19 - Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) of glucose metabolism – importance for the metabolism, chemical reactions, regulation. Role of PPP in the red blood cells. Enzymopathies: Glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
section
what is ppp
2 phases of ppp
oxidative phase
non-oxidative phase
importance of NADPH
Glucose -6-phosphate deficiency
PPP
what is ppp
alternative pathway when ATP doesn’t need to be produced
occurs in cytoplasm
2 phases of ppp
Oxidative
NADPH (not reversible reaction) → functions:
electron donor
anabolic reaction
antioxidant molecules
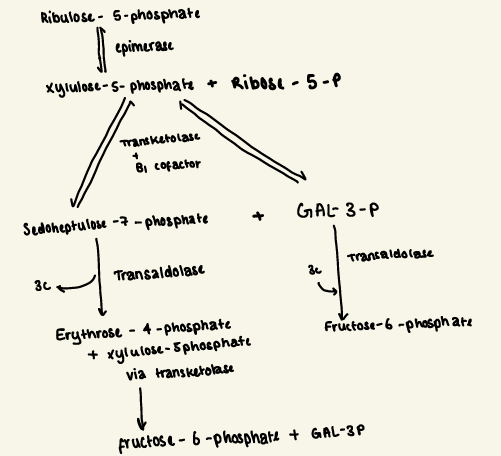
Non-oxidative
Ribose-5-phosphate (reversible) → function:
makes nucleotides for DNA or RNA synthesis
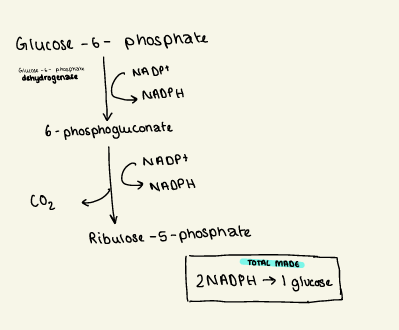
oxidative phase
glucose-6-phosphate undergoes oxidation to form → 6-phosphoglucono delta lactone , reducing NADP+ to NADPH using glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
6-phsophoglucono delta lactone undergoes hydrolysis to form → 6 phosphogluconate, using gluconolactonase
6-phsophogluconate undergoes decarboxylation and a C atom is cleaved to form → ribulose-5-phosphate, reducing NADP+ to NADPH, using 6-phsophogluconate dehydrogenase
non-oxidative phase
importance of NADPH
donate electrons in anabolic pathways
fatty acid synthesis
steroid hormone synthesis
cholesterol synthesis
Glucose -6-phosphate deficiency
impairment of NADPH production, detoxification of H2O2 is inhibited causing cellular damage
lipid peroxidation → erythrocyte membrane breakdown and hemolytic anaemia
Individuals with G6PD deficiency = asymptomatic
PPP
process - ppp
substrate - glucose-6-phsophate
products - NADP + pentoses
enzyme - glucose-6-p DH, 6-p-gluconate DH, cofactor NADP , insulin activates ATP/ADP
localisation - cytoplasm
energy balance -
deficiency - glucose-6-p DH deficiency, hemolysis
role - source ribose-5-p + NADPH