HAP 355 Midterm
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Epidemiology
Study and analysis of the distribution, patterns, and determinants of health & disease conditions in a defined population
Descriptive Epidemiology
Involves characterizations of the distribution of health-related states or events (person, place, time)
Analytic Epidemiology
Involves finding & quantifying associations, testing hypotheses, & identifying causes of health-related states or events
Efficacy
Ability of a program to produce a desired effect among participants in the program compared to those not in the program
Effectiveness
Ability of a program to produce benefits among those who are offered the program
Epidemics
Illness or behavior or health-related event in excess of normal
Endemics
Ongoing, usual, or constant presence of a disease in a community
Pandemics
Epidemic that affects the population of an extensive region
Common-source
Specific source
Common-source
specific source
Propagated
infections that are transmitted from one infested person to another
Case
a person in a population who has a disease, disorder, injury, or condition
Case defined
a standard set of criteria
Primary case
first disease case in the population
Index case
first disease brought to the attention of an epidemiologist
Secondary case
person infected after contact with a primary case
Suspect case
individual or groups who have signs and symptoms but not diagnosed
Case severity
how disabling or debilitating the illness is (hospital length of stay)
Epidemiology Triangle
model for understanding infectious disease
Fomite
inanimate object that can harbor a pathogen and is capable of being a means of transmission
Vector
invertebrate animal that transmits infection by conveying the pathogen from one host to another
Reservoir
habitat in which the agent normally lives, grows, & multiplies
Vehicle
a fomite intermediary that conveys the infectious agent from its reservoir to a susceptible host
Carrier
contains, spreads, or harbors an infectious organism
active carrier
exposed and harbors the pathogen
convalescent carrier
harbors the pathogen, recovery phase
healthy (passive) carrier
not ill, but exposed and harbors the pathogen
incubatory carrier
exposed, & harbors the pathogen, ability to transmit
intermittent carrier
exposed to and harbors, can spread pathogen
Direct
un-interrupted and immediate transfer from person to person
Indirect
transmission through airborne, vector-borne, and vehicle-borne routes
airborne
occurs when droplets or dust carry the pathogen to the host and cause infection
vector-borne
occurs when an arthropod conveys the infectious agent
vehicle-borne
involves an inanimate object that conveys an infection from the host
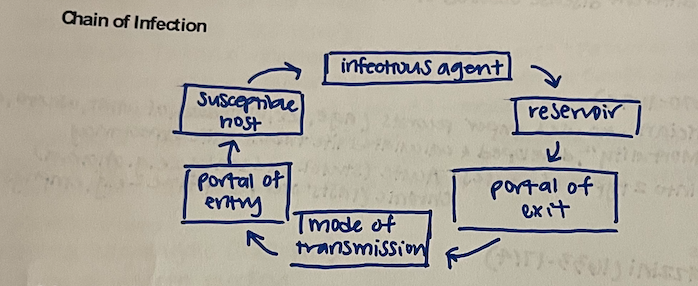
chain of infection
→ infectious agent → reservoir → portal of exit → mode of transmission → portal of entry → susceptible host →
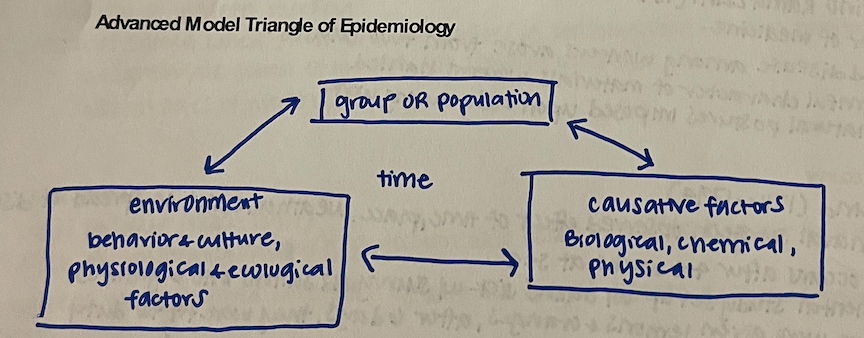
advanced triangle of epidemiology
Hippocrates
Considered the first epidemiologist, he introduced terms like epidemic and endemic, emphasizing a rational perspective on diseases over supernatural beliefs.
John Graunt
An English statistician who developed vital statistics, including life tables and life expectancy calculations, and categorized deaths into acute and chronic causes.
Bernardino Ramazzini
Noted that diseases among workers stemmed from harmful materials and unnatural postures at work, laying the foundation for occupational health.
James Lind
Scottish naval surgeon who conducted an experimental study on scurvy, highlighting the impact of diet, time, and place on disease spread.
Edward Jenner
Rural physician who pioneered vaccination by using cowpox to protect against smallpox, a breakthrough in immunization.
John Snow
Known as the father of Epidemiology, he studied cholera transmission, incubation times, and water sources, contributing significantly to disease control.
Ignaz Semmelweis
Hungarian physician who advocated for hand hygiene to prevent childbed fever, a crucial step in understanding and preventing nosocomial infections.
Florence Nightingale
Revered as the mother of modern nursing, she revolutionized healthcare practices during the Crimean War and established the first nursing school.
Louis Pasteur
Renowned French scientist who developed vaccines for anthrax and other diseases, pioneering the field of microbiology and immunization.
Typhoid Mary
Refers to Mary Mallon, an Irish chef who unknowingly spread typhoid fever, highlighting the importance of asymptomatic carriers in disease transmission.
Communicable disease
Infectious diseases that are contagious or capable of being transmitted
Non-communicable disease
A disease not transmissible directly from one person to another
Vertical Transmission
Transmission from an individual to its offspring through sperm, placenta, milk, or vaginal fluid
Horizontal Transmission
Transmission of infectious agents from an infected person to a susceptible person
Characteristics of infectious disease agents
Viability, communicability, infectivity, pathogenicity, and virulence
Viability
Ability of the infectious agent to survive outside the host and thrive in the environment
Communicability
Ability of the infectious disease to be transmitted from one person to the next or spread in a population
Infectivity
Ability of an infectious agent to cause infection
Pathogenicity
Ability of an infectious agent to cause disease after infection
Virulence
Ability of an infectious agent to cause severe disease
Stages of Disease
Susceptibility, Pre-symptomatic Disease, Clinical Disease, Recovery, Disability, or Death
how the human body resists infection
resistance to infection
→ general resistance
→ immunity
—> active immunity (naturally or artificially acquired active immunity)
—> passive immunity (naturally or artificially acquired passive immunity)
Active Immunity
Body produces antibodies against a specific antigen for permanent immunity
Passive Immunity
Transfer of antibodies from another person for short-lived immunity
Herd immunity
Protection of the population from disease by immunity to limit major epidemics
Environmental Control
Measures like clean water, safer air, and control of vectors to prevent disease
Host-related Control
Quarantine for exposed persons, isolation for non-ill individuals with contagious diseases
Infection-control and prevention
Includes personal hygiene and antibiotic prophylaxis
Descriptive Epidemiology
Describes the extent of a public health problem according to person, place, and time
Population Pyramids
Used to track and compare changes in the population age distributions over time
Constrictive Pyramid
A population pyramid that comes in at the bottom, indicating an older population with low birth rates
Gender or Sex
Sex is biologically founded, while gender is a socially constructed notion
Time Trends
Examples include temperature measured at noon each day and the number of hospital admissions per day
Point Source Epidemic
Individual exposed to the same source over a limited time period
Surveillance
Systematic ongoing collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health data
Health Programs
Aimed at increasing vaccination levels, reducing smoking, and increasing physical activity
Confounding Factors
Always a threat in descriptive studies, analytic epidemiologic studies are better for minimizing the threat
Noninfectious acute conditions
Conditions that occur suddenly, such as car accidents or injuries.
Chronic disease epidemiology
Study of the distribution and determinants of chronic diseases in the human population for preventing and controlling health problems.
Risk factor
A variable associated with an increased likelihood of experiencing adverse health outcomes.
Exposure to radiation pathways
Inhalation, ingestion, and direct exposure to radioactive materials.
Toxicokinetics
Processes including absorption, distribution, biotransformation, and excretion of substances in the body.
Social environment and health
Factors like war, families, social networks, neighborhoods, and public health policies influencing health.
Behavior and chronic health problems
Lifestyles affecting modern diseases, including smoking, diet, body weight, sexual practices, and heredity.
Risk factors of breast cancer
Age, family history, geography, radiation exposure, obesity, breastfeeding, and mammography for screening.
Prevention behaviors
Healthy weight maintenance, dietary choices, alcohol consumption, fruit and vegetable intake, exercise, and protection from various risks.
Health Belief Model
Factors like perceived susceptibility, severity, benefits, barriers, cues to action, and self-efficacy in health decision-making.
Prevention and control of noninfectious diseases
Tailoring prevention programs to societies, cultures, and health determinants for effective control and reduced healthcare costs.
Priorities in disease prevention and control
Identifying impactful diseases, susceptible populations, responsive communities, overlooked diseases, and investigations for improved health states and economic benefits.