ap stats things to remember
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
name 2 measures of center
mean and median
name 3 measures of spread
standard deviation, iqr, range
what is variance
standard deviation squared (σ2)
when is standard deviation 0
when all the data is the same
outlier test formula
> Q3 + 1.5 IQR
< Q1 - 1.5 IQR
right skew
long tail on right side, mean > median
left skew
long tail on left side, mean < median
CUSS
center, unusual features, shape, spread
basic z score formula
how many standard deviations an element is from the mean.
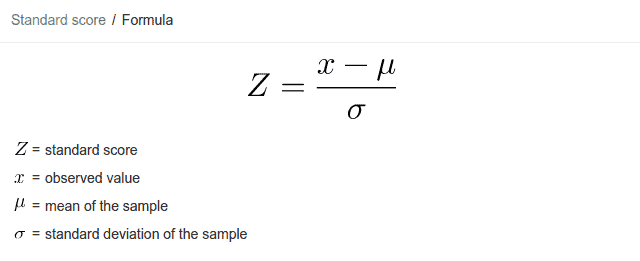
blocking reduces
variation - ensures differences in groups are due to treatment alone
randomization reduces
bias - controls variables we don’t know
formula for 1 samp T int for a sample mean
used to estimate population mean from a sample mean
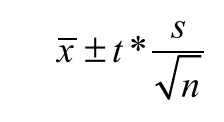
formula for 1 prop z interval
used to estimate a population proportion from a sample proportion.
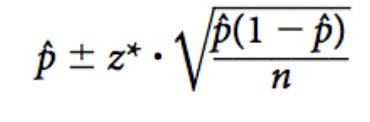
type I error
rejecting a TRUE H0
type II error
failing to reject a FALSE H0
power
probability of correctly rejecting H0
alpha (α)
probability of a type I error (rejecting a true H0)
test for independent variables
P(A) x P(B) = P(A and B)
P(A|B) = P(A)
BINS (binomial condition)
Binary (success/fail)
Independent
Number of trials is fixed
Same probability for each trial
confidence level is ____ to margin of error
proportional (CI goes up when ME goes up)
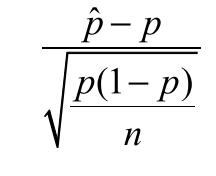
when population variance is known and when n > 30
1 prop z test
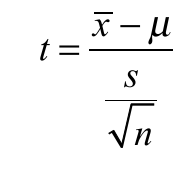
formula for
1 mean T test
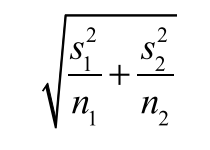
standard deviation formula for:
2 mean T test / interval
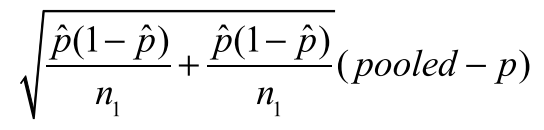
standard deviation for:
2 prop Z test
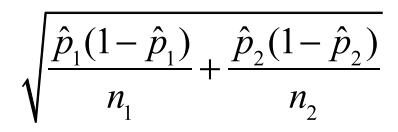
standard deviation for:
2 prop Z int
SOFA for scatterplots/correlation
Strength (r or r2)
Outliers
Form (linear or exponential)
Association (pos or neg)
P(A∪B) =
P(A) + P(B) − P(A∩B)
P(A∩B) =
P(A) x P(B) if independent
P(A’) =
1 – P(A)
P(A|B) =
P(A∩B) / P(B)
formula for binomial mean
np
n = number of trials
p = probability of success
formula for binomial variation
np(1-p)
n = number of trials
p = probability of success
formula for geometric mean
1/p
p = probability of success
formula for geometric variance
(1–p)/p2
p = probability of success