Chapter 22: Age of Empire and American Foreign Policy, 1890-1914
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What drove American overseas expansion in the late 19th and early 20th centuries?
markets for American products and spreading Christianity
U.S. foreign policy in the last decade of the nineteenth century (1890s) can be characterized as
expansionist
Who outlined the building blocks for an overseas empire with a strong navy, a network of naval bases, and canal in Central America?
Alfred T. Mahan
The Boxer Rebellion was an anti-imperialist uprising in which country?
China
Although Theodore Roosevelt and his Rough Riders got all the glory, over twenty-five hundred of us proved our bravery–five Medal of Honor recipients. Who are we?
Smoked Yankees
Who supported an independent Panama (separate from Columbia) and started the building of a canal in Central America?
Theodore Roosevelt
Match to the correct item:
Frederick Jackson Turner
Frontier Thesis
Match to the correct item:
Seward’s Folly
Alaska
Match to the correct item:
Alfred Thayer Mahan
The Influence of Seapower upon History
Match to the correct item:
William Randolph Hearst
New York Journal
Match to the correct item:
Maine explosion
Havana harbor
Match to the correct item:
Lottie Moon
Christian missionary in China
Match to the correct item:
John Hay
Open Door notes
Match to the correct item:
Emilio Aguinaldo
Filipinos' war for independence
An instance of yellow journalism was the?
sensationalized newspaper articles promoting American military intervention in Cuba.
To solidify strategic ports in the South Pacific, the U.S., Great Britain, and Germany divided which island group?
Samoan Islands
Which President focused on securing markets for American business with “dollar diplomacy”?
William Howard Taft
By the end of the Taft presidency (1913), the U.S. was the pre-eminent power in
Western Hemisphere/the Americas
To win hearts and minds, the Taft Commission built schools and hospitals where?
Philippines
American sugar planters and businessmen staged a coup where to depose the monarchy?
Hawaii
What was the main argument of the Frontier Thesis?
American democracy and the unique American character was shaped by European colonists and the wilderness of North America.
The Opium Wars were between China and which country?
Great Britain
As a result of the Russo-Japanese War and the Portsmouth conference, Japan gained which new territory?
Korea
Which amendment enabled the U.S. to keep a base in Cuba, specifically Guantanamo Bay?
Platt Amendment
I fought for independence of my homeland, but capitulated to the U.S.A. in 1901. Who am I?
Emilio Aguinaldo

The image in Figure 22.1 did what?
glorified American imperialism in Cuba
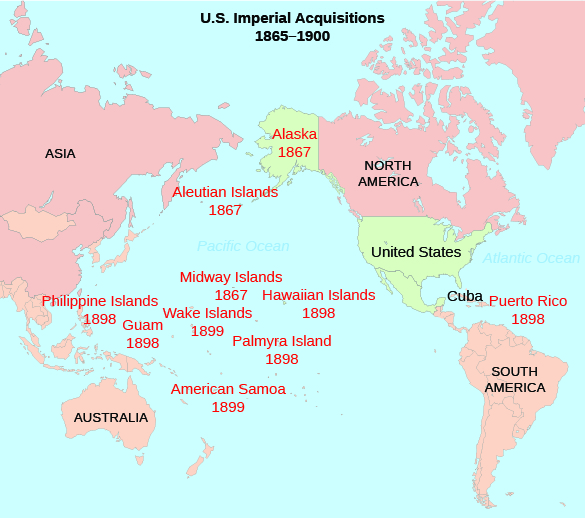
According to Figure 22.5, the U.S. acquired which south Pacific territory in 1899?
American Samoa
The Roosevelt Corollary proclaimed what?
America's right to interfere in Latin American affairs
The U.S. paid Spain $20M in the Treaty of Paris, but did NOT acquire which territory?
Cuba
Who said “speak softly, and carry a big stick.” in regard to U.S. foreign policy?
Theodore Roosevelt