Physics Midterm
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Velocity
Vector, quality that refers to "the rate at which an object changes its position."
formula for velocity
V = d/t (m/s)
Acceleration
Vector quality that is the rate at which an object changes its velocity
formula for acceleration
a=vf-vi/t
Speed:
Scalar quantity that refers to "how fast an object is moving"; the rate at which an object covers distance
speed formula
distance/time
Average speed
total distance traveled/total time
Instantaneous speed
the speed of an object at one instant of time
Distance
how far I traveled; scalar
Displacement
how far I am from where I started; vector
Displacement formula
final position - initial position
What is the difference between displacement and distance?
Distance is the amount of ground covered and displacement is the object's overall change in position.
The direction of the acceleration vector depends on 4 things:
whether the object is speeding up or slowing down, if it is moving in the + or - direction
Two examples of positive acceleration
A car speeding up on the highway, a rocket going into the air.
Two examples of negative acceleration
Dropping your phone, a reversing a car in order to park.
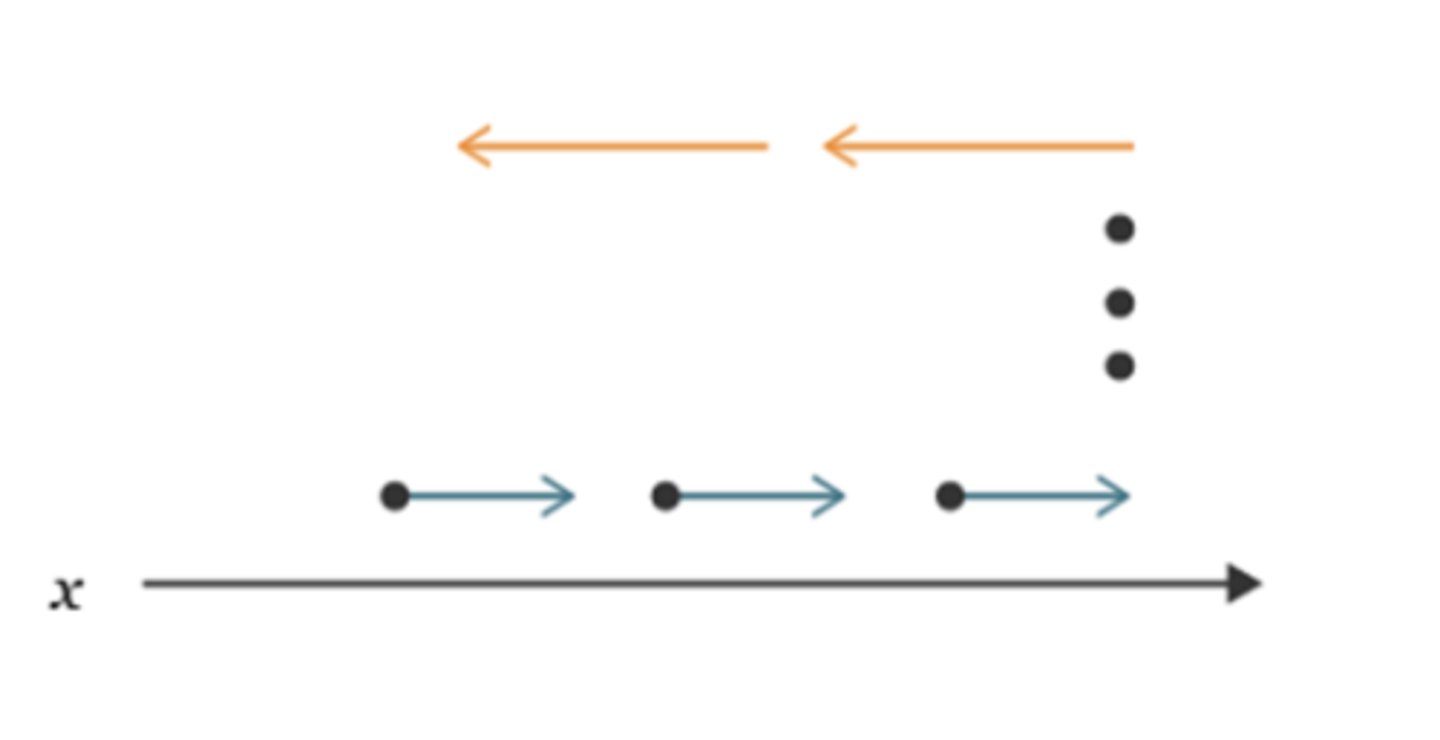
What movement is the motion map describing?
The object is moving in the postive directionan at a constant velocity, stops for 3 seconds, and moves at a faster constant velocity in the negative direction.
p-t graphs
Graph that shows the position of an object over a period of time
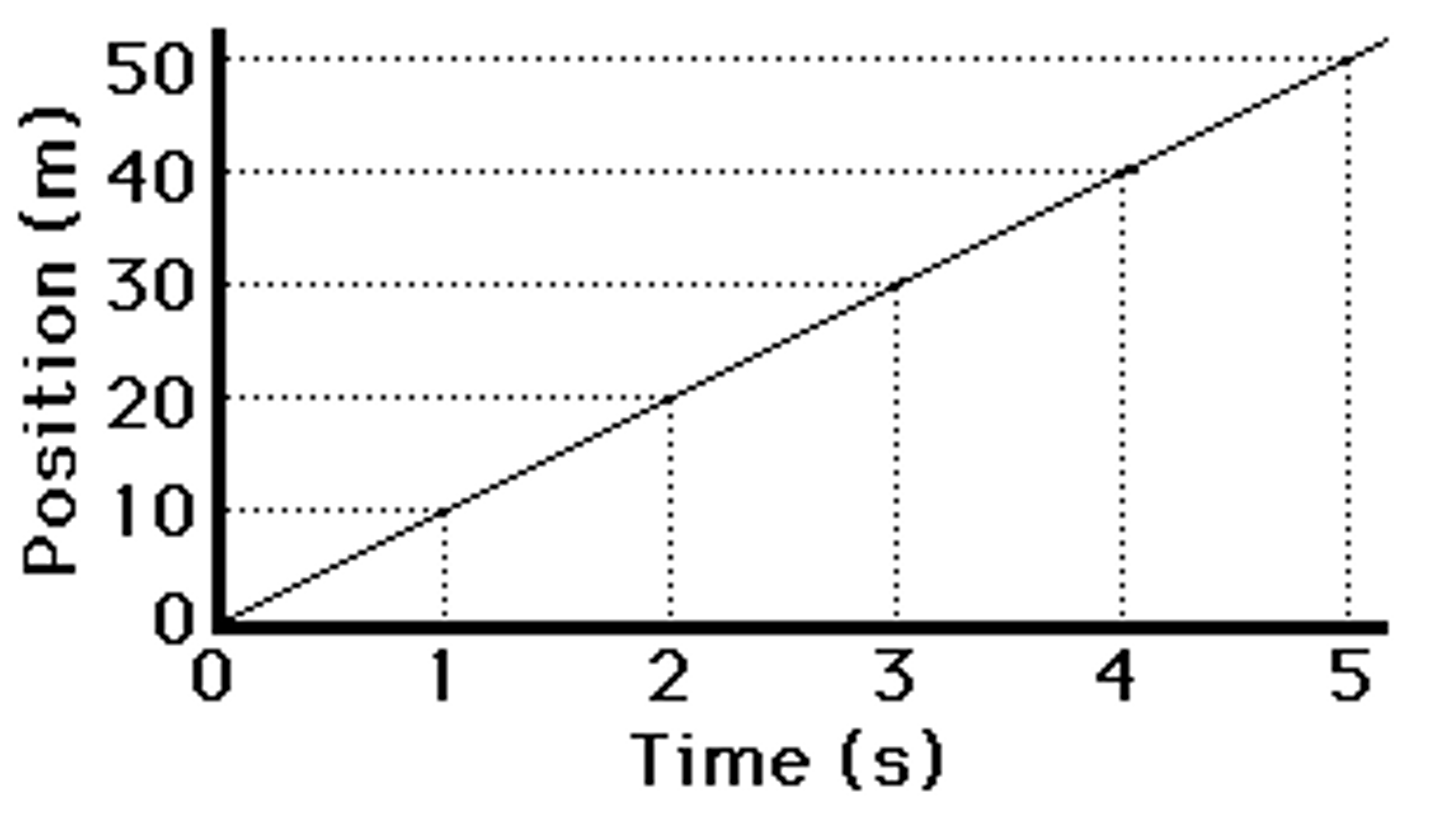
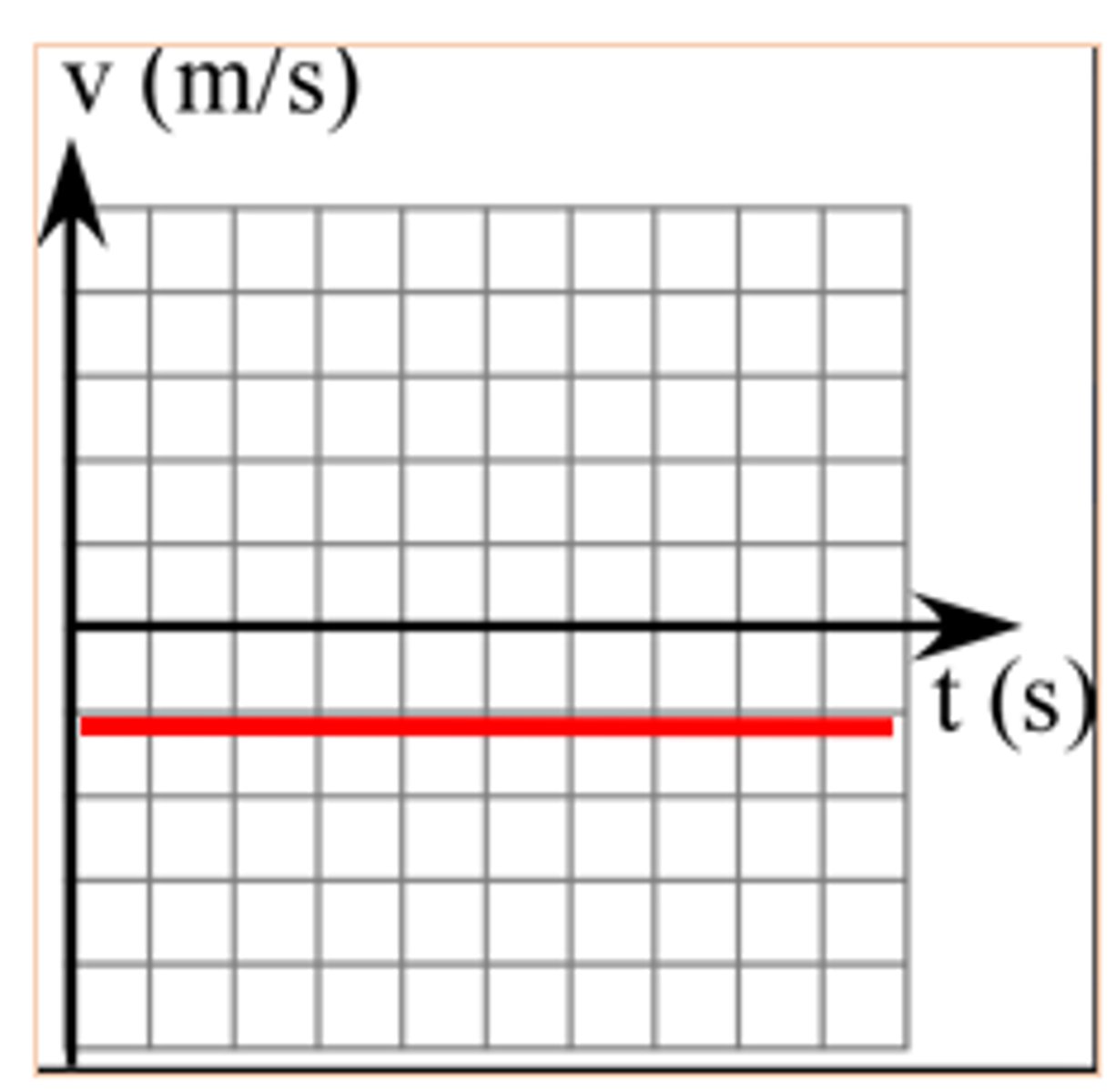
P-t and v-t graphs moving in the positive direction (straight line)

v-t graph moving in the negative direction
p-t graph moving in the negative direction

Objects traveling with a constant velocity have a ______ line
straight
Objects traveling with a changing velocity have a _______ line
curved
In position-time graphs slope=
velocity
The steeper the slope on a straight line position-time graph...
the faster the velocity
The flatter the slope on a straight line position-time graph...
the slower the velocity
Determining the slope of p-t graph (non honors)
use the slope formula, y2-y/x2-x or rise/run
v-t graphs increasing acceleration
velocity time graph
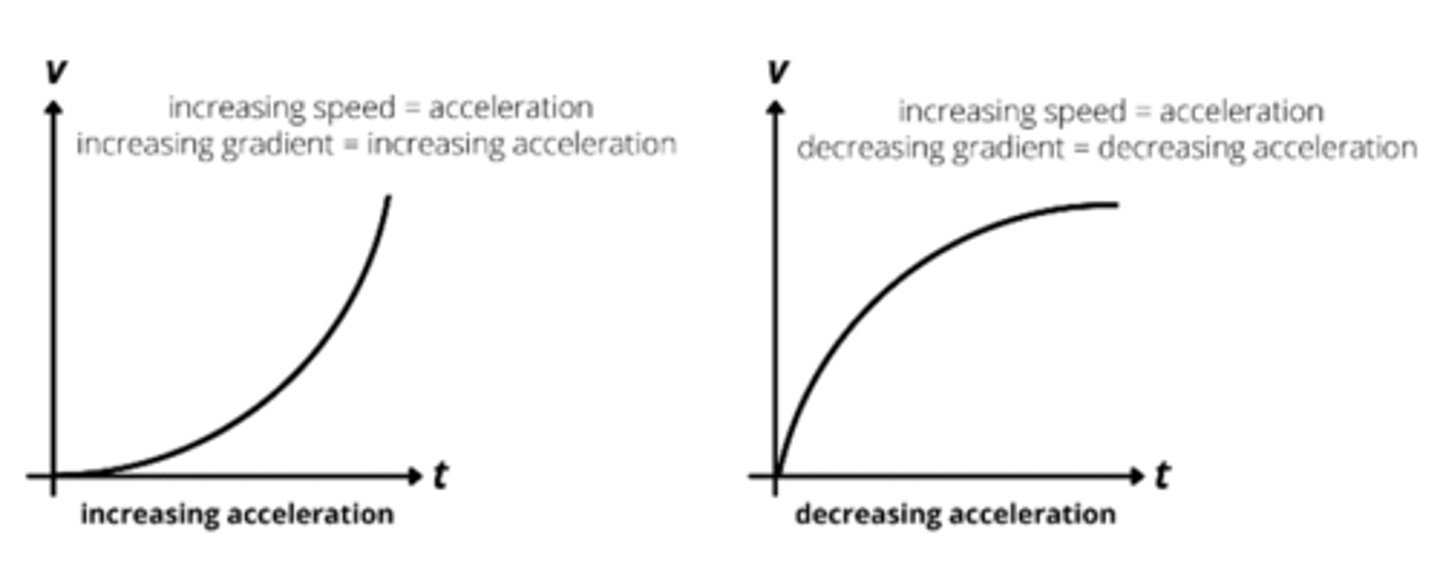
v-t graphs speeding up (straight line)
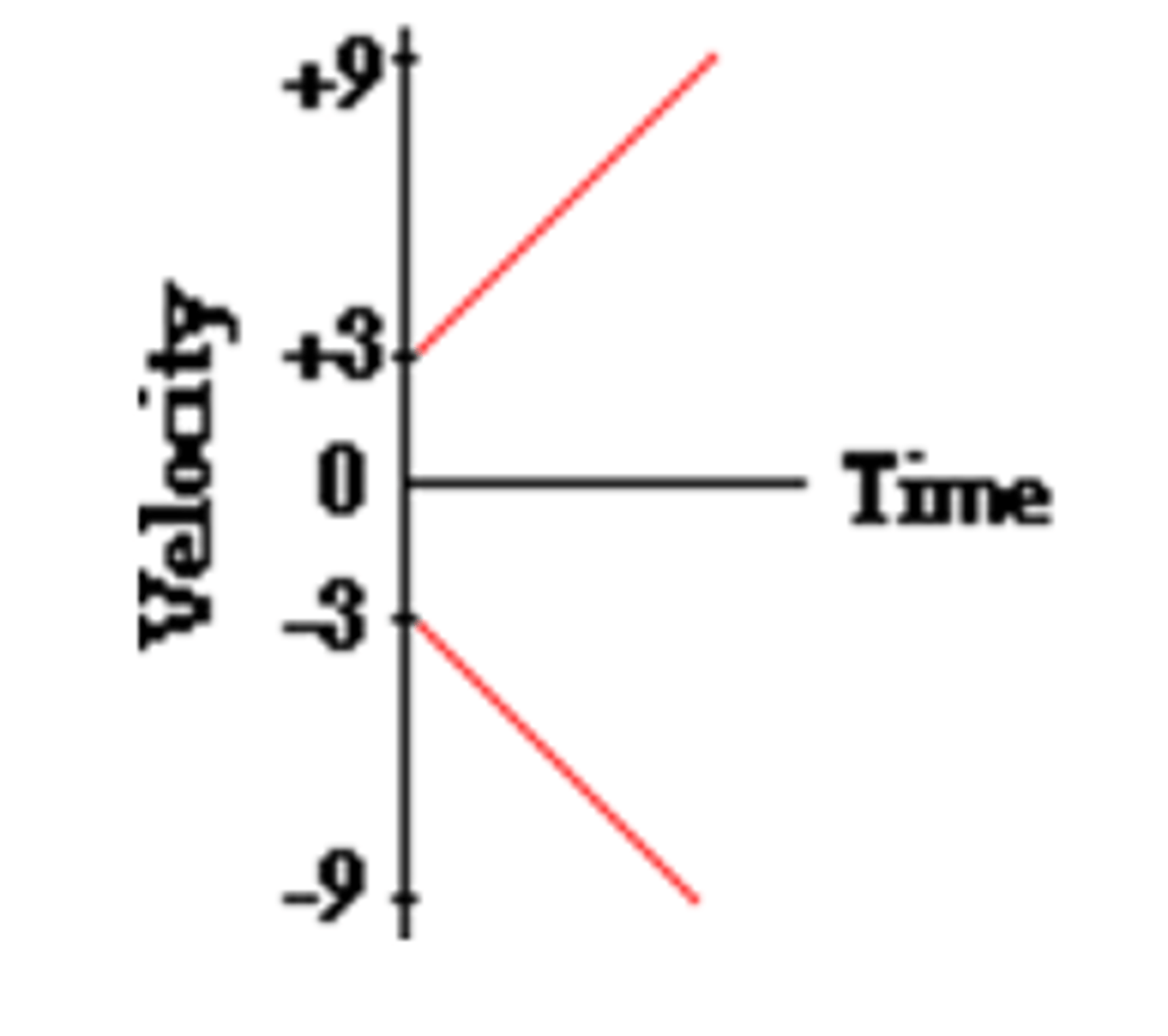
v-t graphs slowing down (straight line)
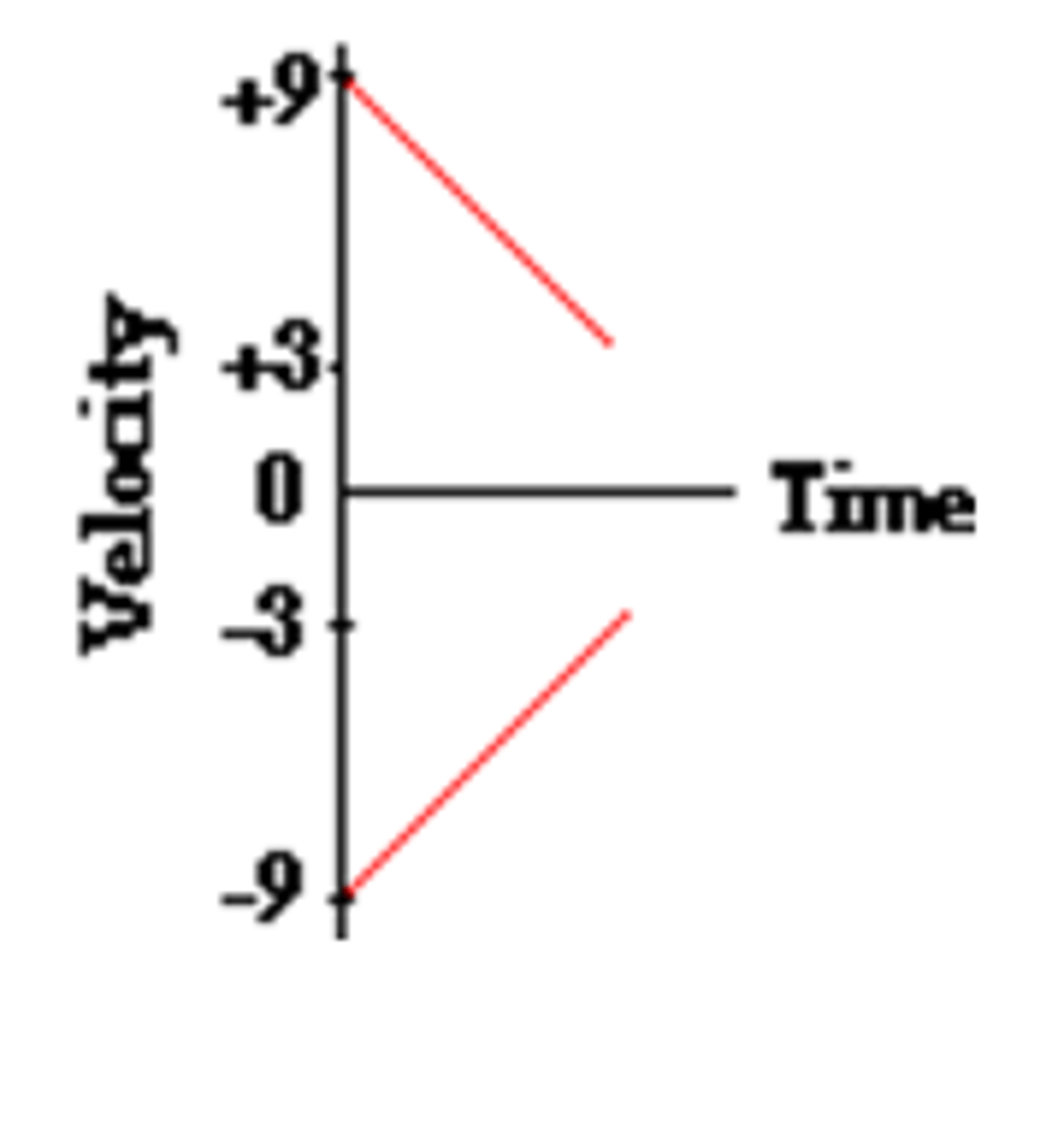
How do you turn a p-t graph into a v-t graph?
Calculate the slope by using slope formula or rise/run
How do you turn a v-t graph into p-t graph
Calculate the area
How do you find the displacement of a p-t graph? (when graph is shaded under)
Break the graph up into shapes, and solve for the area of those shapes
What does the motion map mean? (map on definition page)
The object is moving in the positive direction at a constant acceleration
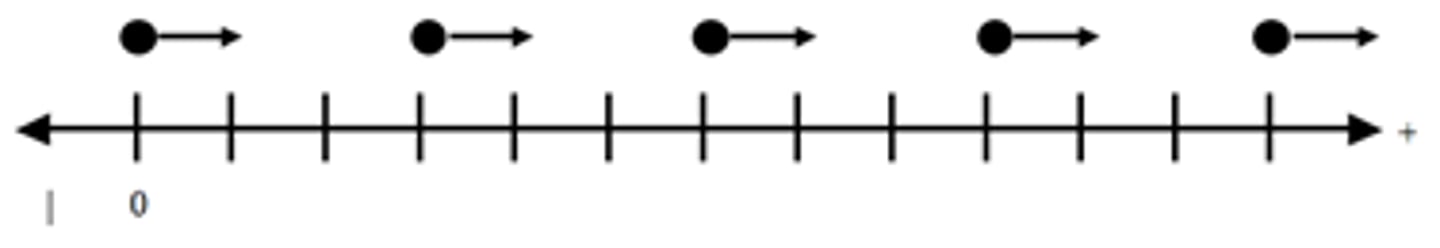
What do the longer arrows mean in motion maps
More acceleration
What did Aristotle say about motion?
Aristotle said objects will move to a state of rest as that is their desired state.
Why did Copernicus work for years without making his thoughts public?
Copernicus was scared of the backlash he would receive when he went against the Aristotleian thinkers.
Did Galileo make is thoughts public?
Yes, but he was scared of backlash he would recive because his went agaist Aristoleian thinkers. He was placed under house arrest.
Inertia
the resistance of any physical object to any change in its velocity.
What did Galileo do from the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa, and what did it demonstrate?
Dropped balls of different masses to see which hit the ground first. They hit the ground at the same time, which demonstrated there is some kind of force pulling the balls down at the same rate.
What is a vacuum (in the terms of science)?
A space devoid of matter
How does the slope of a ramp affect the distance a ball travels down the ramp?
The steeper the slope is, the more distance the ball will cover. The flatter the slope, the less distance the ball will travel.
Law of Inertia
Every object continues in a state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line path unless acted on by a nonzero force.
Why do you launch forward in a car at rest if it's hit from behind?
Your body will try to stay at rest but the car is being moved due to being hit from behind, so you launch forward.
Newtons 1st Law?
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Force
a push or pull, friction, tension, gravity, support/normal
Net force
the sum of all forces acting on an object (positive and negative)
Vector
an arrow drawn to show length and direction of a force
Vector Quantity
requires both magnitude and direction
Scalar Quantity
requires magnitude only
The Equilibrium Rule
An object is in mechanical equilibrium whenever the net force on the object is zero, is at rest, or is moving at a constant velocity.
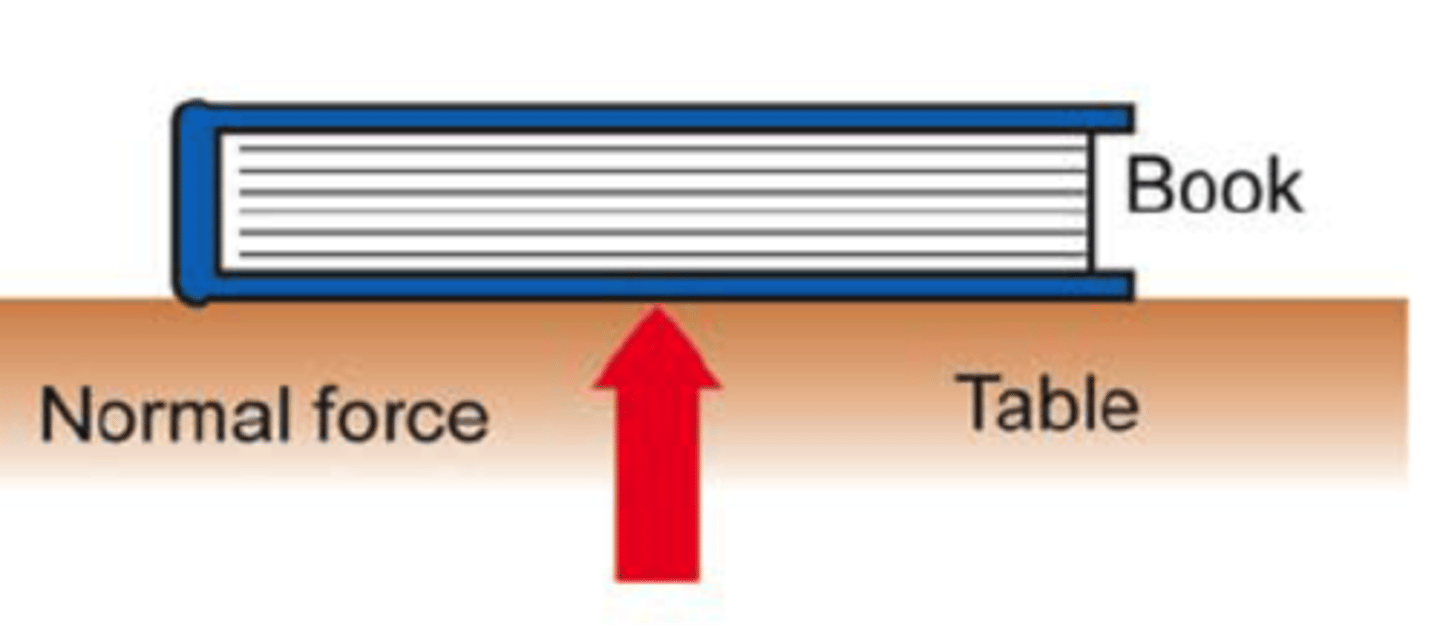
Support Force (aka Normal Force or Fn)
A force that pushes up on something; usually equals the weight of the something.
If an object is under the influence of only one force, can it be in equilibrium?
No, if only one force is acting on an object, the forces are unbalanced, and therefore not in equilibrium.
Support/normal force
the force that pushes up on something; usually equals the weight of the something.
Newton's 2nd Law Formula
F= m x a
Finding mass using Newton's 2nd Law formula
m= f/a
Finding acceleration using Newton's 2nd Law formula
a=f/m
Newton's 2nd Law
The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied.
If an object has more mass, will it have more or less acceleration?
Less acceleration
If an object has less mass, will it have more acceleration or less?
More acceleration
Friction
Usually reduces net force and the resulting acceleration of an object; Caused by irregularities in surfaces that are in contact.
Friction depends on..
The kinds of material and how much they are pressed together.
The direction of friction is always...
opposite the direction of motion
An object at rest experiences how much friction..?
None
Static friction
Friction that builds up before sliding takes place
Sliding friction
Friction that occurs between two surfaces sliding past each other
Mass
quantity of matter in an object
Weight
The force on an object due to gravity
Formula for weight
w= m x g
What is the force of gravity on Earth?
10 m/s^2
Fapp
Applied force
Fn
normal or support force
Fg
Gravity
Fair
air resistance
Ft
tension force
When is Ft present?
When an object is hanging from a string
Free Fall
a state in which something falls due to gravity only
Air drag
Resistance to free fall caused by air (parachute)
Newton's 3rd Law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
In NLM3, as mass increases..
acceleration decreases when force is constant
Why is the acceleration of a bullet greater then the acceleration of a gun ? (short answer question dont even try typing allat)
Newtons 2nd law states that F=ma. So the force is determined by the mass and acceleration of the object. Newton's third law says that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The force that the bullet feels from the gun, is equal in magnitude and opposite direction from the force that the gun feels from the bullet. Because the forces are the same, with an equal force but less mass, there is going to be more acceleration (bullet). Where as for an equal force but more mass the gun feels less acceleration (gun).
A boxer can hit a heavy bag with great force. Why can't he hit a piece of tissue paper in the air with the same amount of force? (short answer question dont even try typing allat)
When a boxer hits a heavy bag, the bag resists the punch. So because of NLM3 the bag exerts and equal and opposite force back on the boxer. A piece of tissue paper offer almost no resistance. When the boxer tries to punch it the tissue simply accelerates away or tears instead of pushing back significantly. The tissue does not exert a large force back, so the boxer cannot exert a large force on it.
Density formula
mass/volume
Characteristic of Atoms
Tiny, neutral, make up everything
Pure substances are either __________ or ___________. There is only one way to make them.
elements and compounds
Mixtures
a physical combination of substances; homogenous and heterogenous
Elements
Atoms of the element itself, nearly all of them are remnants of stars, arranged by atomic numbers
Compounds
2 or more different elements chemically combined
Example of compound
salt
homogeneous mixtures
a mixture that is the same throughout
Example of homogenous mixture
Coffee (you dont see individual sugar pieces + milk)
heterogeneous mixture
mixture that is different through
Example of heterogenous
soil
Molecule
two or more atoms chemically combined, can be two different or two same atoms; pure
Example of molecule
H2O
Proton
positive charge; in the nucleus
Neutron
no charge; neutral; in the nucleus
Electron
negative charge, outside nucleus
On the periodic table of elements the atomic number is the same as..
the protons and the electrons
On the periodic table of elements, the formula to calculate the mass is..
Protons + neutrons
Formula to find how many neutrons a element has
atomic mass-atomic number