ORGS 2100 - Class 7: Learning & Decision-Making
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
What is learning?
relatively permanent knowledge / skill / behaviour change from experience
What is the learning & decision making relationship?
learning impacts decision making
What is decision making?
generating & choosing alternative process
What is 1 example of a reason that inexperience can be problematic?
learning ≠ necessarily easy
What is expertise?
expert v.s. novice knowledge / skill
What explains how one can tell when people have learned?
observe behaviour
What are the knowledge types?
explicit knowledge
>
tacit knowledge
What is explicit knowledge?
easily available knowledge
What is tacit knowledge?
// intuition // skill // insight // belief // mental model // practical intelligence
learned experience knowledge
What are the explicit knowledge characteristics?
easily transferable
readily available
can learn through book
always conscious / accessible & general info
What are the tacit knowledge characteristics?
difficult / impossible to articulate
highly personal
experience base
sometimes not recognized by holder
job- / situation- … specific
What may be the most important strategic company asset?
tacit knowledge
What ways do employees learn knowledge?
reinforcement
observation
experience
What is operant conditioning?
learning by linking voluntary behaviour & consequence
What is the operant conditioning process?
antecedent
behaviour
consequence
⟳

What is an antecedent?
condition before behaviour
What is a behaviour?
employee action
What is a consequence?
result after behaviour
What operant conditioning component primarily drives behaviour?
consequence
What is a contingency of reinforcement?
consequence to modify behaviour
What are the contingencies of reinforcement?
positive reinforcement
negative reinforcement
punishment
extinction
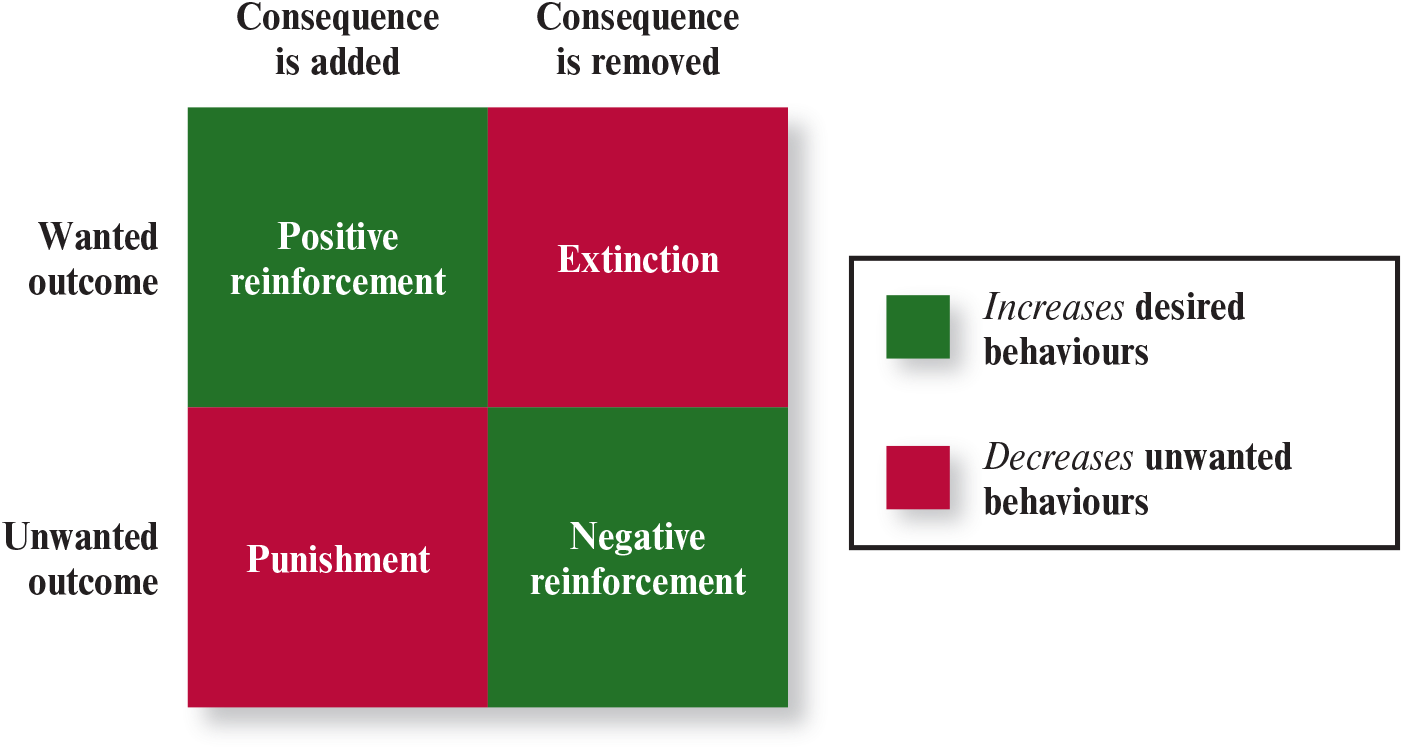
What contingencies of reinforcement increase desired behaviour?
positive reinforcement
negative reinforcement
What contingencies of reinforcement decrease undesired behaviour?
punishment
extinction
What is positive reinforcement?
added consequence
increased desired behaviour
→
wanted outcome
What are the most common contingencies of reinforcement?
positive reinforcement
extinction
What is negative reinforcement?
removed consequence
increased desired behaviour
→
unwanted outcome
What is punishment?
added consequence
decreased undesired behaviour
→
unwanted outcome
What is extinction?
removed consequence
decreased undesired behaviour
→
wanted outcome
What is a schedule of reinforcement?
add / remove consequence time
What are the schedules of reinforcement?
continuous reinforcement
fixed interval
variable interval
fixed ratio
variable ratio
What is continuous reinforcement?
reward after each desired behaviour
What is the simplest, rapidest, & least long lasting schedule of reinforcement?
continuous reinforcement
What is continuous reinforcement’s potential performance level?
high
difficult to maintain
What is interval-based?
based on time
What is fixed interval?
reward after fixed time
What is fixed interval’s potential performance level?
average
What is variable interval?
reward after variable time
What is variable interval’s potential performance level?
moderate high
What is fixed ratio?
reward after fixed desired behaviour number
What is fixed ratio’s potential performance level?
high
What is variable ratio?
reward after varable desired behaviour number
What is variable ratio’s potential performance level?
very high
What are the interval-based schedules of reinforcement?
fixed interval
v.s.
variable interval
What is the most common schedule of reinforcement?
fixed interval
What is behaviour-based?
reinforcement based on behaviour
What is social learning theory?
one learns by observing other
What is the primary way one gains knowledge?
social learning
What is behavioural modeling?
one observes’ other’s action
learn
repeat other’s action
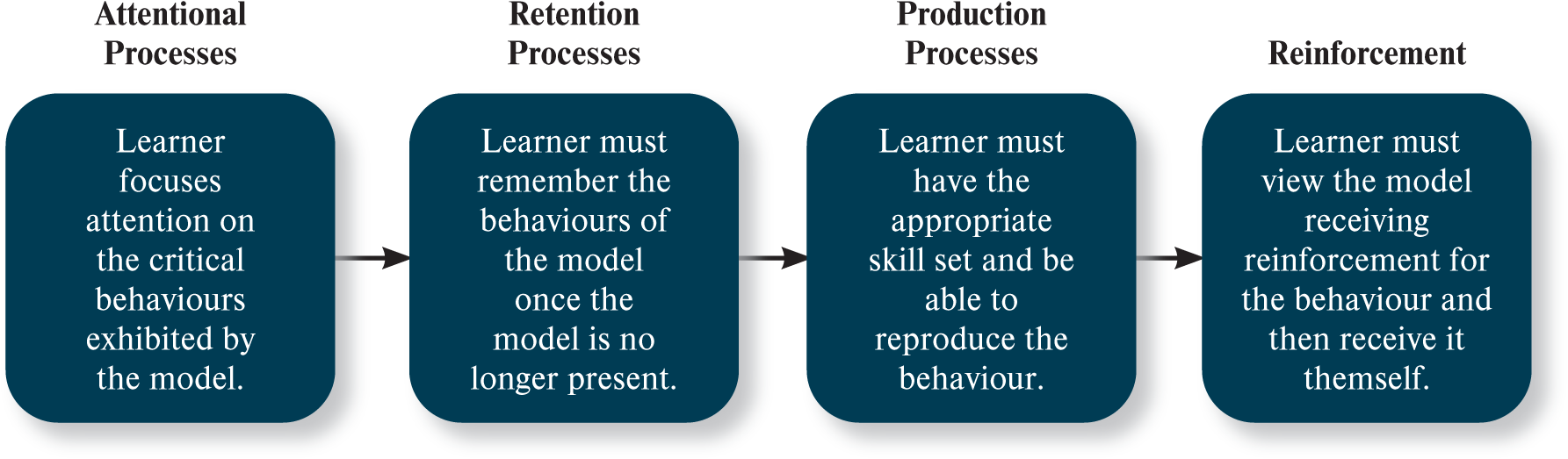
What is the modelling process?
attention process
retention process
production process
reinforcement
What is the best way to acquire tacit knowledge?
modelling
What is an attentional process?
one focuses on model
What is a retention process?
one remembers model behaviour once no longer present
What is a production process?
one has skill & reproduces behaviour
What is reinforcement in social learning theory & behavioural modelling?
one views model receiving reinforcement & receives himself
What can reinforcement in social learning theory come from?
observation
&/
experience
What are the goal orientations?
learning orientation
>
performance-prove orientation
performance-avoid orientation
What is learning orientation?
build competence > prove experience
What is performance-prove orientation?
prove competence so other thinks favourable
What is performance-avoid orientation?
prove competence so other doesn’t think poor
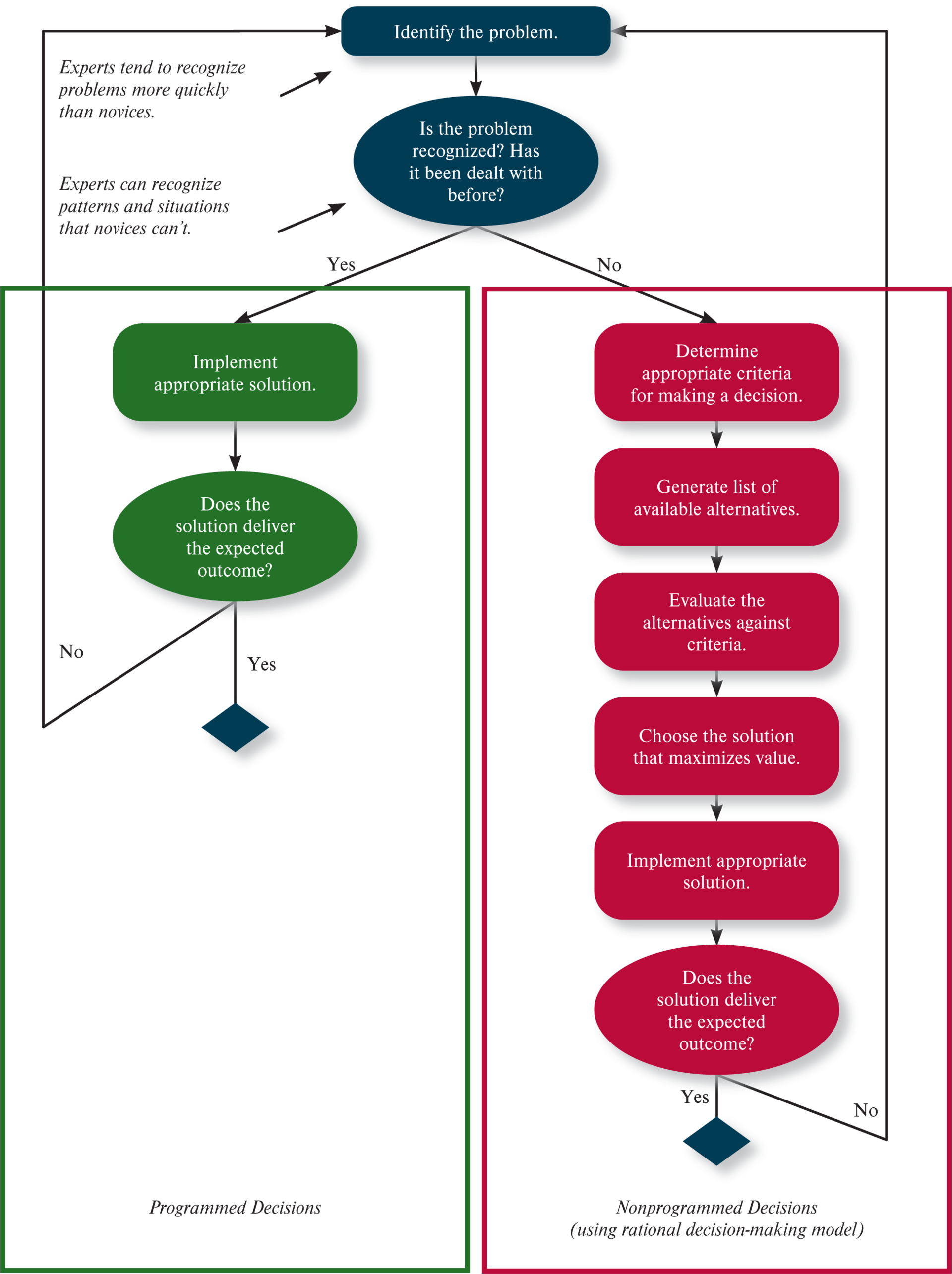
What is a programmed decision?
// intuition // gut feeling
automatic decision between maker’s knowledge & situation & action recognition
What is the programmed decision process?
identify problem
recognize pattern
implement solution
does solution deliver?
What is the rational decision making nonprogrammed decision process?
identify problem
recognize pattern
determine criteria making decision
generable available alternative
evaluate alternative against criteria
choose max solution
implement solution
does solution deliver?
What is 1 crisis key factor example?
quick decision
What questions do managers who make decisions face?
how they ensure other follows
how they confirm faulty intuition
What is Karl Weick’s intent process & communication?
manager perceives situation
make task-focused statement of what manager wants
give reason
ensure correct intuition
confirm everyone understands role
What is a nonprogrammed decision?
new decision
What is the rational decision-making model?
step-by-step decision making maximizing nonprogrammed decision outcome by examining alternative
What problems arise when examining rational decision-making model assumptions?
problem & identifiability
perfect info
time & money ≠ issue
What are the most common bad decision making reasons?
limited info
faulty perception & attribution
escalation of commitment
What is bounded rationality?
people don’t have ability to process all info
What bounded rationality problems arise for decision making?
filter / simplify
miss info
satisfice
What is satisfice?
choose 1st considered alternative
What should rational decision makers do?
identify problem
develop alternatives
simultaneously evaluate
use accurate info
pick maximized alternative
What is bounded rationality likely to do?
boil down problem
come up with similar solutions
evaluate as one thinks
distort info during eval
satisfice
What is selective perception?
see environment as it affects
What is projection bias?
decision maker thinking other’s act
What problems arise when examining selective perception assumptions?
limit ability to develop criteria
What is social identity theory?
people identify / judge according to belonging groups
What explains when stereotypes can be especially problematic?
affect who one thinks is suited for leadership
What is role congruity theory?
lack of fit between stereotype & expected role requirement
What is 1 counteracting bias example?
objective hiring / promoting criteria
evaluate without knowing identity
What is a heuristic?
rule of thumb allowing one to easily decide
What is availability bias?
judge easier recall info
What are some well-researched decision-making bias examples?
anchor
frame
representativeness
contrast
recency
ratio effect
What is an anchor?
make decision relying too heavily on 1 trait
What is a frame?
make decision on phrased question / situation
What is representativeness?
make decision assessing event likelihood by comparing to similar event
What is contrast?
make decision judging based on near reference
What is recency?
make decision weighting recent event more
What is ratio effect?
make decision judging unlikely event as lower when presented in small number ratio
What is fundamental attribution error?
judge other behaviour due to internal factor
ability
motivation
attitude
What is self-serving bias?
own failure → external factor
v.s.
own success → internal factor
What explains why blame might be different depending on the world part?
East Asia
group = entity
v.s.
North America
acting individual
What is the attribution process model?
familiar other → more detailed decision frame
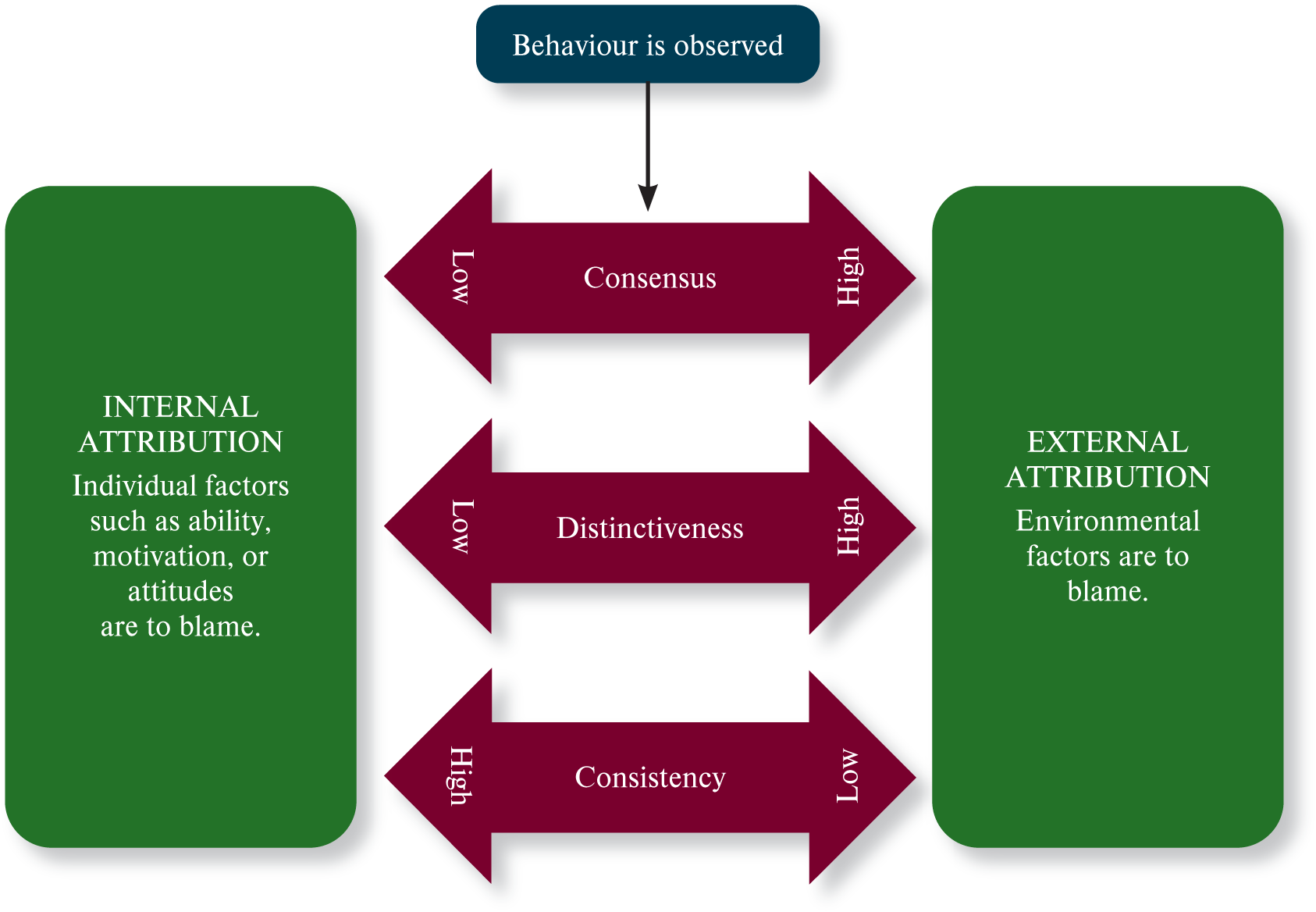
What questions does the attribution process model ask?
consensus
distinctiveness
consistency
What questions does the attribution process model relate to high external attribution if high?
consensus
distinctiveness
What questions does the attribution process model relate to high internal attribution if high?
consistency
What is escalation of commitment?
continue following failing act
What is 1 escalation of commitment explanation example?
obligation to avoid looking incompetent
What is 1 escalation of commitment solution example?
leader change