Chapter 10 (Glencoe Biology)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is the law stating that there's random distribution of alleles during gamete formation?
Law of independent assortment
Passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring.
Heredity
Branch of biology that studies heredity.
Genetics
Male and female sex cells; sperm and eggs.
Gamete
Fusion of male and female gametes.
Fertilization
Alternative forms of a gene for each variation of a trait of an organism.
Allele
Observed trait of an organism that masks the other form of a trait.
Dominant
Trait of an organism that can be masked
Recessive
Mendelian law stating that two alleles for each trait separate during meiosis
Law of segregation
Outward appearance of an organism, regardless of its genes.
Phenotype
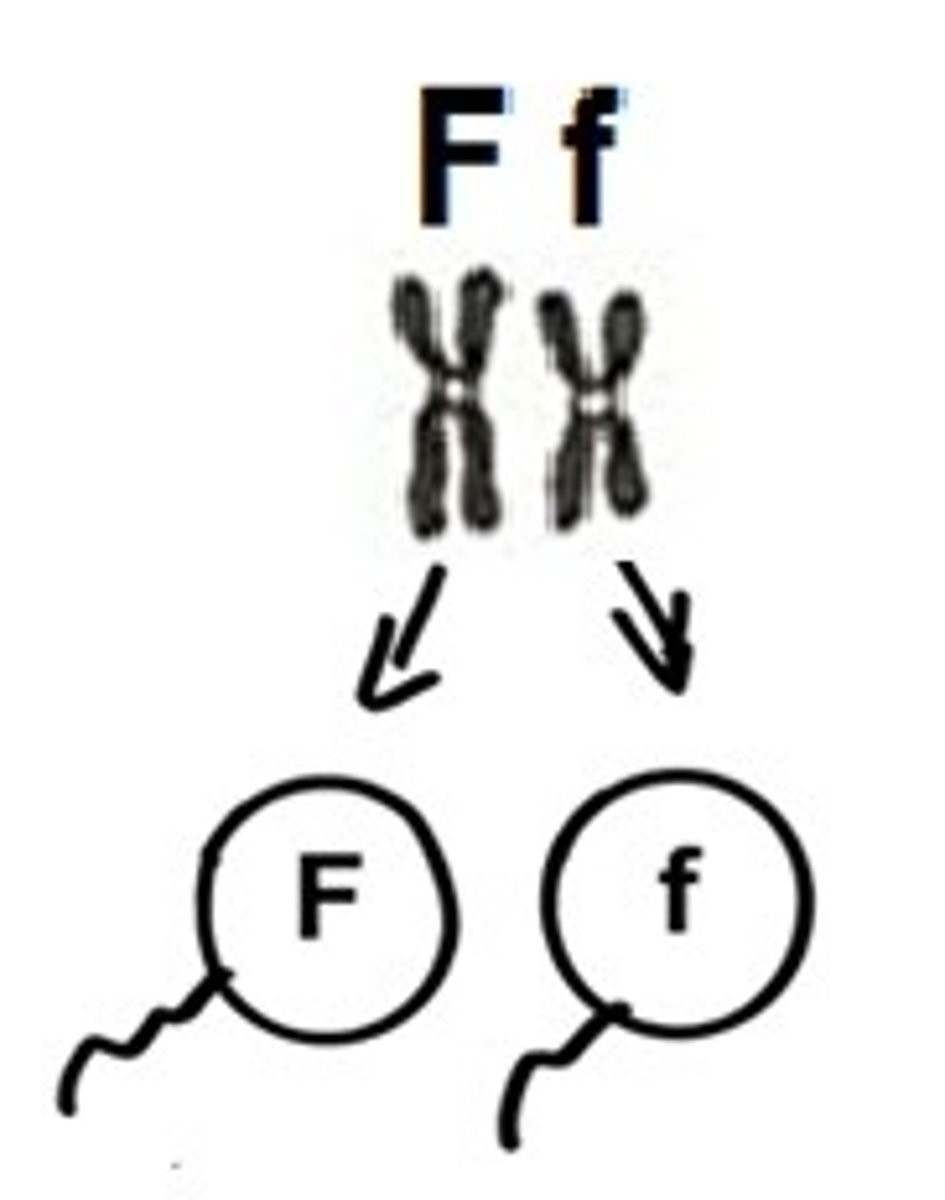
Combination of genes in an organism.
Genotype
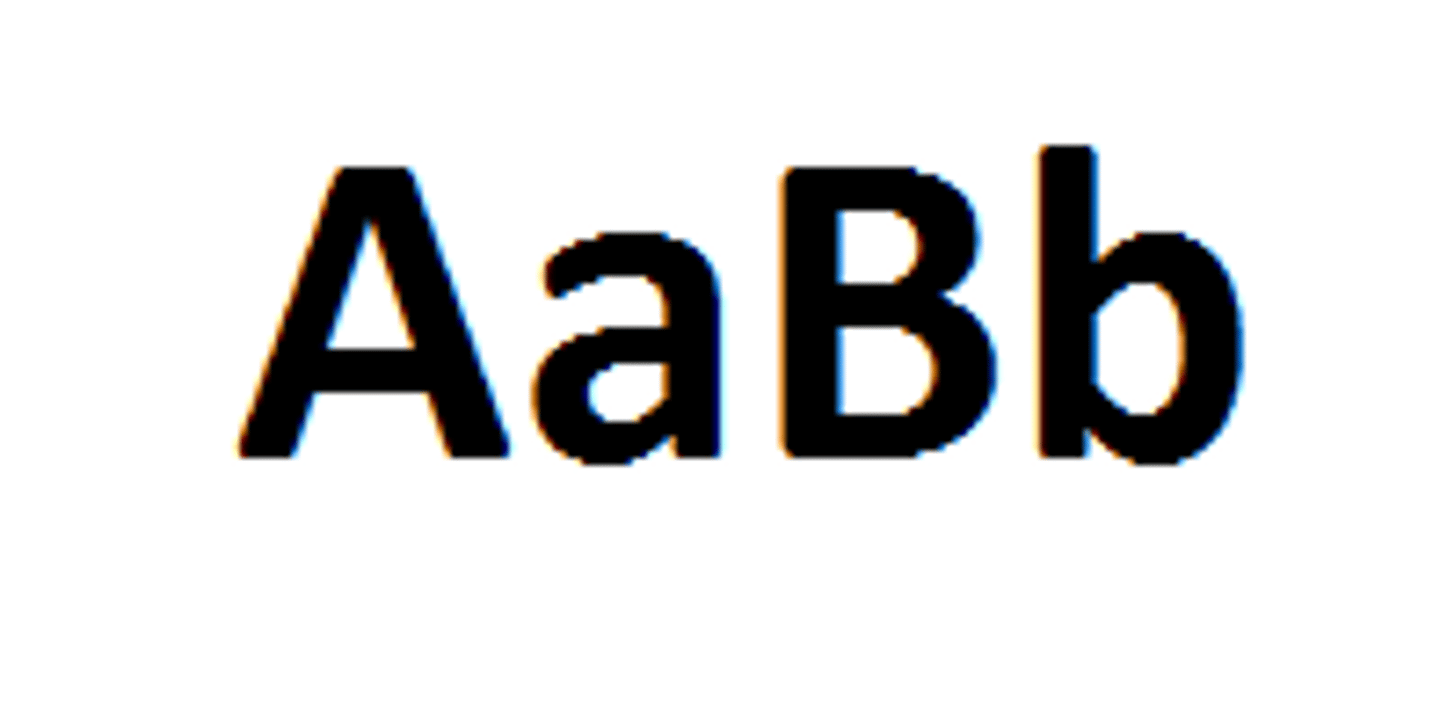
When there are two identical alleles for a trait.
Homozygous
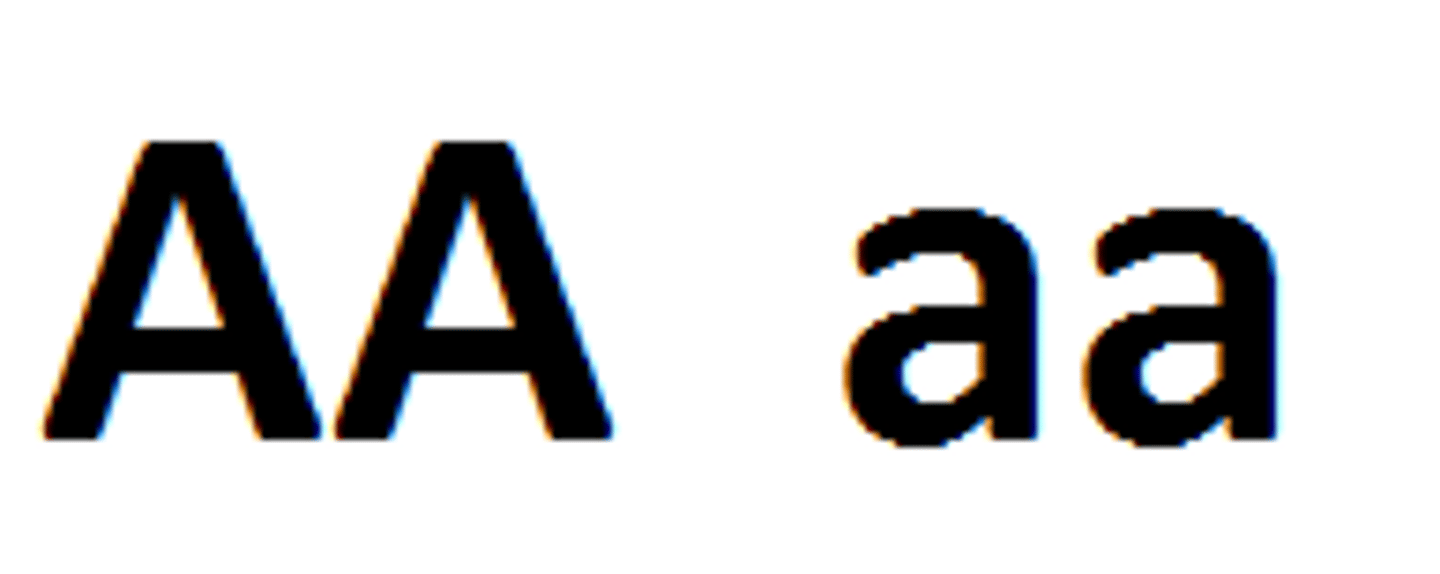
When there are two different alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous

Mendelian law stating that genes for different traits are inherited randomly during the formation of gametes.
Law of independent assortment
Cell with two copies of each chromosome; or 2n, number of chromosomes.
Diploid
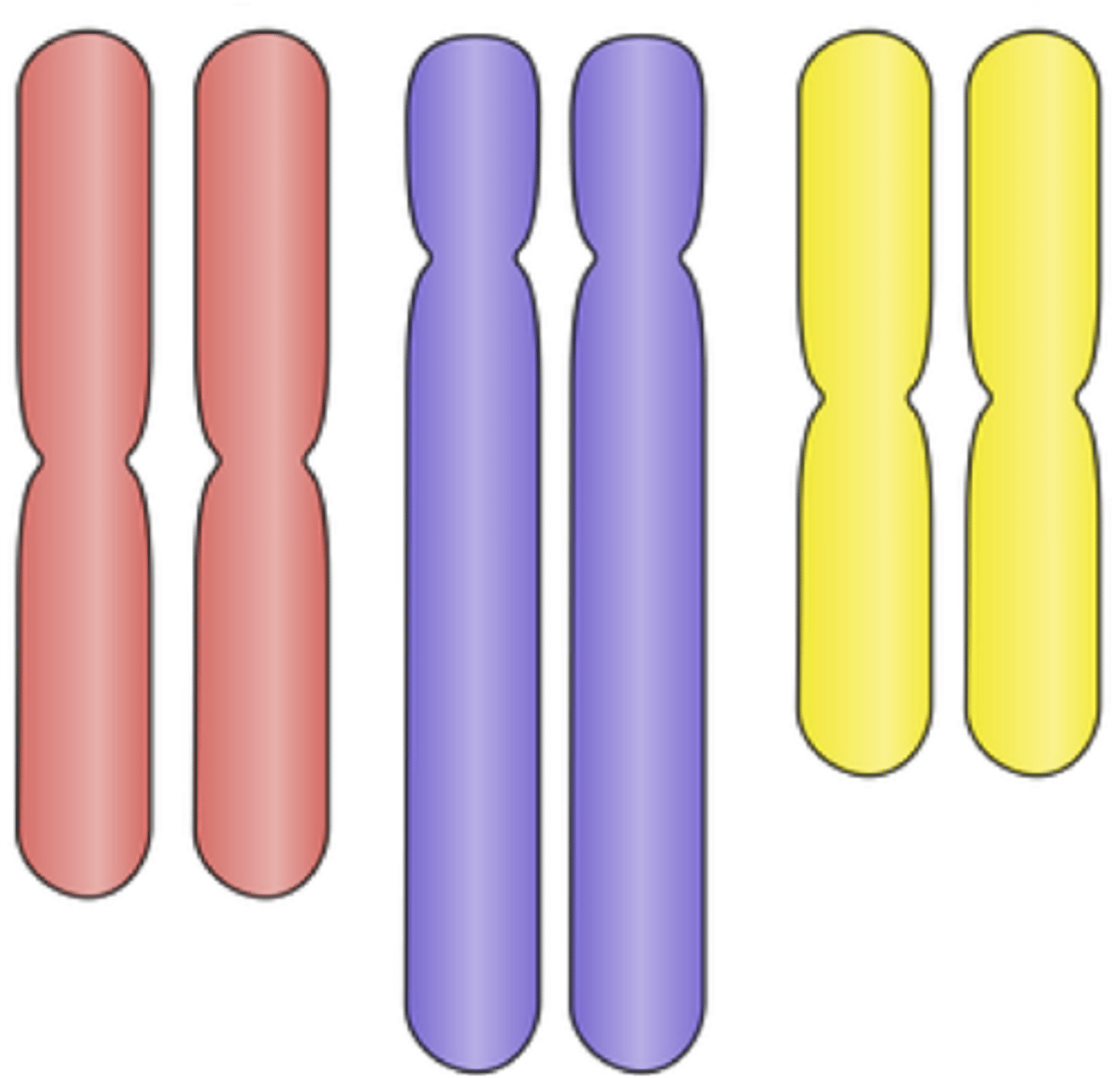
Cell with one copy of each chromosome; is n, number of chromosomes.
Haploid
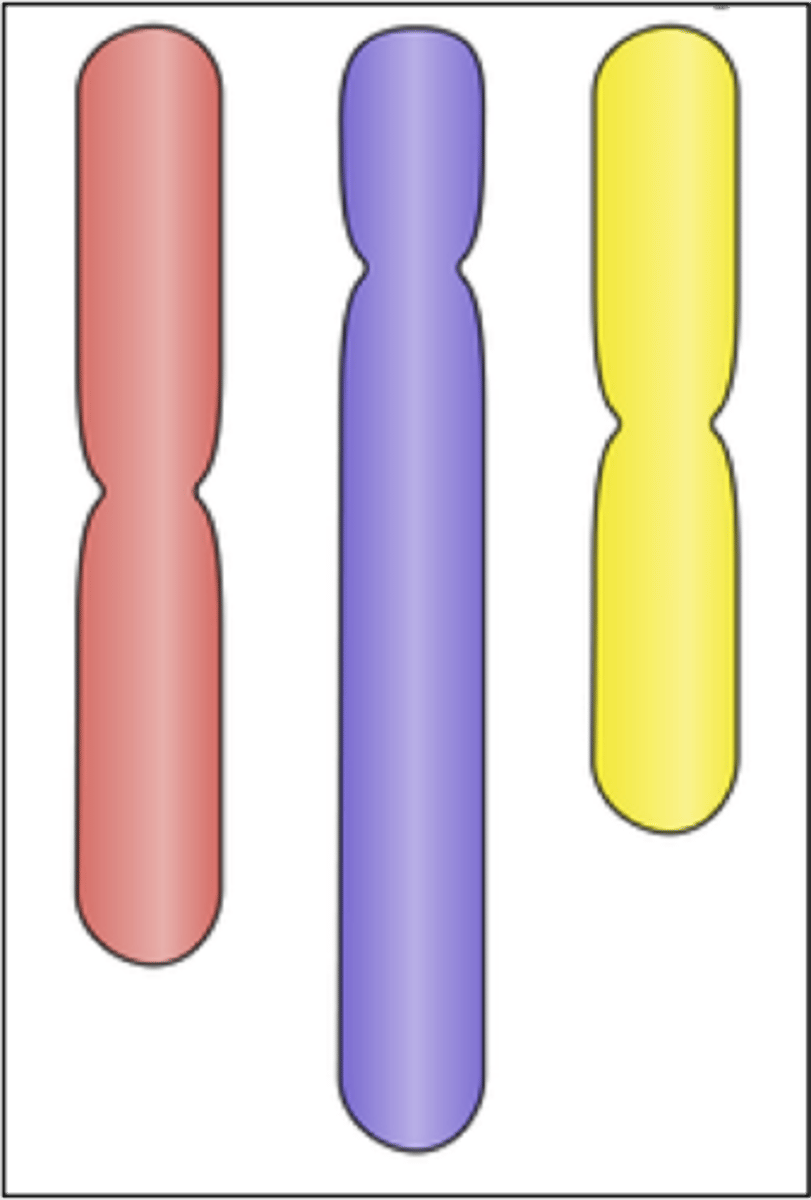
Paired chromosomes, one from each parent with genes for the same traits arranged in the same order.
Homologous chromosome
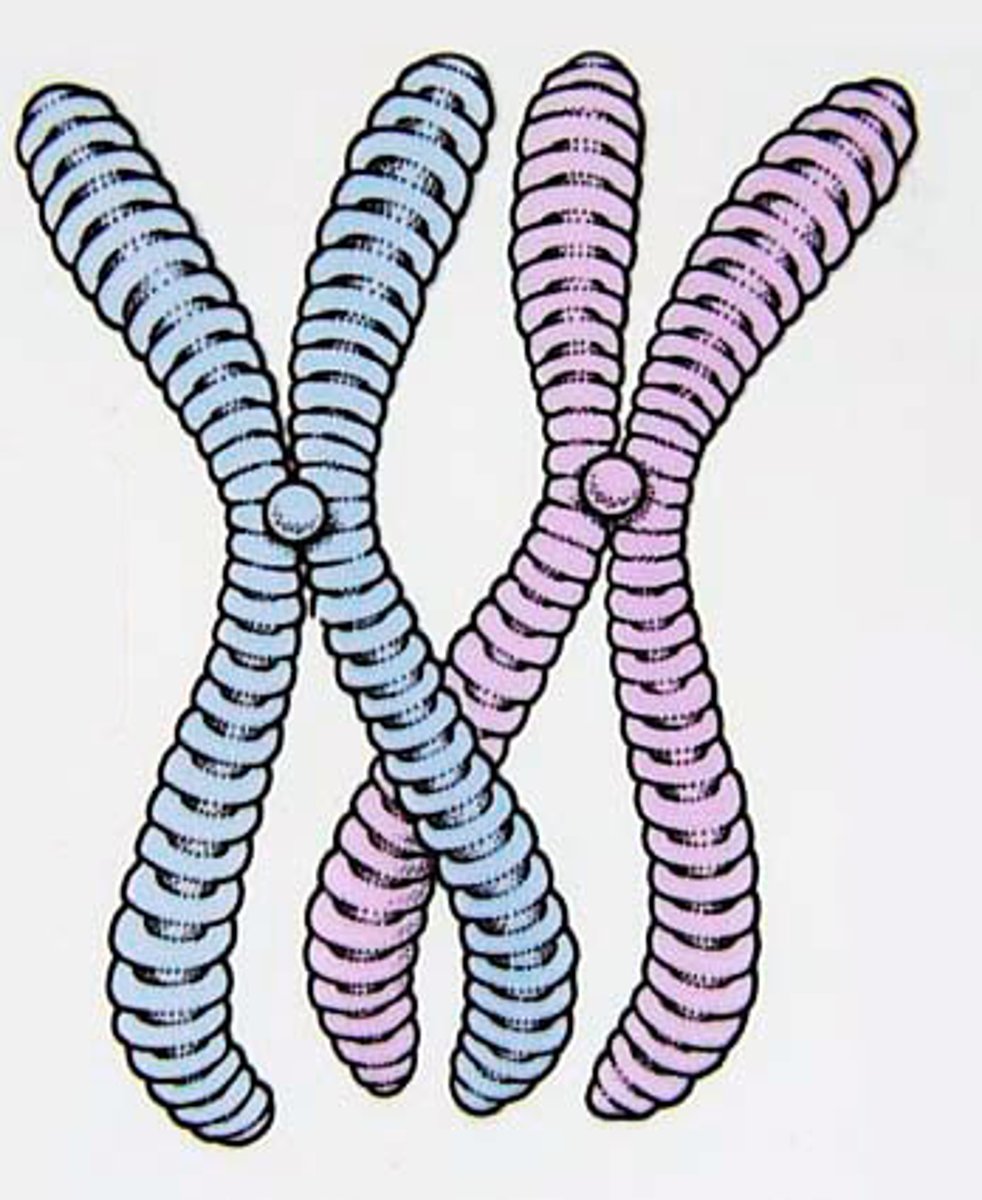
Type of cell division that produces gametes, each containing the haploid number of chromosomes
Meiosis
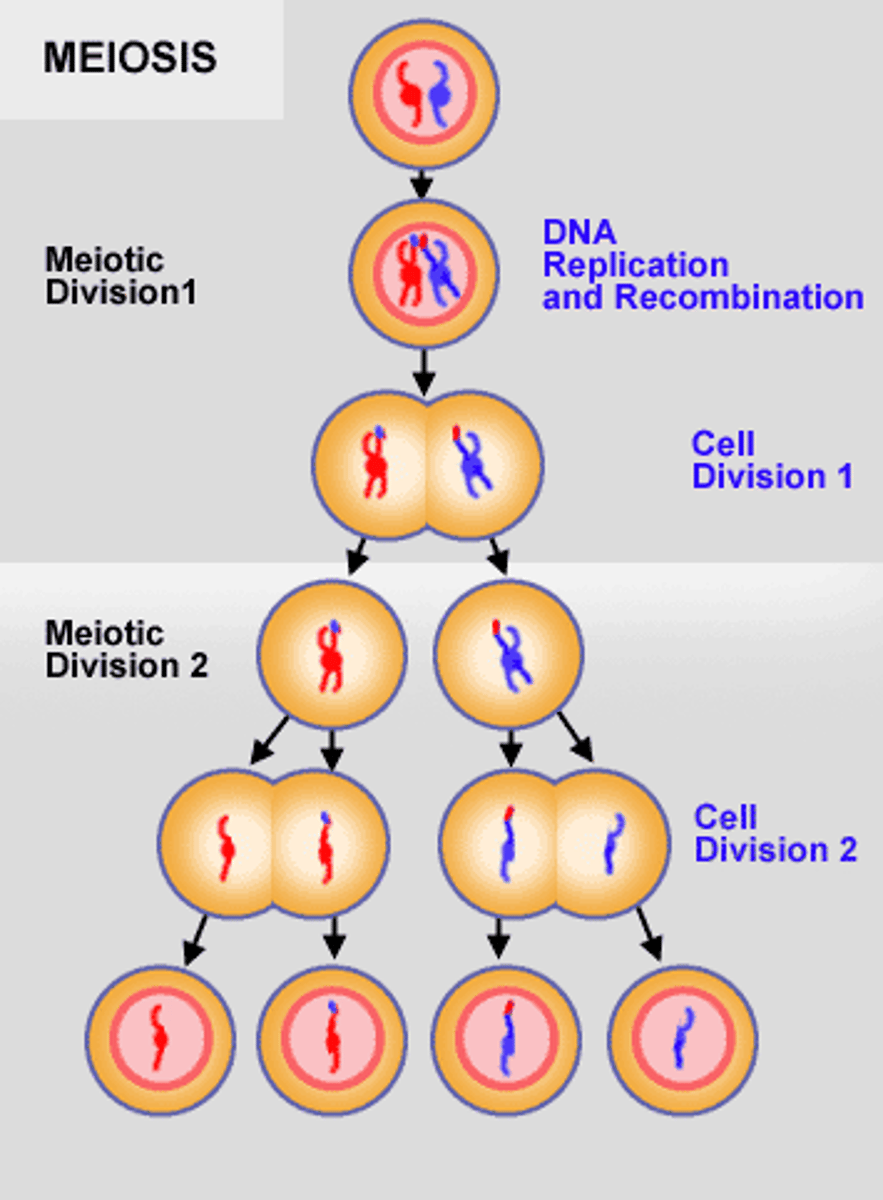
Major source of genetic variation among organisms caused by re-assortment or crossing over during meiosis.
Genetic recombination
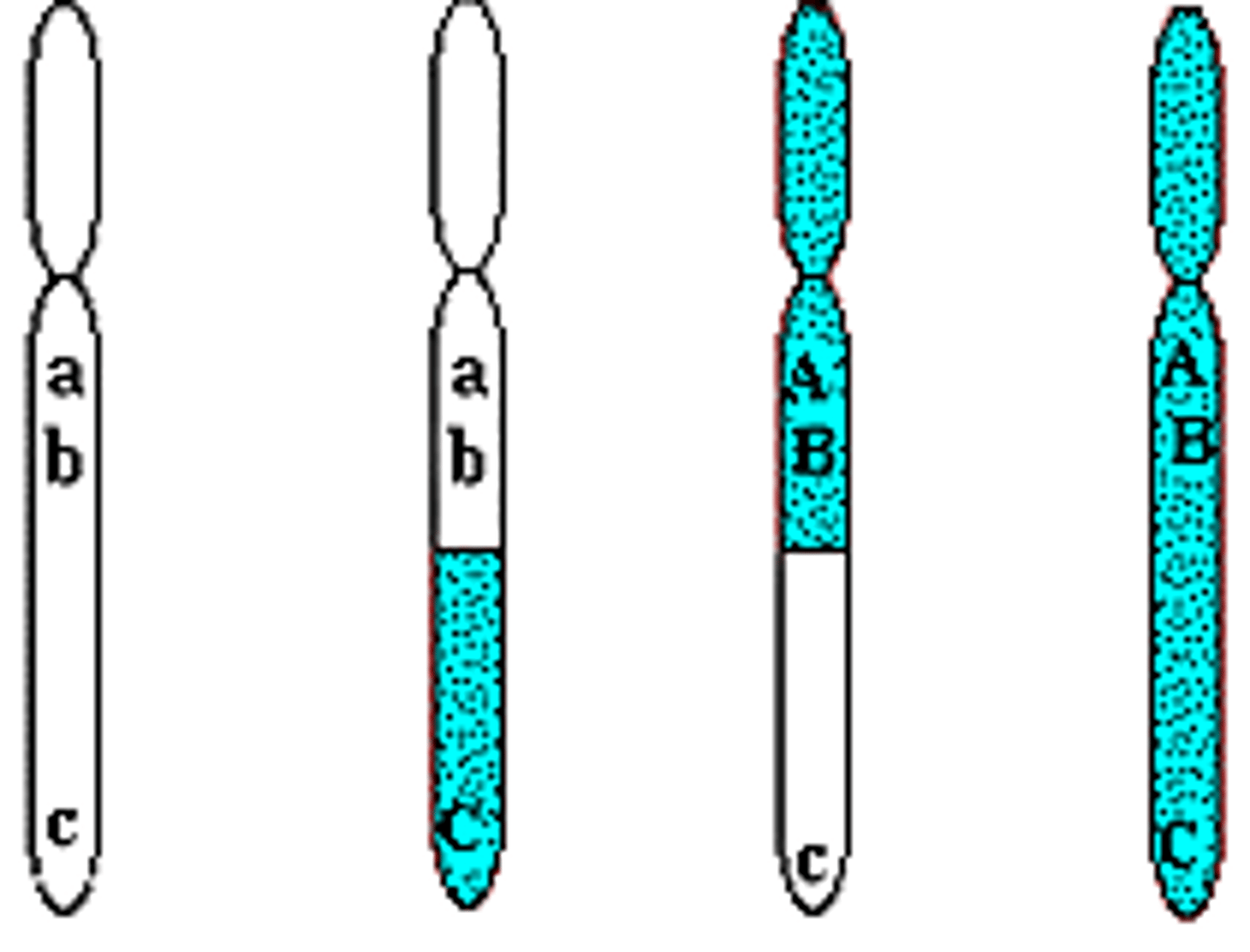
unit that controls the traits that are passed from one generation to the next.
Gene
organism that is heterozygous for a specific traits
Hybrid
having one or more extra sets of chromosomes
polyploidy
What are the 7 different traits Mendel studied?
seed or pea color, flower color, seed pod color, seed shape or texture, seed pod shape, stem length, and flower position
What is the first generation.
The f1 generation is the first hybrid produced by crossing homozygous parents
What is the offspring from the F1 cross.
The F2 generation
How many chromosomes does the Human body cell have?
46 chromosomes
How many chromosomes does a human gamete have?
23 chromosomes
When gametes combine in fertilization, what happens to the number of chromosomes?
restored
What type of cells are formed during meiosis?
gametes
What is the process where chromosome segments are exchanged between a homologous chromosome pair?
crossing over
What are the two consecutive cell divisions during formation of gametes called?
Meiosis I and II
Polyploidy plants often have what type of increased characteristics?
increased vigor and size
Who is known as the Father of Genetics?
Mendel
How many chromosomes does the zygote have?
46 chromosomes
What is the phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross between heterozygous parents?
9:3:3:1
What is Mendel's law of segregation? 2 alleles separate during mitosis
2 alleles separate during mitosis
What is Genetic Recombination?
New combination of genes produced by crossing over and independent assortment
What happens during fertilization?
2 gametes unite
What is Polyploidy?
Occurrence of one or more extra sets of all chromosomes in an organism
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
Random distribution of alleles occur during gamete formation
What is a Punnet Square Dihybrid Cross?
shows cross for two traits
What does a Triploid organism have?
Has 3 complete sets of chromosomes
What is a punnet square used for?
To predict possible genetic outcomes
What are unspecialized cells that can develop into specialized cells when under the right conditions?
Stem cells
What is programmed cell death?
Apoptosis
What is made from crossing over and fertilization?
Genetic Variation
What plant did Mendel use in his study of genetics?
Pea plants
Can mutations be beneficial?
Yes
Which phase of meiosis? NORMAL CELLULAR ACTIVITY - REPLICATION OF CHROMOSOMES
INTERPHASE
Which phase of meiosis? REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES BECOME VISIBLE, CROSSING OVER OCCURS, and SPINDLE BEGINS TO FORM
PROPHASE I
Which phase of meiosis? EACH CHROMOSOME PAIR ALIGNS ACROSS THE MIDDLE OF THE CELL.
METAPHASE I
Which phase of meiosis? HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOME PAIRS SEPARATE AND MIGRATE TO THE OPPOSITE POLES.
ANAPHASE I
Which phase of meiosis? CHROMOSOMES (EACH WITH SISTER CHROMATIDS) COMPLETE MIGRATION TO THE POLES AND NEW NUCLEAR MEMBRANES MAY FORM.
TELOPHASE I
DIVISION OF CYTOPLASM GIVING MULTIPLE CELLS
CYTOKINESIS
Which phase of meiosis? CHROMOSOMES CONDENSE (WITH NO REPLICATION) AND MOVE TO THE MIDDLE
PROPHASE II
Which phase of meiosis? KINETOCHORES ATTACH TO THE SPINDLE FIBERS. CHROMOSOMES LINE UP ON THE MIDDLE.
METAPHASE II
Which phase of meiosis? SISTER CHROMATIDS SEPARATE AND MOVE TO OPPOSITE POLES AS CHROMOSOMES.
ANAPHASE II
Which phase of meiosis? NUCLEAR MEMBRANE FORMS AROUND CHROMOSOMES AND CHROMOSOMES UNCOIL. NUCLEOLUS REFORMS.
TELOPHASE II