Boron Group (13)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the typical oxidation state for boron and aluminum?
+3, forming M³⁺ cations.
What oxidation states are possible for gallium, indium, and thallium?
Can form +1 or +3 cations; +3 is more common, except thallium, which prefers +1 due to the inert pair effect.
What is the inert pair effect?
The tendency of the outermost s electrons (especially in heavy elements like Tl) to remain non-bonding, favoring a lower oxidation state.
Which group 13 element is a metalloid, and what type of bonding does it prefer?
A: Boron, which prefers covalent bonding.
What kind of bonding is common in aluminum?
Aluminum tends toward covalent bonding, but also forms ionic compounds.
How do bonding tendencies change down the group from Ga to Tl?
Bonding becomes increasingly metallic/ionic, though borderline covalent/ionic behavior is observed.
What is the structure of elemental boron?
Built from B₁₂ icosahedra; boron has several allotropes based on how these units pack together.
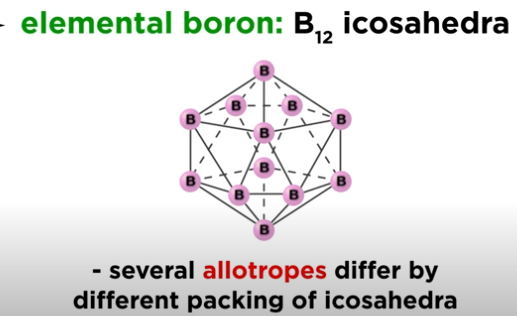
How reactive is elemental boron?
Very inert; reacts only with hot oxidizing agents.
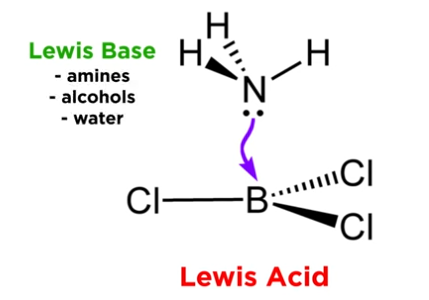
What type of compounds are boron trihalides, and what role do they play in chemistry?
Lewis acids; accept electron pairs into an empty p orbital from amines, alcohols, water, etc.
What is diborane (B₂H₆), and why is it unusual?
A pyrophoric gas with 3-center 2-electron (3c-2e) bonds, featuring bridging hydrogens — not standard covalent bonds.

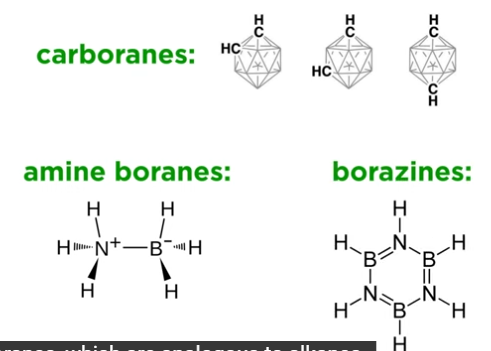
What are carboranes, amine boranes, and borazines?
Carboranes: Boranes with CH⁺ replacing BH groups
Amine boranes: Alkane analogs
Borazines: Benzene analogs
How is boron prepared?
B₂O₃ + 3Mg → 2B + 3MgO
How is aluminum prepared?
Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al (electrolysis of alumina in cryolite)
How are Ga, In, and Tl prepared?
M³⁺ + 3e⁻ → M
What are some applications of boron?
In laundry detergents (binds calcium)
Used in biochemical buffers
What are key uses of aluminum?
Industrial metal: strong, light, excellent thermal conductor
What is gallium used for?
In galinstan, a non-toxic mercury replacement in thermometers
What are some uses of indium?
Indium-tin oxides (ITO) used in touchscreens and displays
Transparent conductors
What is a common use of thallium?
TIS (Thallium(I) sulfide) used in photoresistors
Why does nihonium have no applications?
Too radioactive and unstable for practical use