glass ID, lab procedures, math equations
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms

what type of beaker is this
griffin beaker

what type of flask is this
erlenmeyer flask

what type of flask is this
volumetric flask

what is this
graduated cylinder

what is this
cuvette
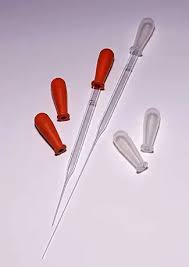
what kind of pipette
pasteur pipette

what kind of pipette
plastic transfer pipette
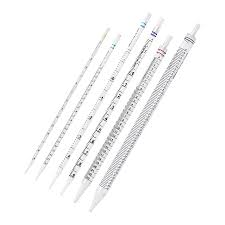
what kind of pipette
serological pipette

what kind of pipette
volumetric pipette
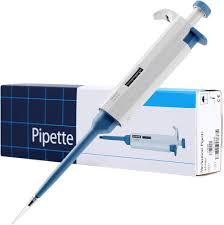
what kind of pipette
automatic pipette/micro pipette
what speed and time is blood ran at
6000 rpm / 5 minutes
what speed and time is urine spun at
1500 rpm / 3 min
what speed are fecals spun at
1200 rpm / 5 min
examples of wet chem analyzers
spectrophotometer
examples of dry chem analyzers
idexx catalyst, heska, abaxis
what is the purpose of keeping a log of quality control
aaha requirement, detects shift in values to help with repair
what two things interfere with lab results
hemolysis, lipemia
why are blood chemistries run on serum and what is the exception
use serum to avoid anticoagulant interference
exception: lithium heparin plasma
why should plasma/serum be removed and placed into a clean labeled tube as soon as possible, especially for glucose tests?
rbcs utilize glucose and it can decrease by 10% in an hour
t/f whole blood can be frozen
false
what are the 2 general ways to preserve a pt specimen
decrease temp, chemical
what does TC on a volumetric pipette mean
to contain
what does TD on a volumetric pipette mean
to deliver
what tube should body fluids (effusions) be put into
edta tube (prevents clotting and preserves cells)
RTT for bacterial culture
when should CSF cell counts be done within
15-30 minutes
what are the reasons to do a simple dilution
blood sample too concentrated for machine to read, need to dilute cleaner (like rescue), need to dilute drug
what do each parts mean in a 1p + 2p = 3p
1p = concentrate (cleaner, drug, blood)
2p = diluent (water, saline)
3p = final dilution
what is needed for a needxneed/have problem
high to low concentration and total volume
what is the true lab value equation
true lab value = diluted lab value x dilution factor (1:x)
what are serial dilutions used for
antibody titer (measure concentration of abs in blood)
what happens when agglutination is seen
ag binding to ab