ANP causes human diversity_15
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
patterns of variation
within a population
frequencies of phenotypes, genotypes alleles
ex. blood type
between populations
the geographical pattern of frequencies
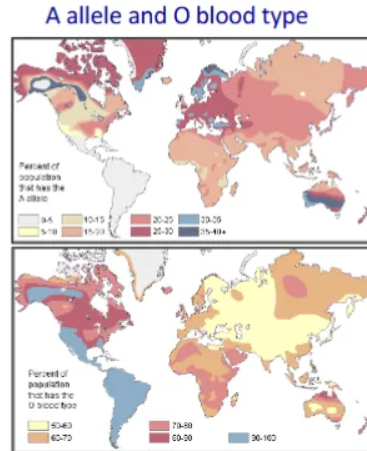
cline
gradual phenotypic change (= gradual change in allele frequencies)
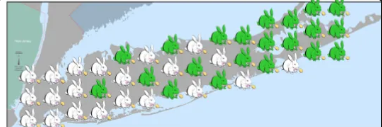
discontinuous distribution
little or no gradation in phenotypic change
causes of genetic variation
individual variation (between individuals)
- alleles inherited from parents
genetic variation within/between populations
- mutation, gene flow, genetic drift
- Natural selection is often caused by environmental variation (incl. variation in culture
precondition for natural selection
inheritance
- heritable traits are passed on to offspring
genetic variation
- traits vary between individuals
environmental pressure
- filter which selects advantageous traits
→ results(natural selection)
- individuals with advantageous traits survive better and have more offspring
- advantageous traits will be more common in the next generation (more individuals have the traits)
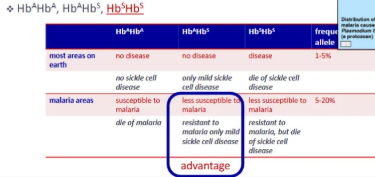
Environmental stressor: disease
sickle cell disease
autosomal recessive traits
environmental stressor: novel food
red indicates high lactase persistence
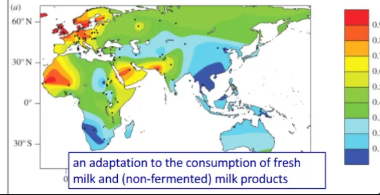
environmental stressors

behavioral responses
environmental stress → behavioral response
behavioral adjustment
short-term, cultural
→ almost no change in phenotype
different cultural solutions may affect the phenotype
individual (single generation)
- biological plasticity
= acclimations which is short-term phenotypic change that's reversible
= Adaptability is the developmental effects on phenotype; not reversible
over many generations
- natural selection leads to adaptation
- genetic fitness variation
→ together produce phenotypic variation
effects of environmental stressors
natural selection
- different environments may favor different traits
- Gene flow tends to homogenize populations
- If the selection is strong enough, genetic differences between populations will be maintained
examples of natural selection and genetic variation among human groups
- effects of heat and cold stress
- effects of the sun
- effects of high altitude
body size and shape
vary with climate
adaptation to cold and heat
animals
in cold places are large, stocky
in hot places are small, thin
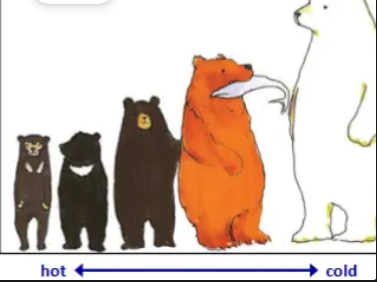
bergmanns rule
larger animals (have less relative surface area and) lose heat less rapidly than small mammals
animals
- in cold places are large, stocky, with short limbs
- in hot places are small, thin, longer-limbed

allens rule
mammals in cold environments have shorter, bulkier limbs, in warmer environments thinner longer limbs
same principle for modern humans

skin color
hemoglobin - red blood cells
carotene - yellowish pigment and the top layer of the skin (epidermis)
melanin - red/dark brown pigment
basal layer in the skin. produced by melanocytes and triggered by UVB
- absorbed UV and protects
a similar number of melanocytes but differences in..
- rate of melanin production
- size of melanin particles
- location melanin in cell
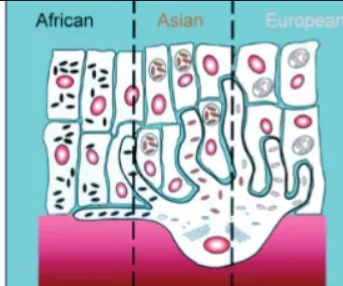
geographical distribution of skin color
clinal distribution; darker at equator
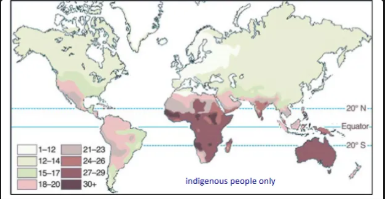
glogers rule
Within the same species, there is a tendency for the more heavily pigmented populations to be located near the equator and the lighter populations farther from the equator

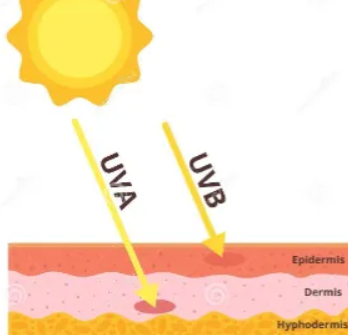
effects of UV rays
harmful
- damage DNA - skin cancer
- destroy folate (vitamin B) - neural tube defects
beneficial
- vitamin B synthesis
- calcium absorption; rickets
- immune function
synthesis of pre-vitamin D3
for humans with lightly pigmented skin
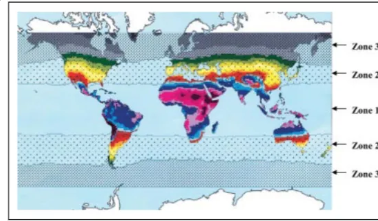
UV stress and responses
behavioral adjustment
- clothing; sunscreen lotion
acclimatization - tanning

skin color as an adaptation
1. near the equator - more UV radiation
- dark skin protects against skin cancer and folate destruction
2. northern latitude - less UV radiation
- light skin for better vitamin D production supports bone growth and a healthy immune system
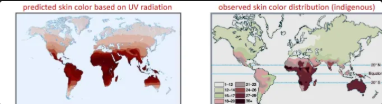
additional skin color variation
within a geographic area
- long-term residents - darker or lighter (depending on latitude}
- more clothing - lighter
- gender - women usually lighter than men

skin color
neanderthals
- ca. 300-30 ka B.P.
- Europe
first Homo sapiens
- ca. 200 ka B.P.
high altitude environment
- partial oxygen pressure reduced with increasing height
- humans affect starting at ca. 5,000 ft
—hypoxia
- reduced oxygen saturation of hemoglobin
- reduced oxygen transport to tissue
—altitude sickness
- headache, nausea, etc, (above ca. 8000 ft)
- high altitude edema (above ca. 11,500 ft)
reponses to lack of oxygen (1)
behavioral adjustment
- change to the environment
- e..g.. airplanes pressurized
- increases breathing and heart rate, more inactive
acclimatization
- increases the number of red blood cells
responses to lack of oxygen (2)
adaptations
- reduced oxygen consumption
mechanisms
- increases the amount of hemoglobin
—Andean populations
- less hemoglobin, but more effective oxygen use including,
- Tibetan populations
- gene variant from Denisovans
→ different adaptations
conclusion: human biological diversity
often environmental adaptations
- important to our survival
not fixed characteristics
- have changed; are changing; will change
variation between groups
result of
- mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift
differences reduced
- gene flow
learning objectives
