Plant Domestication, Breeding, and Biotechnology: Key Concepts and Modern Techniques
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is plant domestication?
A process by which plants or animals are selected and genetically modified over time for traits that make them more advantageous or desirable for human use.
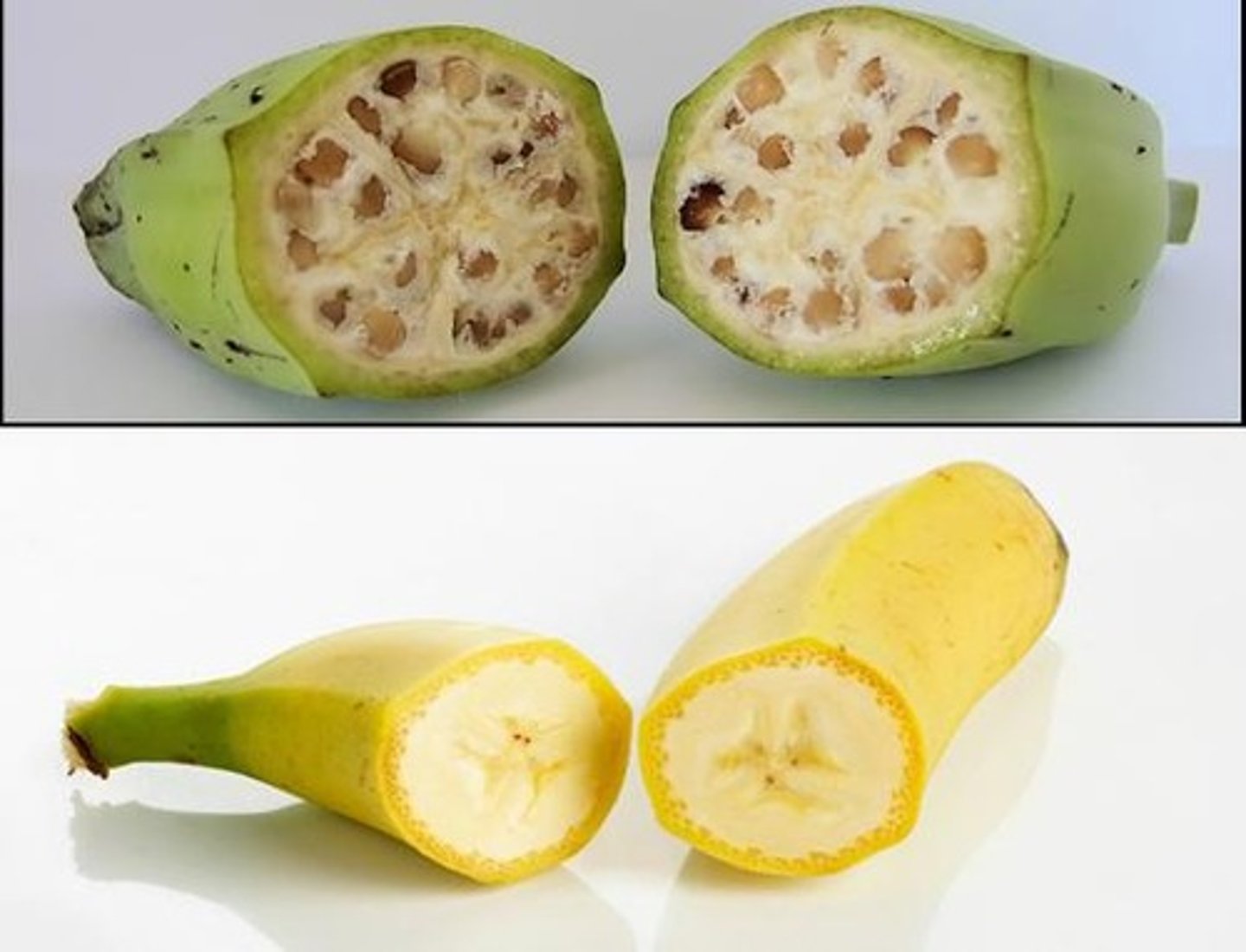
What are some common traits selected during plant domestication?
Traits include large fruit/seed, loss of seed dormancy, loss of seed shattering, improved plant architecture, uniform maturation, reduction in undesirable flavors, and loss of seeds (e.g., bananas).
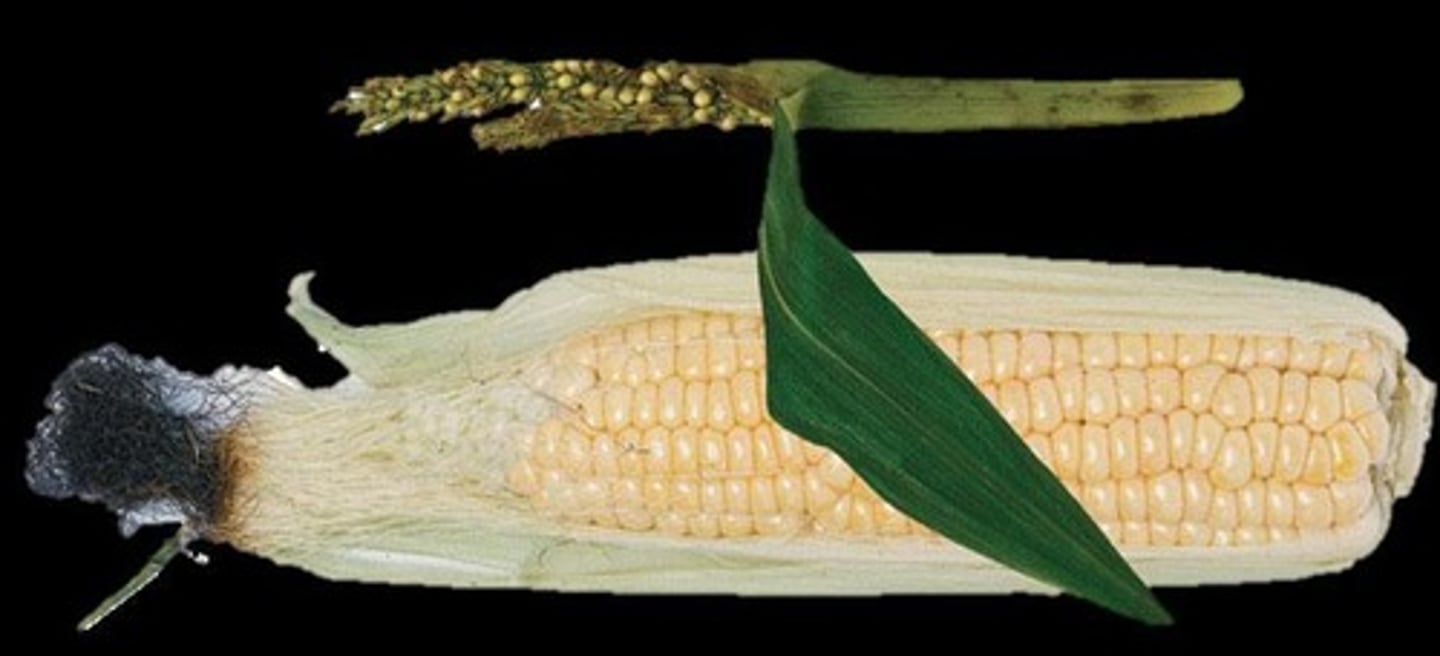
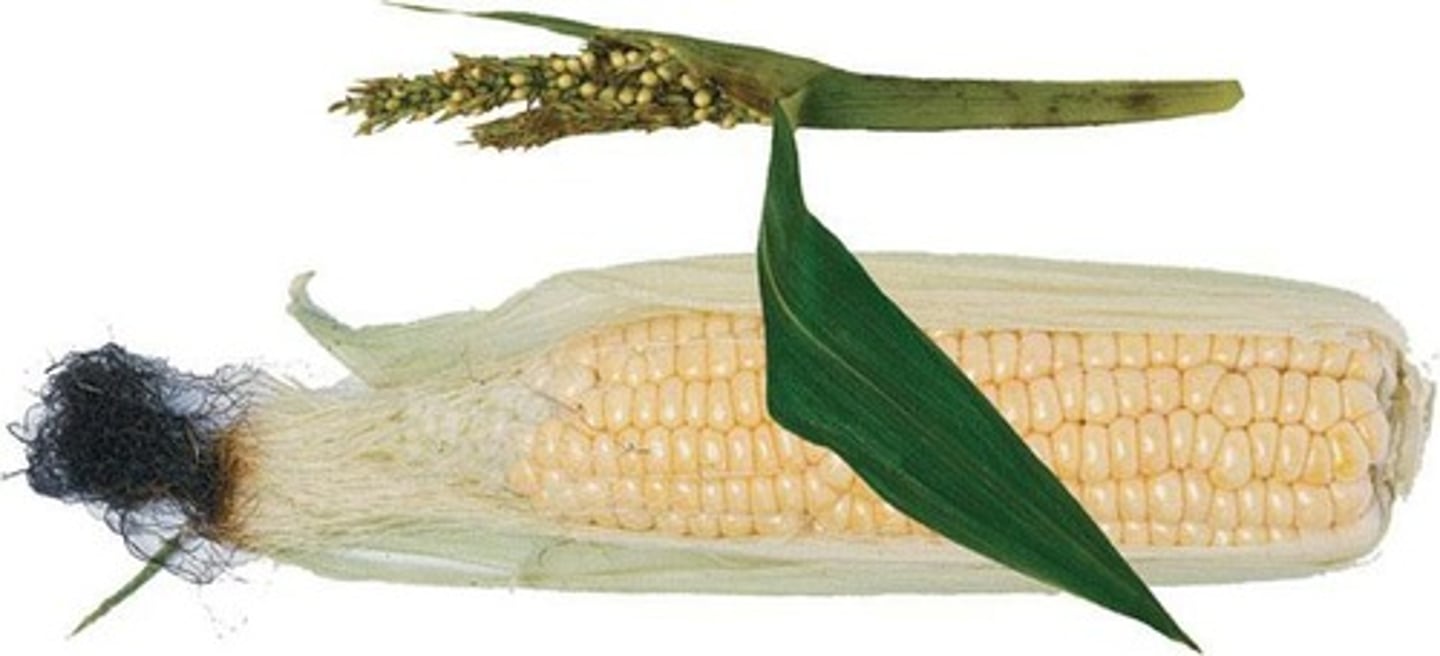
What is teosinte?
Teosinte is the wild ancestor of modern corn, characterized by small grains and a hard shell.
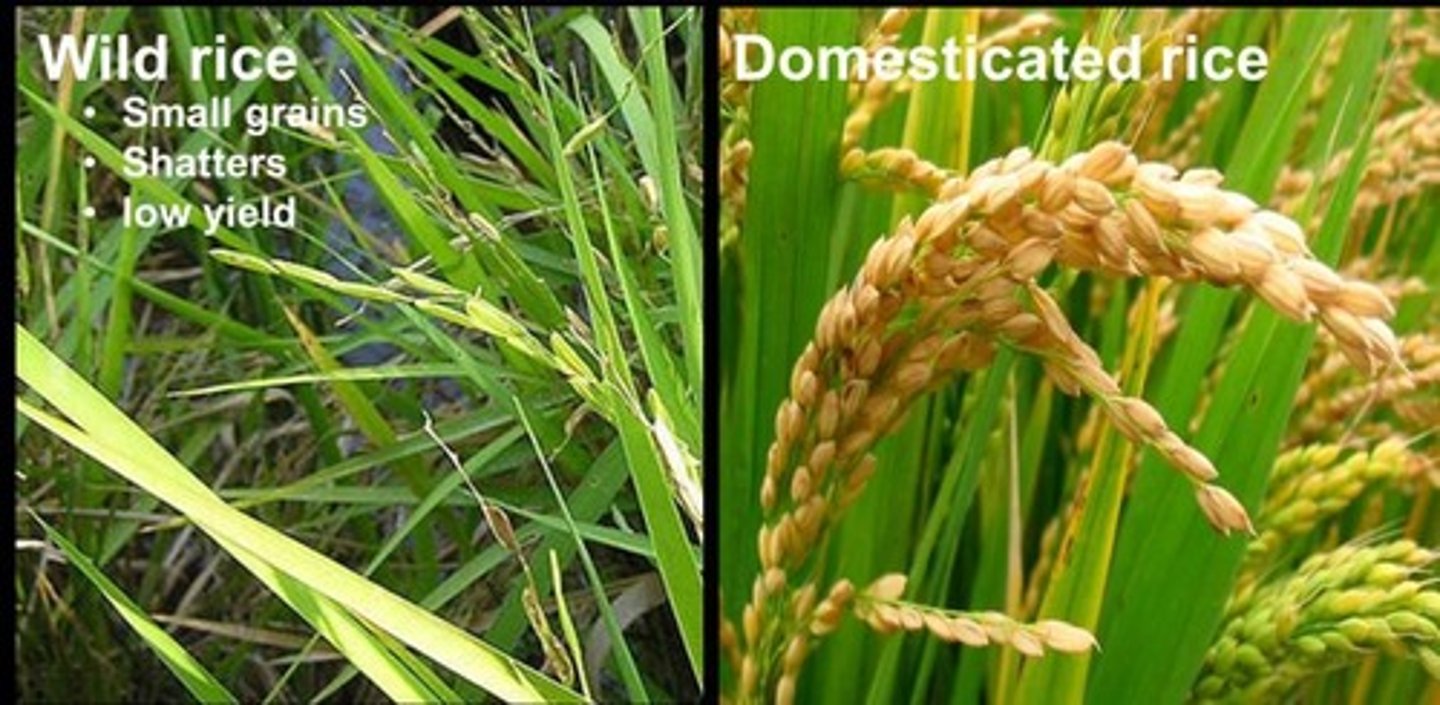

How does modern corn differ from teosinte?
Modern corn has large grains, no covering, and features such as permanent attachment of seeds to the cob.

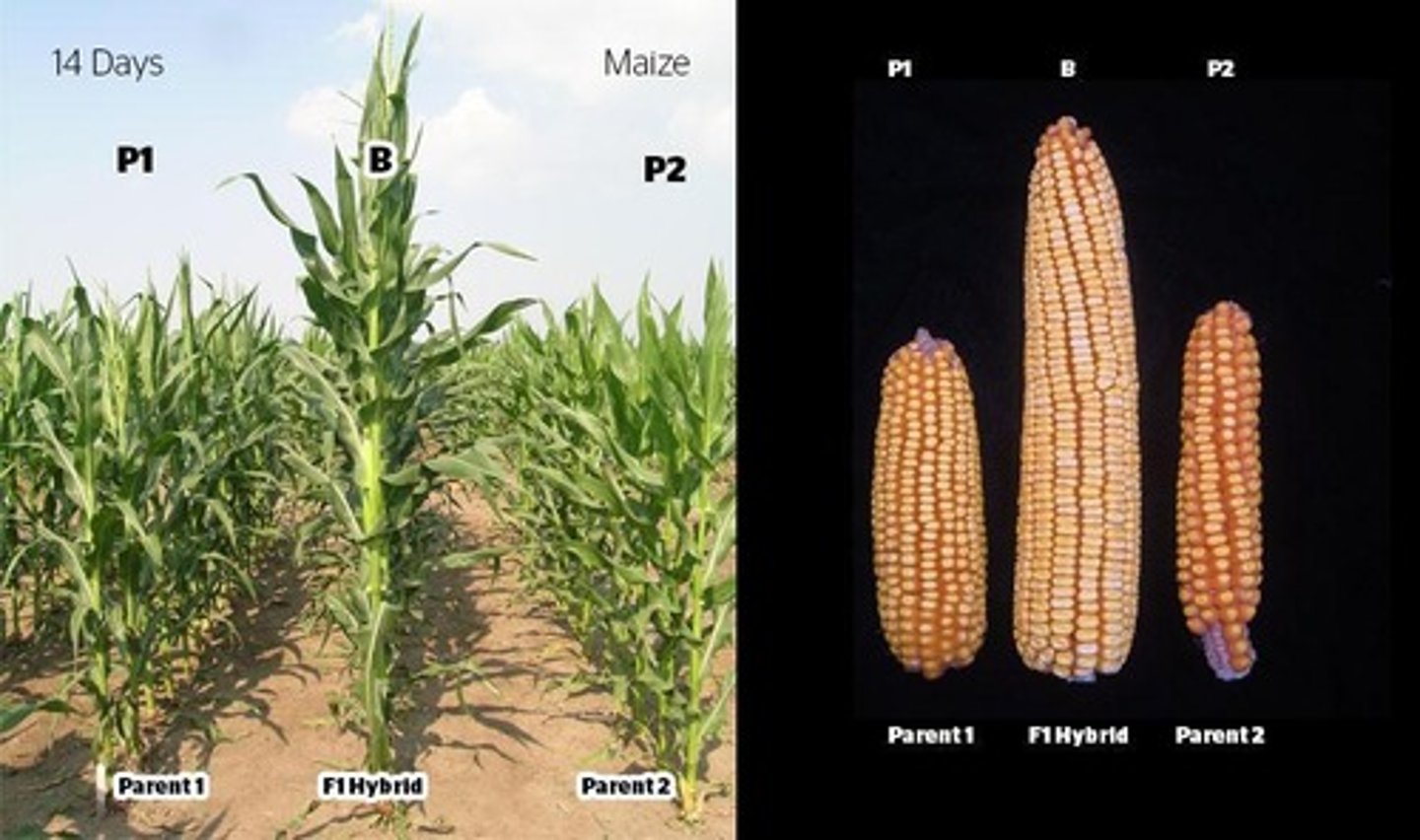
What is heterosis in plant breeding?
Heterosis is the tendency of a crossbred individual to show qualities superior to those of both parents.
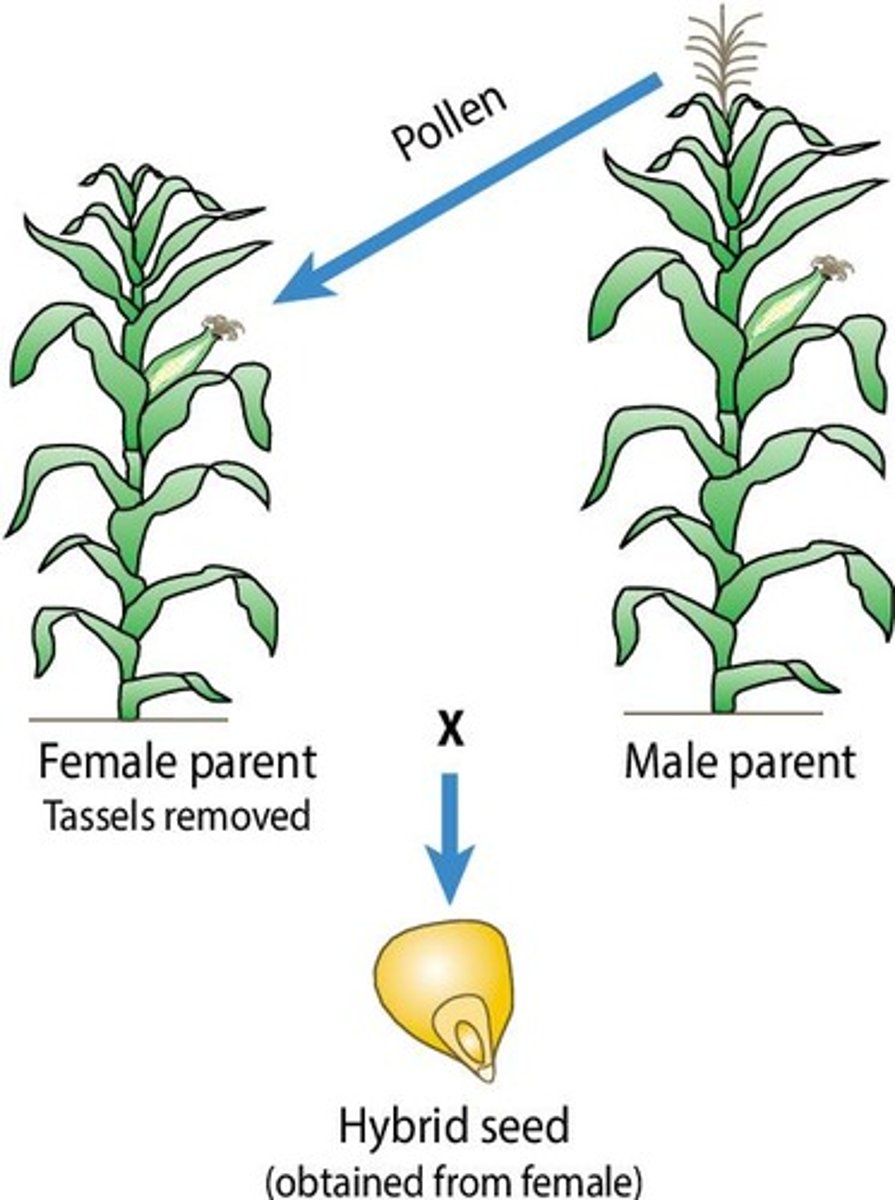
What is the purpose of plant breeding?
Plant breeding is the purposeful genetic manipulation and selection of plants to create genotypes/varieties with characteristics useful to humans.
What drives genetic diversity in plant breeding?
Genetic diversity is driven by sexual reproduction, which results in unique offspring and is influenced by crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilization.
What are some sources of genetic variability in plants?
Sources include wild relatives, related species, and natural or induced mutations.
What is an example of a conventional plant breeding technique?
Artificial hybrid crosses, such as crossing wheat (Triticum) with rye (Secale) to produce triticale.
What is genetic transformation in plant biotechnology?
Genetic transformation involves altering a plant's genetic makeup to introduce traits like herbicide resistance or improved quality.
What is the significance of F1 hybrid strawberry breeding?
F1 hybrid strawberries can exhibit hybrid vigor, higher yield, and robustness against stresses, while also reducing infection risks.
What are the disadvantages of F1 hybrids?
Disadvantages include the need to purchase seeds each year, labor-intensive cultivation, and biodiversity concerns.
What is the breeding goal for strawberry production?
Goals include increasing yield, size, taste, disease resistance, and improving nutritional value and visual appeal.
How long does it take to register a new strawberry cultivar?
It typically takes 12 to 15 years to register a cultivar.
What are some day neutral cultivars released by U of Guelph?
Examples include Summer Daisy, Summer Flavor, Summer Evening, 226GY43, and Governor Simcoe.
What is the impact of inbreeding depression in hybrid plants?
Inbreeding depression can lead to a loss of vigor due to the expression of deleterious traits determined by recessive alleles.
What is the role of genetic variability in plant breeding?
Genetic variability allows for the selection of desirable traits and the development of new plant varieties.
What is the historical significance of the garden strawberry?
The garden strawberry was first bred in France in the 1750s and is not classified as a true berry botanically.
What is the total worldwide production of strawberries?
Strawberry production exceeds 9 million tonnes per year globally.
What are the benefits of day-neutral strawberry plants?
Day-neutral plants can be grown from seed, reducing pest and disease risks, and they continuously flower and produce fruit.

What is the significance of genetic diversity in meiosis?
Meiosis results in a large number of genetic configurations, contributing to the genetic uniqueness of offspring.
What is a transgenic organism?
An organism that has been genetically modified to contain genes from another organism.
What is the role of Agrobacterium in plant transformation?
Agrobacterium is a soil bacterium that can transfer T-DNA into plant cells, leading to genetic modification.
What is the Ti plasmid?
A tumor-inducing plasmid found in Agrobacterium that is used as a vector for transferring genes into plants.
What is T-DNA?
Transfer DNA that is integrated into the plant genome during Agrobacterium-mediated transformation.
What is the purpose of using selectable markers in genetic modification?
Selectable markers, like kanamycin resistance, allow for the identification of successfully transformed plant cells.
What are some genetically modified crops approved in Canada?
Examples include corn, canola, potato, tomato, squash, apple, soybean, flax, cottonseed oil, and sugar beet.
What is the purpose of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxin in genetically modified crops?
Bt toxin is used to provide insect resistance, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
What is the FLAVR SAVR tomato known for?
It is genetically modified to have an extended shelf life by reducing polyphenol oxidase levels.
What is Golden Rice designed to address?
Golden Rice is engineered to provide a source of Vitamin A to combat deficiency in children.

What is CRISPR/Cas9 technology used for?
CRISPR/Cas9 is used for precise gene editing, allowing changes in DNA without introducing foreign DNA.
What are the health benefits of Bt technology?
Bt technology helps reduce mycotoxin levels in crops, which can be harmful to humans and animals.
What is the significance of totipotency in plant regeneration?
Totipotency allows a single transgenic cell to develop into a complete plant.
How does gene editing with CRISPR work?
CRISPR uses guide RNA to direct the Cas9 protein to a specific DNA location, where it makes precise cuts.
What is the role of the Canadian Food Inspection Agency regarding GMOs?
The agency oversees the approval and regulation of genetically modified food products in Canada.
What is the impact of herbicide-resistant crops?
Herbicide-resistant crops allow farmers to control weeds more effectively while reducing herbicide use.
What are the potential risks associated with GMOs?
Concerns include environmental impact, health risks, and ethical considerations regarding genetic modification.
What is the purpose of using gene editing in agriculture?
Gene editing aims to improve crop traits such as yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content.
What is the significance of the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry related to CRISPR?
The prize was awarded for the discovery of CRISPR/Cas9, which revolutionized genome editing.
What is the relationship between GM crops and pesticide use?
GM crops, particularly those with insect resistance, can lead to reduced pesticide applications.
What is the main concern regarding the use of GMOs in food production?
The main concerns include potential health effects, environmental impact, and loss of biodiversity.
What are the benefits of using transgenic crops for farmers?
Benefits include reduced labor, increased yields, and lower pesticide costs.