Neurodegenerative Conditions Huntingdon's Disease, Motor Neuron Disease and Multiple Schlerosis
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms

When do HD symptoms typically develop?
30-40yrs

What is the typical lifespan after the onset of Huntingdon's?
15-20 years

What causes HD?
Expansion of chromosome 4- increase changes the shape and function of the Huntingtin protein and makes it toxic to certain nerve cells in the brain

Why would someone develop HD?
inherit from parent (only need one affected parent to inherit)
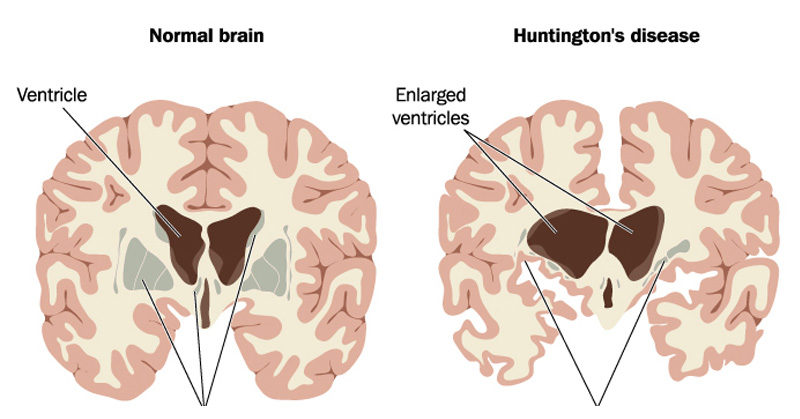
What is Huntingdon's disease?
condition that affects the central nervous system and stops parts of the brain that control movements, memory and mood from working properly over time
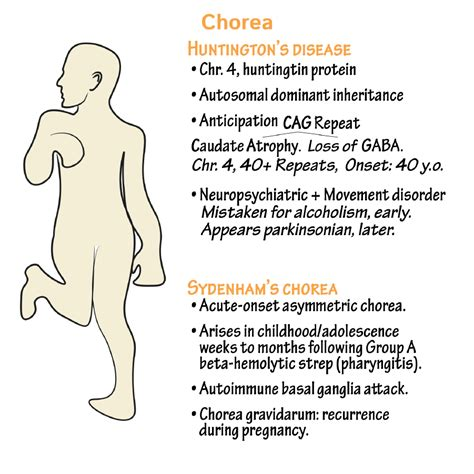
What is chorea and what is it a symptom of?
exaggerated movements, HD

What is hypertonia and what is it a symptom of?
rigidity, HD
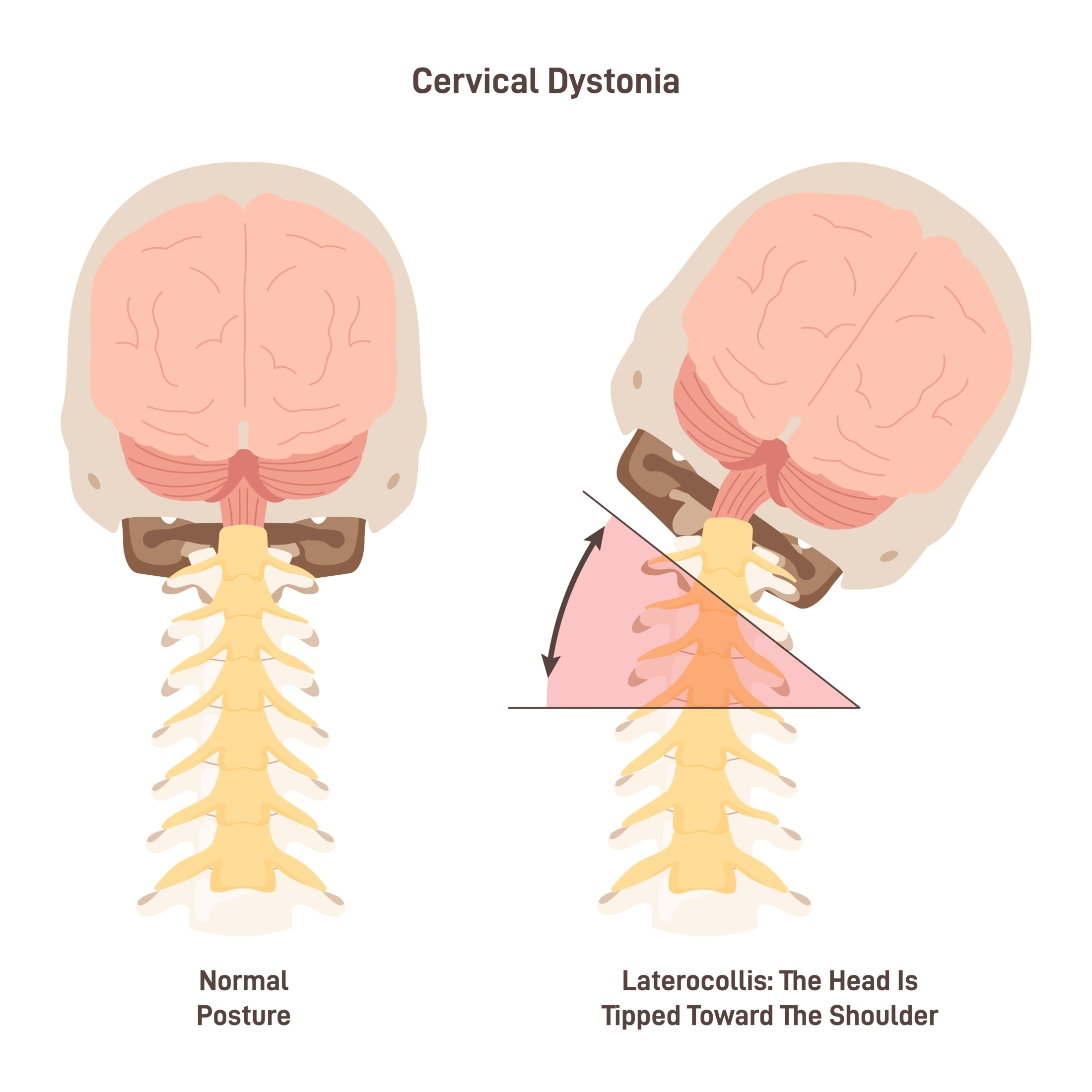
What does hypertonia lead to?
dystonia: twisting of the body caused by rigidity (HD)

Which type of dysarthria is associated with HD?
hyperkinetic
HD: symptoms
}Incoordination
}--- movement abnormalities
}Weight ----
}Dementia
}Dysphagia
} ----- changes
}------- deficits
}Dementia
}Depression
}Specific ------ deficits
eye
loss
personality
attention
language
HD language tasks - connected speech
------ number of words
Decreased -------- complexity
Decreased melody line
Decreased phrase -----
Decreased articulatory -----
Increased paraphasic errors
reduced
syntactic
length
agility
HD: word-finding difficulties
More ---------based errors than normal
Decreased ---------- naming (ability to spontaneously name things)
visually
confrontation

HD language tasks - auditory comprehension
------- understanding of subtle prosodic aspects
Reduced Token Test scores
-------- comprehension
decresead
reduced
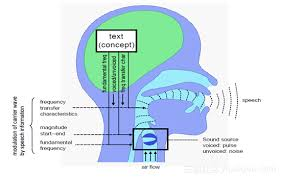
Which three parts of the speech production process can hyperkinetic dysarthria affect?
respiration, phonation, articulation

How does hyperkinetic dysarthria affect respiration?
intensity may be affected, sudden forced expiration/ inspiration

How does choreic movemenet / hyperkinetic dysarthria affect phonation?
raised pitch, harsh vocal quality

How does choreic movement / hyperkinetic dysarthria affect articulation?
phonemes may be prolonged and distorted
How to manage mild hyperkinetic dysarthria?
laryngeal relaxation techniques

How to manage moderate hyperkinetic dysarthria?
creating more supportive communication environment, supported conversation

How to manage severe hyperkinetic dysarthria?
AAC (but may be difficult or unviable due to physical, cognitive, behavioural issues)
HD: swallowing
}Physical, ------ difficulties
}Whole body chorea
}Choreic movements of lips/ jaw/ tongue impact on ---- stage
}-------- issues may affect swallow safety, e.g. eating inappropriate consistencies, too big mouthfuls of fluids.)
}Need for additional calories
positioning
oral
behavioural
HD: specific management issues
}Issues related to inherited nature of disease:
- seeing an ------ family member
- children
- ------ testing
genetic
older
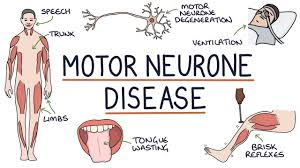
What is Motor Neurone Disease (MND)?
Progressive degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord
MND is characterised by loss of motor neurons in:
}motor cortex (UMN)
}brainstem (UMN and LMN)
}cranial nerves (LMN)
}spinal nerves (LMN).

When are people typically diagnosed with MND?
50-70yrs
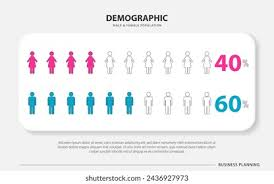
What is the male / female ratio of MND?
2:1
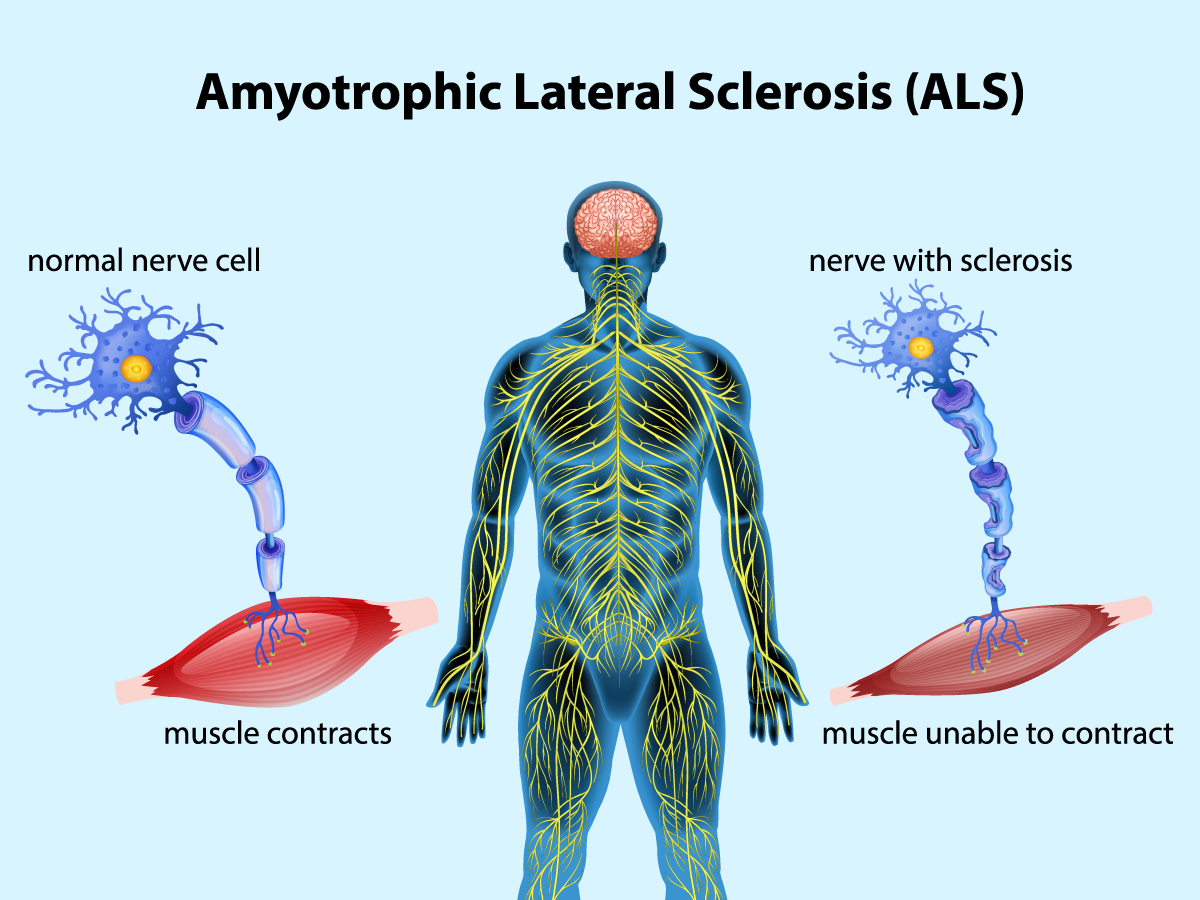
What does ALS stand for?
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (= most common type of MND)
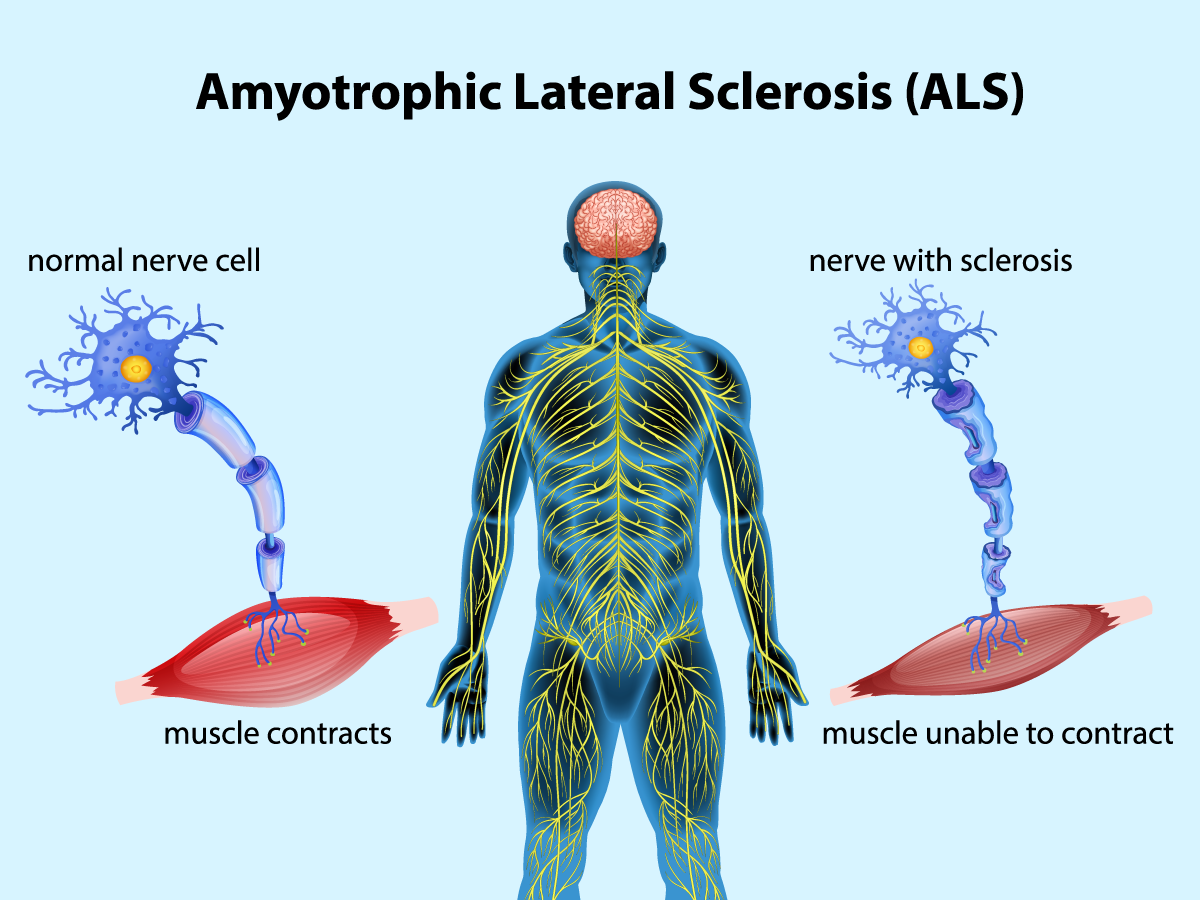
What is ALS?
progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord (Damage to corticospinal tract and anterior horn cells - UMN and LMN)

The motor nerves affected when you have ALS are the ------ neurons that provide --------- movements and --------- control.
motor
voluntary
muscle
Early symptoms of ALS often include ------- weakness or stiffness
muscle
Other early symptoms of ALS vary but can include tripping, dropping things, abnormal ------- of the arms and/or legs, ------ speech, muscle cramps and twitches and uncontrollable periods of laughing or --------.
fatigue
slurred
crying
What is the life expectancy of ALS?
2-5 years after onset of symptoms

What proportion of MND cases are ALS?
8/10
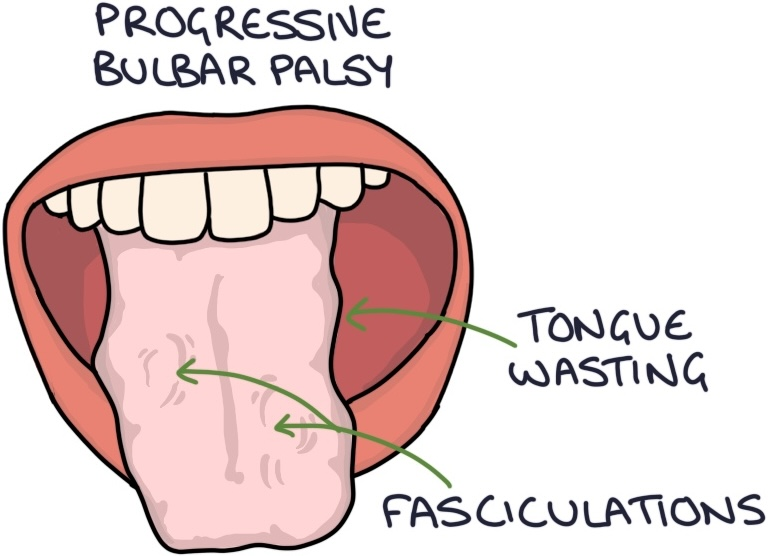
What does PBP stand for?
progressive bulbar palsy
What are the primary symptoms of PBP?
affects muscles in the face, throat and tongue, causing slurred speech and problems swallowing
(= Damage to CN nuclei -UMN and LMN)
What is the typical life expectancy after the onset of PBP?
6 months to 3 years
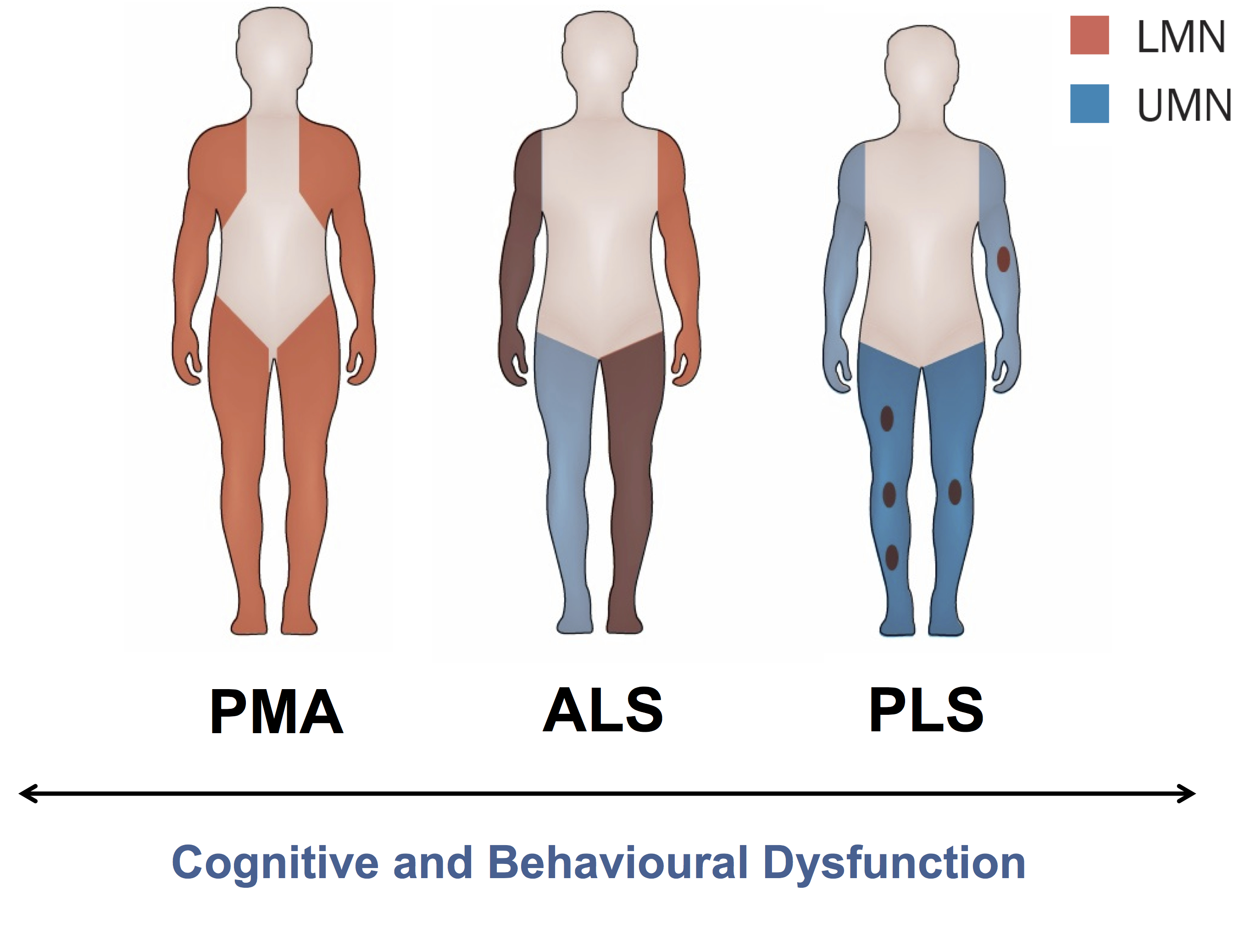
What does PLS stand for?
primary lateral sclerosis

What are the early symptoms of PLS?
Weak legs, speech problems
(=Damage to corticospinal tract)
What does PMA stand for?
progressive muscular atrophy

What are the typical early symptoms of PMA?
Weakness in the hands
(= Damage to anterior horn cells - Spinal nerves (LMN)
What is the typical life expectancy post onset of PMA?
5-10 years
What type of dysarthria is caused by damage to upper UMNs?
spastic

What type of dysarthria is caused by damage to LMNs?
flaccid

What type of dysarthria does MND often cause?
mixed
SLT diagnoses in MND
}Anarthria - lack of ability to ----
}AOS
}------ issues
}Dysphagia
speak
cognitive

MND: SLT role in communication - early intervention
addressing difficulties before they arise
Begin therapeutic relationship as early as possible

Why is early intervention important?
allows client and family time to "come to terms with" changes

What intervention might benefit someone with MND?
articulation tips (e.g. over-articulation, final consonant stress)
}Compensatory techniques, strategies, changes to environment, advice to listeners)
AAC

Why are muscle strengthening exercises not reccomended in MND?
cause too much fatigue
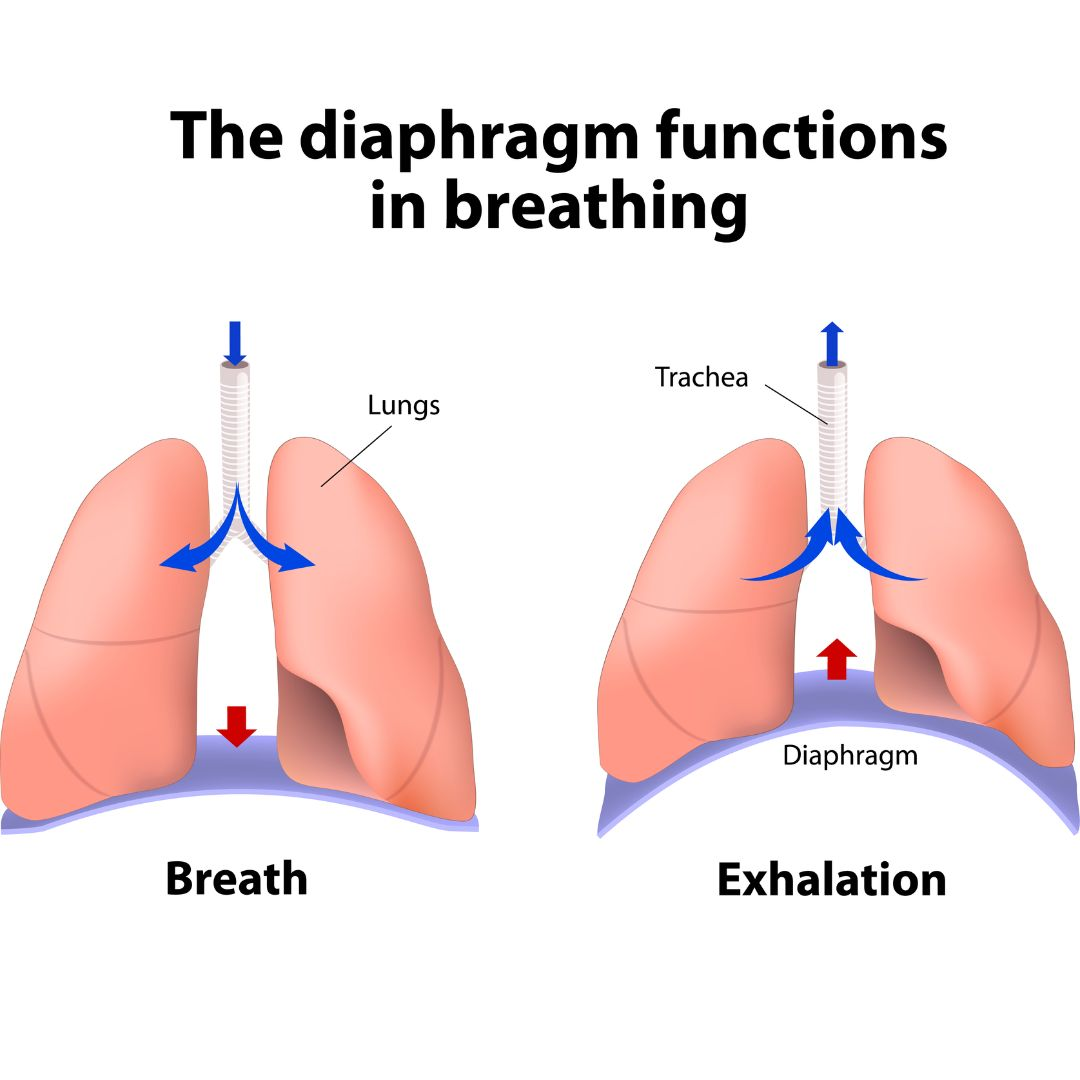
What is a consequence of reduced breath support in MND?
reduced airway protection, reduced possibility of surgical intervention

What is an initial sign of dysphagia?
coughing on thin liquids
Swallowing problems in MND
}Speech and swallow problems OFTEN co-occur
}-------- pattern of decline but can be variability in ---- of decline
}Fatigue (reduced breath support exacerbated by ----- apnoea, no breathing when swallowing)
}------ changes: texture/ xerostomia/ escape
consistent
rate
swallow
saliva
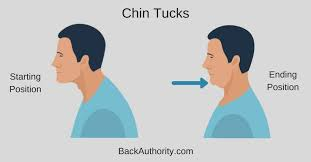
MND: Early stage dysphagia intervention
} ---- tuck
}Swallow manoeuvres (e.g super supraglottic swallow)
}Texture modification: (e.g. avoid foods requiring a lot of ------, crumbly foods, thickened fluids)
} feeding tube discussions
chin
chewing

MND: later dysphagia management
}More texture modification (soft, puree)
}Thickening of fluids
Increase sensory awareness (eg temperature, taste)
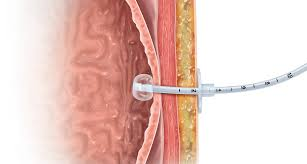
MND: Late stage dysphagia management
}Enteral feeding (PEG)
}May be indicated: multiple choking/ aspiration episodes, fear/ aversion, pt not meeting nutrition/ hydration needs orally
}Oral + PEG, Nil by mouth
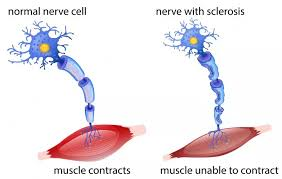
What causes MS?
damage to myelin in the CNS (immune system mistakes it for foreign substance and attacks it, causing inflammation and damage to axons)

Why is demylienation such a big problem in MS?
transferring messages along nerve fibres is slowed or stopped

What factors are thought to influence the development of MS?
environmental and genetic
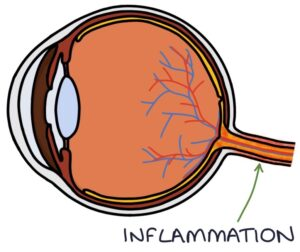
What is often the first symptom of MS?
Optic neuritis (problems in one eye e.g. pain, vision loss or colour blindness)
MS: symptoms
uncontrolled muscle movements, difficulties with balance and co-ordination, and fatigue
MS: Communication
}Speech: AOS rare, dysarthria (spastic-ataxic, mixed) occurs in approx 50%
}Language: aphasia rare, higher level language deficits possible
}Cognitive: memory, learning, problem-solving
}Affect: depression
}Fatigue
MS: management of communication issues
}Dysarthria:
-Breath control exercises for phonation and volume
Beware fatigue
-Working on appropriate rate (pacing)
Beware fatigue
-Speech augmentation, e.g. use of alphabet board
- AAC options but NB tremor, visual issues, spasticity, ataxia
MS: EDS
1/3 experience dysphagia
}Delayed swallow reflex - risk of aspiration

MS: EDS solution
texture modification, positioning, reduction of distractions