cell
53
New cards
Mitosis steps
1. prophase
2. metaphase
3. anaphase
4. telophase
5. cytokinesis
2. metaphase
3. anaphase
4. telophase
5. cytokinesis
54
New cards
prophase
microtubules spindles form and nuclear membranes breaks down
55
New cards
metaphase
chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate
56
New cards
anaphase
separating sister chromatids, separates cleaves the proteins that hold the sister chromatids together
57
New cards
telophase
nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes recodenses, triggers cytokinesis
58
New cards
cytokinesis
pulls membranes together to split, uses myosin and actin filaments
59
New cards
meiosis
cells are not identical to the parent cell, generate gametes (egg or sperm cell)
60
New cards
meiosis I
separates homologs (2n---> 1n)
61
New cards
meiosis II
separates sister chromatids
62
New cards
Prophase I (meiosis I)
homologous chromosomes pair up
crossing over occurs
crossing over occurs
63
New cards
metaphase I (meiosis I)
chromosomes line up at metaphase plates
where independent assortment occurs
where independent assortment occurs
64
New cards
Anaphase I (meiosis I)
pull homologous chromosomes apart- separating one from mom and one from dad
65
New cards
telophase I/ cytokinesis (meiosis I)
separates the cell to make 2 different cells
66
New cards
meiosis II
separates sister chromatids (similar steps to mitosis)
67
New cards
central dogma
DNA---> RNA---> protein
68
New cards
essential characteristics of DNA
1. stores genetic information
2. genetic material is subject to mutations
3. genetic material is precisely replicated in cell division
4. genetic material is expressed as a phenotype
2. genetic material is subject to mutations
3. genetic material is precisely replicated in cell division
4. genetic material is expressed as a phenotype
69
New cards
gel electrophoresis
- grew bacteria in heavy nitrogen
- take DNA in gel and run electricity through it so it runs down through the gel
- DNA has a negative charge so it wants to move towards positive pols
- how it was discovered that DNA uses a semi conservative method in replication
- take DNA in gel and run electricity through it so it runs down through the gel
- DNA has a negative charge so it wants to move towards positive pols
- how it was discovered that DNA uses a semi conservative method in replication
70
New cards
steps of DNA replication
1. unwind parental DNA (separate the two strands)
2. add new nucleotides by complimentary base pairing
2. add new nucleotides by complimentary base pairing
71
New cards
helicase
unwinds and separates the two strands of DNA
72
New cards
DNA polymerase
synthesizes DNA in the 5'-3' direction
73
New cards
primer
made by primase
RNA sequence to start the replication
can't add DNA from nothing so it needs a 3' hydroxyl
RNA sequence to start the replication
can't add DNA from nothing so it needs a 3' hydroxyl
74
New cards
single stranded binding proteins
holds DNA strands apart
75
New cards
topoisomerase
relieves supercoiling tension
76
New cards
DNA ligase
seals nicks left by Pol I
77
New cards
telomerase
extends the ends of chromosomes
78
New cards
PCR
- replicates DNA in lab
1) heat run to 95C
2) cool to allow primer to bind
3) maintain temp to taq polymerase
4) repeat
1) heat run to 95C
2) cool to allow primer to bind
3) maintain temp to taq polymerase
4) repeat
79
New cards
mRNA
messenger
carries of copy of gene sequences to ribosomes
carries of copy of gene sequences to ribosomes
80
New cards
rRNA
- ribosomal
- provides structure and framework of ribosomes
- catalyzes formation of a peptide bond
- provides structure and framework of ribosomes
- catalyzes formation of a peptide bond
81
New cards
tRNA
- transfer RNA
- carry an amino acid to ribosomes
- carry an amino acid to ribosomes
82
New cards
transcription steps
1. initiation
2. elongation
3. termination
2. elongation
3. termination
83
New cards
initiation (transcription)
promoter binds an directs RNA polymerase
84
New cards
elongation (transcription)
RNA polymerase unwinds DNA about 10 BP at a time
- 5'-3' direction
- 5'-3' direction
85
New cards
termination (transcription)
happens via unique sequence of DNA
86
New cards
initiation (translation)
- the start codon initiates an amino acid to bind
the tRNA with an amino enters through the A site
the tRNA with an amino enters through the A site
87
New cards
elongation (translation)
amino acids build on each-other as the ribosome moves through down the RNA strand
88
New cards
termination (translation)
protein enters the A site and H2O attaches to break off the aa chain
89
New cards
gene transformation in bacteria
2 strands- Smooth and rough
smooth- virulent causes you to get sick
rough- non virulent, don't get sick
heat s strain- not virulent
heat killed s stain + R strain= virulent
R stain was transformed- discovered that DNA is what is transformed
smooth- virulent causes you to get sick
rough- non virulent, don't get sick
heat s strain- not virulent
heat killed s stain + R strain= virulent
R stain was transformed- discovered that DNA is what is transformed
90
New cards
restriction digest
endonuclease recognizes certain sequences of nucleotide and cleaves them at a certain point
when there is a change that does not match the specific recognized sequence then it will not cut it
the fragments will show up on a gel electrophoresis and help us differentiate the DNA
when there is a change that does not match the specific recognized sequence then it will not cut it
the fragments will show up on a gel electrophoresis and help us differentiate the DNA
91
New cards
primary structure
chain of amino acids
92
New cards
secondary structure
chain of aa start to fold on themselves to form hydrogen bond and form alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
93
New cards
tertiary structure
interaction between alpha helix and beta pleated sheet- bonds between these two forms
- give the basic shape of the protein
- give the basic shape of the protein