NCM 109 (Unit 7): Intro to Genetics and Nursing Clients with Genetic Disorders
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Genetics
The study of heredity or how such disorders occur
Heredity
Biological process where a parent passes certain genes onto their children or offspring
DNA
A molecule that encodes an organism's genetic footprint
Chromosomes
Location of DNA
Chromosomes
Are thread-like structures of nucleic acids and proteins
Chromosomes
Carry genetic information
Gene
Basic unit of heredity
Determined both the physical and cognitive characteristics of people
A set of DNA
Nucleus
Center portion of the cell
46 chromosomes
Number of chromosomes in DNA
Gene 23
The sex chromosome
Gametes
Haploid cells
Each cell carries only one copy of each chromosome
Zygote
Formed when haploid cells unite and fertilize together = 23 pairs of chromosomes
Diploid cells
Has 2 complete sets of genes
Haploid cell
Only has a single set of chromosomes which are only the sex cells
Gene locus
Certain areas in a chromosome where specific genes are located for a specific character or trait
Locus
The specific physical location of a gene or other DNA sequence
Allele
Alternative variations or versions of a specific gene
Genotype
Refers to the genetic code of an individual
All the info that is found inside the individual’s cells
Everything that someone inherited from their parents
Depends on hereditary information
Phenotype
The expression of the genotype that is visible to other people and can be observed
Can be influenced by the environment
Genotype
The particular combination of alleles for a particular gene or locus
Homozygous dominant
2 capital letters e.g. HH
Heterozygous
1 capital letter + 1 small letter e.g. Hh
Homozygous recessive
2 lowercase letters e.g. hh
Examples of observable characteristics (phenotype)
Behaviour
Biochemical properties
Color
Shape
Size
Alleles
Are the codes of the specific variation written in DNA
Phenotype
The expressed trait as a result according to the alleles
Punnett squares
Graphical representation of the possible genotypes of offspring arising from a particular cross breeding event
Genogram
Helps identifying the possibility of a chromosomal disorder occuring in a particular couple's children
Certain body areas where particular attention is needed during physical assessment
Space between eyes
Height
Contour and shape of ears
Number of fingers and toes
Presence of webbing (syndactyly)
Note abnormal fingerprints or palmar creases
Abnormal hair whorls or hair color
Diagnostic tests
Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein
Chorionic villi sampling
Amniocentesis
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling
Ultrasound
Fetoscopy
Preimplantation diagnosis
Newborn screening test
Karyotyping
Process of pairing and ordering all the chromosome of an organism
Artificial Insemination by Donor

Use of a surrogate mother

Surrogate embryo transfer

Nondisjunction abnormalities

Deletion abnormalities

Translocation abnormalities

Mosaicism

Isochromosomes

Down syndrome or Trisomy 21

Clinical features of down syndrome

Mgmt of down syndrome

Edward's syndrome
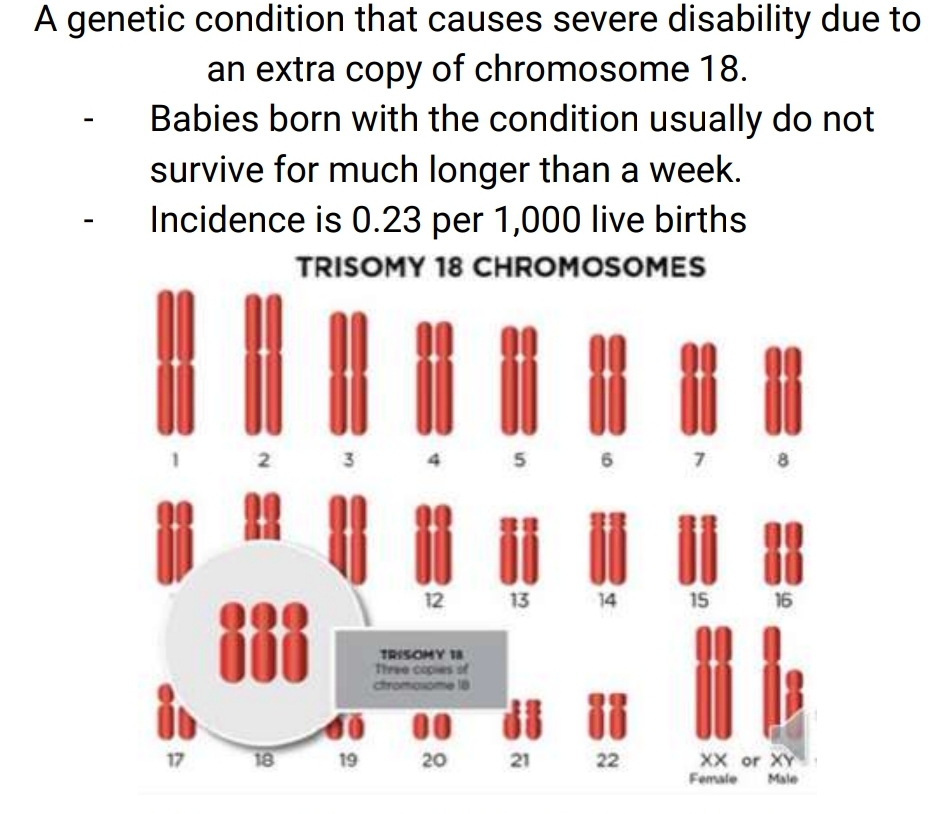
Clinical features of Edward's syndrome
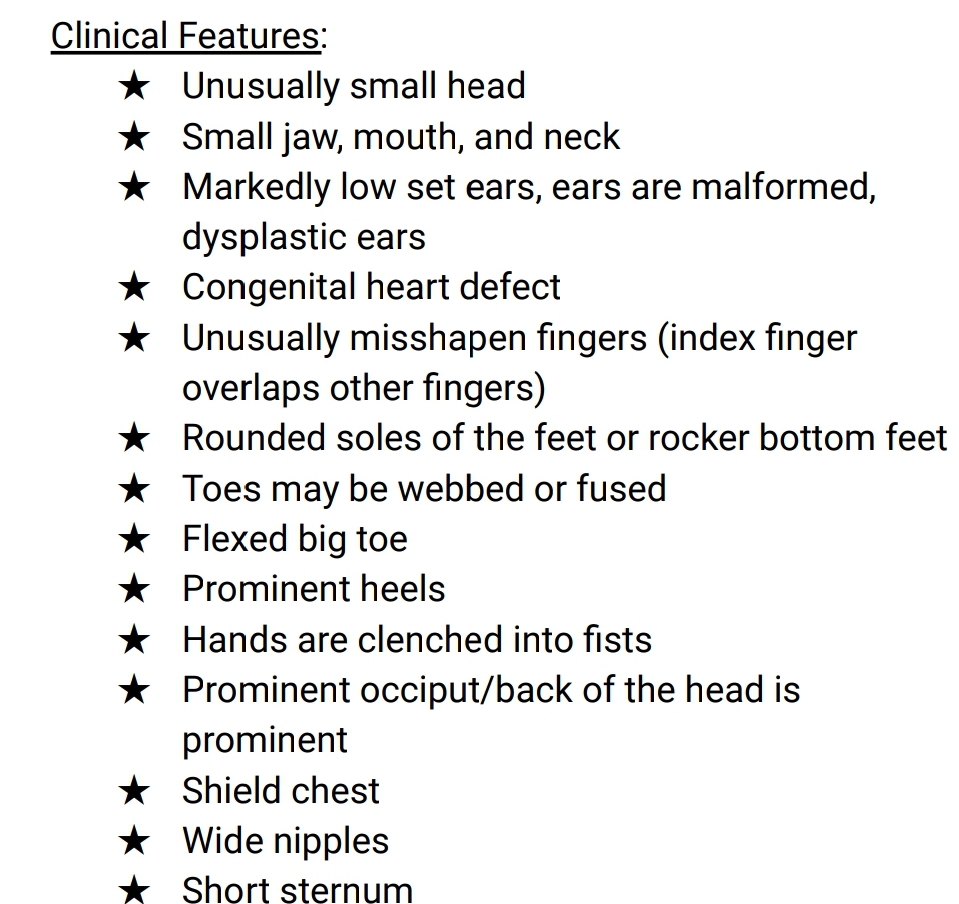
Mgmt of Edward's syndrome

Patau Syndrome

Clinical features of Patau syndrome

Defects of Patau syndrome

Mgmt of Patau syndrome

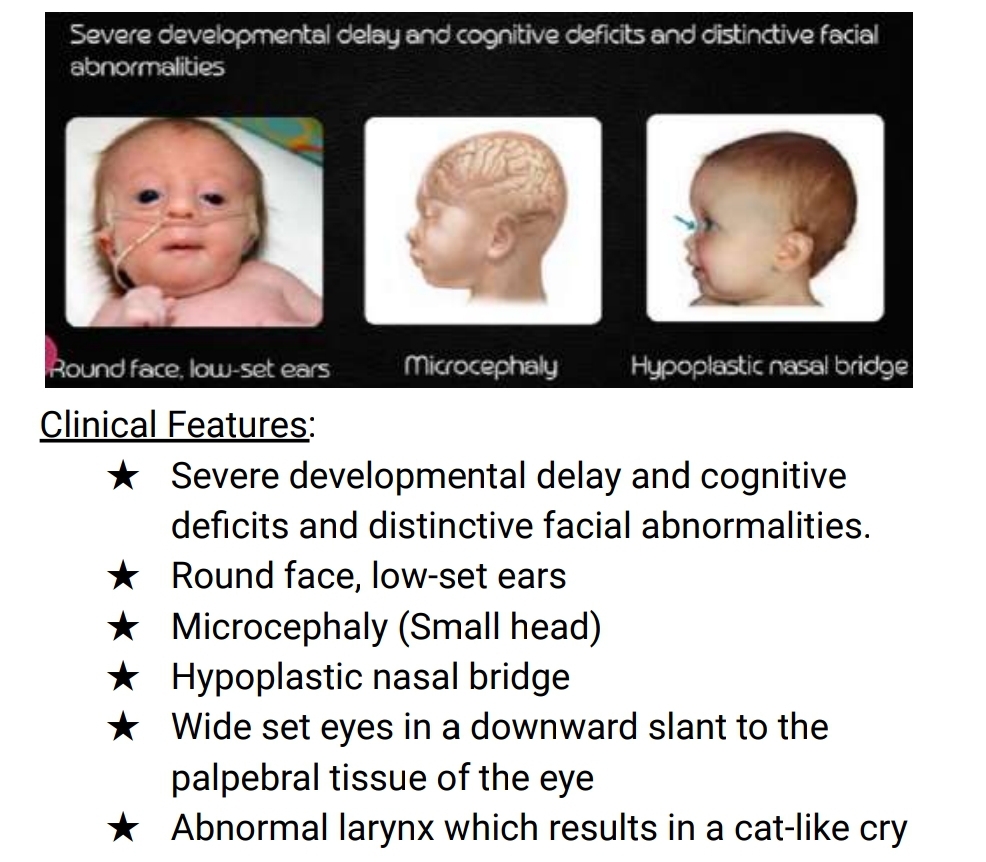
Cri-du-chat or Cat-cry syndrome

Clinical features of cri du chat syndrome
Turner's syndrome

Clinical feature of Turner's syndrome

Clinical features of Turner's syndrome

S/sx of Turner's syndrome

Mgmt of Turner's syndrome

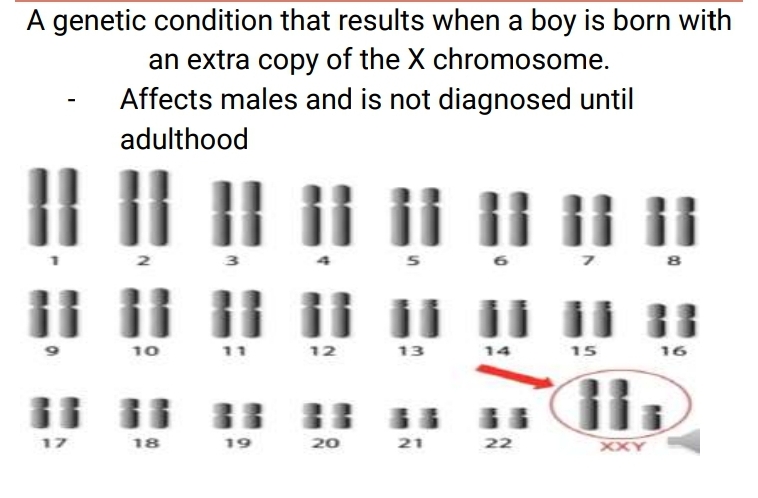
Klinefelter syndrome
administration of estrogen
given to pxs with Turner’s syndrome to promote normal sexual development
if begun at approximately 13 yrs old, secondary sex characteristics appear
osteoporosis
bone disease prevented during growing years when px with Turner’s syndrome takes estrogen
menstrual flow/ withdrawal bleeding
effect of taking estrogen 3 out of every 4 weeks in Turner’s syndrome
does not correct problem of sterility
testosterone therapy
treatment given to pxs with Klinefelter syndrome as they enter puberty
increases strength and muscle size
increases growth of facial and body hair
inadequate protein synaptic response
effect of fragile x syndrome in which one long arm of an x chromosome is defective
serotonin agents
given to pxs with Fragile X syndrome to control behavior
Behavioral features of Fragile X syndrome

Mgmt of Fragile X syndrome

Pompe disease

Pompe disease
Insufficient functioning of lysosomal acid alpha 1 or acid-alpah glucosidase due to mutation of GAA gene
causes glycogen build-up; cellular damage in muscles
Mgmt of Pompe disease

Algucosidase alfa
Enzyme med given to px with Pompe disease to remove glycogen in lysosomes
Supportive therapies of Pompe disease
Mechanical ventilation
Physical and occupational therapy
Feeding tube
Tay-Sachs Disease

Tay-Sachs Disease

TSD symptoms (infantile, juvenile, chronic)

TSD (late onset)
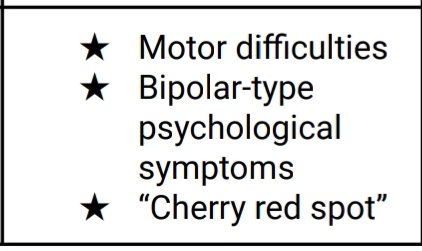
Infantile TSD
Onset is 3-6 months TSD
Juvenile TSD
Onset is 2-5 yrs
Chronic TSD
Onset is 10-20 yrs old
Late Onset TSD
20-30 yrs old
S/sx of TSD

Mgmt of Tay-Sachs disease

Mgmt of Tay-Sachs disease (late onset)

Wilson's disease

ATP7B gene
Cause of mutation leading to copper accumulation in liver and brain in Wilson's disease
S/sx of Wilson's disease

Kyser-Fleischer rings
Brownish rings from copper deposits in the cornea
Wilson's disease clinical feature
Clinical features of Wilson's disease

Copper chelation
involves using medications, like trientine or penicillamine, to bind to and remove excess copper from the body, primarily used to treat Wilson's disease, a genetic disorder causing copper buildup
Mgmt of Wilson's disease

Penicillamine
Copper chelating agent
Binds free copper in body making it easier to excrete
Trientine
Reduces copper reabsorption in urine, therefore increasing the amount of Cu that is excreted in urine
Hereditary hemochromatosis

Clinical features of Hereditary Hemochromatosis

Clinical features of hereditary hemochromatosis

Chondrocalcinosis
Sx of hereditary hemochromatosis causing arthritis
Mgmt of Hereditary hemochromatosis

Venesection
Weekly removal of blood thus removing excess Fe in the bloodstream
Alkaptonuria

Clinical features of Alkaptonuria
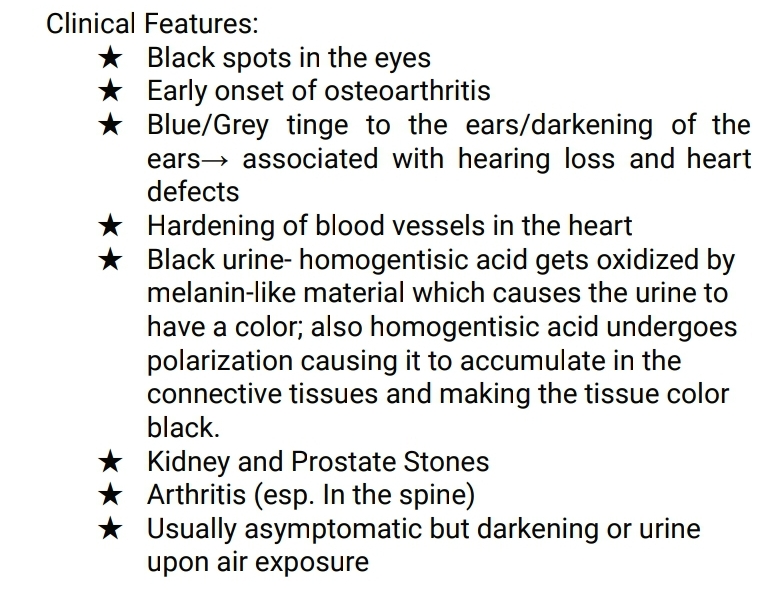
Mgmt of Alkaptonuria

Maple Syrup Urine Disease
