(Whole Chapter) Ch 2 Chemistry Vet Tech A & P 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be broken down into simpler substances
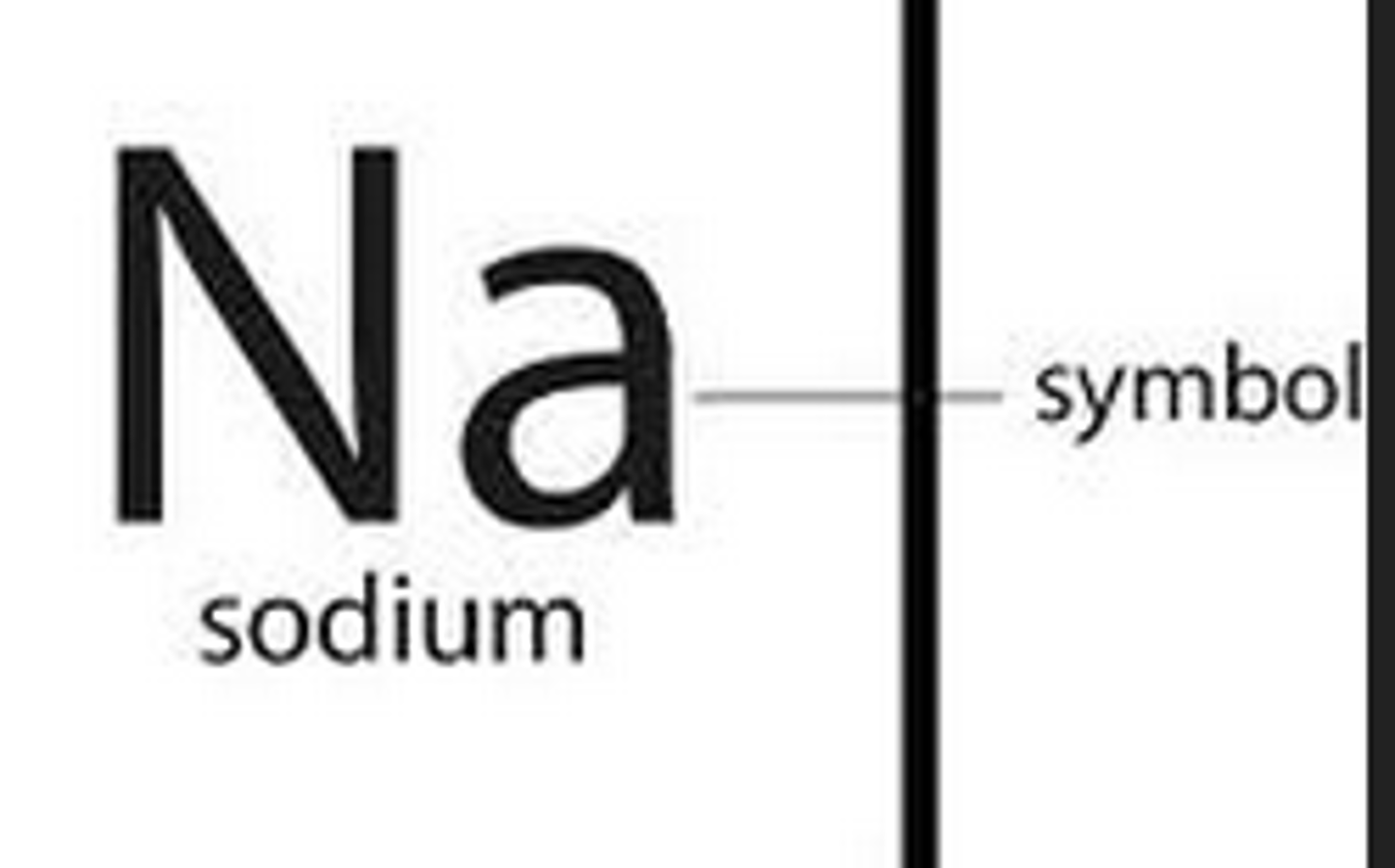
chemical symbol
A one or two letter representation of an element
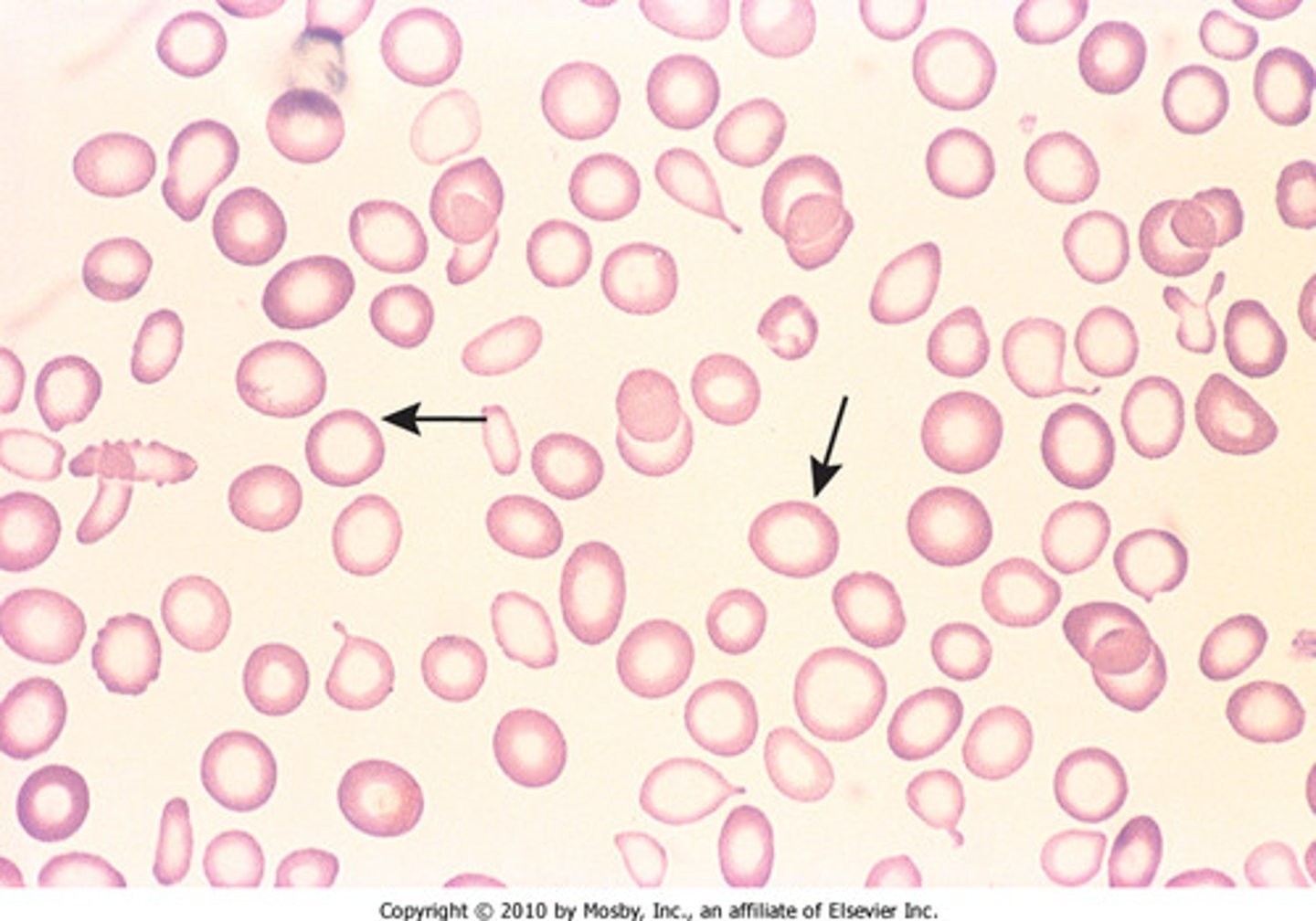
iron deficiency anemia
anemia caused by inadequate iron intake or chronic blood loss
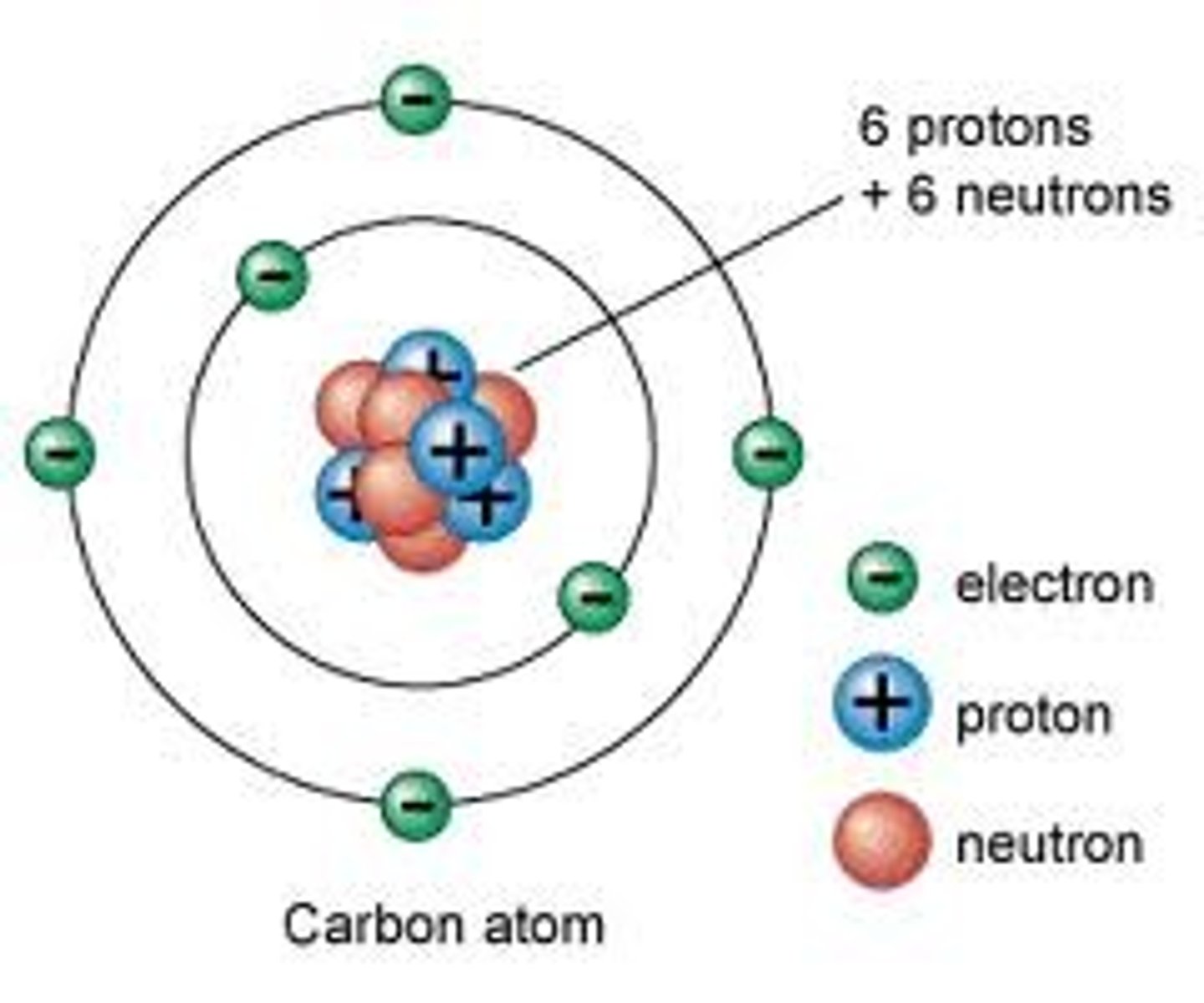
Atoms
Basic unit of matter
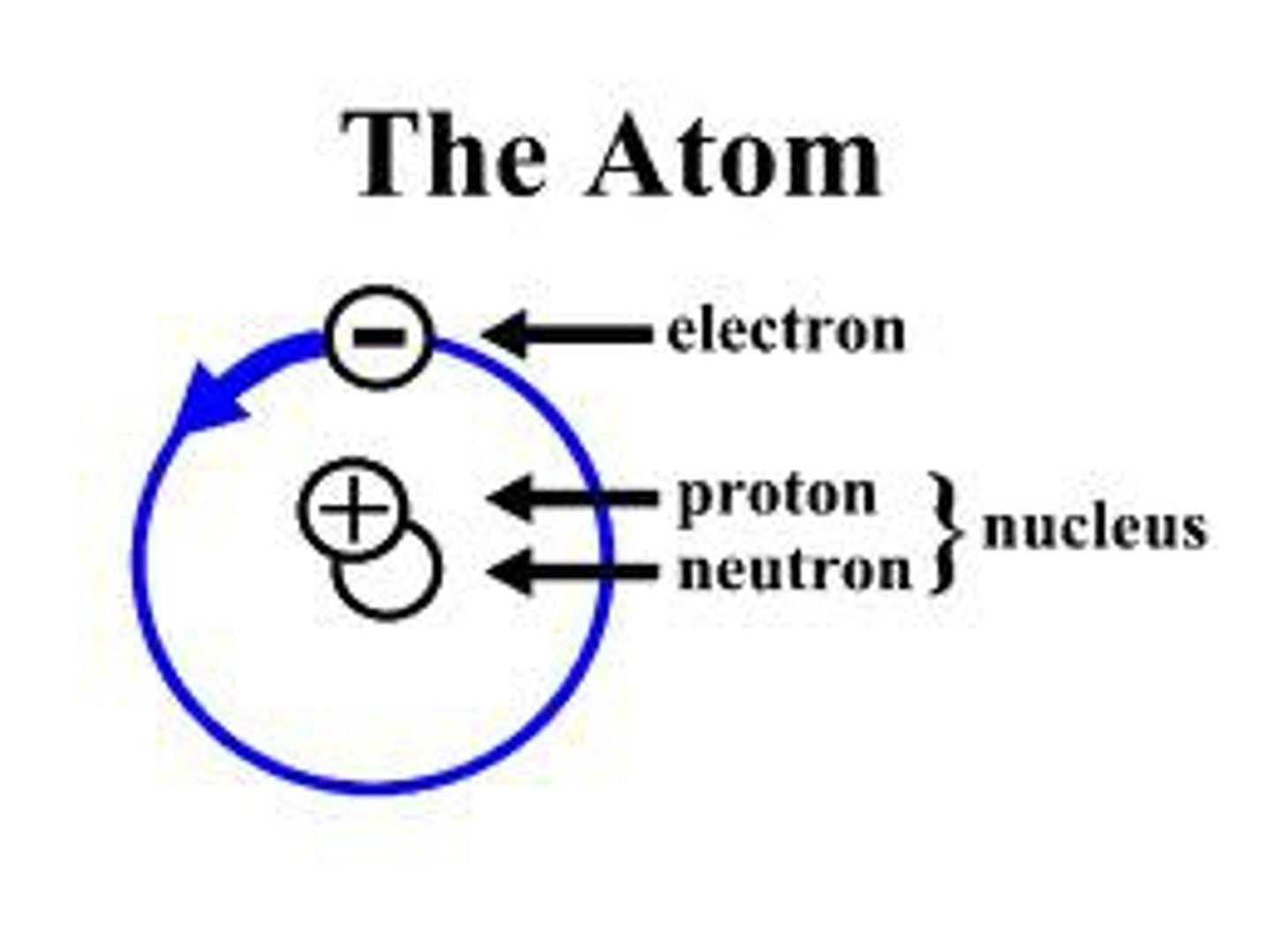
Protons
positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus
Neutrons
the particles in the nucleus that have no charge

Electrons
Negatively charged particles surrounding the nucleus
ion
A charged atom that has gained or lost an electron

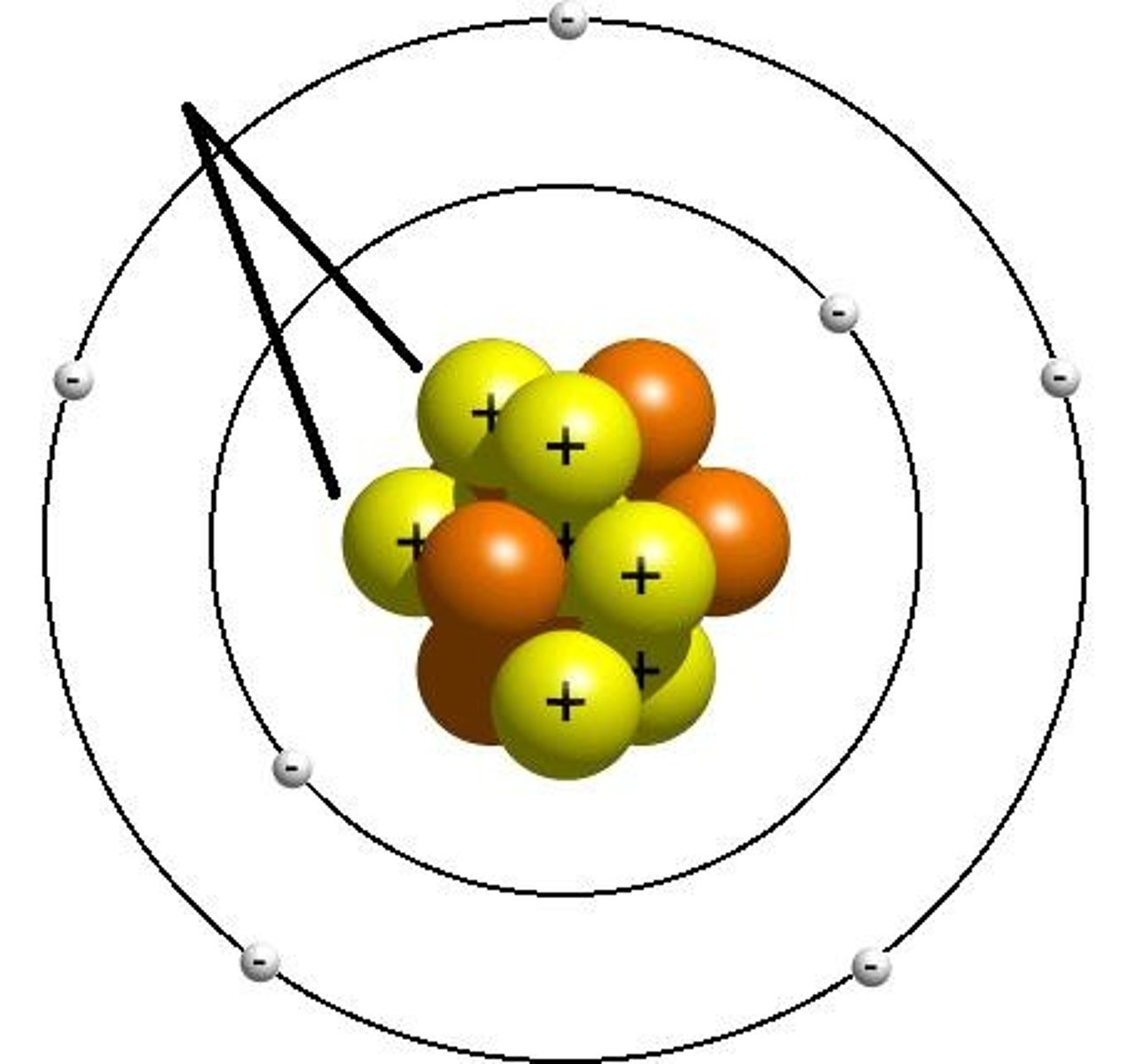
atomic nucleus
Center of an atom with protons and neutrons
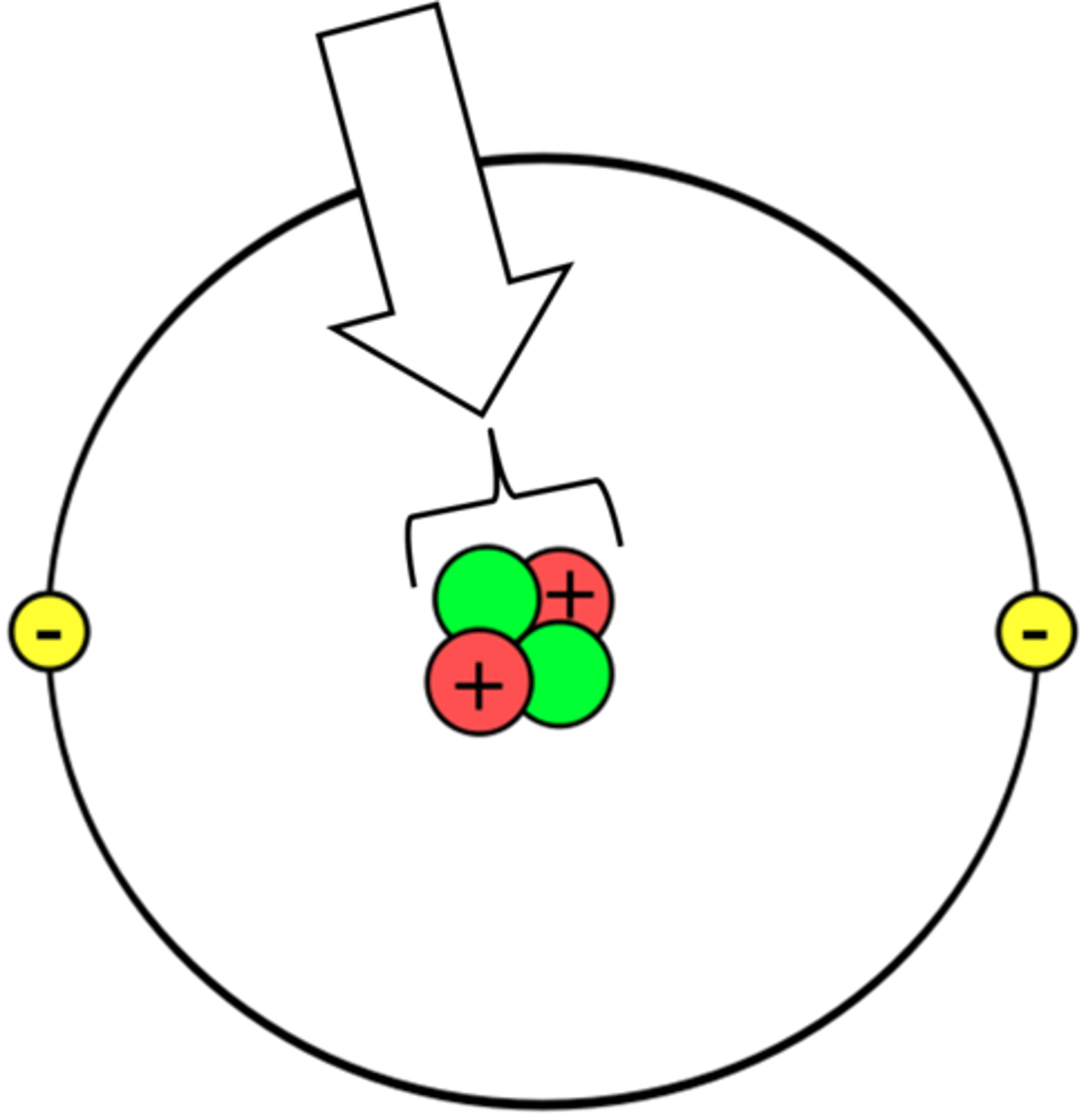
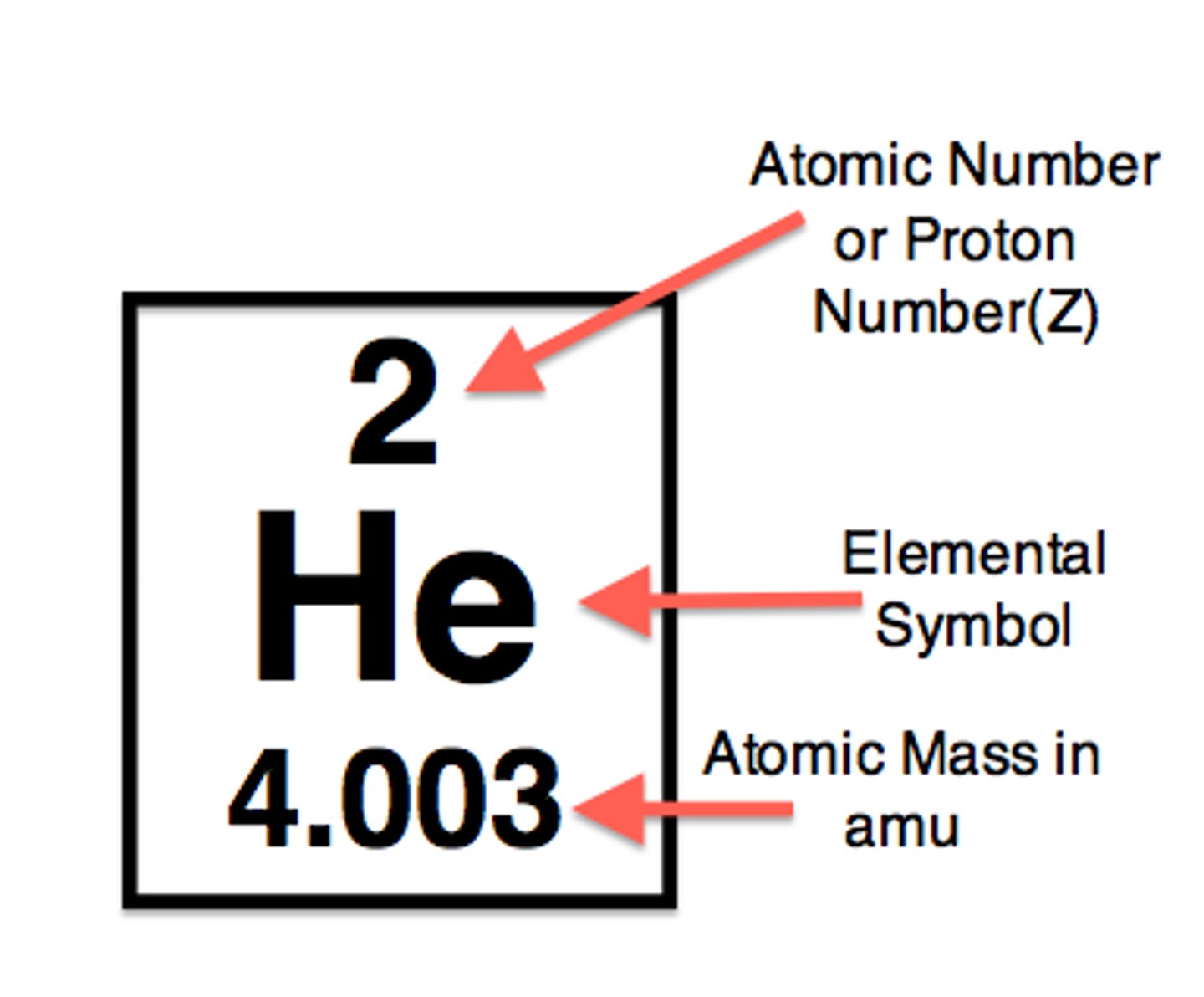
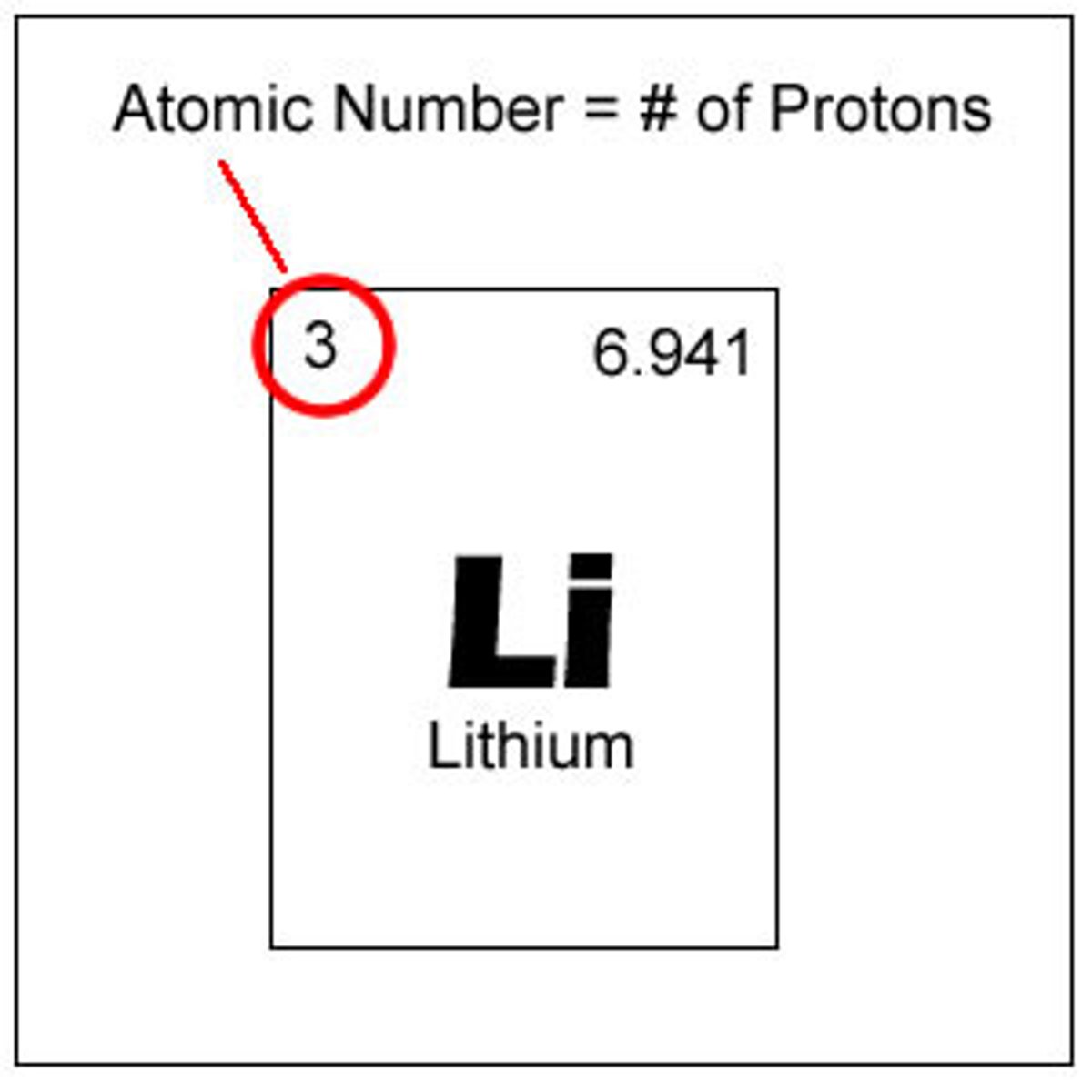
atomic number
the number of protons in an atom, defines the element
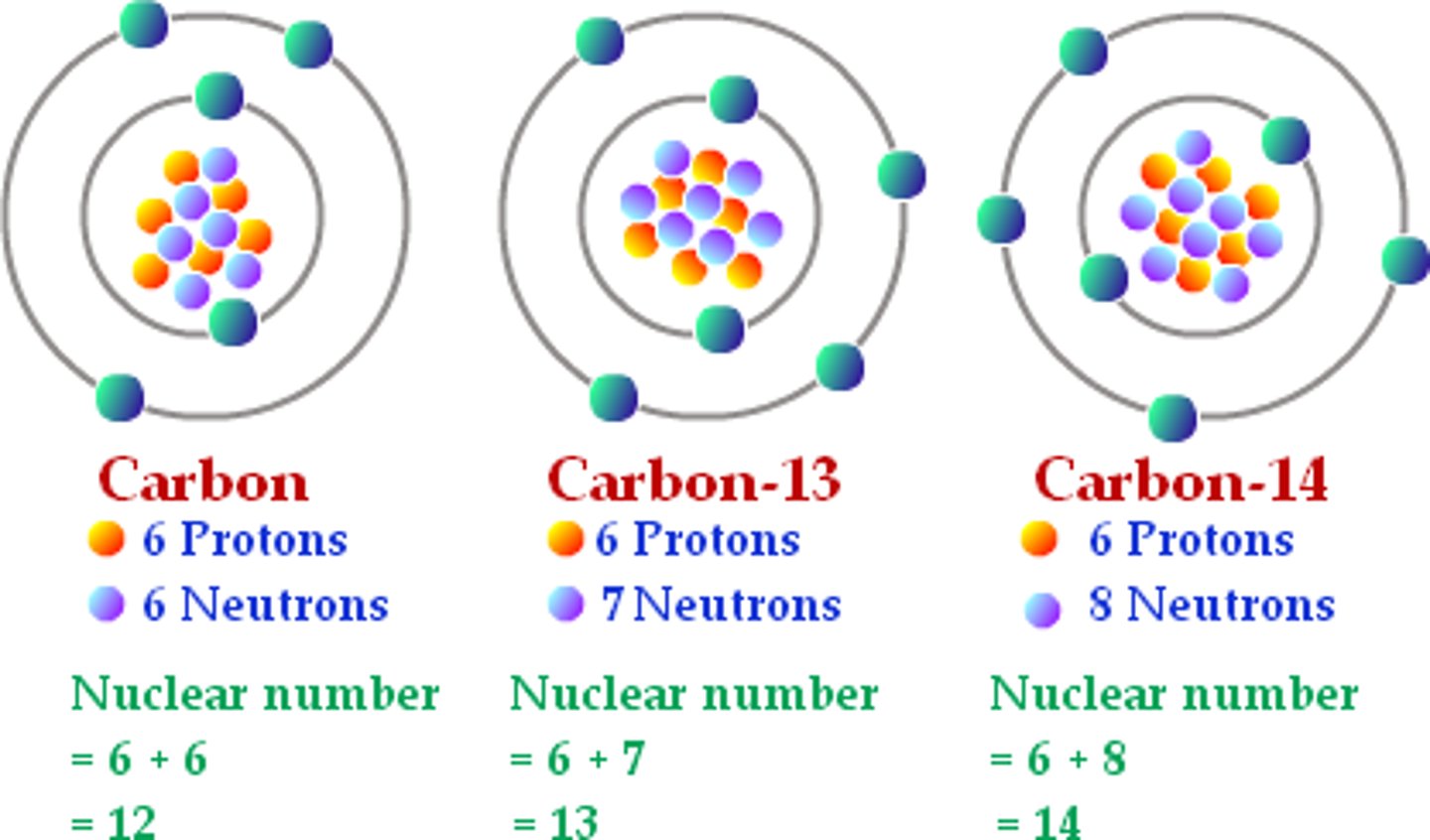
isotopes
Atoms of the same element (same protons) with different numbers of neutrons
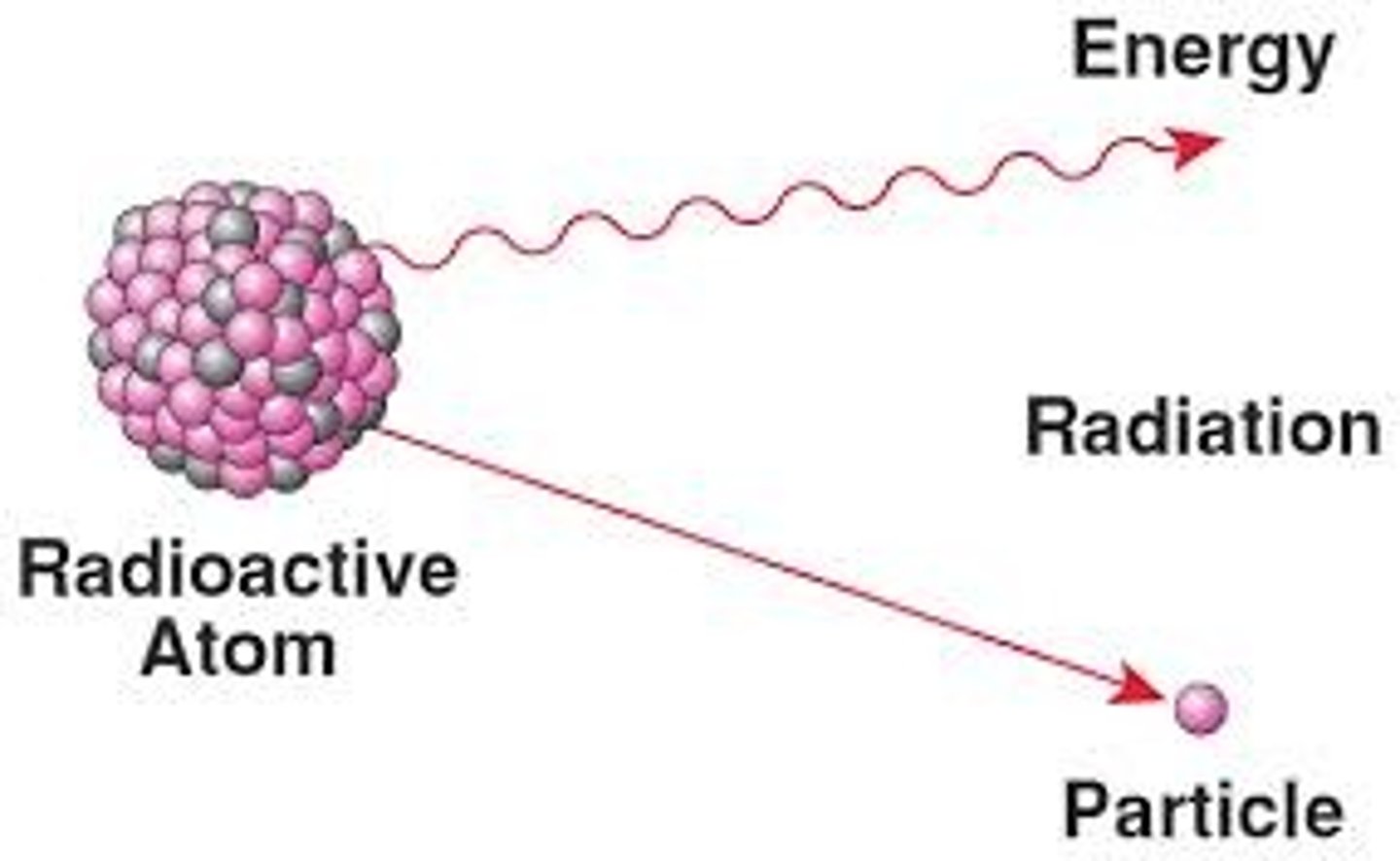
radioactive isotope
an isotope that has an unstable nucleus and that emits radiation
electron shell
electrons inhabit the space around there nucleus
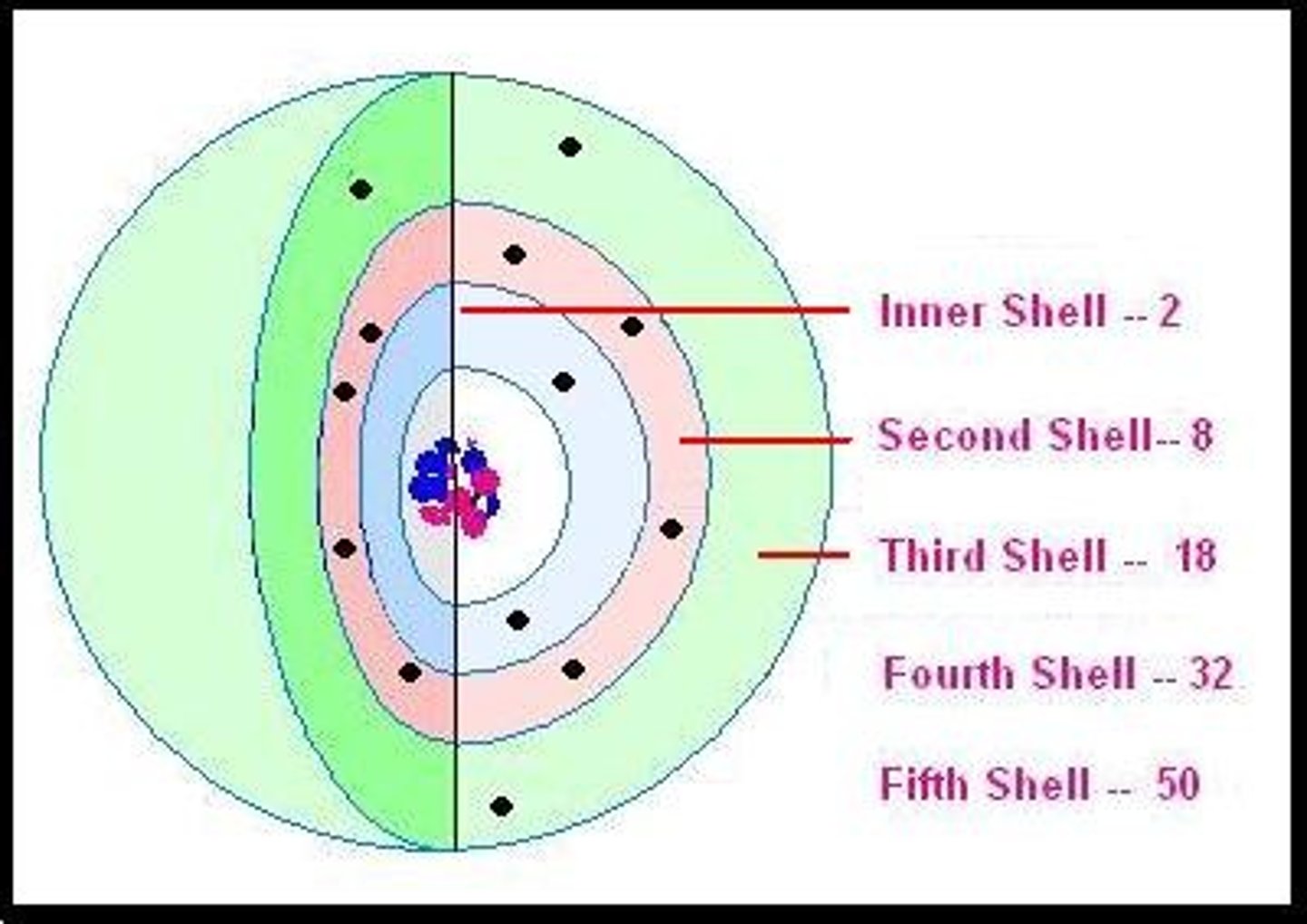
first electron shell
closest to the nucleus, holds 2 electrons
second electron shell
filled with 8 electrons
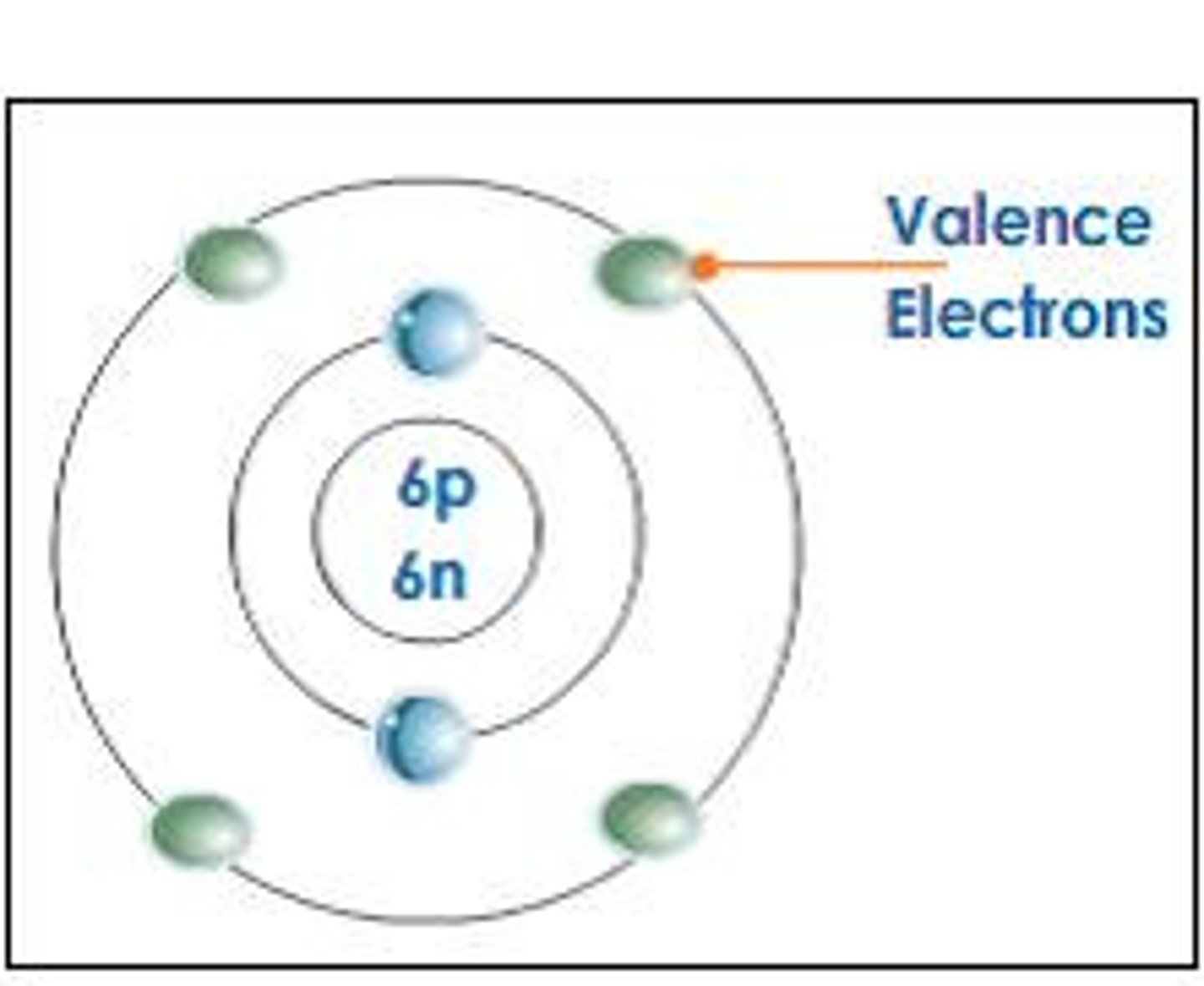
valence shell
outmost electron shell with an electron
valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell, may form bonds
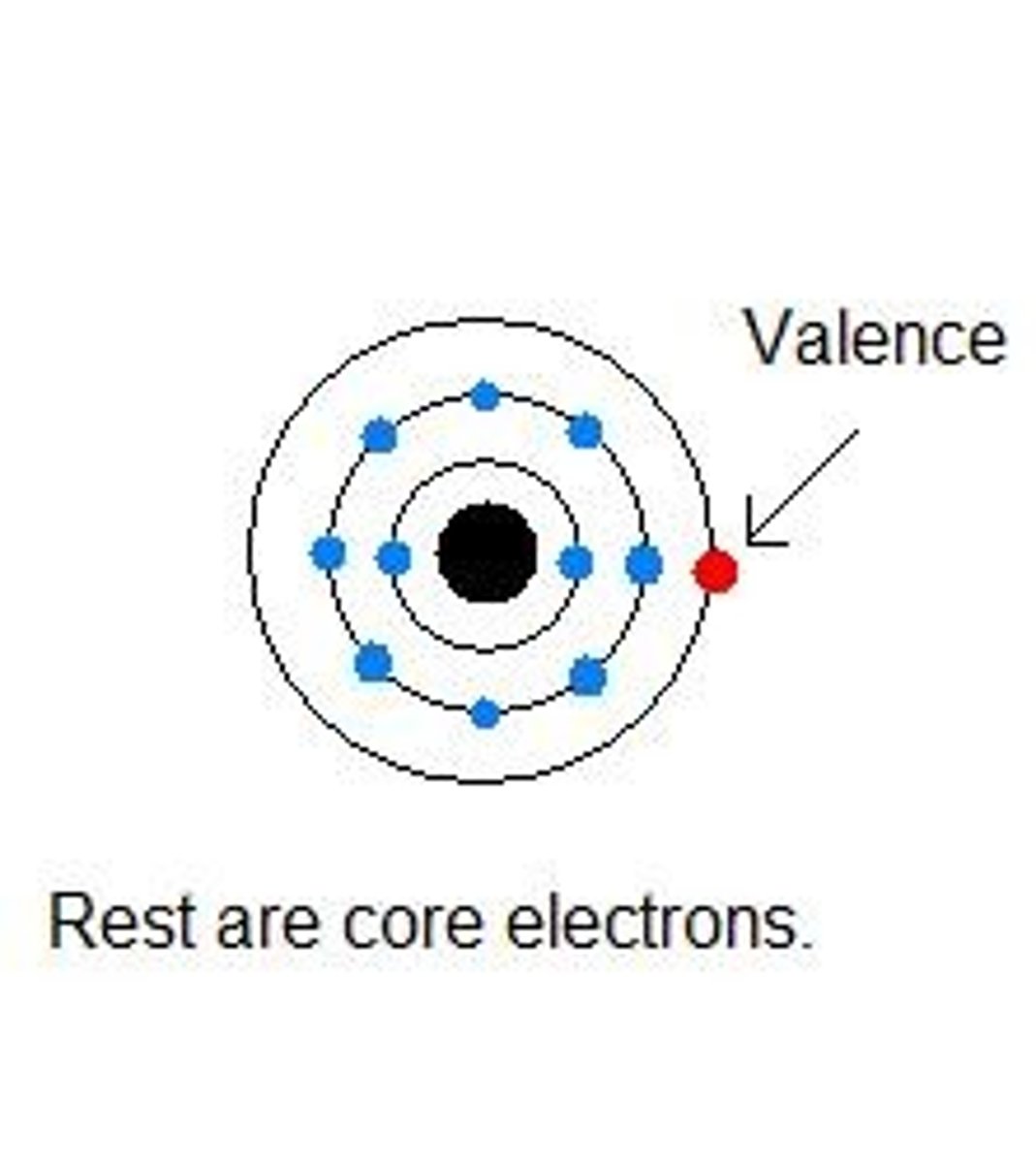
Incomplete valence shell
Not full with electrons, chemically reactive
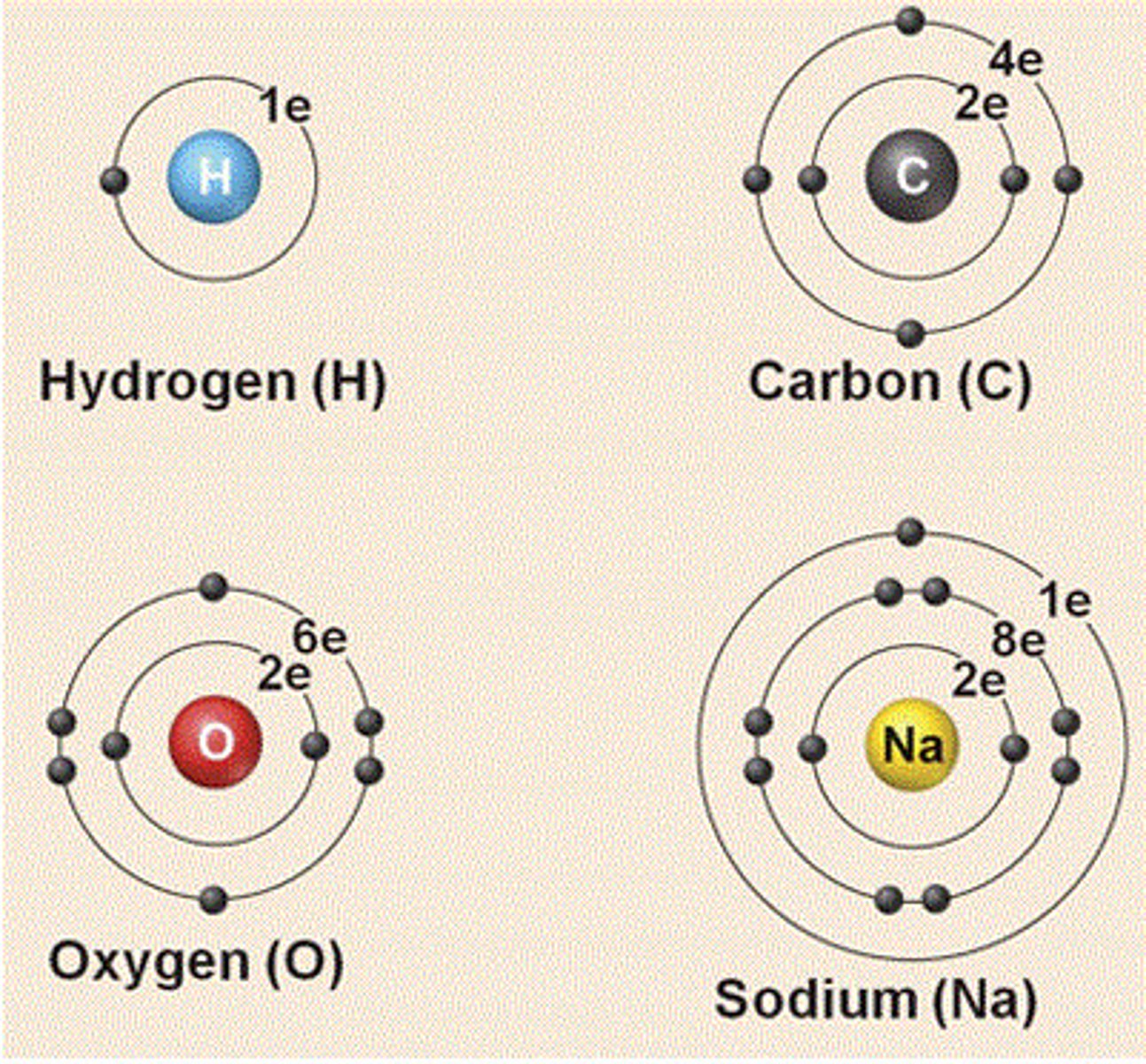
complete valence shell
outermost shell filled with electrons, unreactive and stable.
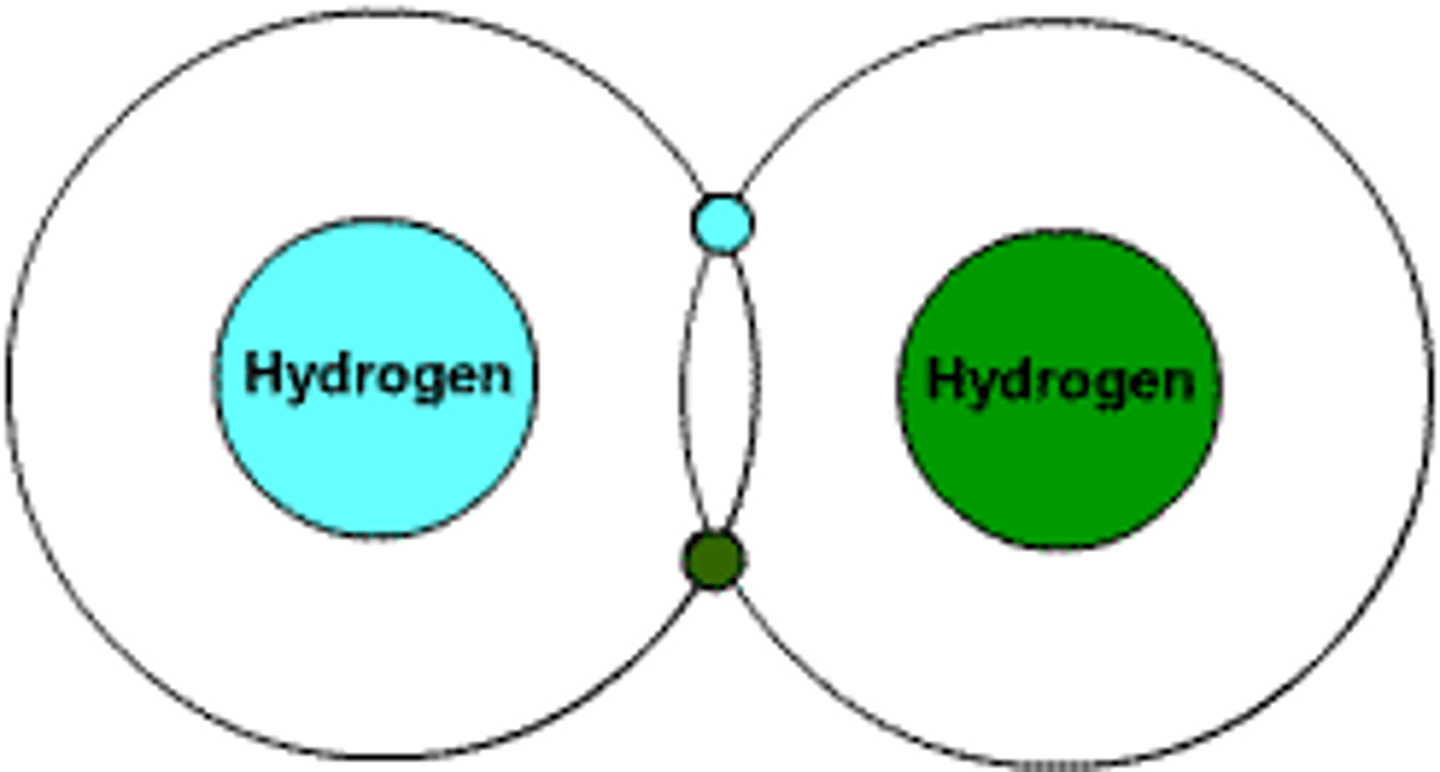
Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together
Compound
substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more different atoms
solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another
[Solute (solid) + Solvent (liquid)= Solution}

Colloid
A mixture containing small, undissolved particles that do not settle out.

Suspension
mixture of liquid and non-dissolved material

Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances (like water)

Solute
the substance that is dissolved (solid) in fluid

covalent bond
A chemical bond formed when two atoms share electrons
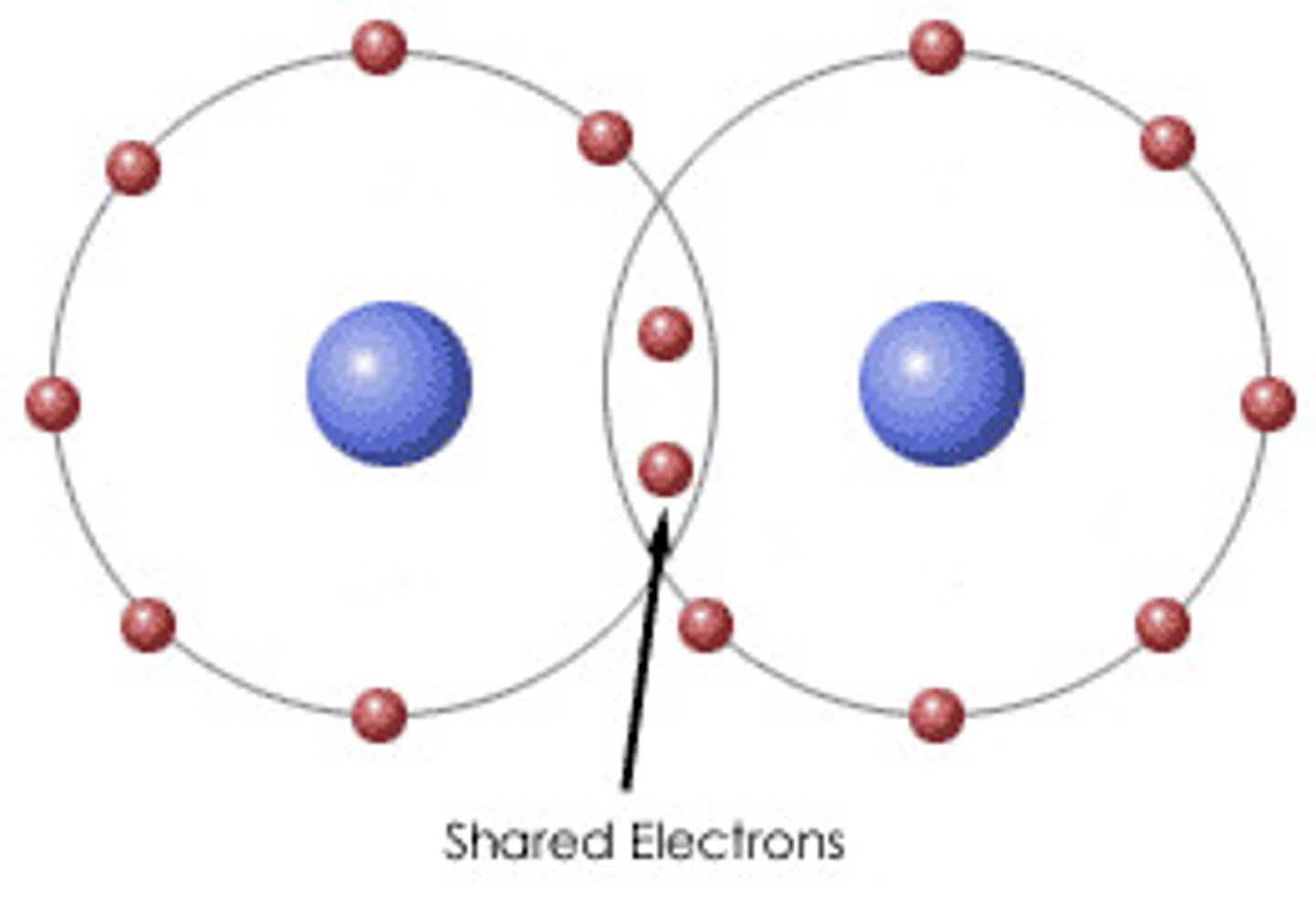
single covalent bond
a bond formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons
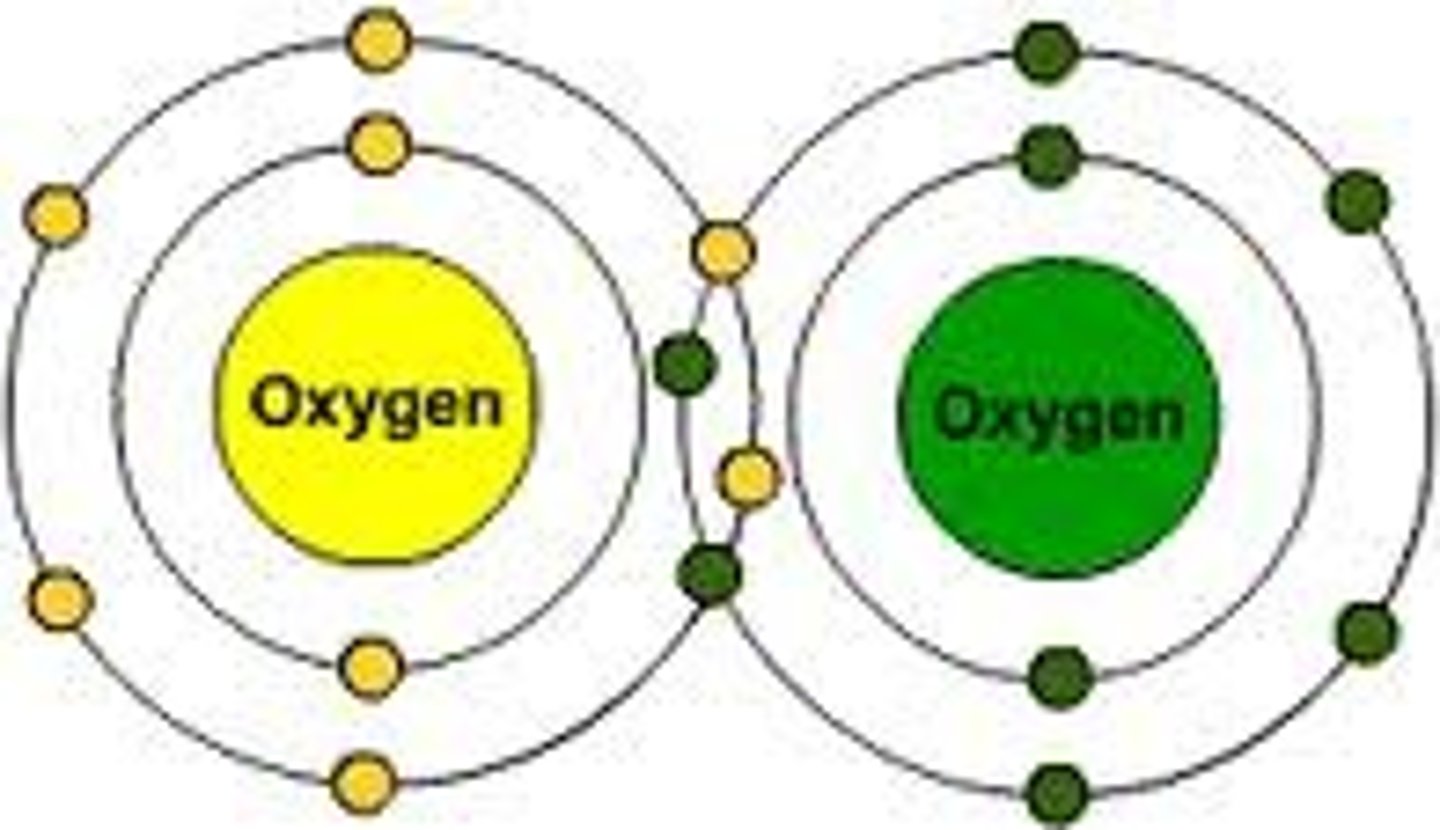
double covalent bond
sharing two pairs of electrons
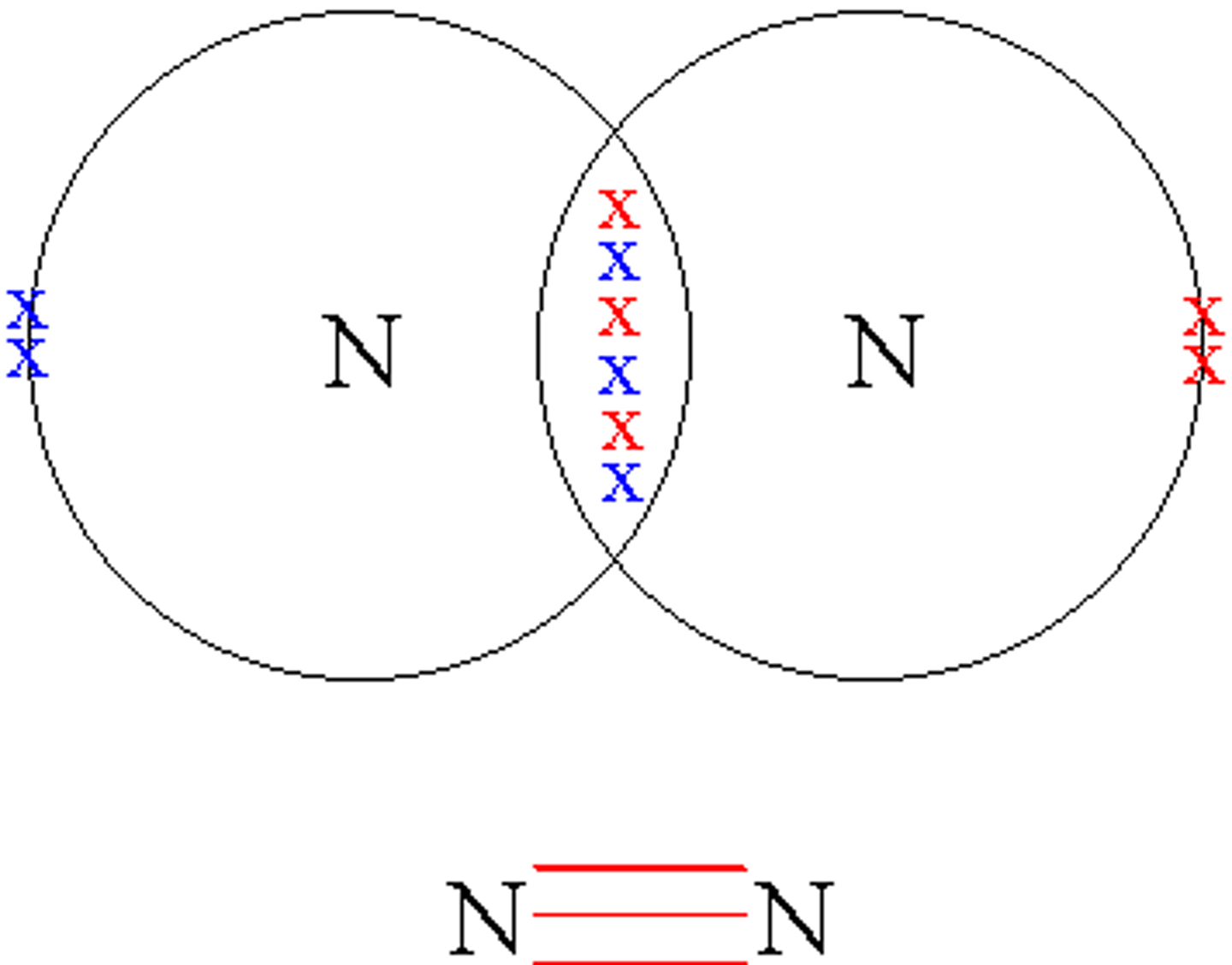
triple covalent bond
a bond formed by sharing three pairs of electrons
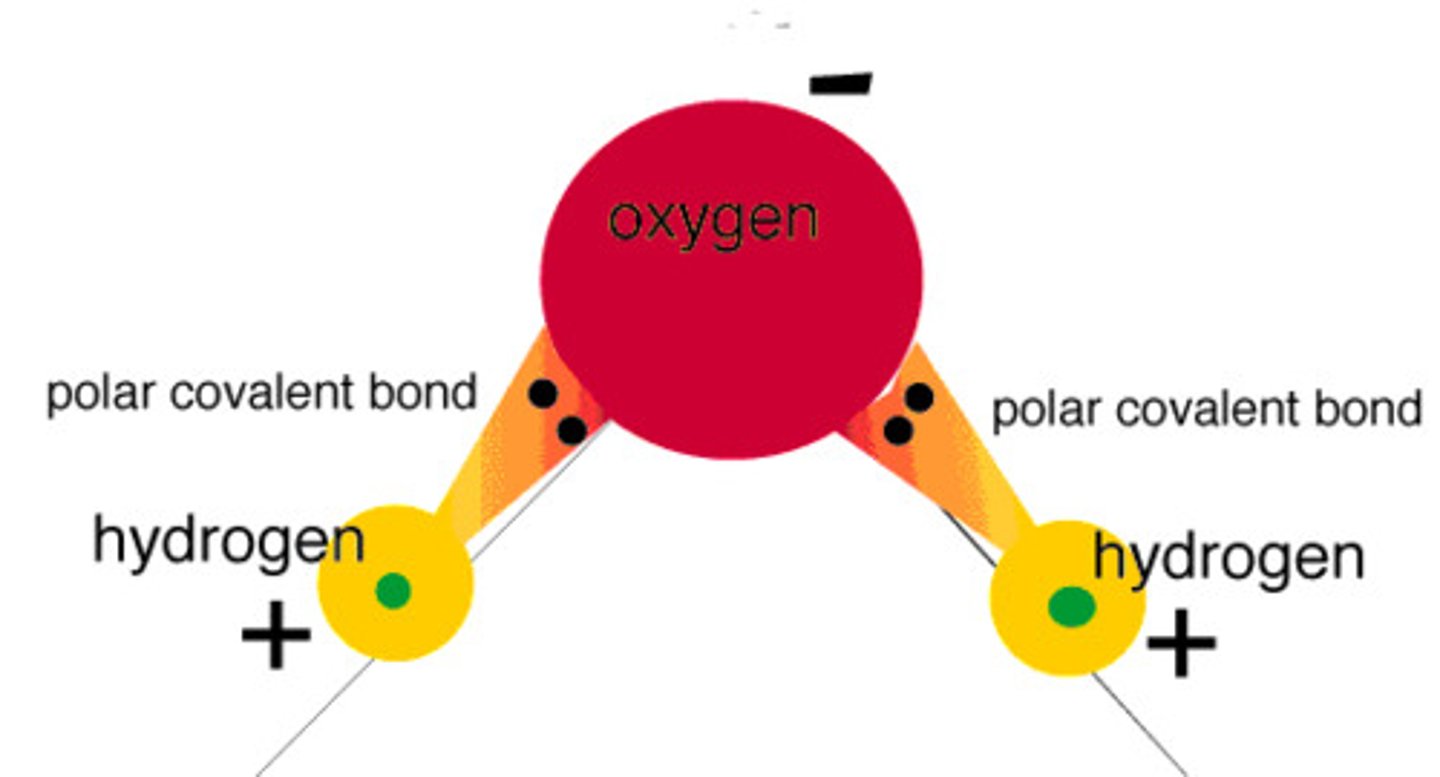
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
non polar covalent bond
equal sharing of electrons
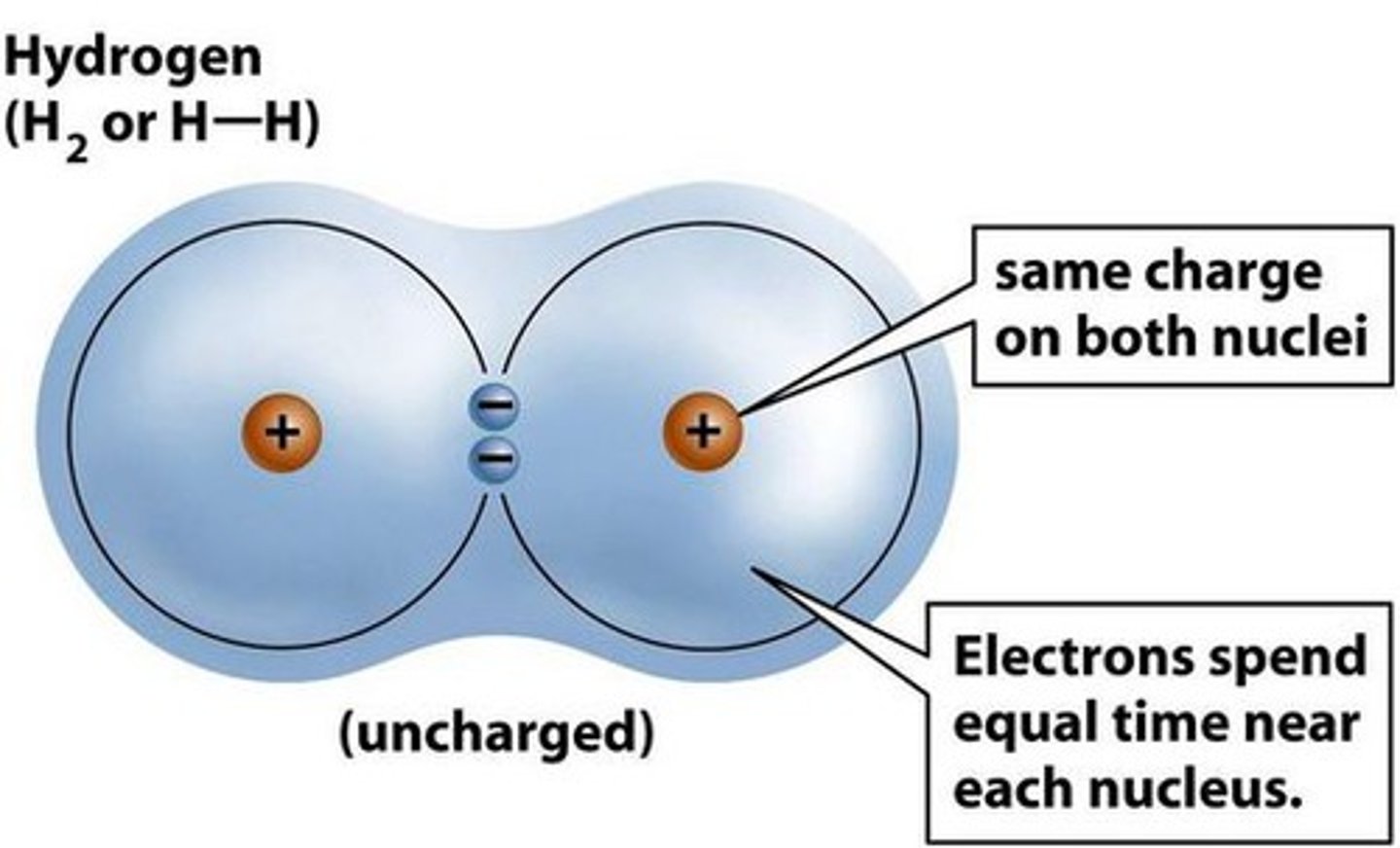
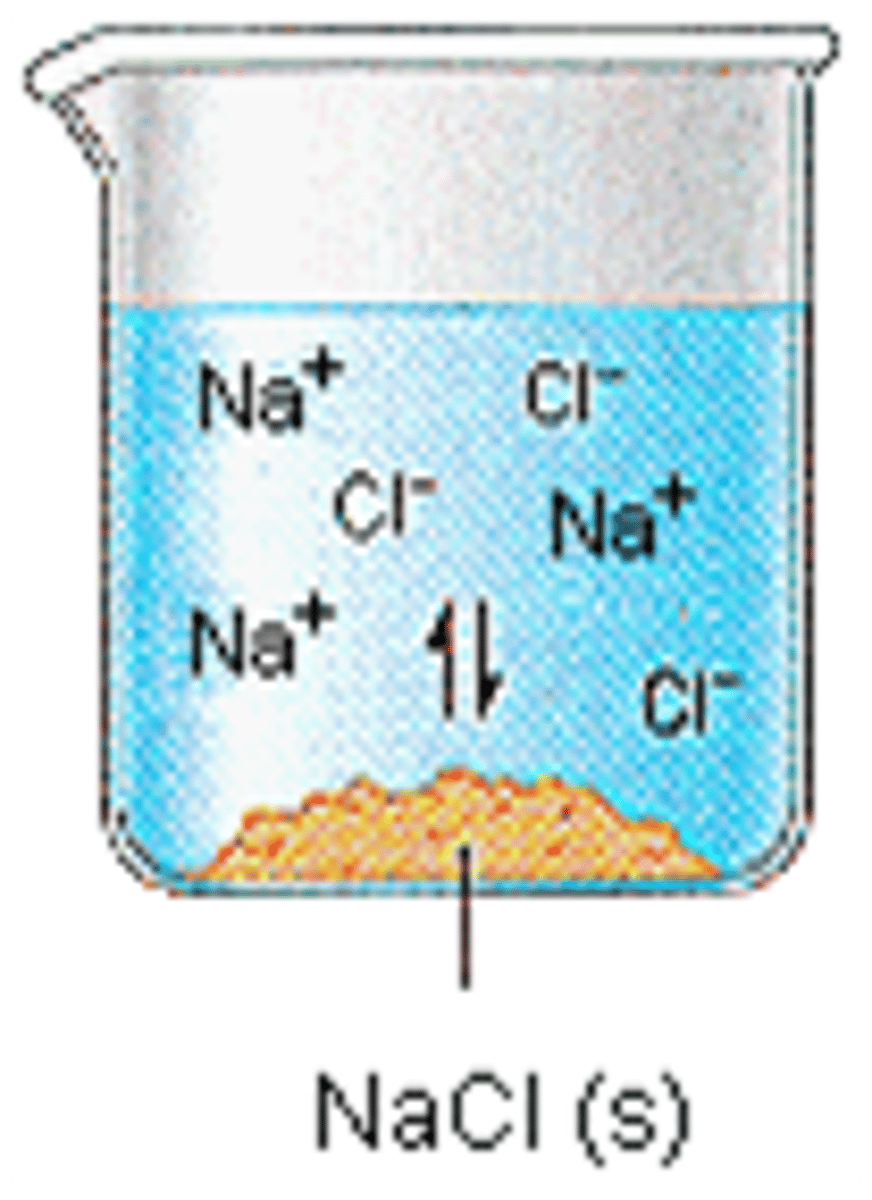
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
cations
An atom loses an electron and becomes positively charged

Anions
An atom gains an electron and becomes negatively charged

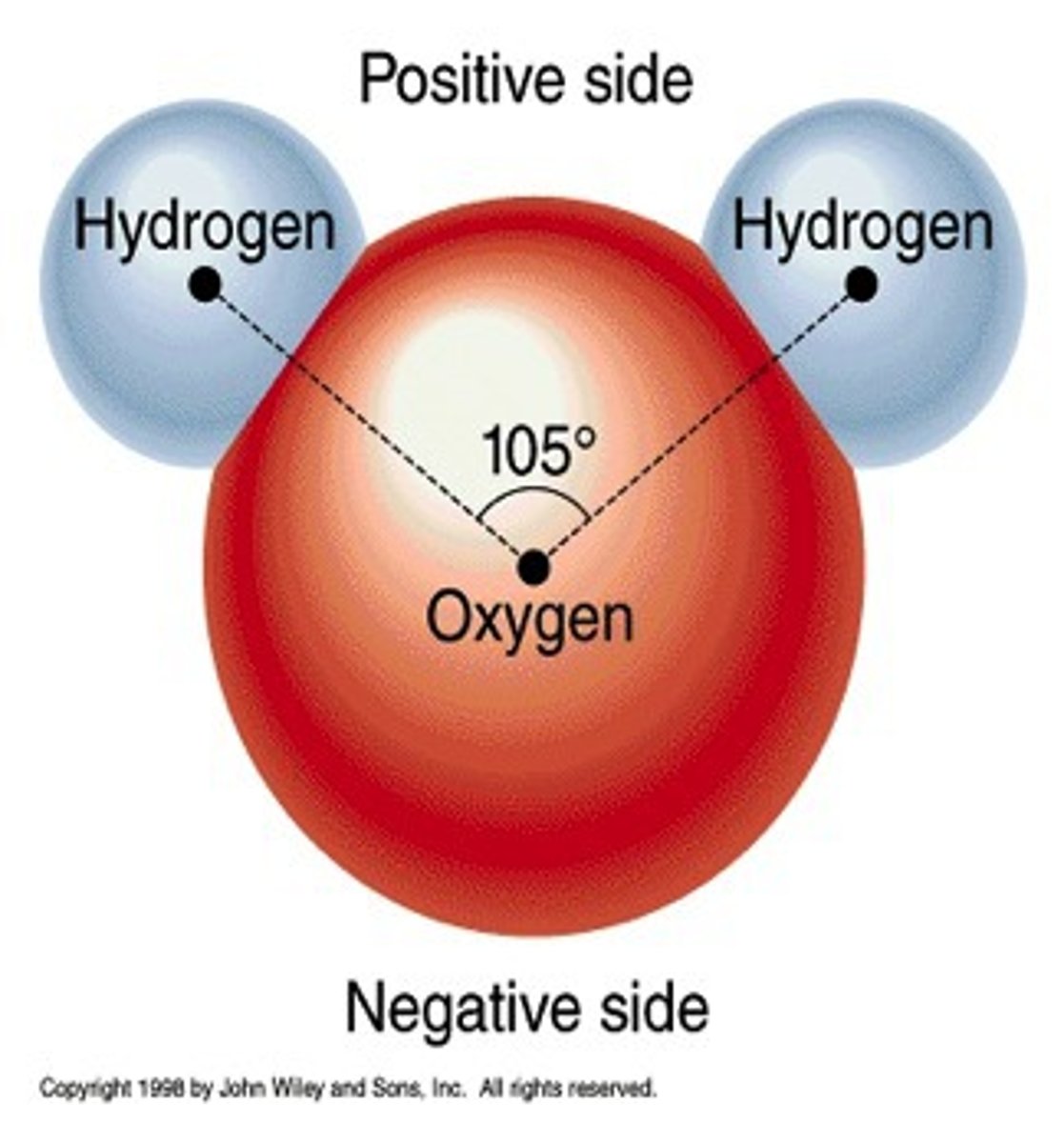
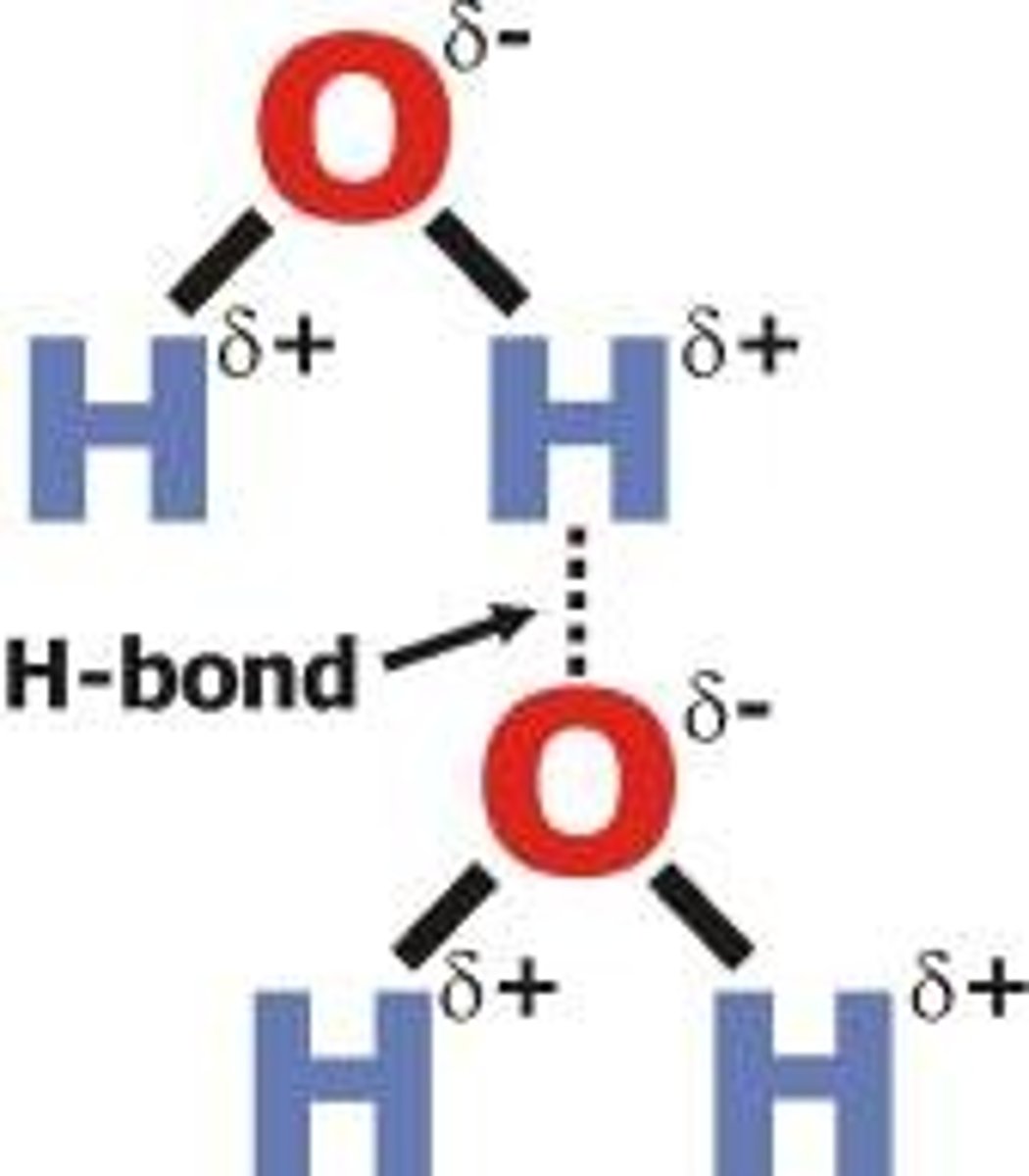
hydrogen bond
A weak chemical bond formed when the slightly positive end of a polar covalent bond is attracted to the slightly negative end of a polar covalent bond in another molecule.
chemical reaction
process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals
Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction (Na + Cl)
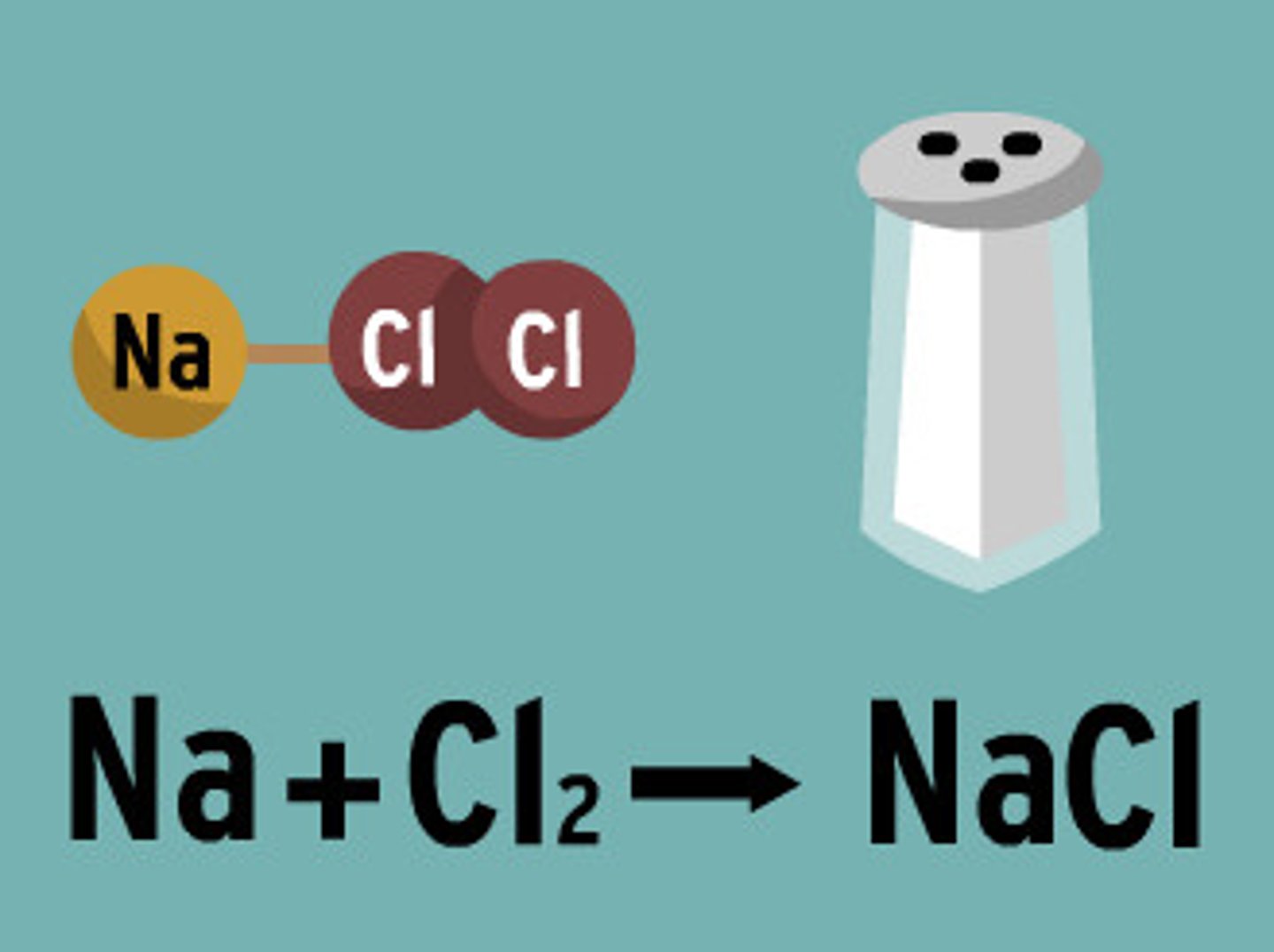
Products
the substances that are formed by the chemical change (NaCl)
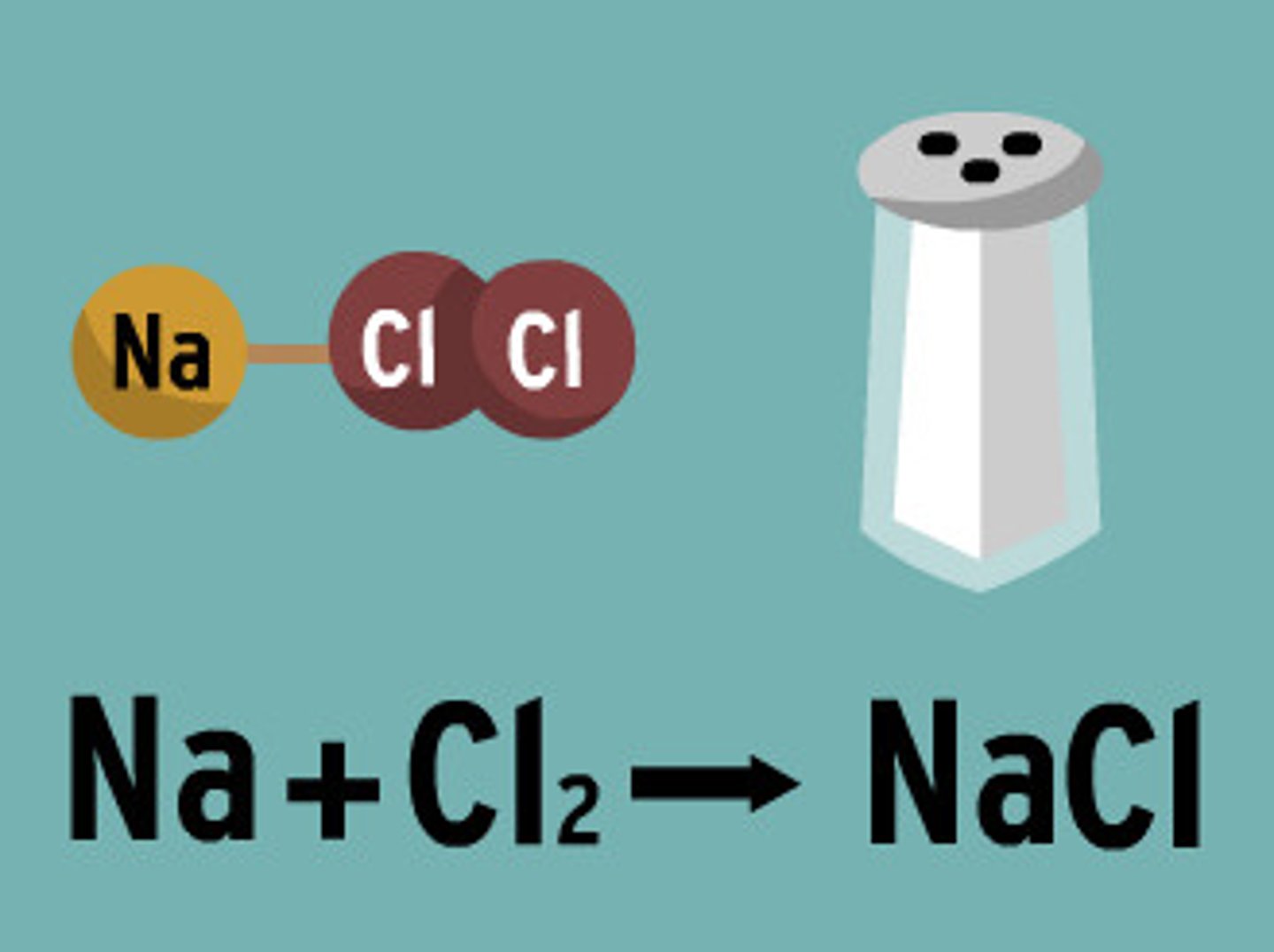
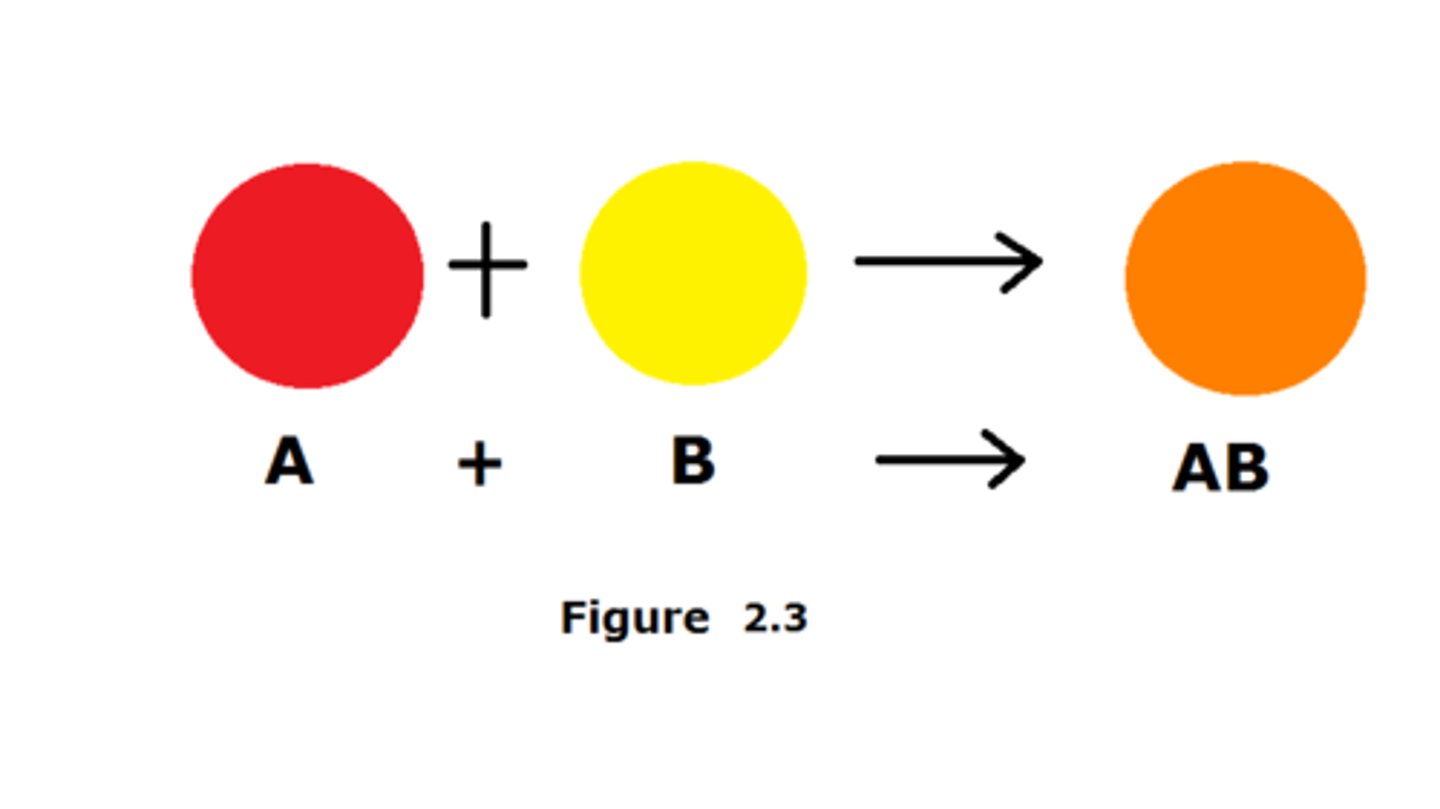
synthesis reaction
Building reaction: forms a bigger molecule. two or more substances combine to form another substance
decomposition reaction
A breakdown reaction, AB --> A + B
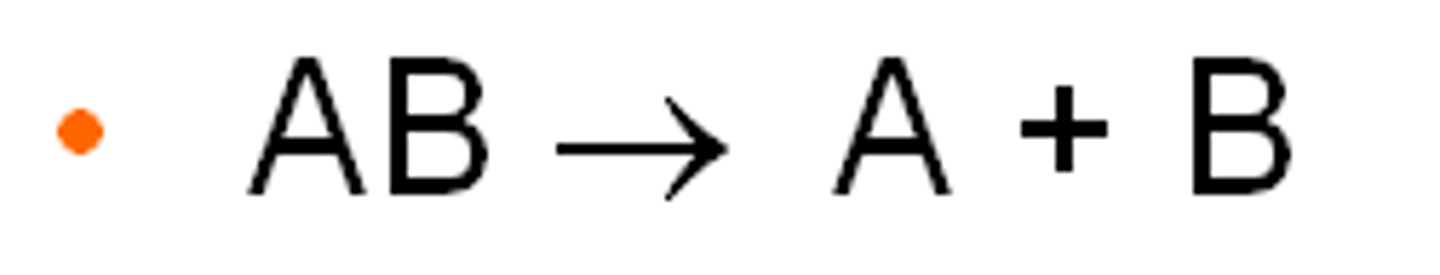
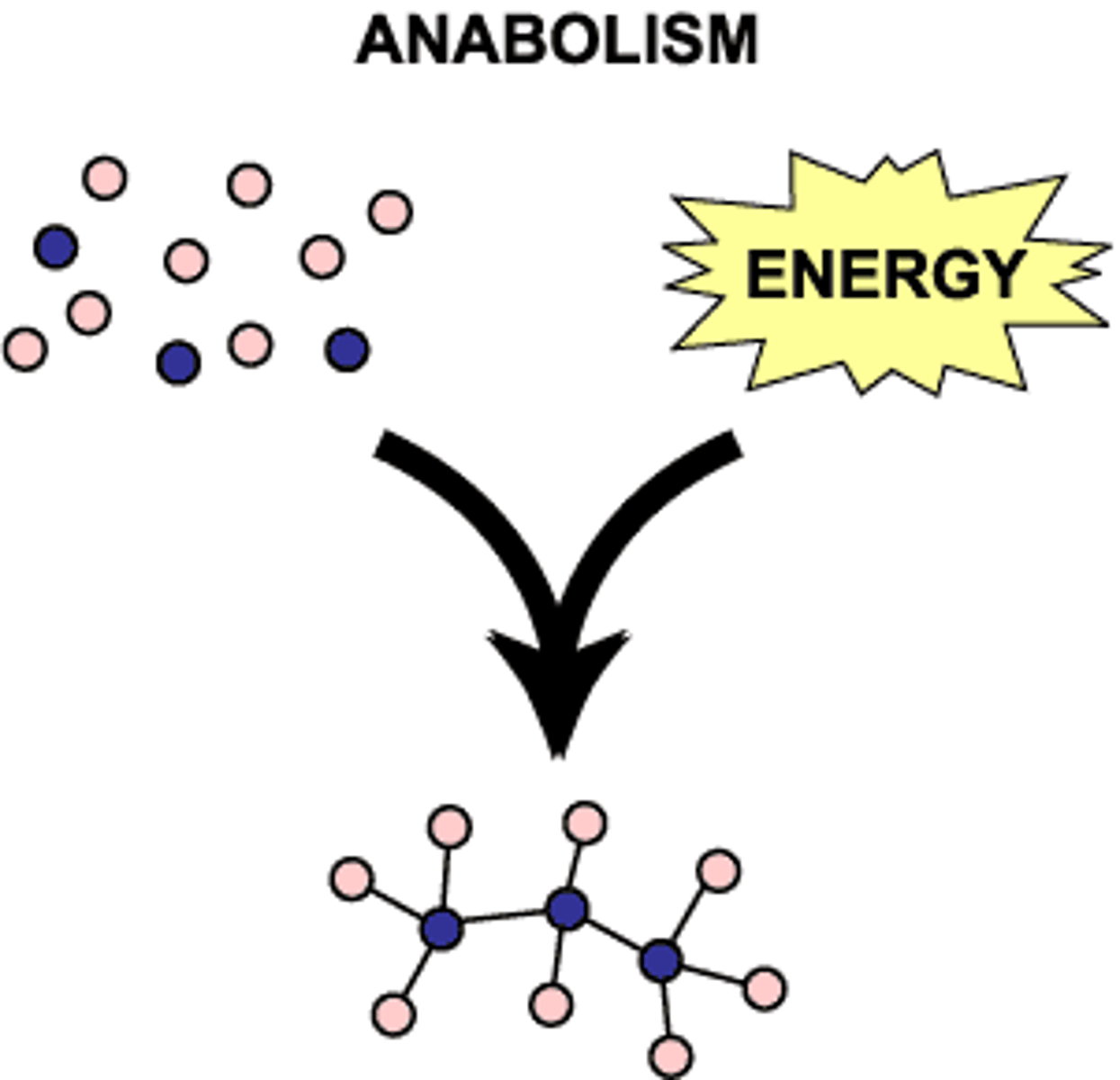
Anabolism
Reactions that construct molecules, requiring energy. (Synthesis)
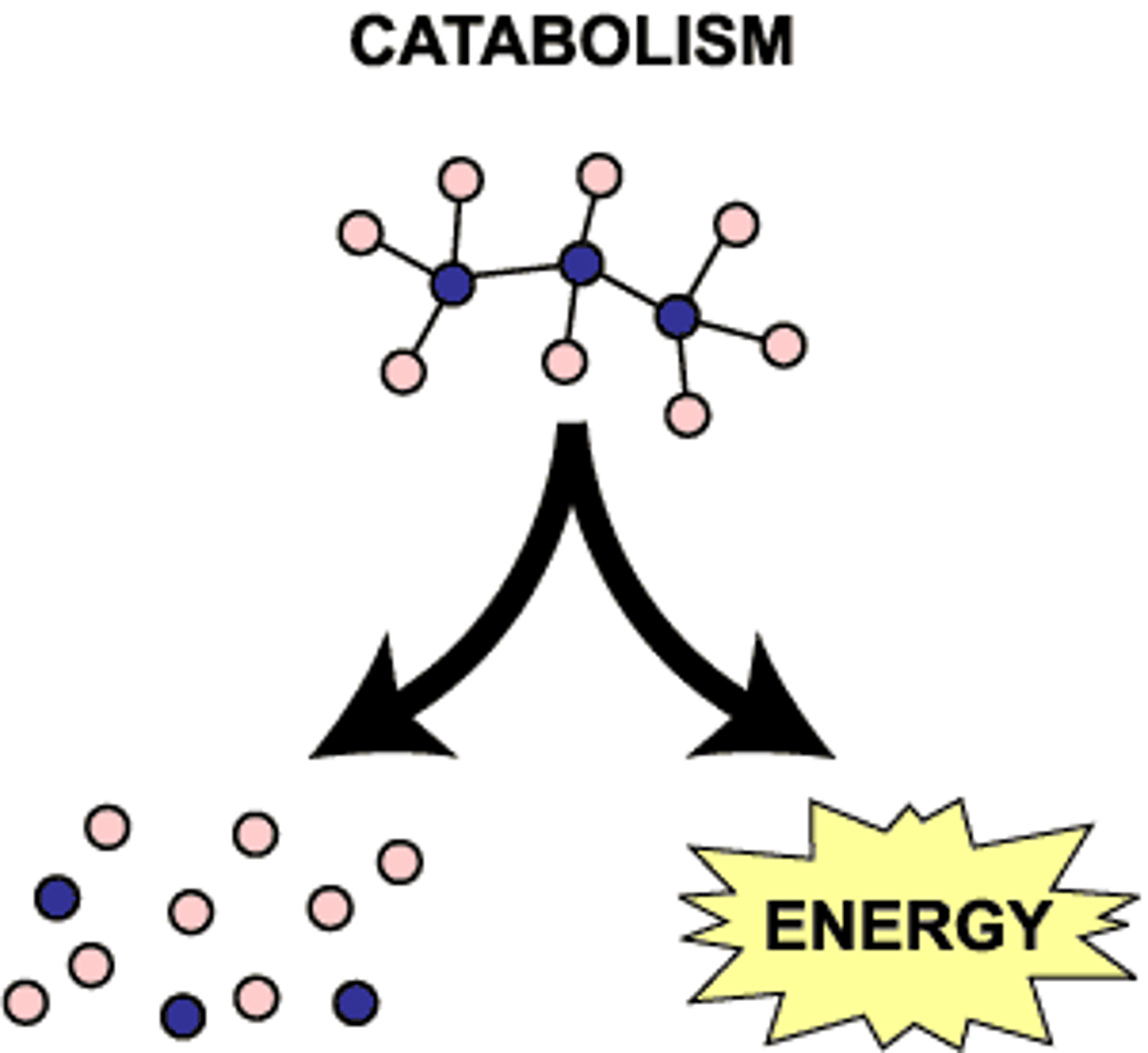
Catabolism
Metabolic reactions that break down molecules, releasing energy. (Decomposition)
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction

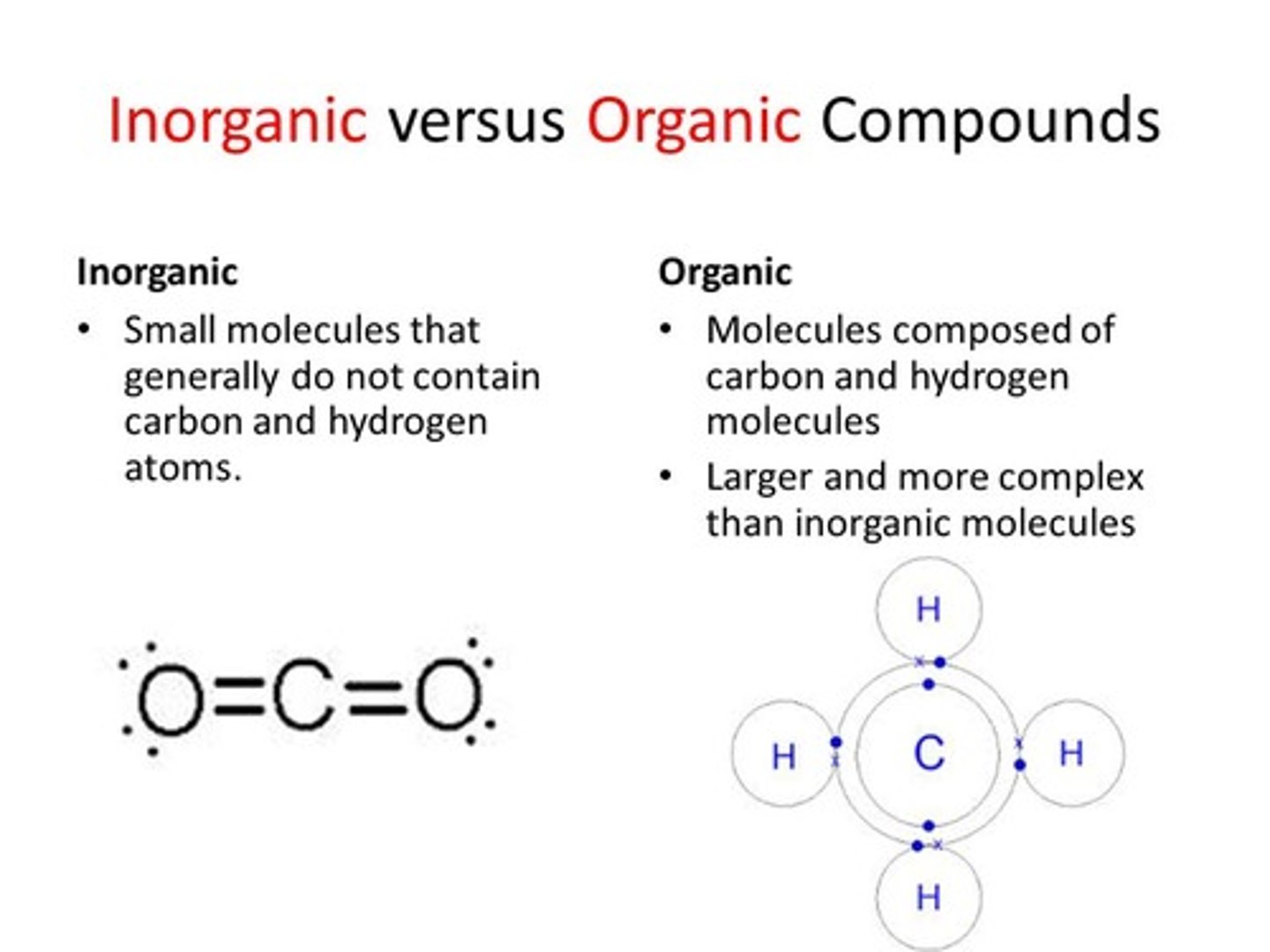
organic compounds
compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen
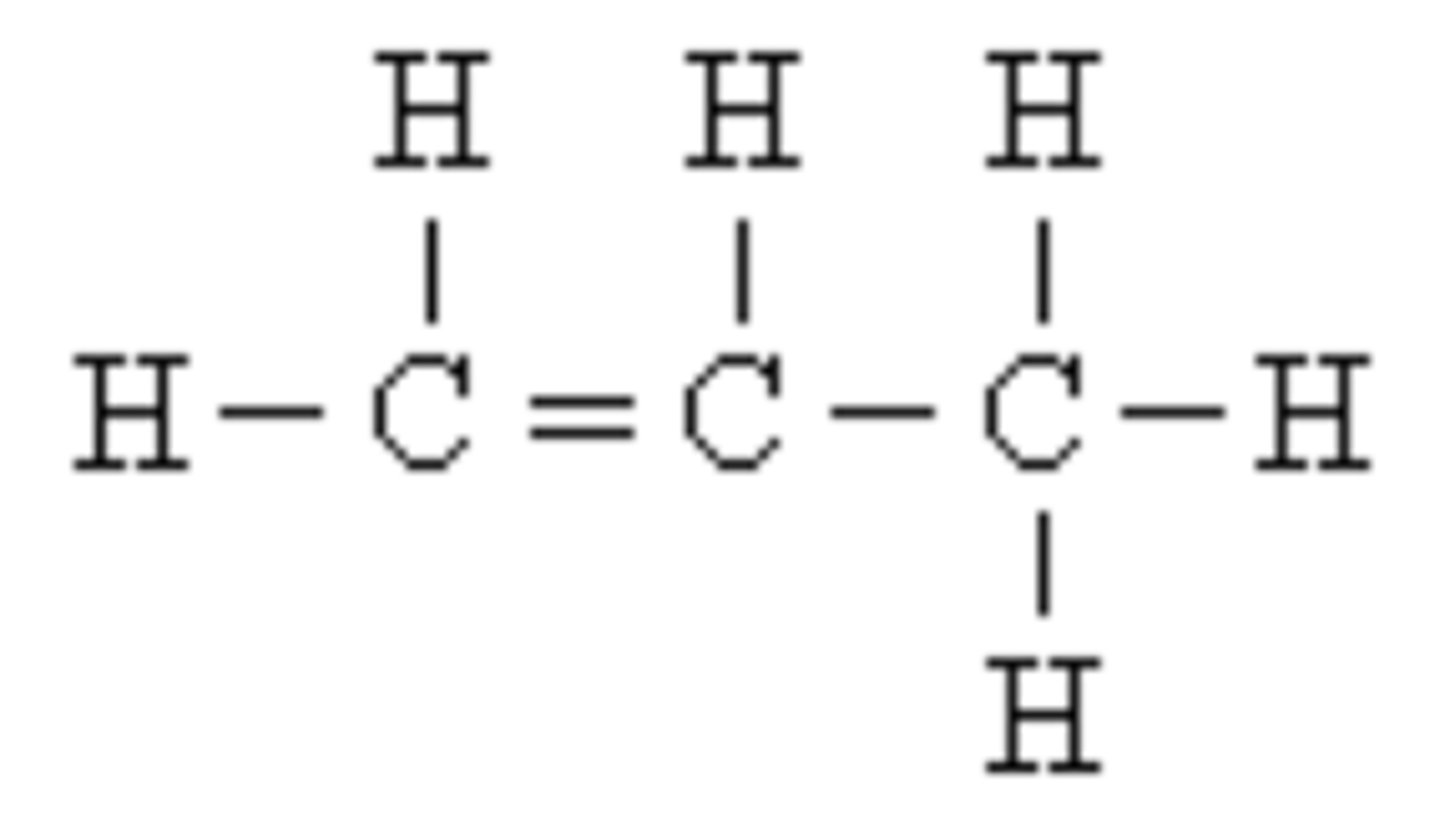
Inorganic molecules
molecules that do not contain carbon
functional groups
chemical groups attached to carbon skeletons that give compounds their functionality
Hydrophobic
water hating, molecules that won't dissolve in water (oil)
Hydrophilic
water loving, molecules that will dissolve in water (Salt)
universal solvent
Water- due to its polarity and ability to dissolve many different solutes

Electrolytes
minerals that carry electrical charges that help maintain the body's fluid balance (Na, Cl, K, Mg)
Acids
substances that release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
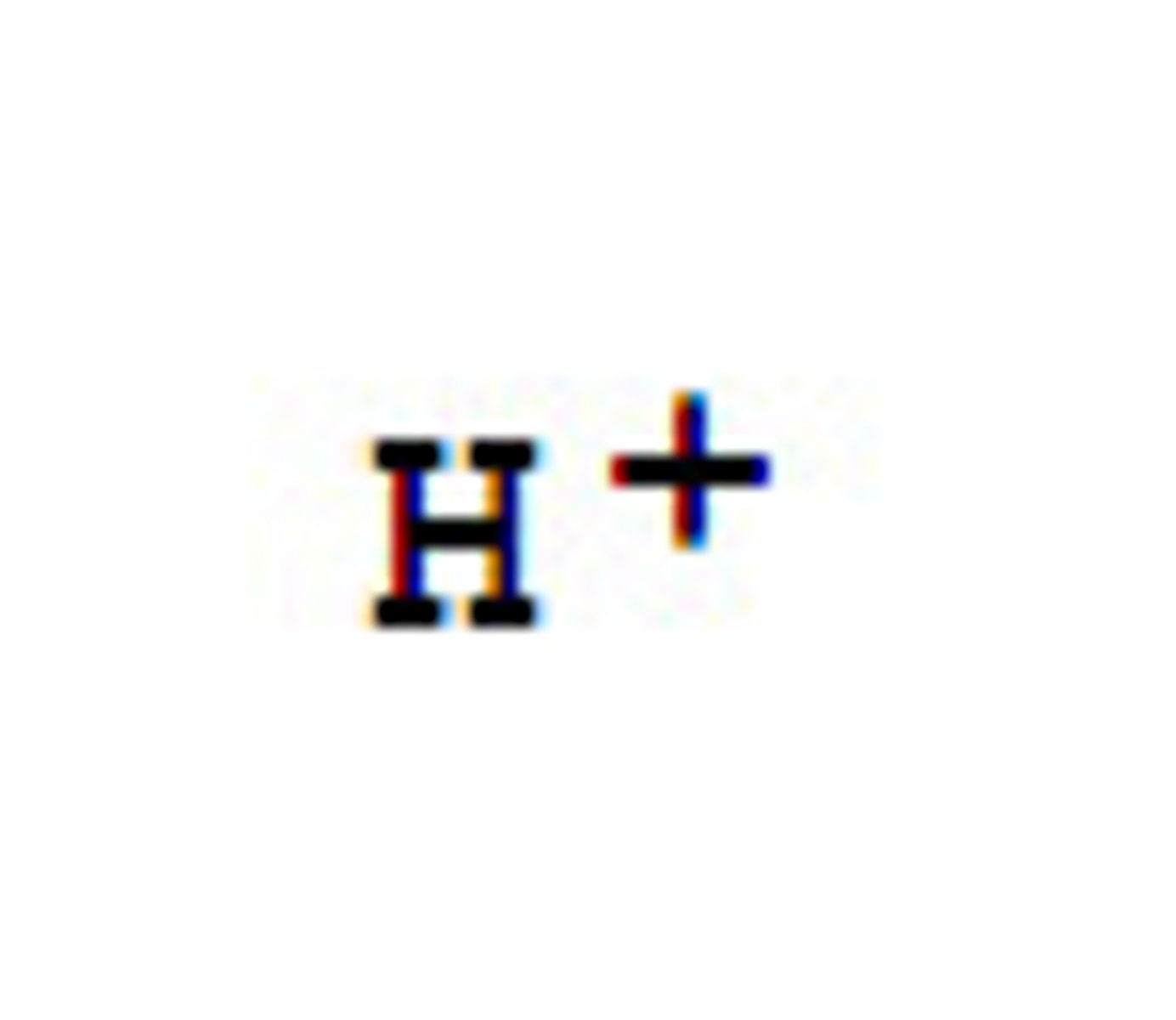
Bases
Compounds that remove hydrogen ions from a solution.

neutral
pH of 7
acidic
pH less than 7
basic
pH greater than 7
pH scale
scale with values from 0 to 14, used to measure the concentration of H+ ions in a solution
Buffers
Stabilizes the body pH
4 organic molecules of life
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
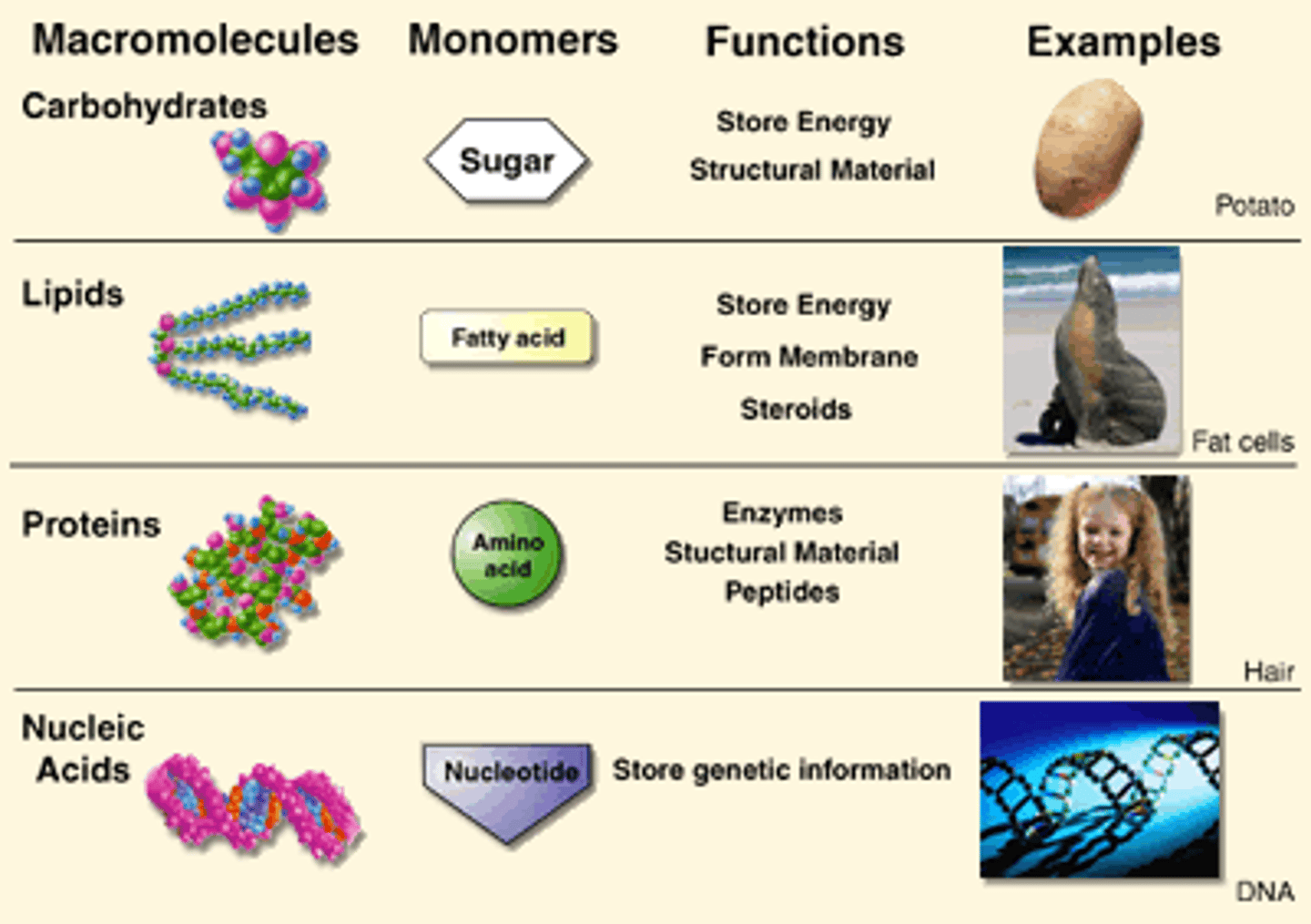
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
Glucose
the monosaccharide that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. (blood sugar)

Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined together
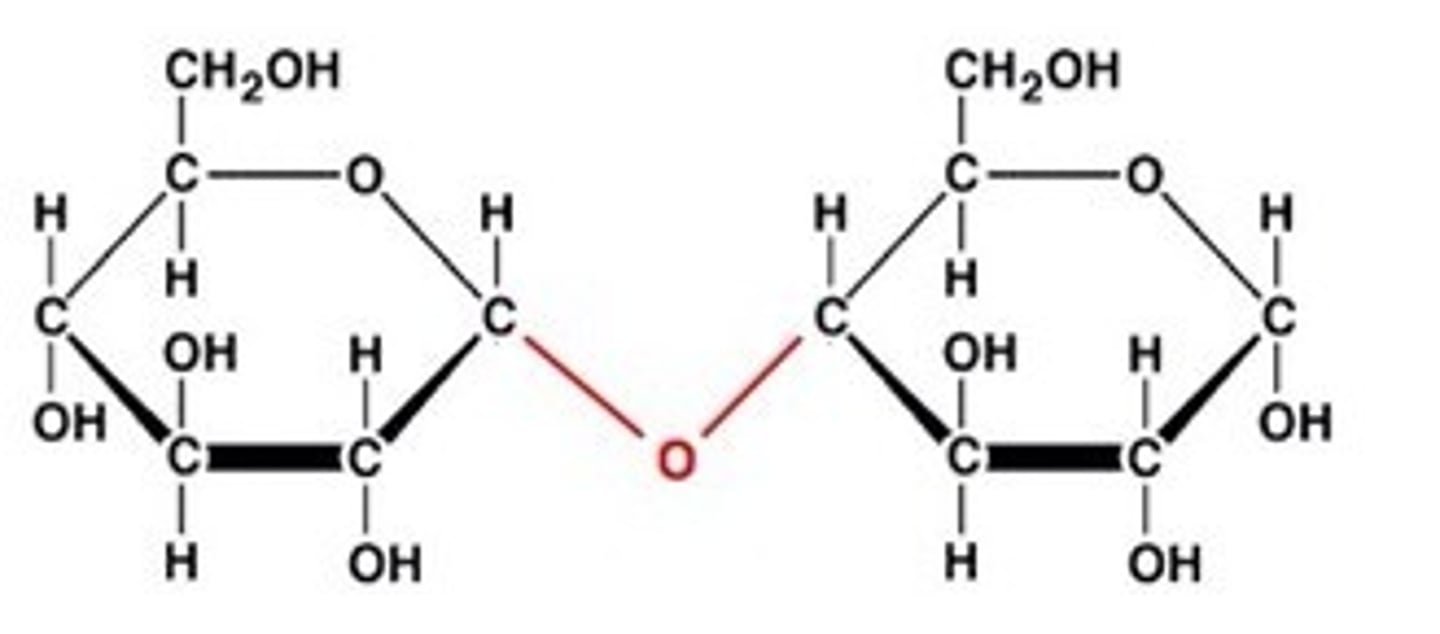
complex carbohydrates
starches from plants, fiber from plants, glycogen from the liver/muscles.

Polysaccharides
large macromolecules formed from many monosaccharides bonded together (starches, glycogen, fiber)
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.

Triglycerides
Fats and Oils: energy-rich compounds made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid.
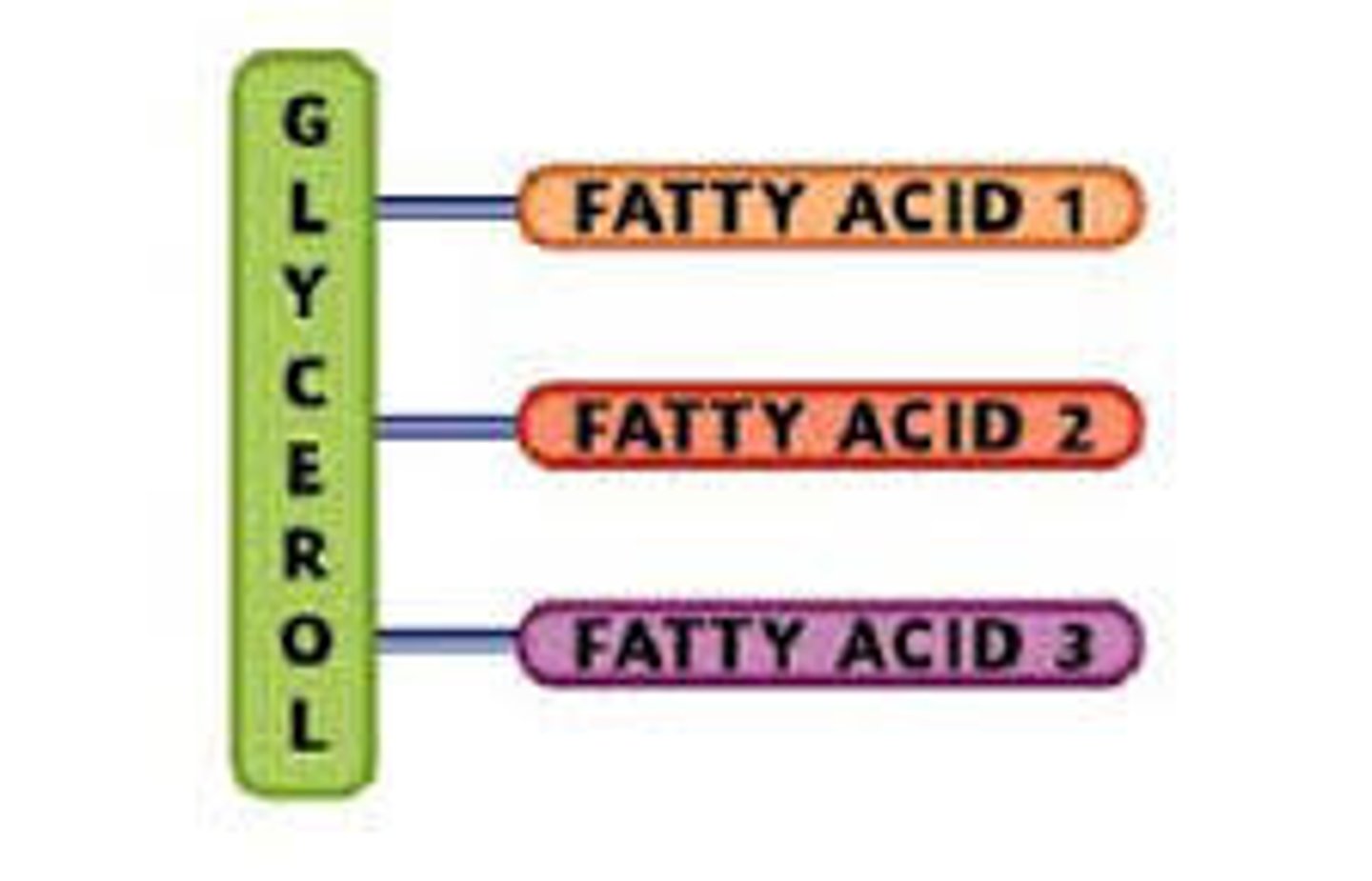
Fatty acids
Building Blocks of Lipids, chains of carbons bonds to hydrogens
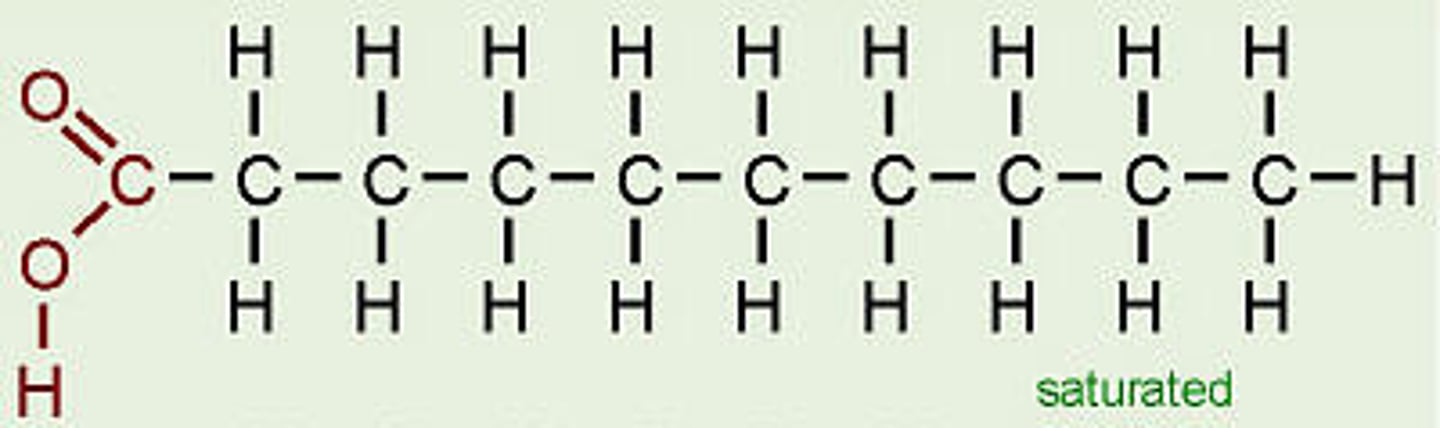
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with no double bonds between carbons.
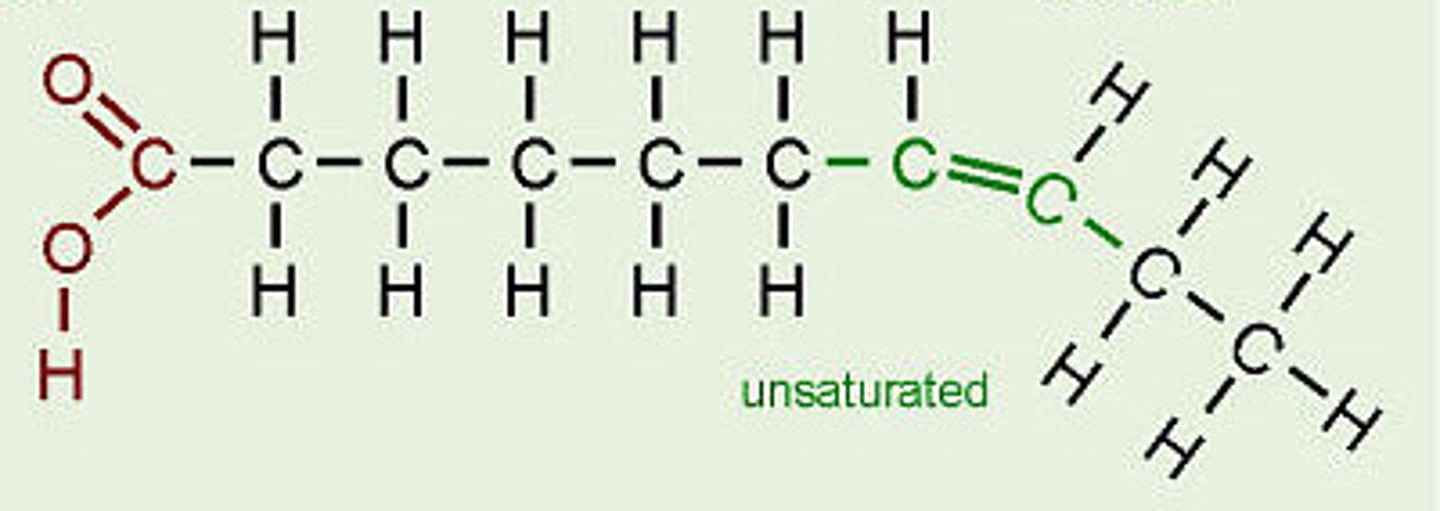
Unsaturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with one or more double bonds.
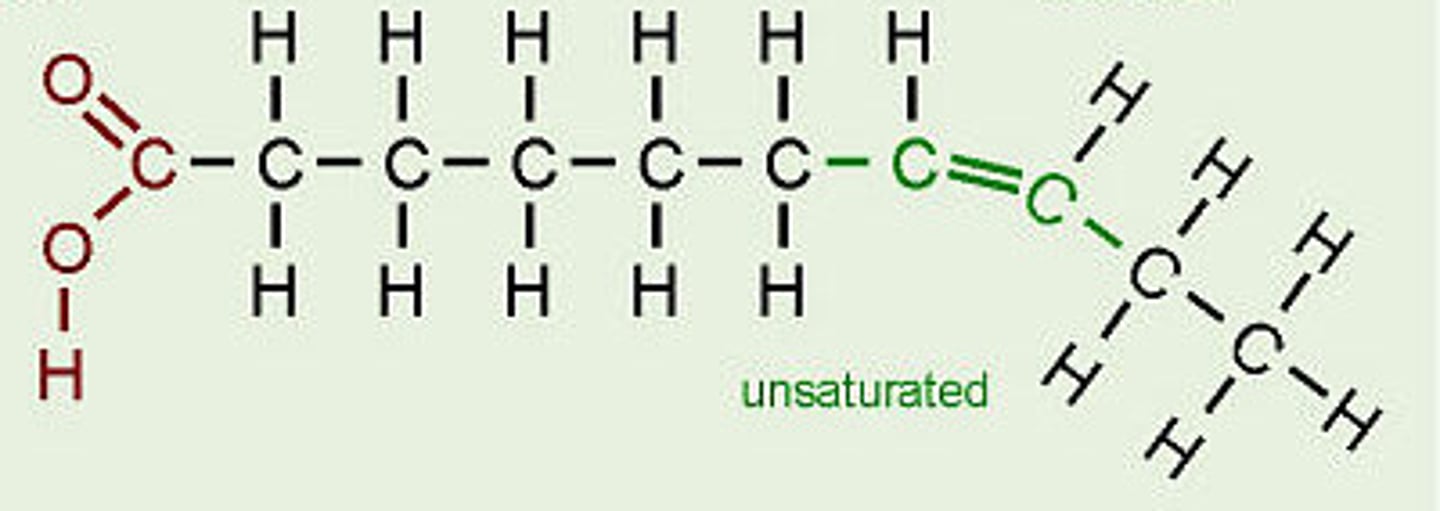
Oils
lipids that are liquid at room temperature, made of fatty acids with double bonds
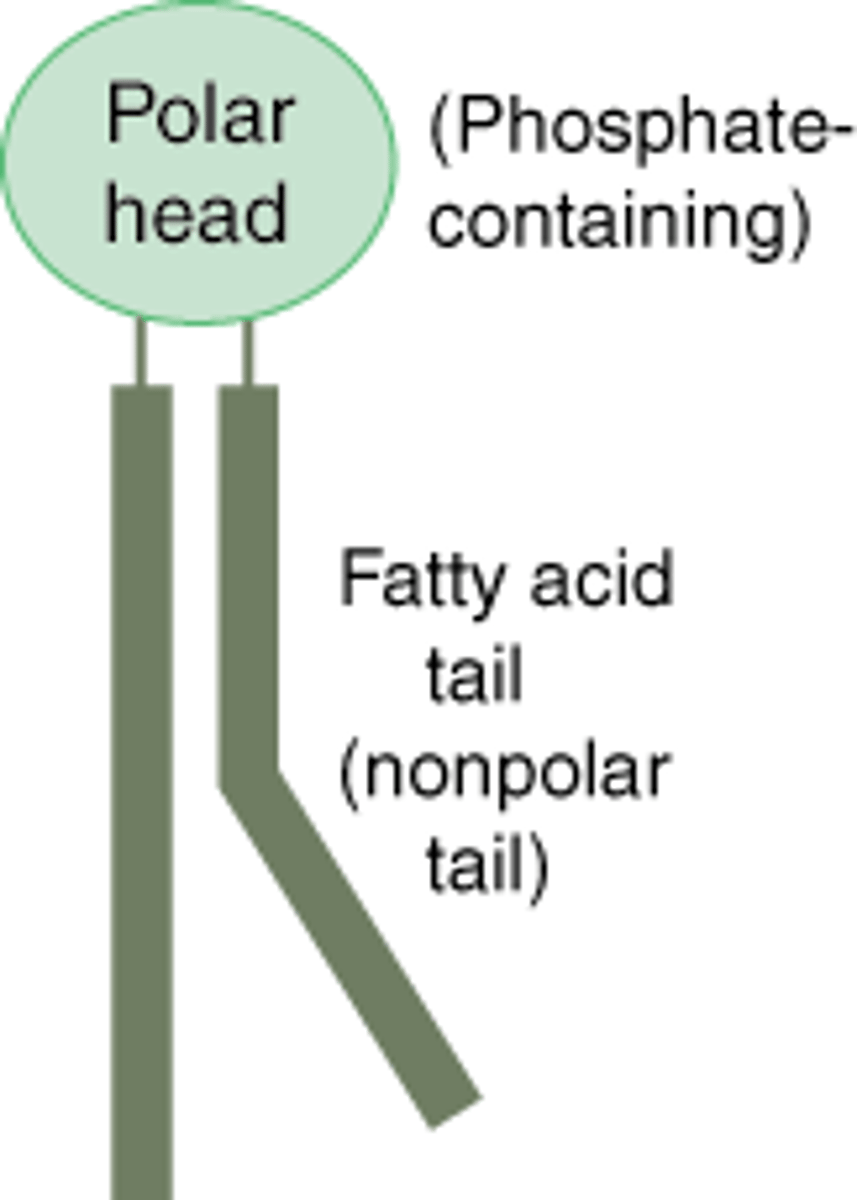
phospholipids
a lipid containing a phosphate group and 2 fatty acids. Found in high numbers in cell membranes
cell membrane
the semipermeable membrane surrounding the outside of a cell.
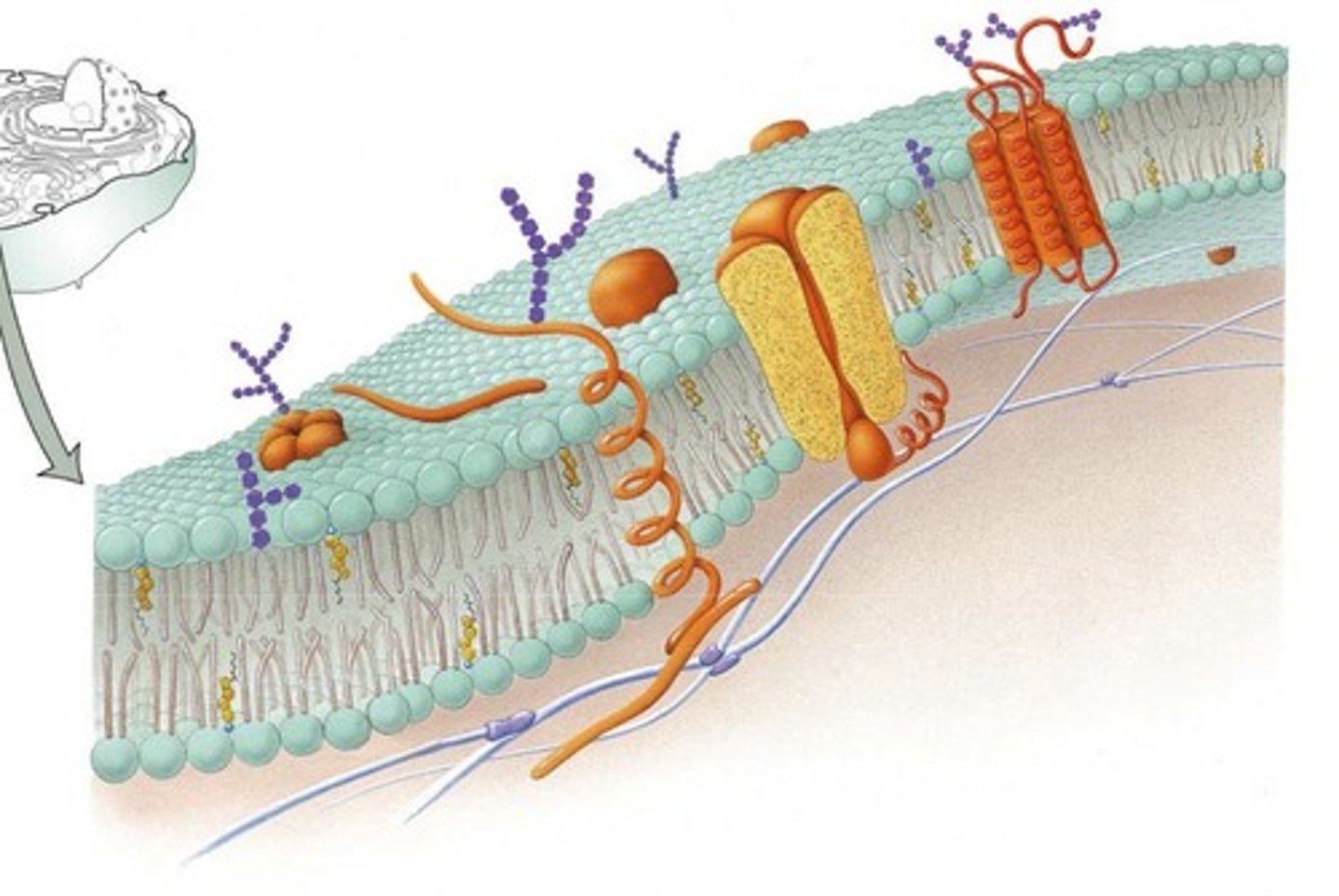
lipid bilayer
double-layered sheet that forms the core of nearly all cell membranes
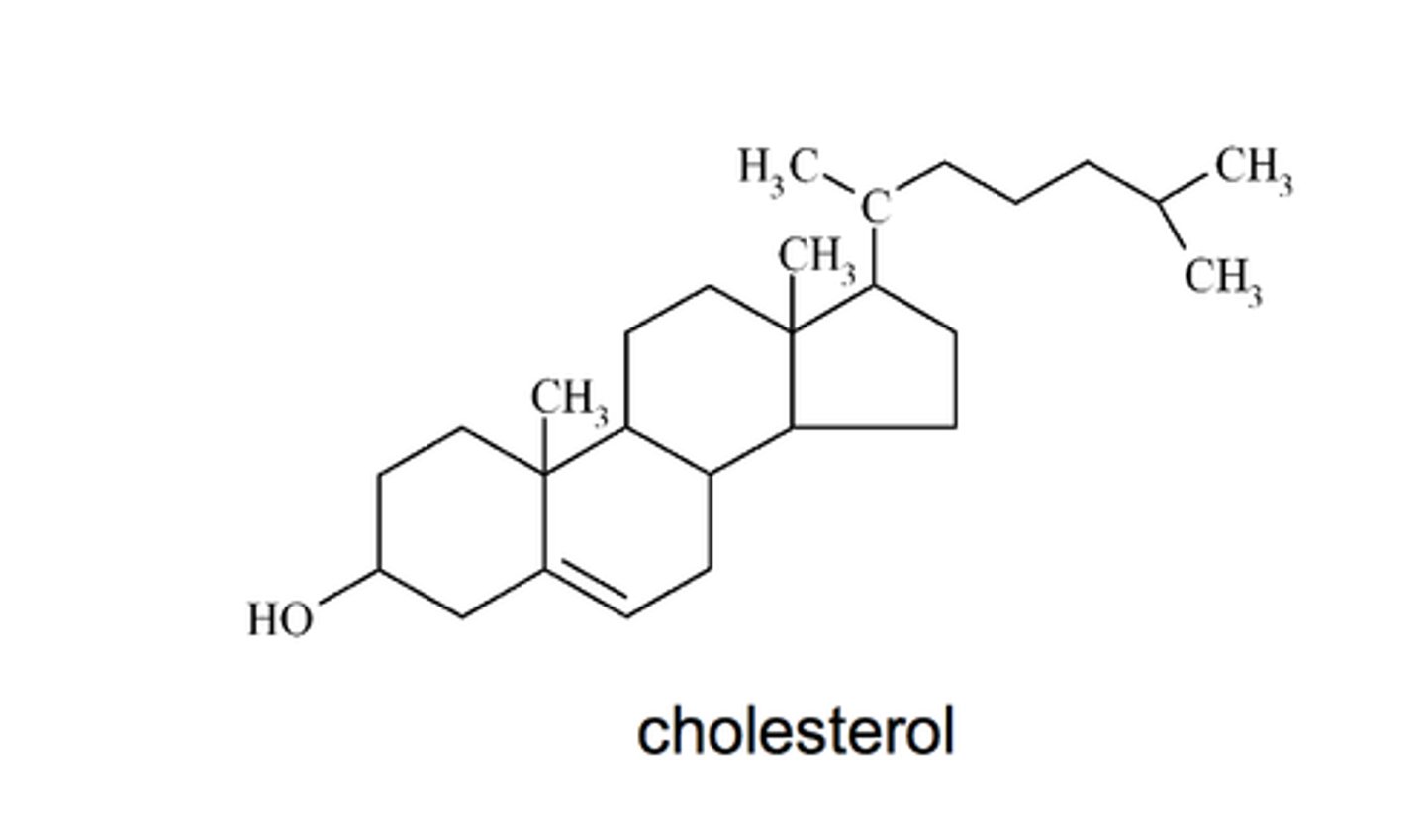
Steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings, found in hormones
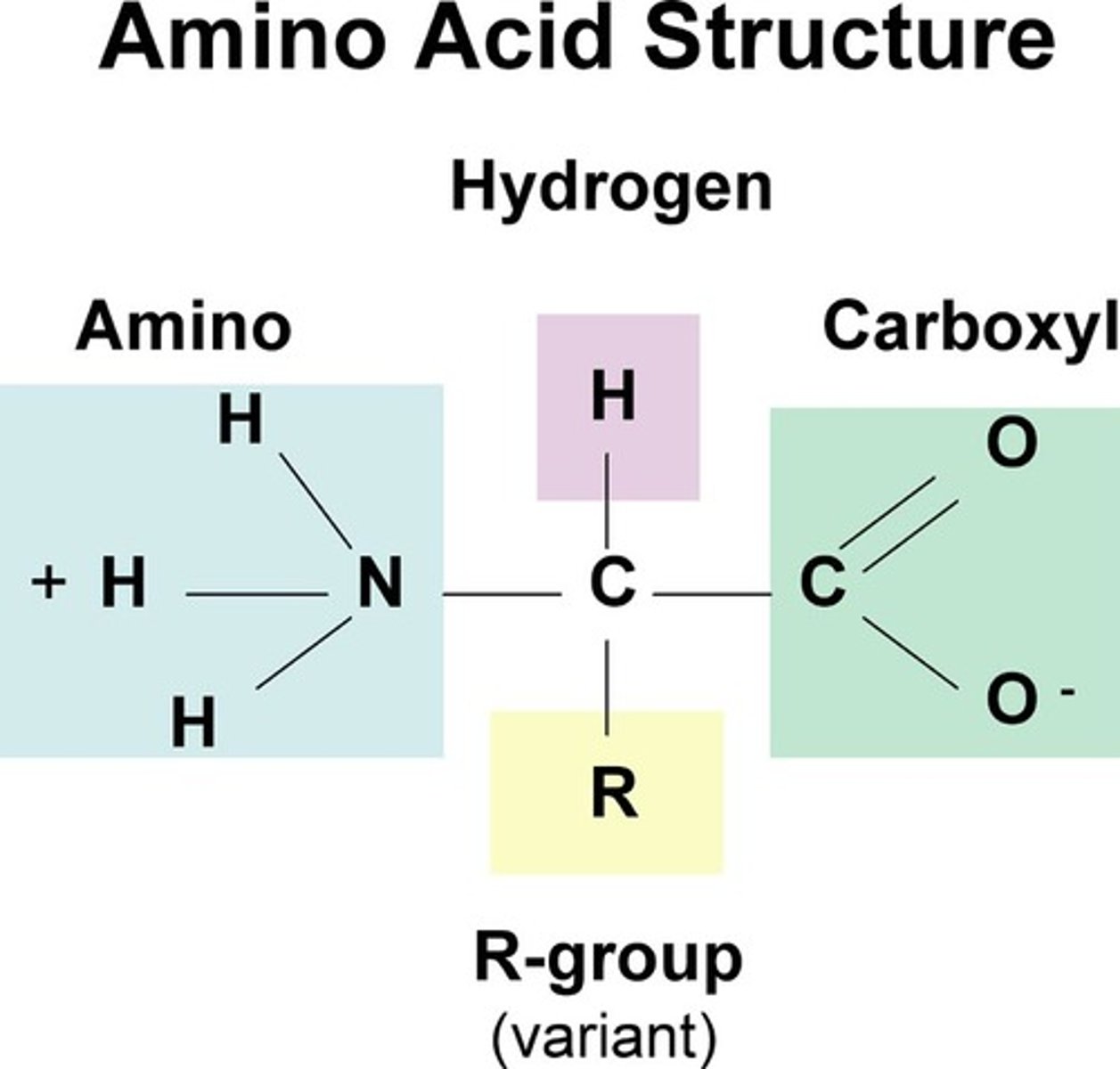
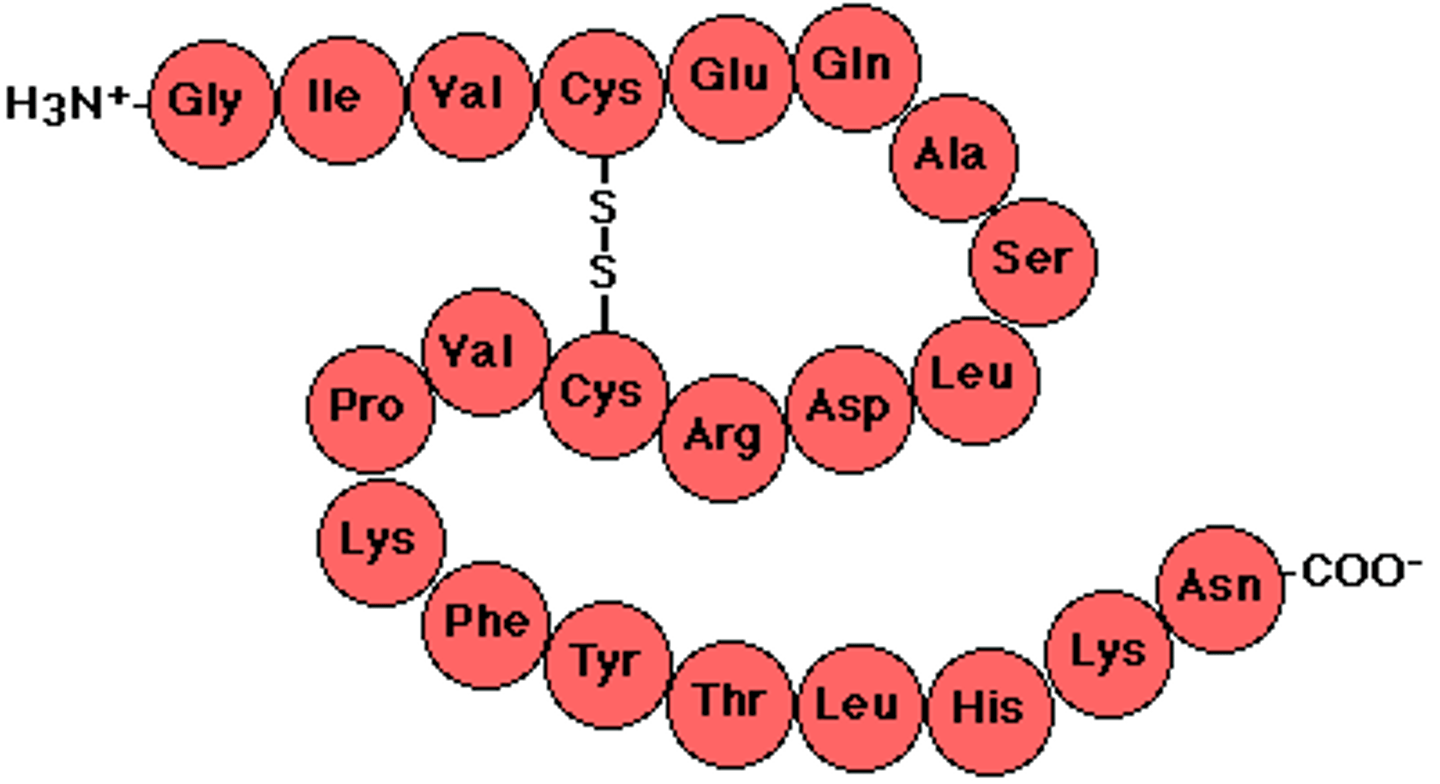
Proteins
Made of amino acids bonded together with a wide variety of functions in the body

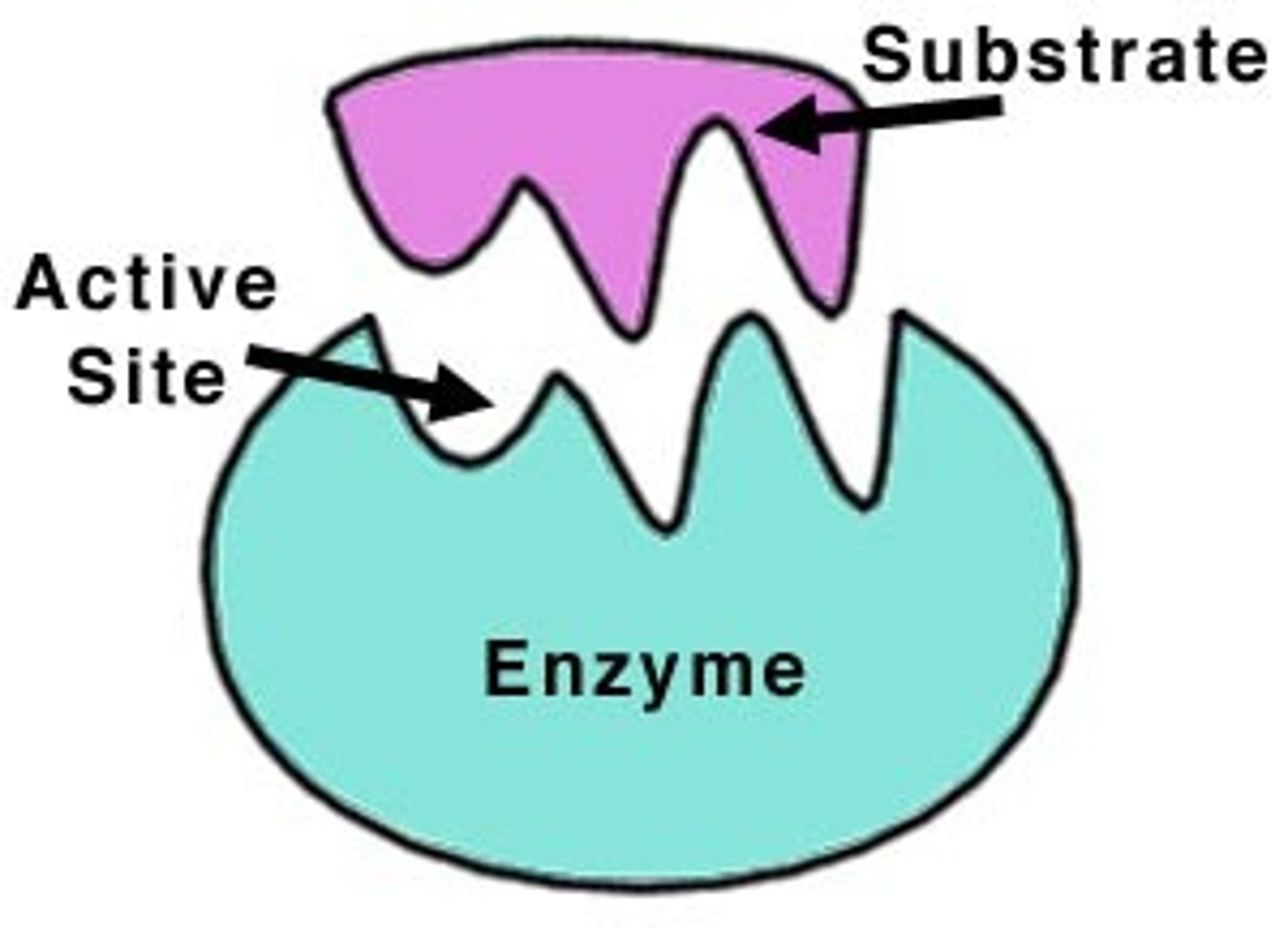
Catalysts
Chemicals that speed up chemical reactions, made of proteins

amino acids
building blocks of proteins
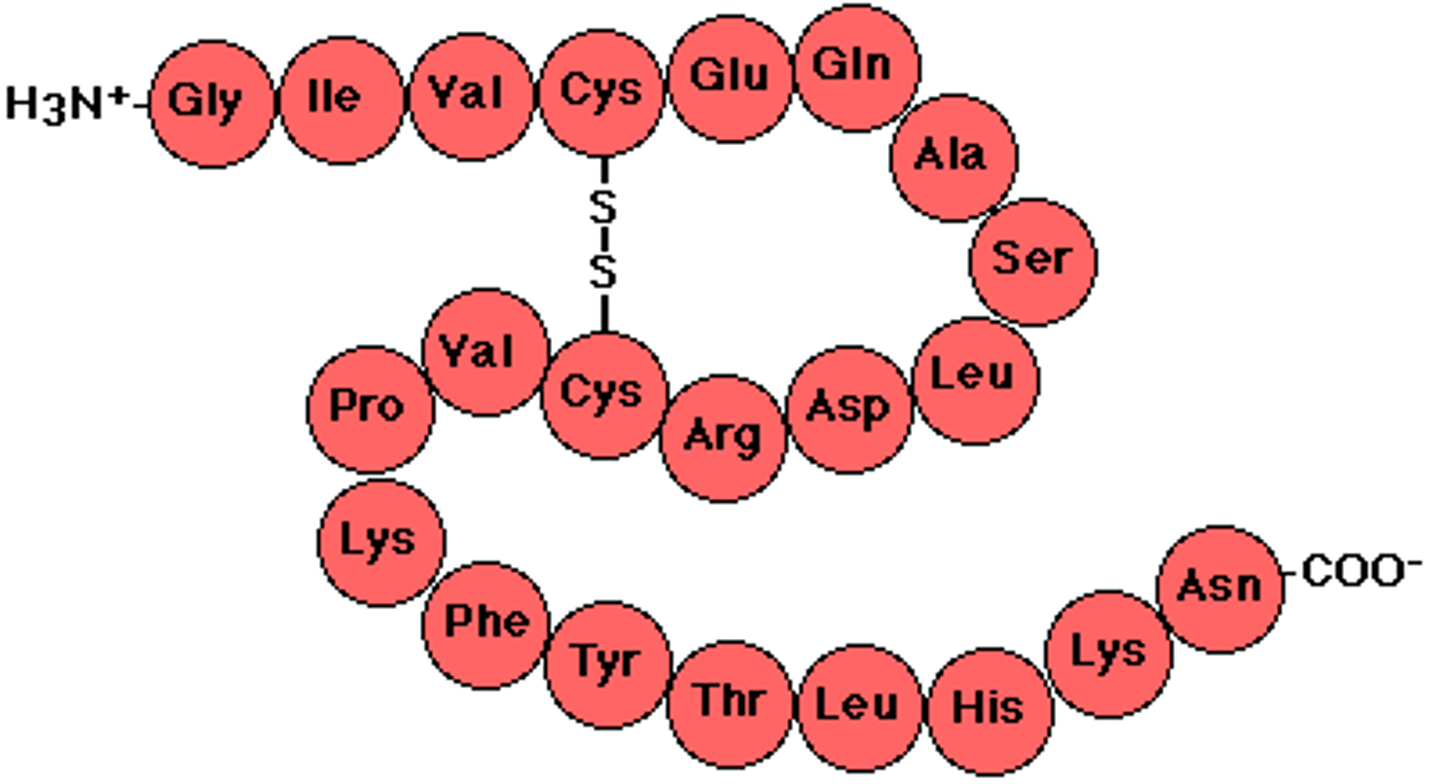
Polypeptide
Unfinished long chain of amino acids that makes proteins when folded
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions
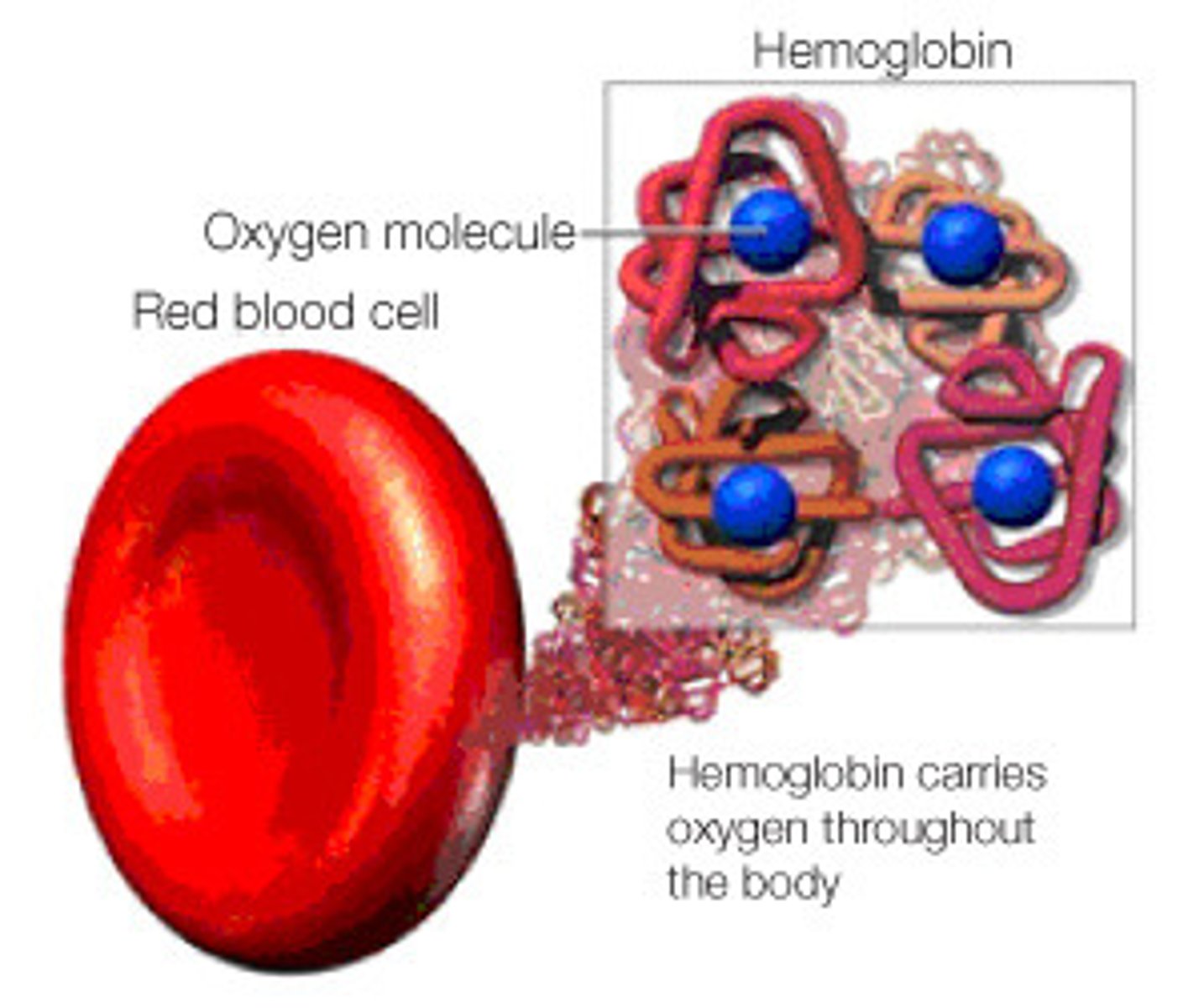
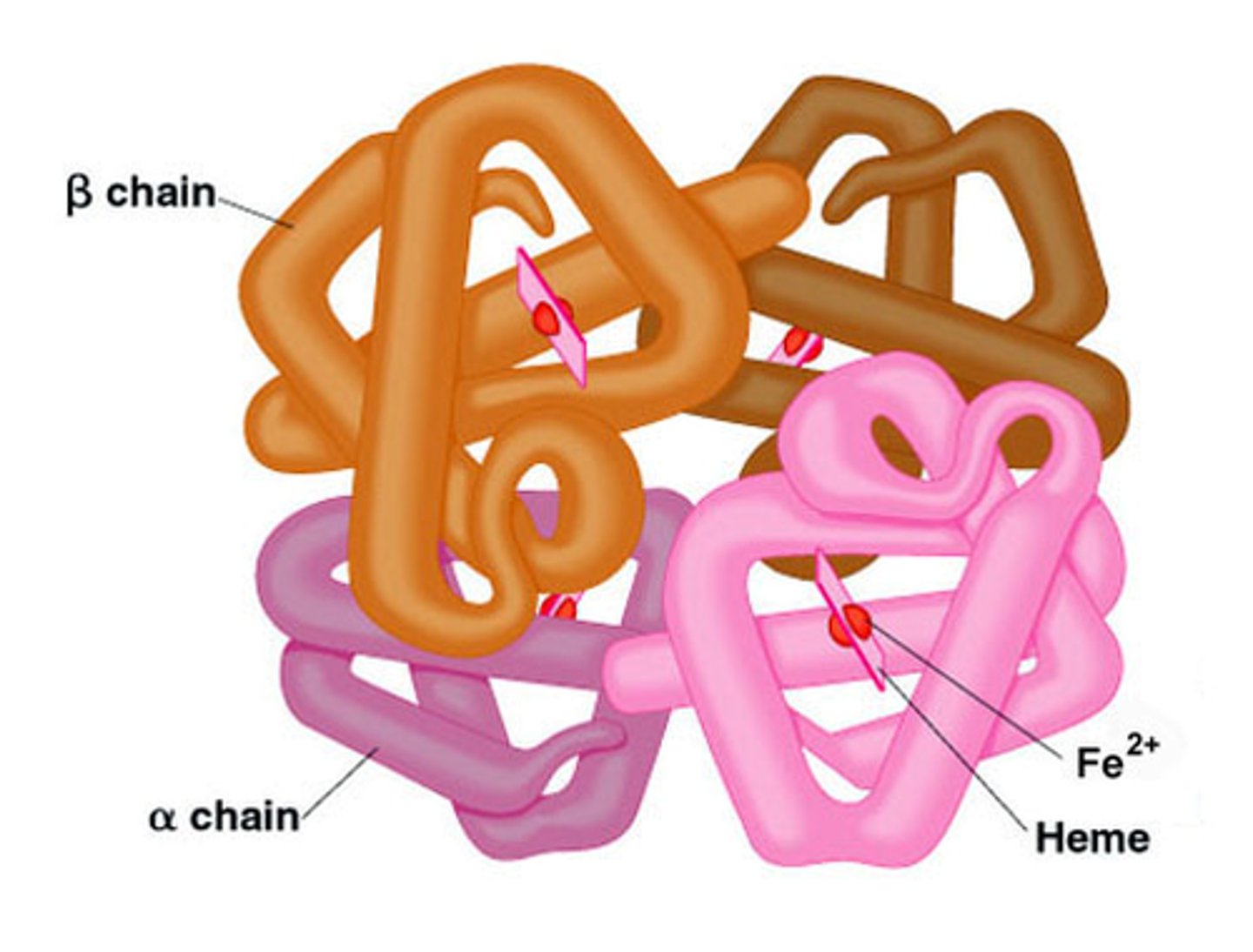
Hemoglobin
A protein found in red blood cells that transports oxygen.
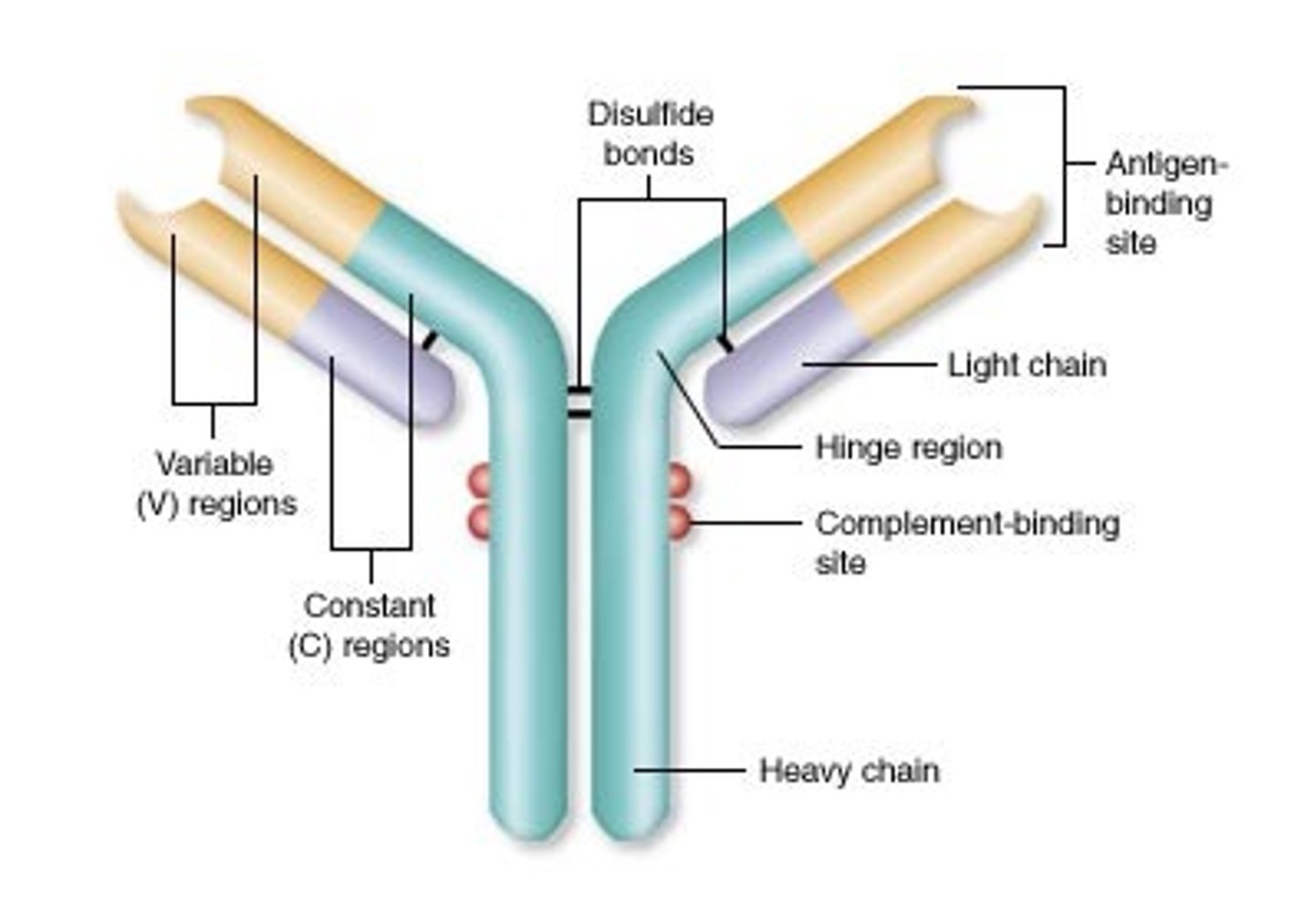
Antibodies
Proteins that destroy infectious agents
Protein structures
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
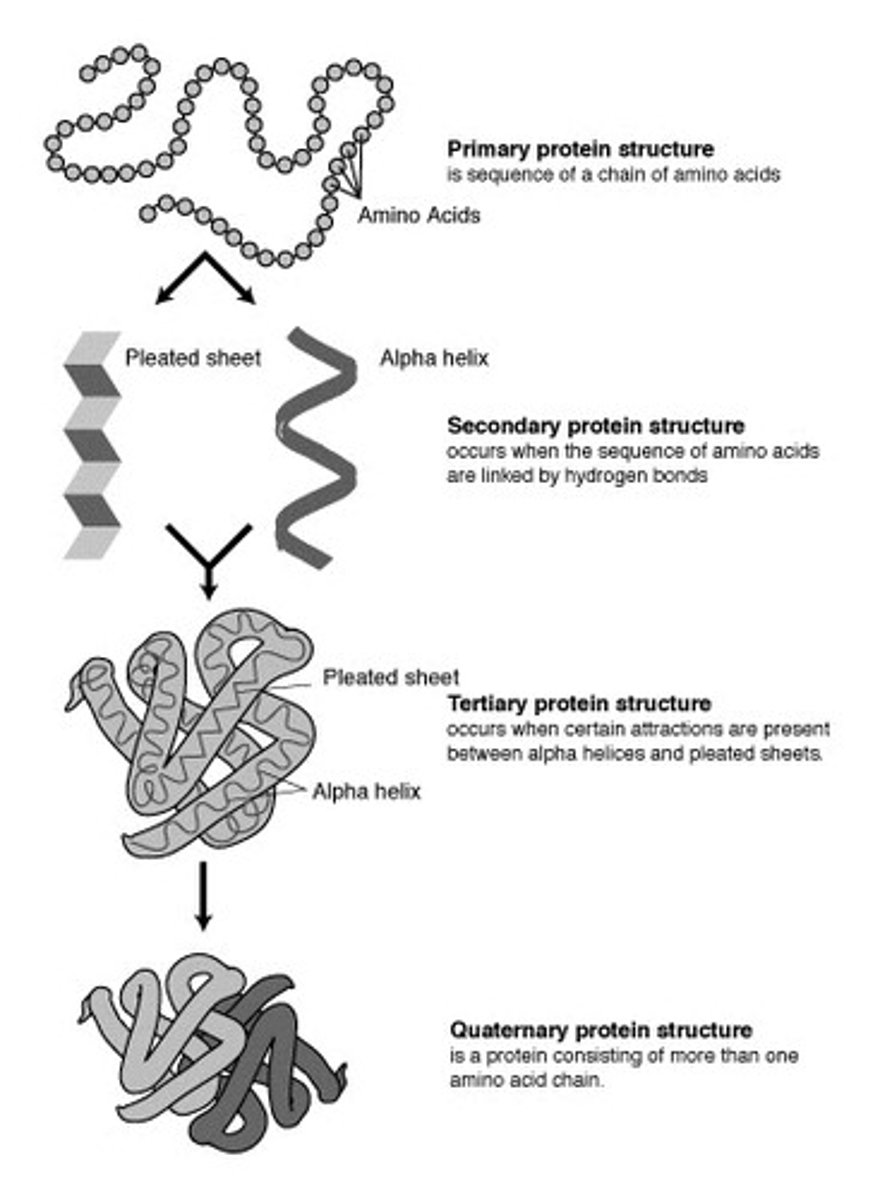
primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
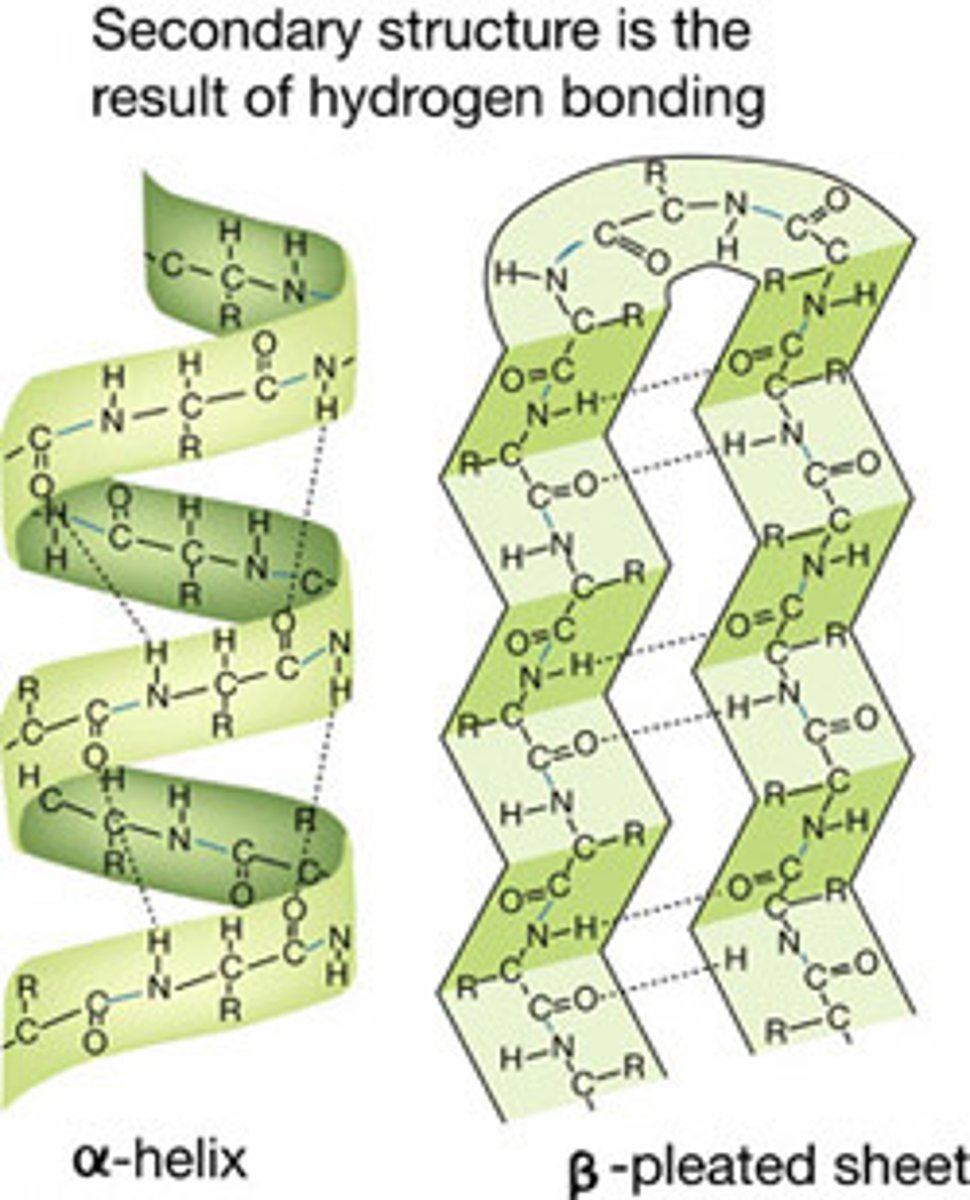
Secondary protein structure
occurs when the sequence of amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds (helix and pleats)
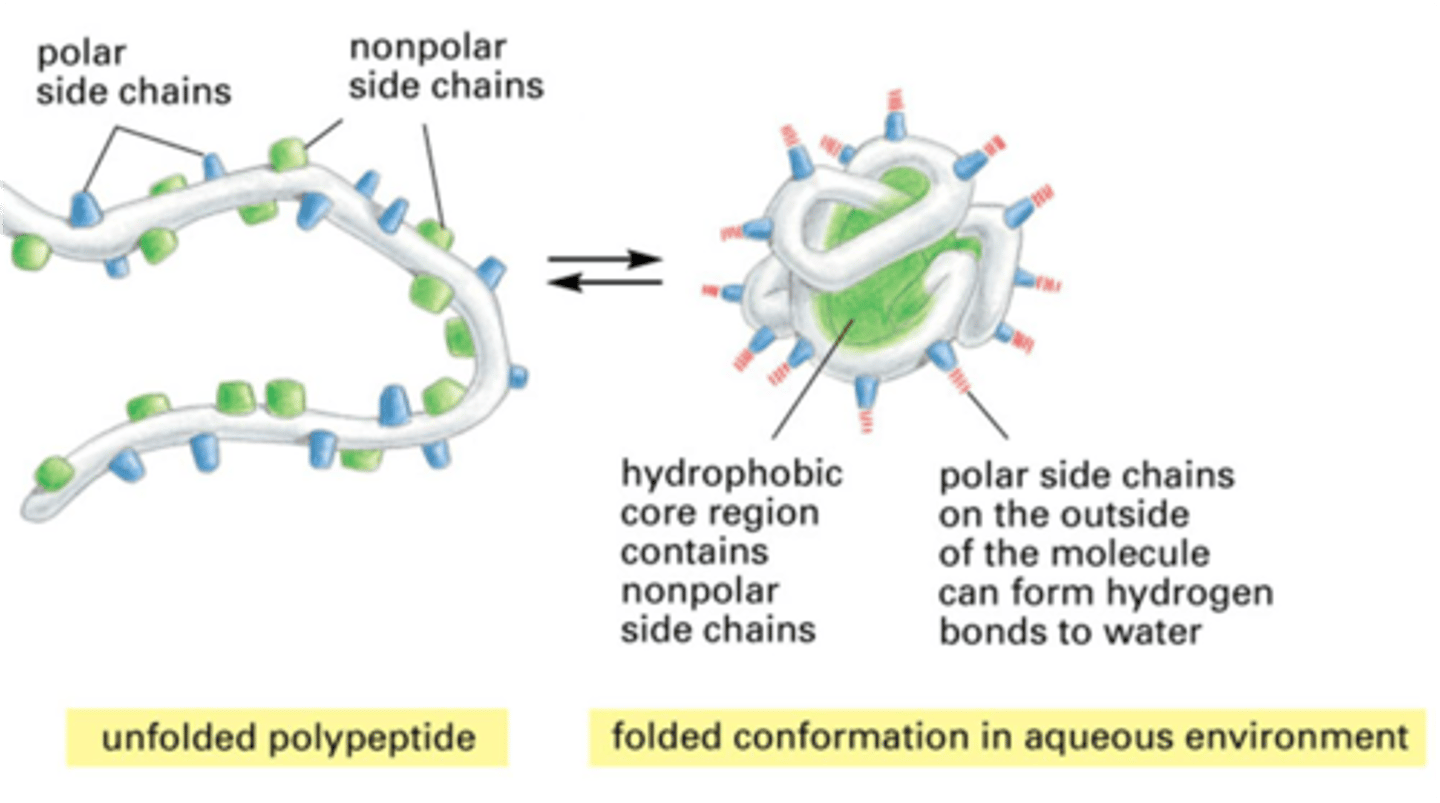
tertiary protein structure
3D folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
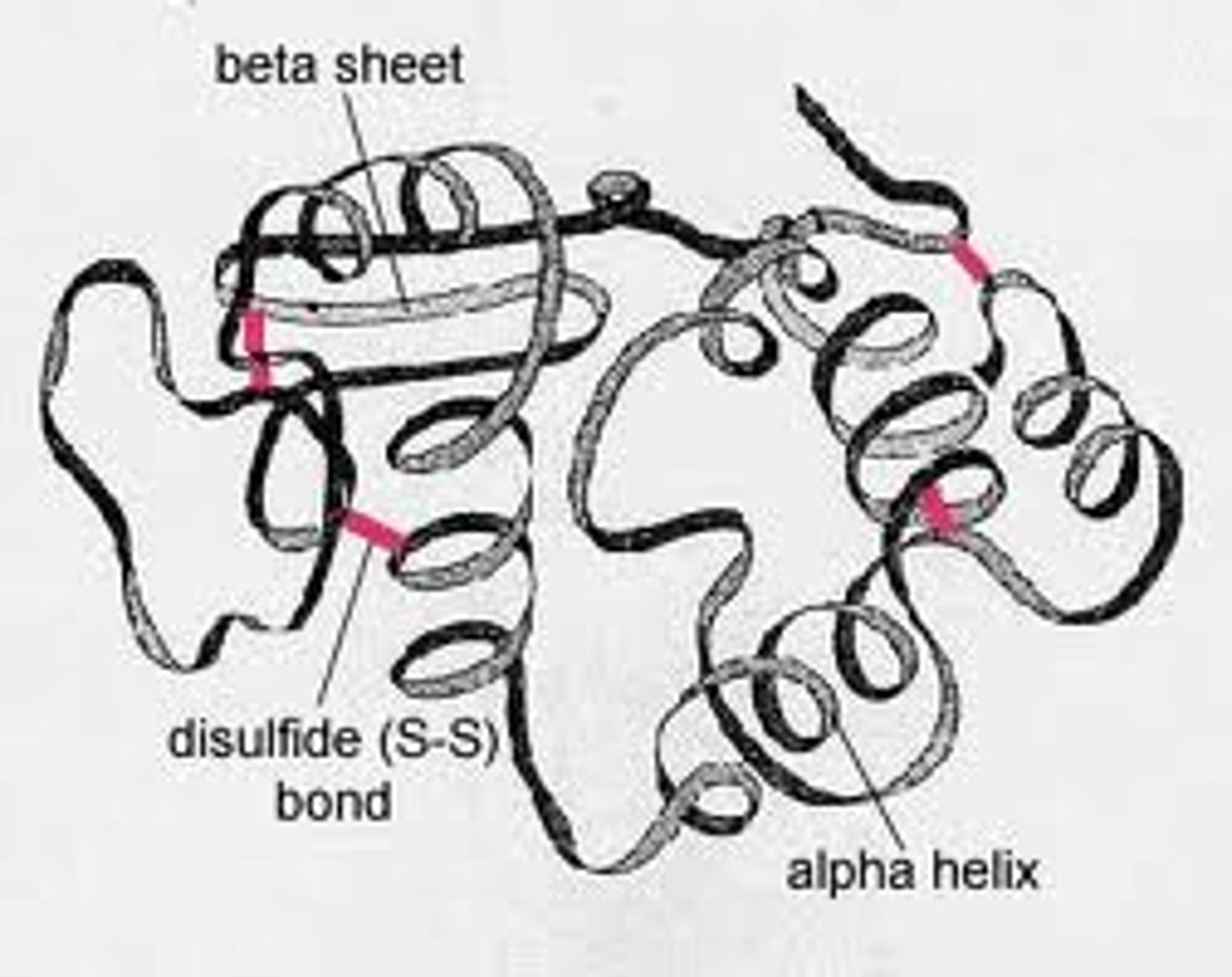
quarternary protein structure
protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain (hemoglobin has 4 polypeptides bonded together)
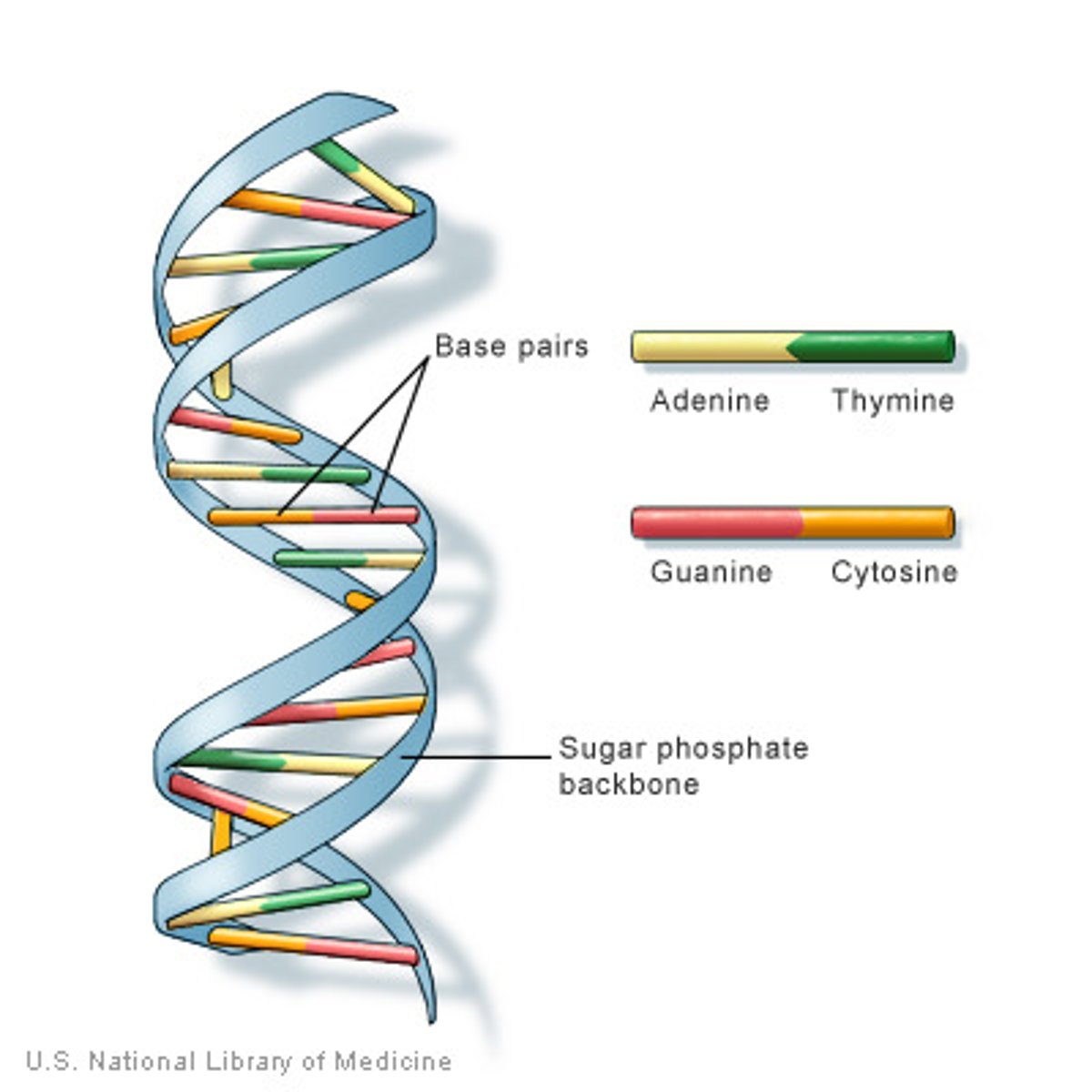
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
DNA
Contains genetic information that makes up the chromosomes. (Protein "recipe" book in the nucleus)
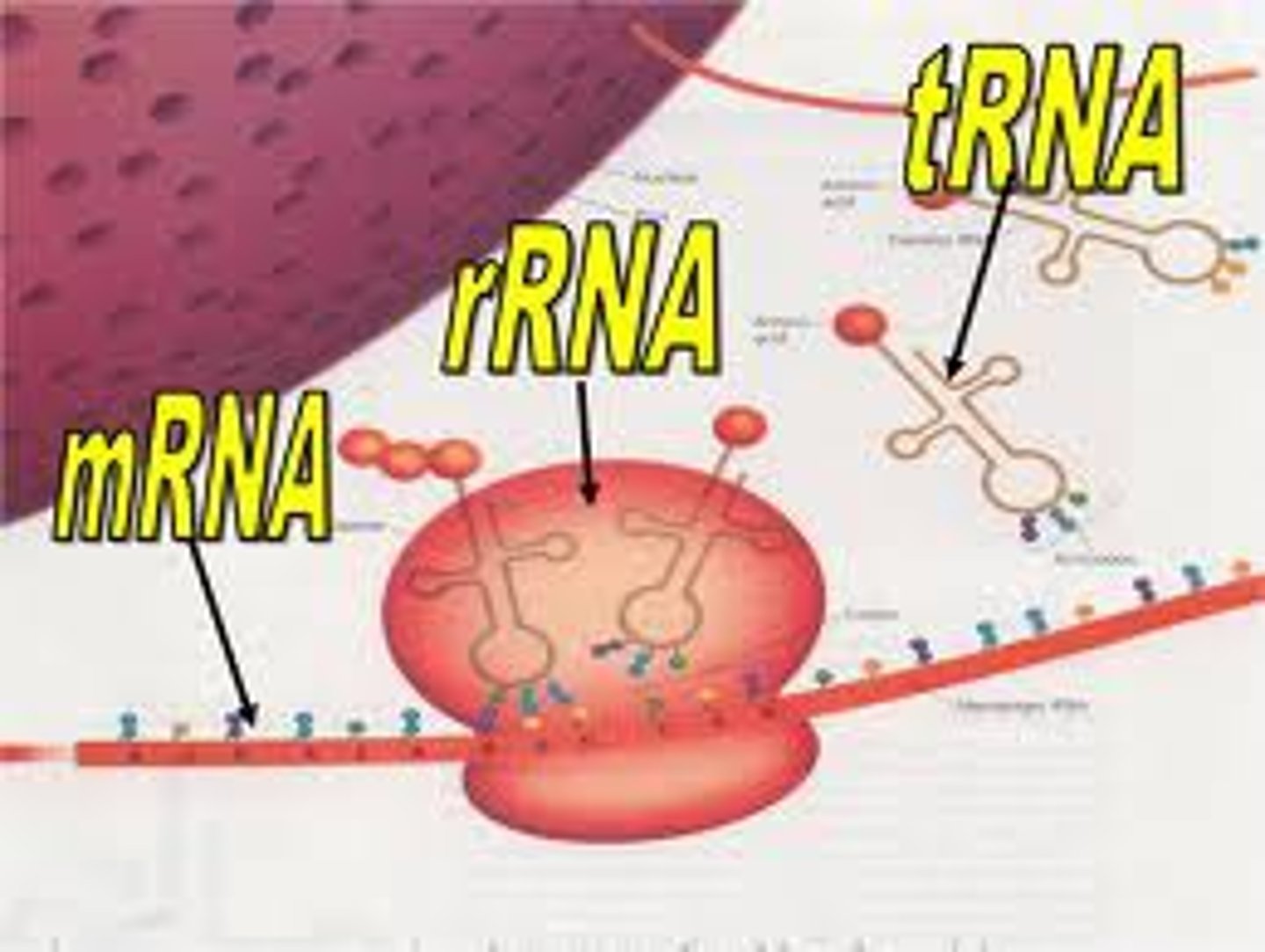
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that assists in building proteins
Nucleotides
Building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA.
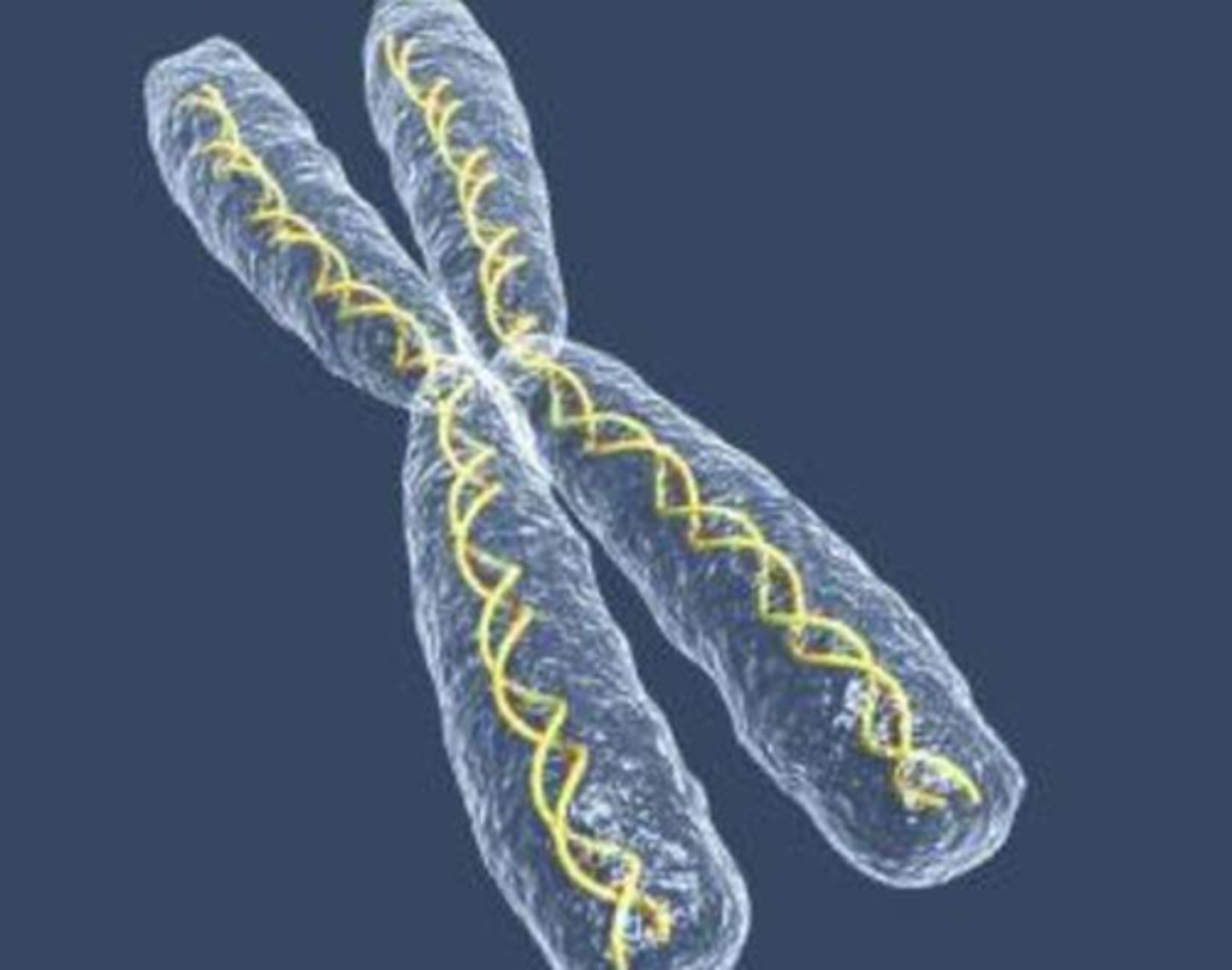
Chromosomes
long strands of DNA wound together that contains the genes found in the nucleus
Genes
DNA segments that code for one protein (many genes are found in a chromosome)
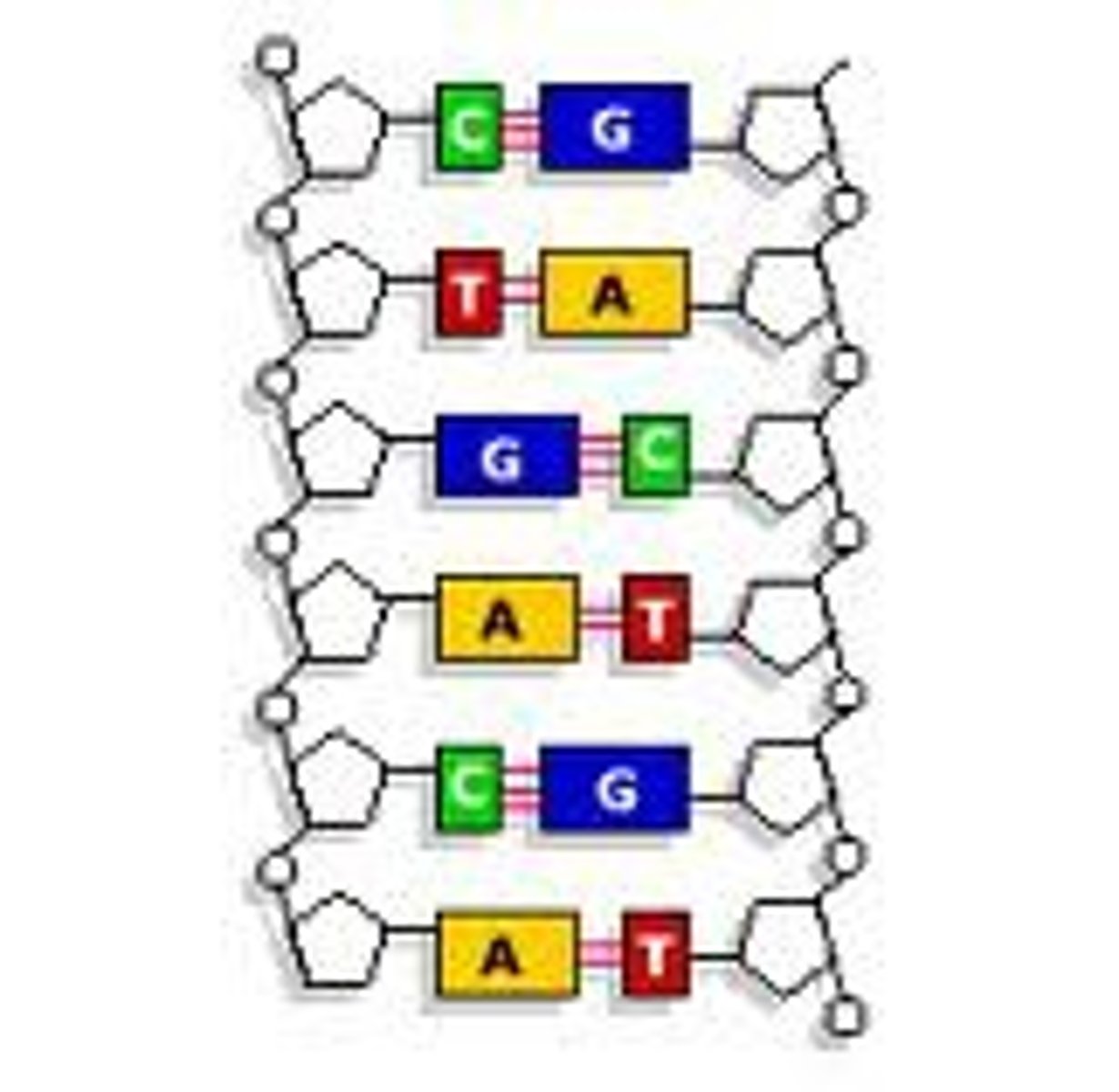
DNA Bases
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C)
RNA Bases
Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G)
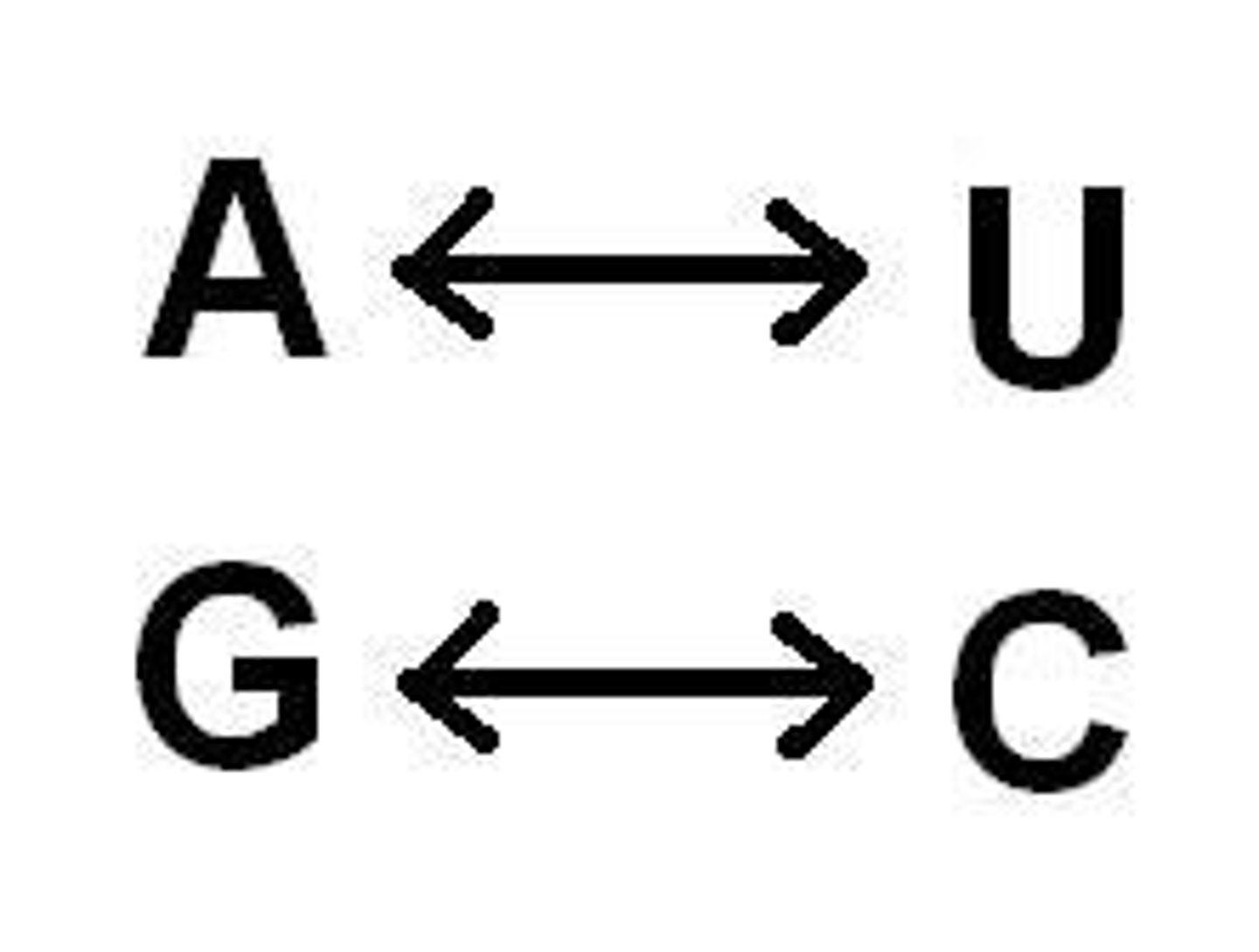
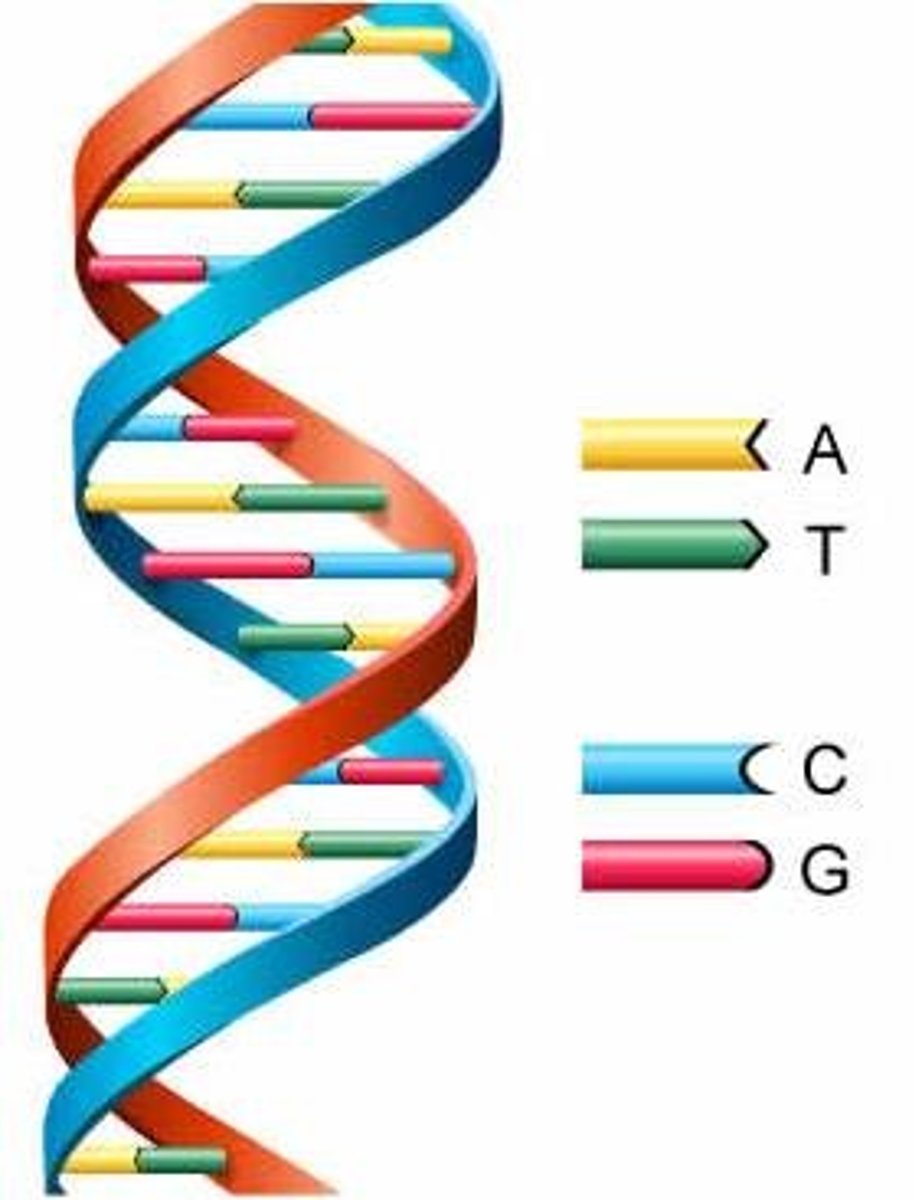
double helix
two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA
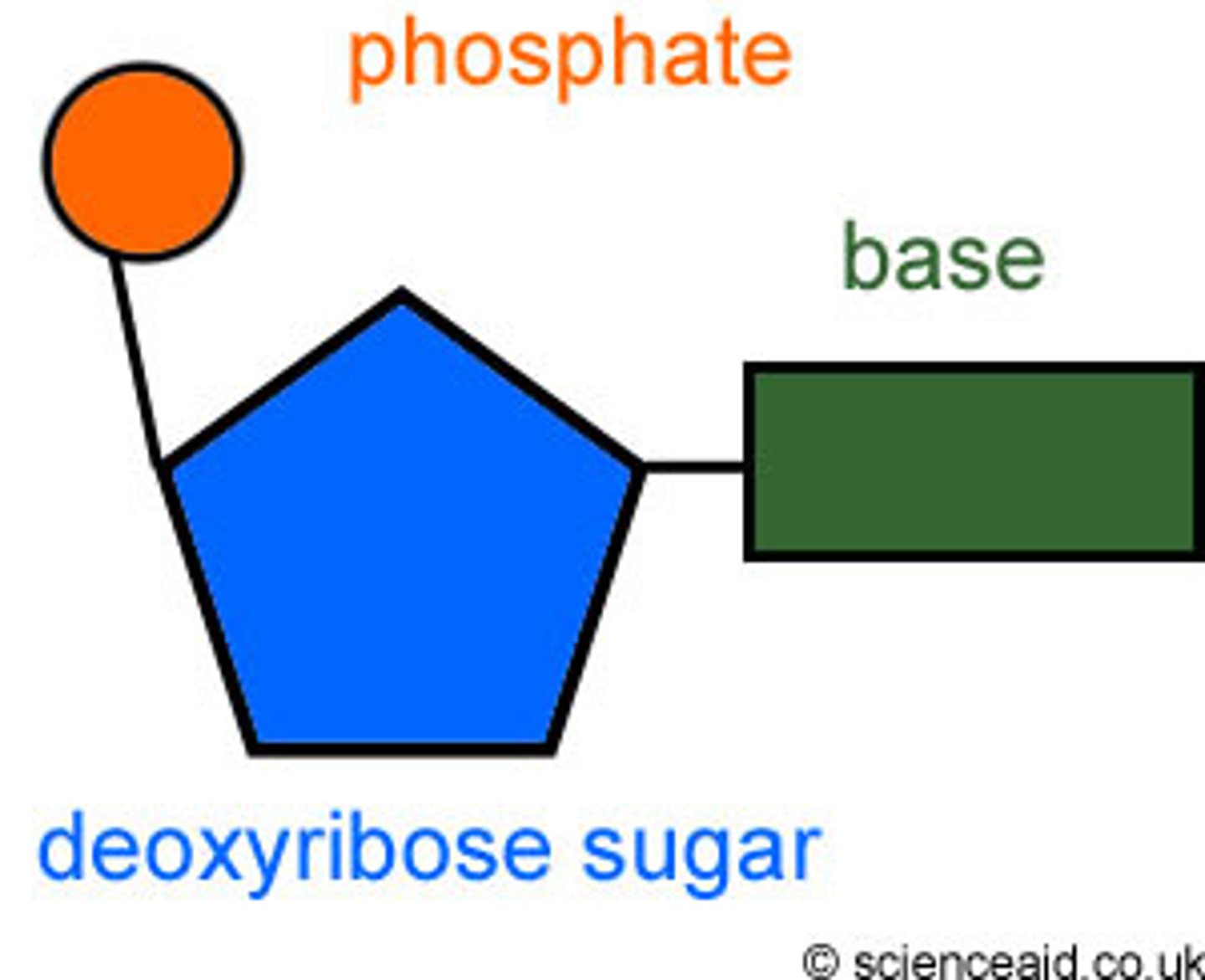
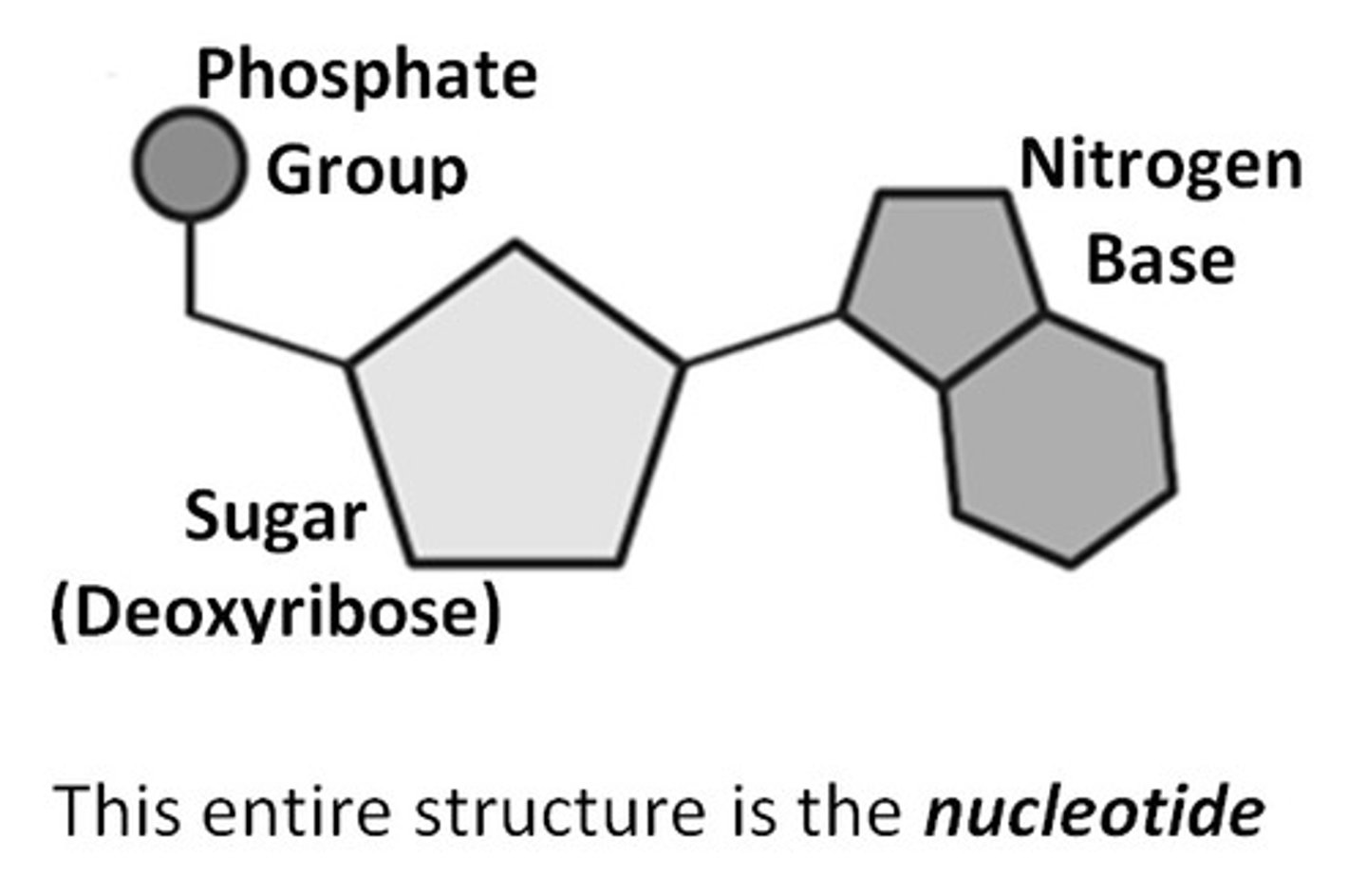
3 parts of a nucleotide
sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base
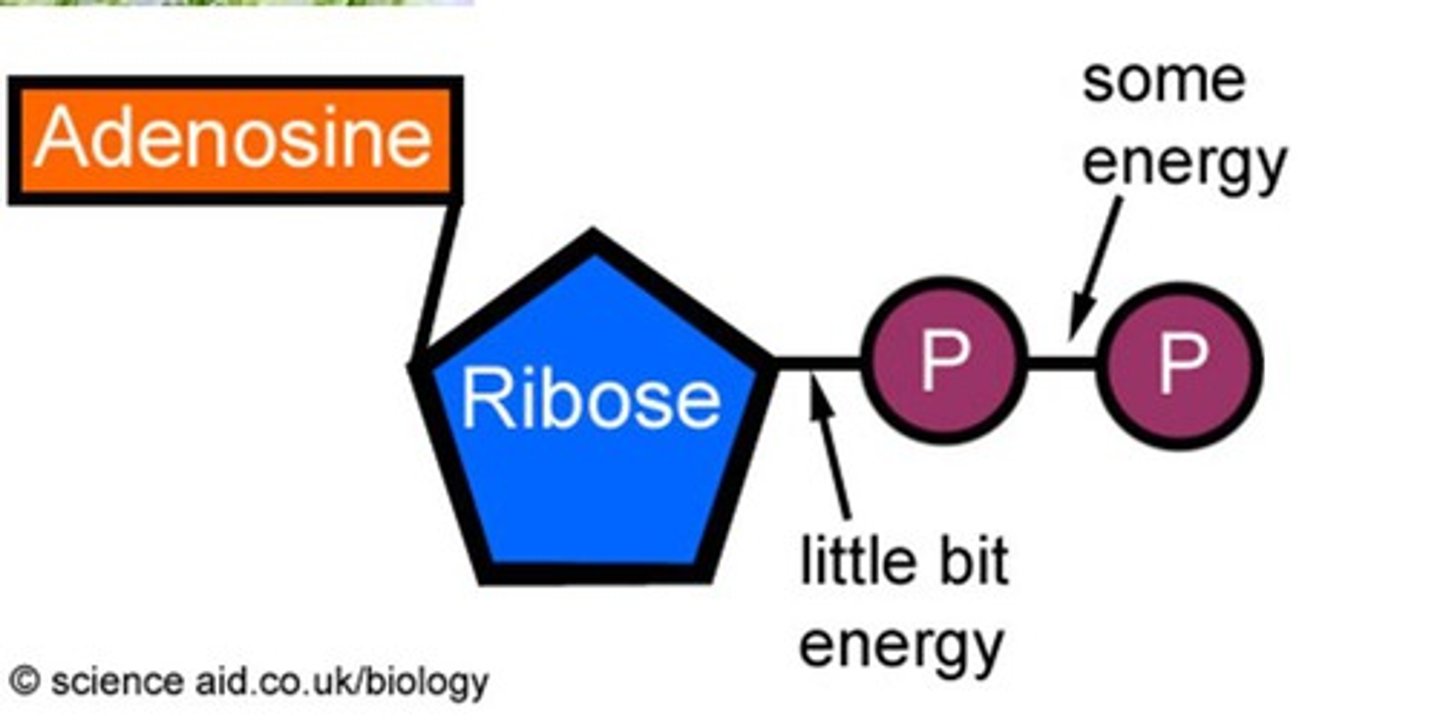
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work (3 phosphates)
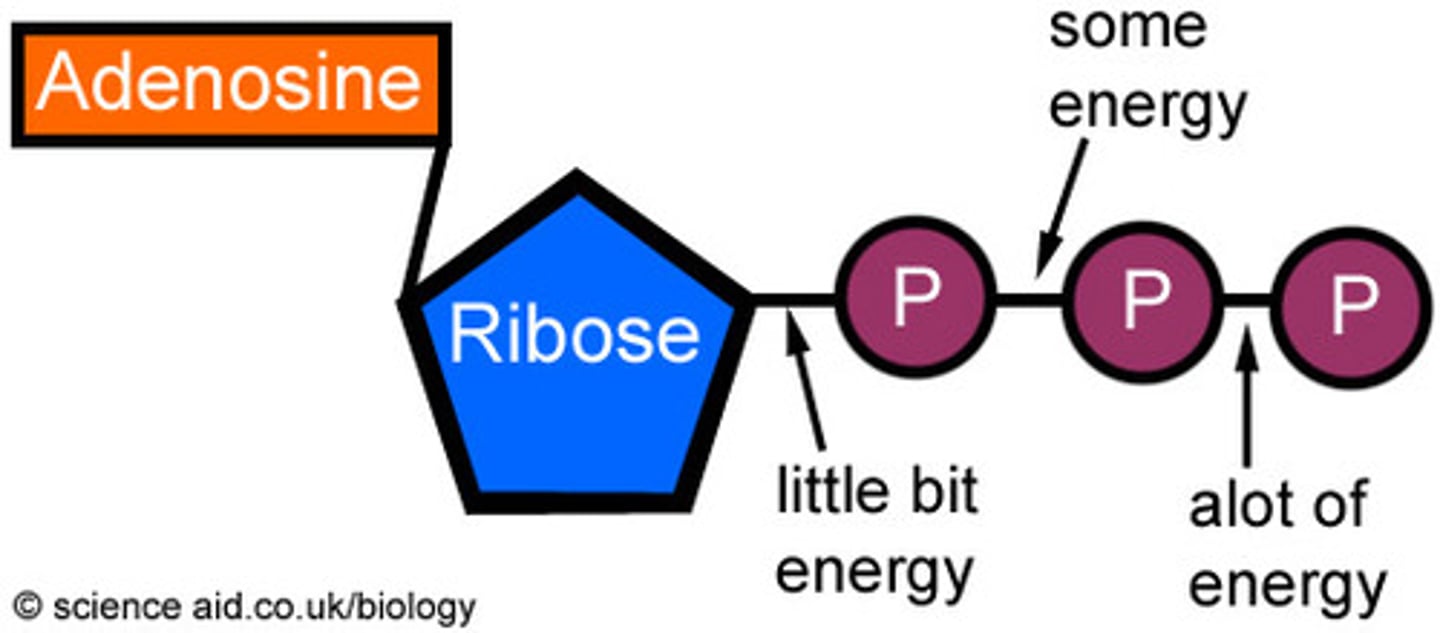
ADP
(Adenosine Diphosphate) A phosphate group is removed from ATP, releasing energy.