Understanding Carbohydrates in Nutrition, Understanding Dietary Fats and Their Health Impacts
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
227 Terms
Carbohydrates
Nutrients providing 4 kcals/g energy.
Refined Carbohydrates
Processed foods with altered natural state.
Unrefined Carbohydrates
Foods remaining in their natural state.
Added Sugars
Sugars added during food processing.
Empty Calories
Foods with minimal nutritional value.
Dietary Guidelines
Recommendations for healthy carbohydrate intake.
Sugar Content in Beverages
65 grams equals 16.25 teaspoons of sugar.
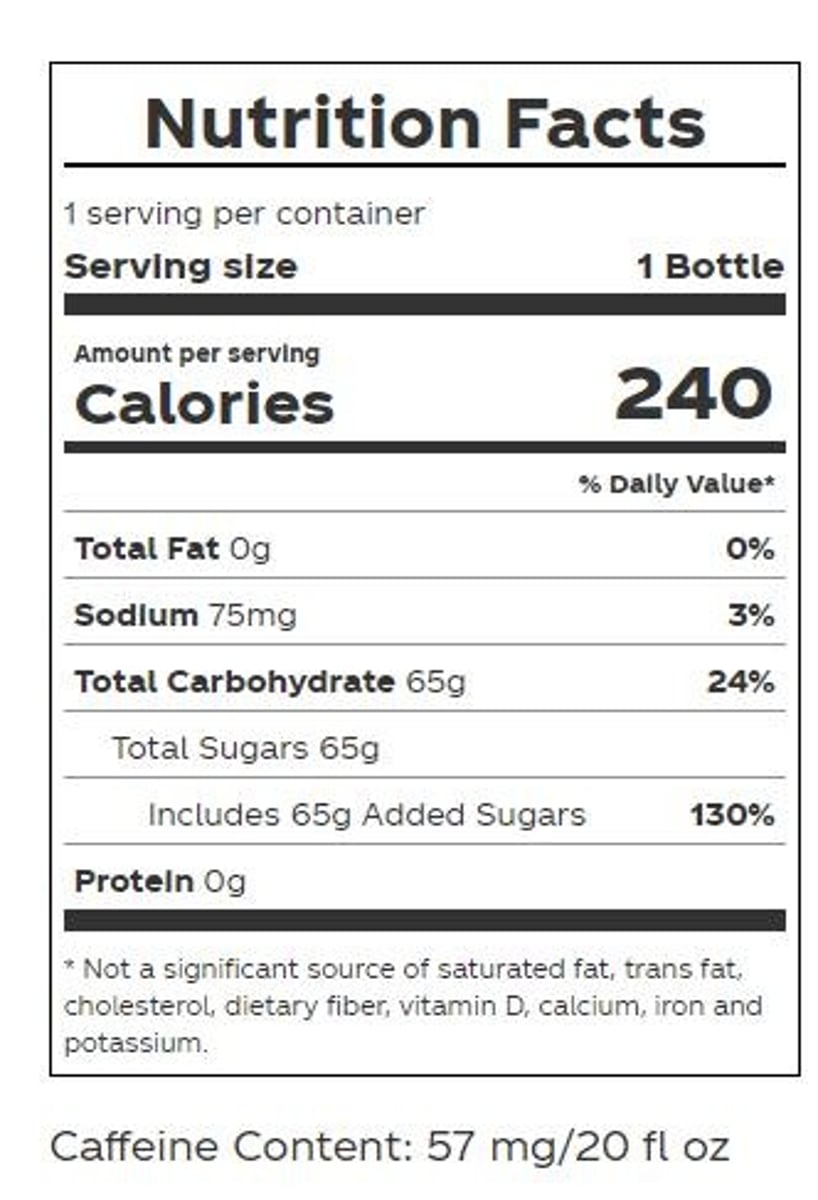
Sugar Content in Donuts
13 grams equals 3.25 teaspoons of sugar.

Endosperm
Largest grain kernel part; contains starch.
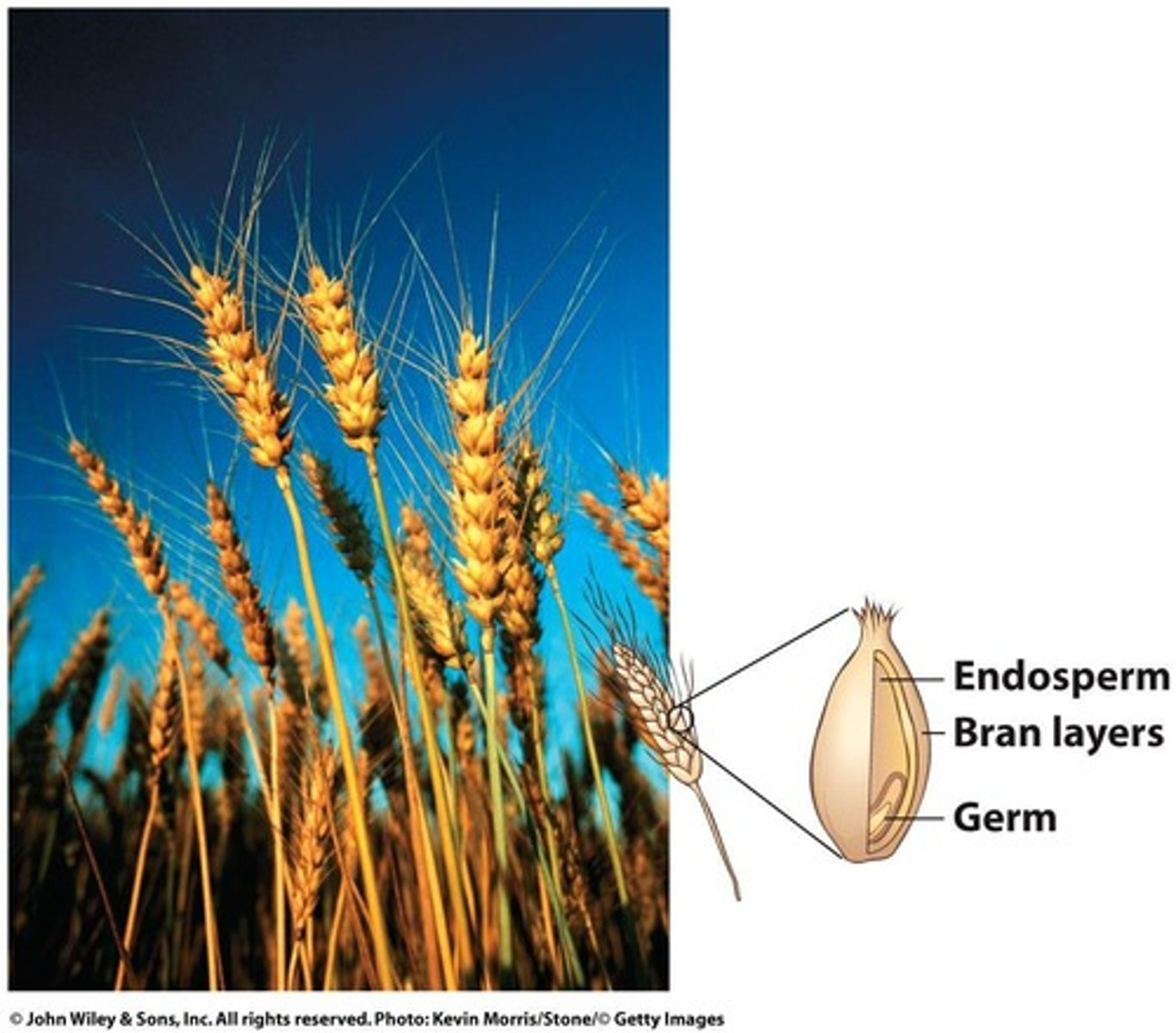

Bran
Outer layer of grain; high in fiber.
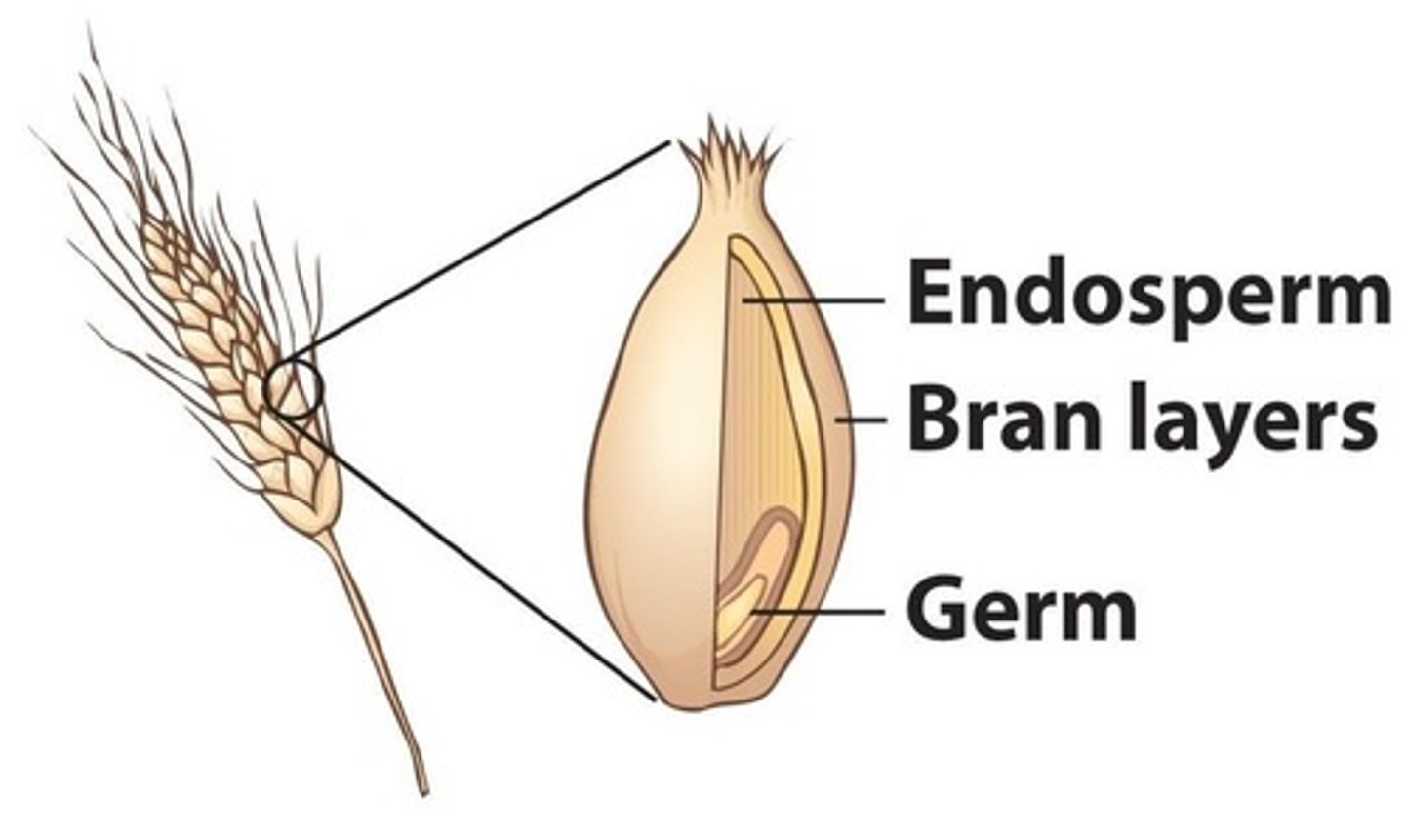
Germ
Kernel base; source of oils and vitamin E.
Enriched Flour
Nutrients added post-processing loss.
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars; basic carbohydrate units.
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked together.
Oligosaccharides
Short chains of monosaccharides.
Glycogen
Storage form of glucose in animals.
Starch
Storage form of glucose in plants.
Fiber
Indigestible carbohydrate; aids digestion.
Soluble Fiber
Dissolves in water; helps lower cholesterol.
Insoluble Fiber
Does not dissolve; promotes bowel health.
Dietary Recommendations for Added Sugars
<10% of calories from added sugars.
Teaspoon Conversion
1 teaspoon equals 4 grams of sugar.
Galactose
Component of lactose, a milk sugar.
Fructose
Sweeter sugar found in fruits and honey.
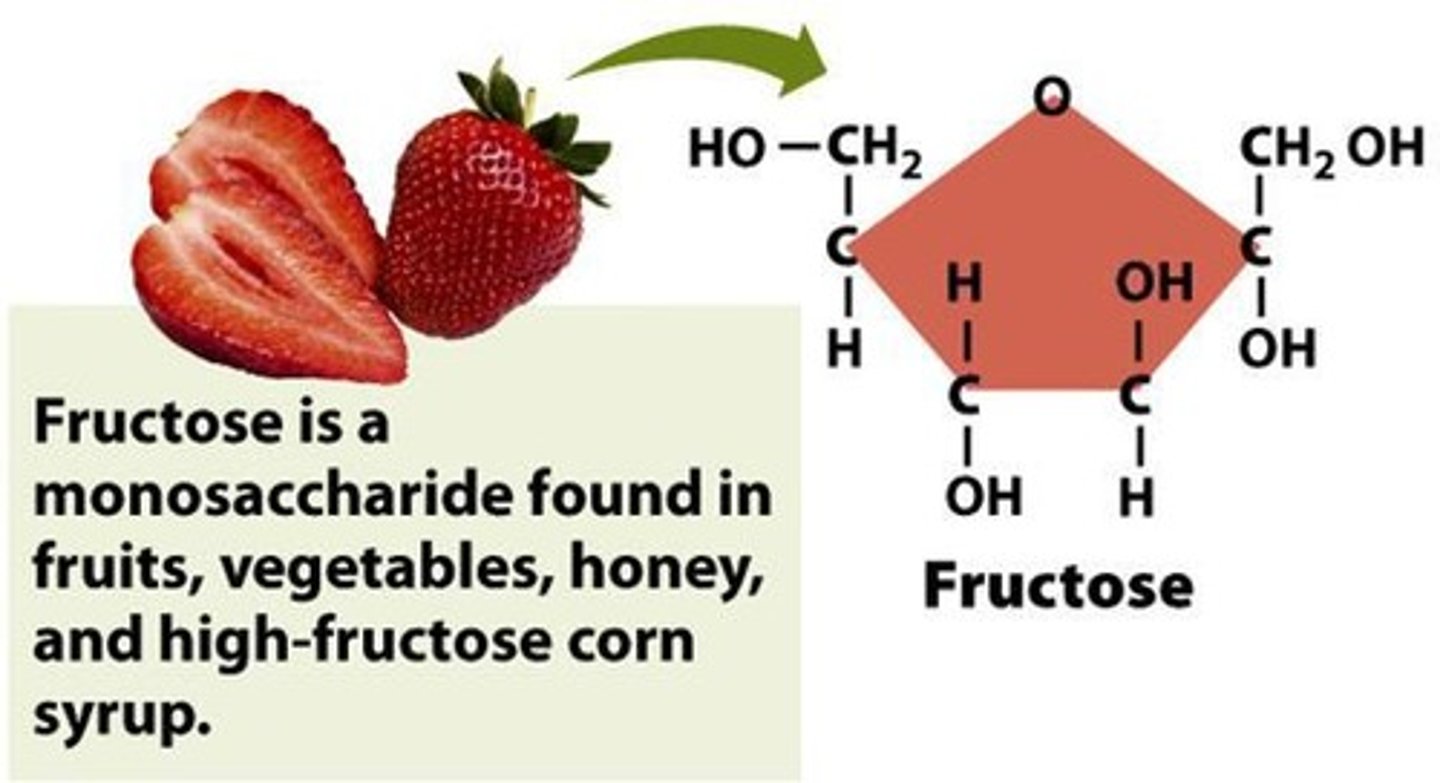
High Fructose Corn Syrup
Common sweetener derived from corn starch.
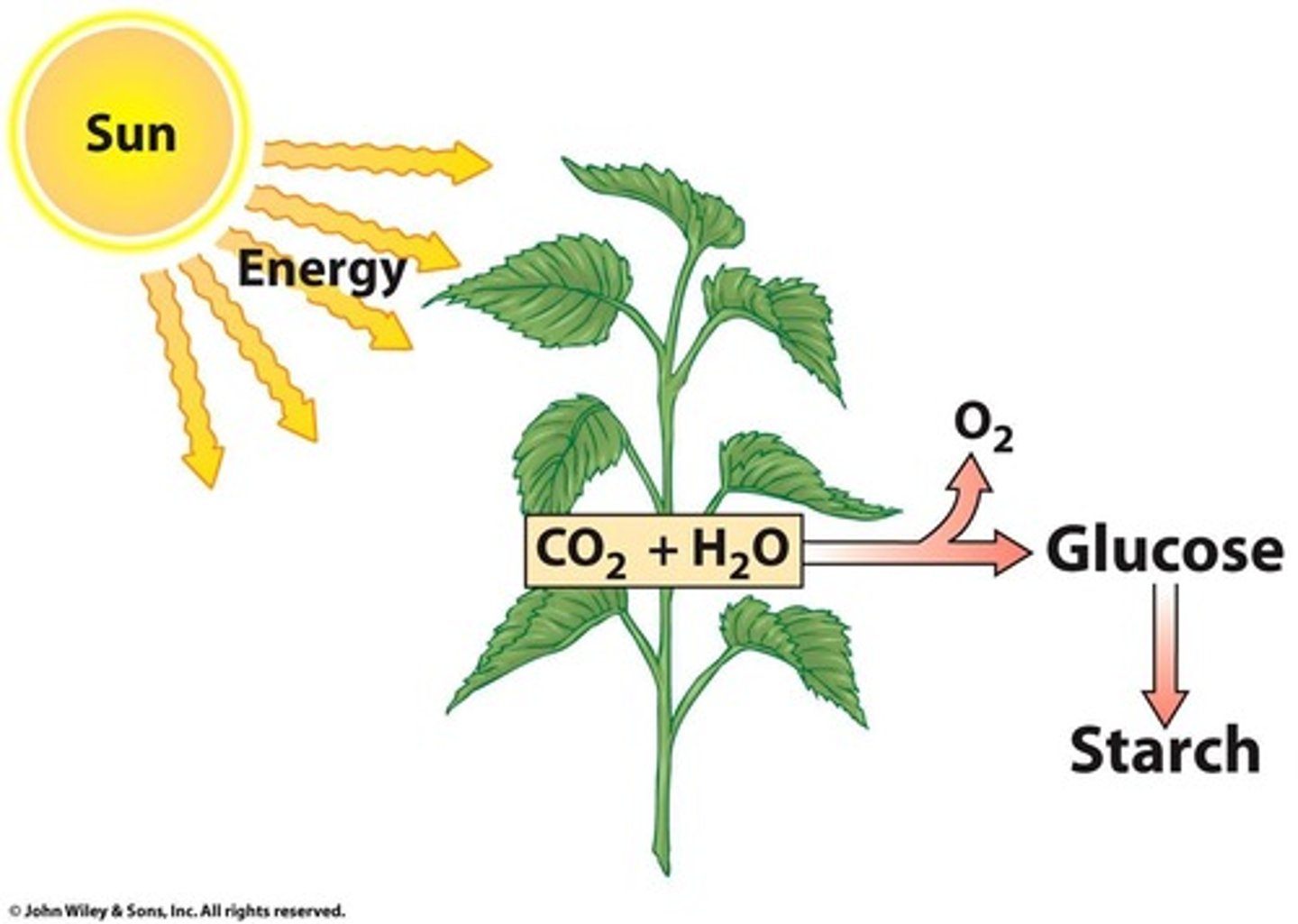
Glucose
Primary sugar formed in plants via photosynthesis.
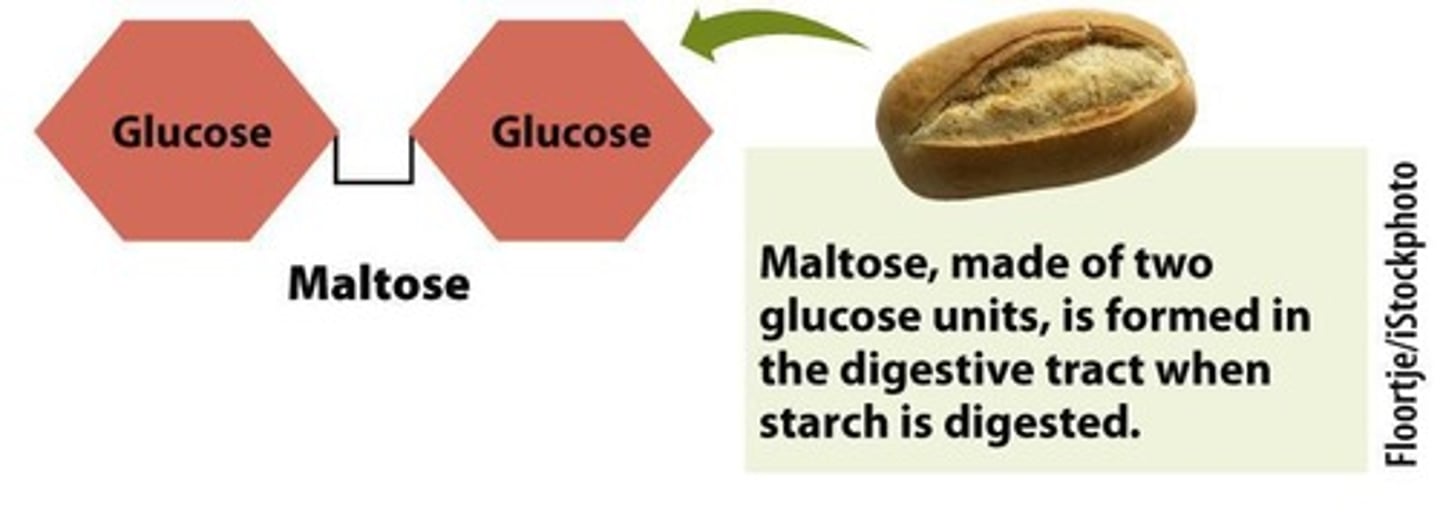
Maltose
Disaccharide of two glucose molecules.
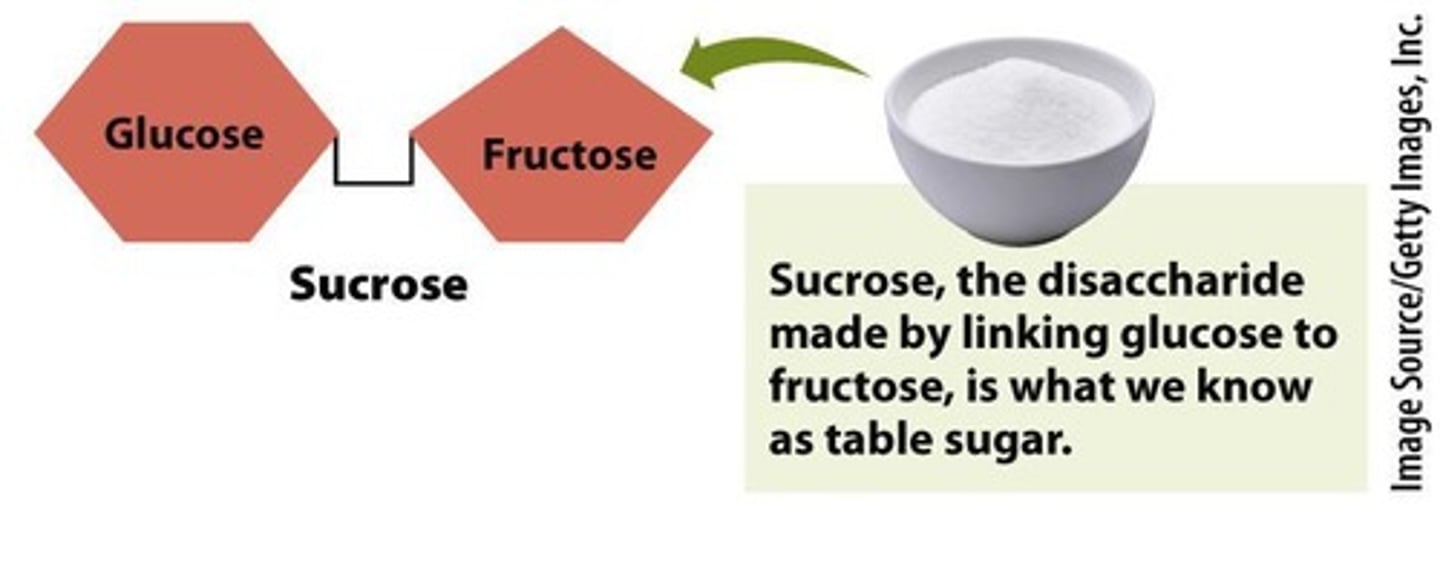
Sucrose
Disaccharide of glucose and fructose.
Lactose
Disaccharide of glucose and galactose.
Hydrolysis Reaction
Breakdown of disaccharides into monosaccharides.
Condensation Reaction
Formation of disaccharides from monosaccharides.
Oligosaccharides
Carbohydrates with 3-10 monosaccharides.
Prebiotics
Substances that nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
Amylose
Linear form of starch, less branched.
Amylopectin
Highly branched form of starch, easily digested.
Glycogen
Storage form of carbohydrate in animals.
Carbohydrate Loading
Strategy to increase glycogen before endurance events.
Dietary Fiber
Fiber found intact in plant foods.
Functional Fiber
Fiber providing health benefits beyond nutrition.
Soluble Fiber
Dissolves in water, forms viscous solutions.
Insoluble Fiber
Does not dissolve in water, adds bulk.
Pectin
Soluble fiber used as a thickening agent.
Xanthan Gum
Soluble fiber that stabilizes food mixtures.
Wheat Bran
Insoluble fiber used in breads and muffins.
Pepsin
Enzyme that digests proteins in the stomach.
Secretin
Hormone that stimulates pancreatic juice secretion.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Hormone that triggers bile release from gallbladder.
Disaccharides
Double sugars formed from two monosaccharides.
Pancreatic Amylase
Enzyme that breaks starch into smaller carbohydrates.
Simple Sugars
End products of carbohydrate digestion absorbed into blood.
Salivary Amylase
Enzyme that initiates starch digestion in the mouth.
Polysaccharides
Long chains of glucose units in starch.
Lactose Intolerance
Inability to digest lactose due to low lactase.
Lactase
Enzyme that breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance
Cramps, bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea.
Fiber
Indigestible carbohydrate that aids digestion and health.
Oligosaccharides
Short chains of monosaccharides, often indigestible.
Resistant Starch
Starch that resists digestion in the small intestine.
GI Motility
Movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract.
Bile
Digestive fluid produced by the liver, stored in gallbladder.
Gallbladder
Organ that stores bile for digestion.
Carbohydrate Digestion Steps
Processes converting starches to simple sugars.
Undigested Lactose
Lactose that reaches the large intestine unprocessed.
Health Benefits of Fiber
Promotes gut health and slows nutrient absorption.
Calcium-Fortified Foods
Foods enhanced with calcium for lactose intolerant individuals.
Incidence of Lactose Intolerance
Affects 30-50 million adults globally.
Fiber
Slows digestion and nutrient absorption in intestines.
Low-fiber meal
Nutrients are more concentrated in digestion.
Gastrointestinal contents
Material present in the digestive tract.
Delayed digestion
Slower breakdown of food in the stomach.
Healthy bowel function
Promoted by larger, softer stool from fiber.
Constipation prevention
Fiber helps maintain regular bowel movements.
Transit time
Duration for food to pass through intestines.
Glycogen
Storage form of carbohydrates in animals.
Blood glucose levels
Concentration of glucose in the bloodstream.
Metabolizing glucose
Process of converting glucose into ATP.
Insulin
Hormone regulating blood glucose levels post-meal.
Glycemic response
Blood glucose rise after food consumption.
Carbohydrate consumption
Amount and type influence glucose levels.
Refined sugars
Quickly raise blood glucose levels.
Glycemic index
Ranking of food's impact on blood glucose.
High glycemic index
Foods with index > 70 affect glucose significantly.
Low glycemic index
Foods with index < 55 have minimal impact.
Glycemic load
Index of glycemic response from food consumption.
Glycemic load score
Calculated from glycemic index and carbohydrate grams.
Feasting state
Insulin release after high carbohydrate meals.
Glucose uptake
Insulin facilitates glucose storage in cells.
Hepatic portal vein
Transports nutrients from intestines to liver.
Glucagon
Hormone released during low blood glucose levels.
Glycogen Breakdown
Process of converting glycogen to glucose.
Fasting State
Period when the body relies on stored energy.
Insulin Response
Hormonal reaction to elevated blood glucose levels.
Blood Glucose Peak
Maximum glucose level after carbohydrate intake.
Blood Glucose Dip
Decrease in blood glucose due to glucagon.
Anabolism
Building larger molecules from smaller ones.
Glycolysis
First step of glucose metabolism, producing pyruvate.
Acetyl CoA Formation
Conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA in mitochondria.
Citric Acid Cycle
Aerobic process generating ATP and CO2.
Electron Transport Chain
Final stage of cellular respiration producing ATP.
Anaerobic Metabolism
Energy production without oxygen.